Preface
Mounting evidence suggests that acute and chronic stress, especially the stress-induced release of glucocorticoids, induces changes in glutamate neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus, thereby influencing some aspects of cognitive processing. In addition, dysfunction of glutamatergic neurotransmission is increasingly considered to be a core feature of stress-related mental illnesses. Recent studies have shed light on the mechanisms by which stress and glucocorticoids affect glutamate transmission, including effects on glutamate release, glutamate receptors and glutamate clearance and metabolism. This new understanding provides insights into normal brain functioning as well as the pathophysiology and potential new treatments of stress-related neuropsychiatric disorders.
Introduction
Selye originally described stress as a non-specific response of the body to any demand placed upon it1. Now it is customary to speak of a stressor as an event or experience that threatens the ability of an individual to adapt and cope2. As a result, the stressor evokes a stress response, which involves the release of hormones and other cellular mediators that can promote adaptation when the response is efficiently turned on and shut off, but which can also promote pathophysiological processes when the response is overused or dysregulated3. The brain is central in the adaptation to stress, perceiving and determining what is threatening, and orchestrating the behavioural and physiological responses to the stressor4. The brain is also a target of stress, with animal models showing stress-induced remodelling of brain architecture, such as dendritic atrophy and loss of dendritic spines in neuronal populations5–7. The effects of stress on the brain have long been associated with the onset and exacerbation of several neuropsychiatric disorders.
Depending on the age of the animal at the time of exposure, and the duration and type of stressor experienced, stress also has marked and often divergent effects on learning and memory8,9. In relation to these effects, stress is known to influence several distinct cognitive processes, including spatial and declarative memory (which involves the hippocampus), the memory of emotionally arousing experiences and fear (which involves the amygdala), and executive functions and fear extinction (which involves the prefrontal cortex). This Review focuses primarily on the prefrontal cortex (PFC), as it may play an important role in mediating the effects of stress on both cognition and psychopathology. The PFC is an essential component of a neural circuit for working memory10,11 — the ability to keep in mind something that has just occurred or bring to mind events in the absence of direct stimulation. PFC neurons show spatially tuned, persistent activity during the delay period of working memory tasks, a phenomenon that is thought to arise from recurrent excitatory connections involving AMPA and NMDA receptor synapses onto PFC pyramidal neurons11,12. The PFC is also essential for behavioural adaptation, inhibiting inappropriate actions and allowing for a flexible regulation of behaviour that enables a proper response to changes in the environment. Multiple lines of evidence from rodent and human studies also implicate the ventromedial PFC as the major site controlling extinction of conditioned fear13,14. Moreover, impaired PFC function and plasticity is thought to be a core pathological feature of several neuropsychiatric disorders15–17. As stress seems to induce some effects in the PFC that are unique to this region and others that are common to the hippocampus and other regions, regional comparisons will be made where possible (see supplementary online information S1 (table)).
For the purposes of clarity and focus, and to highlight the importance of several recent findings, this Review will mainly address the effects of stress and glucocorticoids on the glutamatergic neurotransmitter system within the PFC (Box 1). However, it must be acknowledged that a host of neurotransmitter and neuromodulatory systems in various brain regions have been shown to be crucial in mediating the effects of stress (see10,18,19 for recent reviews), with some having very clear effects on glutamatergic neurotransmission20.
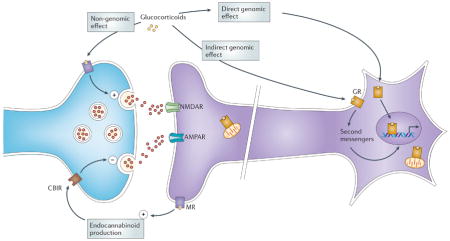
Box 1. Adrenal steroids and neurotransmission.
Glucocorticoids are released from the adrenal glands. Basal release varies in a diurnal pattern, and release increases several fold after exposure to a stressor. Glucocorticoids can bind, with different affinities, to glucocorticoid (GR) and mineralocorticoid (MR) receptors, which are expressed throughout the brain and seem to exist in both membrane-bound form and nuclear form. Adrenal steroids can have both rapid and delayed effects. The effects can result from non-genomic mechanisms (mediated by membrane receptors, see the figure), indirect genomic mechanisms (mediated by membrane receptors and second messengers, see the figure) and genomic mechanisms (mediated by cytoplasmic receptors that move to the nucleus and act as transcription factors, see the figure)193,194, as seems now to be the case for all steroid hormones195,196. Although mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors seem to mediate many of these effects197,198, other membrane-associated receptors, including G-protein coupled receptors, may also be involved in some of these actions49,199–201. In addition, activated glucocorticoid receptors can translocate to mitochondria and enhance their calcium buffering capacity202,203. Glucocorticoids rapidly induce glutamate release in the hippocampus via a mechanism that is absent when the mineralocorticoid receptor is deleted and which may involve a membrane-associated form of the mineralocorticoid receptor42,204. An indirect way by which glucocorticoids can influence neurotransmission (glutamatergic, as well as GABAergic, cholinergic, noradrenergic and serotonergic) is through cross-talk with the endocannabinoid (eCB) system205. They rapidly stimulate endocannabinoid production in the brain, whereupon eCBs bind to the CB1 and TRPV1 receptors and inhibit neurotransmitter release206,207 (see the figure). Although a G-protein coupled receptor is implicated in endocannabinoid production208, there is also evidence for a mechanism blocked by Ru486 — a selective antagonist or the classical cytoplasmic glucocorticoid receptor — in the rapid actions of glucocorticoids in prefrontal cortex209.
Glutamatergic neurotransmission occurs predominantly within the confines of a tripartite synapse (Figure 1). Several points of regulatory control within the synapse, including basal and stimulated presynaptic glutamate release; postsynaptic receptor trafficking and function; and transporter-mediated uptake and recycling of glutamate through the glutamate–glutamine cycle are sensitive to regulation by stress and glucocorticoids. Here we review studies exploring the effects of stress and glucocorticoids on each of these components of the synapse, and attempt to synthesize the findings to understand how stress may either have beneficial effects on cognitive function or noxious effects, which in turn might lead to the development of neuropsychiatric disorders.
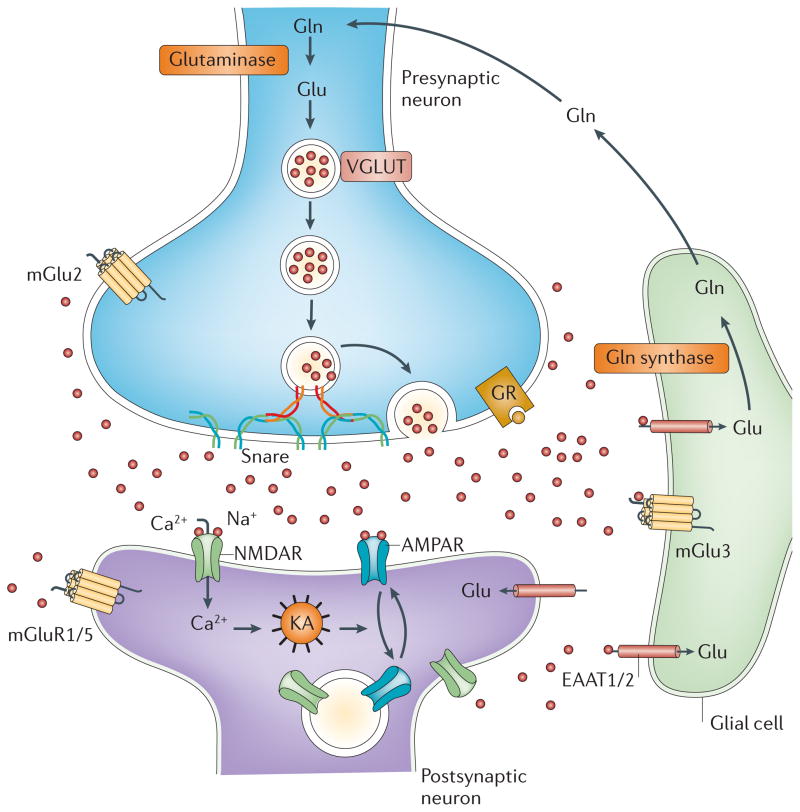
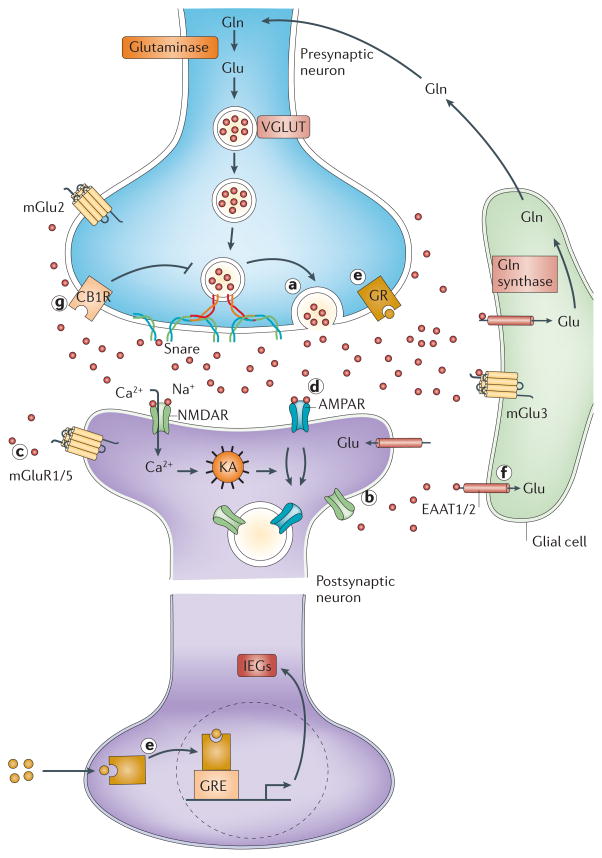
Figure 1. The tripartite glutamate synapse.
Neuronal glutamate is both synthesized de novo from glucose (not shown) and from glutamine (Gln) supplied by glial cells. Glutamate is then packaged into synaptic vesicles by vesicular glutamate transporters (vGluT). SNARE complex proteins mediate the interaction and fusion of vesicles with the presynaptic membrane. After release into the extracellular space, glutamate binds to ionotropic (NMDA, AMPA) and metabotropic (mGluR 1–8) receptors on the membranes of both post-synaptic and pre-synaptic neurons and glial cells. Upon binding, the receptors initiate various responses, including membrane depolarization, activation of intracellular messenger cascades, modulation of local protein synthesis and, eventually, gene expression (not shown). Surface expression and function of NMDARs and AMPARs is dynamically regulated by protein synthesis and degradation and receptor trafficking between the postsynaptic membrane and endosomes. The insertion and removal of postsynaptic receptors provide a mechanism for long-term modulation of synaptic strength. Glutamate is cleared from the synapse through excitatory amino acid transporters (EAATs) on neighbouring glial cells (EAAT1 and 2) and, to a lesser extent, on neurons (EAAT 3–5). Within the glial cell, glutamate is converted to glutamine by glutamine synthetase and the glutamine is subsequently released via system N transporters and taken up by neurons through System A sodium-coupled amino acid transporters to complete the glutamate–glutamine cycle.
The glutamate tripartite synapse
In addition to its role as the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain, glutamate is a key intermediary metabolite in the detoxification of ammonia and a building block used in the synthesis of peptides and proteins. Consistent with its multiple intracellular functions, glutamate is present at extremely high concentrations within the cells of the CNS. The high concentrations of intracellular glutamate require that extremely tight regulatory processes be in place to limit extracellular levels and modulate glutamate receptor activity in order to ensure optimal neurotransmission and prevent against potential excitotoxicity (Figure 1).
Neuronal glutamate can be synthesized de novo from glucose via the Krebs cycle and the transamination of a-oxoglutarate, and it can be recycled through the glutamate–glutamine cycle21. Exocytotic vesicular release of glutamate, which underlies the vast majority of excitatory neurotransmission in brain, is a strictly regulated process in which the synaptic vesicles that store glutamate merge and then fuse with the presynaptic membrane in response to stimulation. In glutamatergic synapses, presynaptic terminals are normally associated with specialized postsynaptic structures (dendritic spines), unlike synapses at which monoaminergic neurotransmitters (dopamine, noradrenaline, adrenaline, serotonin, histamine) are released.
The core of the presynaptic machinery for vesicular neurotransmitter release, including glutamate release, is the so-called soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein attachment protein receptor (SNARE) complex. The SNARE complex is formed by the interaction of two synaptic membrane proteins (syntaxin-1 or syntaxin-2 and SNAP-25) and a vesicular protein (synaptobrevin-1 or synaptobrevin -2), and is thought to mediate the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane22–24.
Glutamate regulates synaptic transmission and plasticity by activating ionotropic (AMPA and NMDA) and metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1-8). The number and stability of these receptors at the synaptic membrane is an important factor in determining excitatory synaptic efficacy. Several mechanisms have been proposed to control the surface expression of NMDA receptors (NMDARs) and AMPA receptors (AMPARs), including PDZ domain-mediated interactions between channel subunits and synaptic scaffolding proteins25–27, clathrin-dependent endocytosis regulated by phosphorylation28–30, and motor protein-based transport along microtubule or actin cytoskeletons31–33. The Rab family small GTPases, which function as key regulators for all stages of membrane traffic34, is involved in the internalization, recycling and spine delivery of NMDARs and AMPARs35,36. The synthesis and degradation of postsynaptic glutamate receptors are dynamically regulated37,38.
Glutamate is cleared from the extracellular space via high-affinity excitatory amino acid transporters (EAATs), which are located on neighbouring glial cells (EAAT1-2) and, to some extent, on neurons (EAAT 3–5)39. In glial cells, glutamate is converted into glutamine by glutamine synthetase. Glutamine is then transported back into the glutamatergic neuron, where it is hydrolyzed into glutamate by glutaminase21. Owing to the lack of degradative enzymes in the synapse, uptake by EAATs is the primary mechanism through which the action of extracellular glutamate is terminated. The following sections will discuss evidence that stress and glucocorticoids can influence glutamate neurotransmission through actions at several sites within the system, namely at the levels of glutamate release, ionotropic glutamate receptor activity and glutamate clearance and metabolism.
Stress effects on glutamate release
Acute stress and glucocorticoids increase extracellular glutamate levels
Glucocorticoids secreted during the diurnal rhythm and during stress (Box 1) affect the basal release of glutamate in several limbic and cortical areas, including the hippocampus, amygdala and PFC40,41. Converging lines of evidence from animal studies suggest that acute exposure to stress or administration of glucocorticoids rapidly increases glutamate release in these brain areas40,42–45. For example, in vivo microdialysis studies have shown that exposure of rats to tail-pinch, restraint- or forced-swim stress induces a marked, transient increase of extracellular glutamate levels in the PFC44,45. However, it has been objected that a large portion of amino acid neurotransmitters sampled by microdialysis is of non-neuronal origin, resulting from reverse transporter activity and/or derived from glial cells46,47. Nevertheless, recent evidence from rapid microelectrode measurements suggest that tail-pinch stress-induced glutamate release is largely of neuronal origin48.
In different studies using patch-clamp recordings, application of 100 nM corticosterone, the major glucocorticoid in rodents, to hippocampal slices rapidly enhanced the frequency of miniature excitatory postsynaptic potentials in CA1 pyramidal neurons and reduced paired-pulse facilitation (PPF) — a form of synaptic facilitation that reflects presynaptic release — suggesting that corticosterone increases glutamate release probability in this area49. This rapid action of corticosterone was found to be non-genomic and mediated by a mineralocorticoid receptor located in or near the plasma membrane (Box 1)49,50.
Stress also has an effect on depolarization-evoked release of glutamate in the prefrontal and frontal cortex, as shown in studies using isolated synaptic terminals (synaptosomes) in superfusion. This method allows precise and selective measurement of endogenous or labeled neurotransmitter release (see Box 2). Rats subjected to acute footshock-stress in a paradigm that induces learned helplessness51 showed a marked, rapid change in the depolarization-evoked release of glutamate52. The increased release of glutamate in prefrontal and frontal cortex was dependent on glucocorticoid receptor activation. The short latency of the effect suggested that the receptor acted non-genomically, although the results of patch-clamp recordings (see below) are also compatible with the timing of genomic actions. Thus, both genomic and non-genomic pathways may be involved in the effect of stress on glutamate release. A similar rapid effect of corticosterone, mediated by glucocorticoid receptors, has been shown in synaptosomes isolated from rat hippocampus53. As shown by recent findings54, recruitment of endocannabinoid signalling could be involved in the enhancement of glutamate release induced by corticosterone.
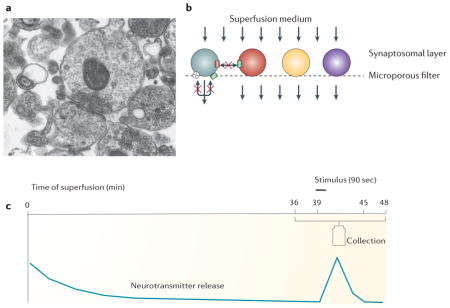
Box 2. Measuring release of endogenous neurotransmitters from purified synaptosomes.
The technique for measurement of neurotransmitter release from isolated synaptic terminals (synaptosomes) in superfusion was originally developed by Maurizio Raiteri and co-workers at the University of Genova210,211. The problem they faced was that when neurotransmitter release is evoked from a population of synaptosomes or cells in bulk (i.e. in a test tube), any released molecule will hit receptors and transporters on the same terminal and on neighbouring terminals. This elicits a chain of reactions that in turn modify the release of the same as well as of other neurotransmitters. The problem was solved by applying a thin layer of semi-purified or purified synaptosomes (see the figure, part A.) on a microporous filter and applying a constant up-down superfusion to the sample (see the figure, part B.). Through this method, any released endogenous transmitters and modulators are immediately removed by the superfusion medium before they can be taken up by transporters and activate autoreceptors or heteroreceptors on synaptic terminals. Reuptake can therefore not occur and indirect effects are minimized or prevented. During superfusion all the presynaptic targets (transporters, receptors, channels, enzymes, etc.) can be considered virtually free of endogenous ligands; each of these targets can therefore be studied separately by adding the appropriate ligand at the desired concentration to the thin layer of synaptosomes. Any observed effects on the release of one neurotransmitter can reasonably be attributed to direct actions at the terminals storing that neurotransmitter. Today, superfused synaptosomes represent the method of choice for the functional characterization of the properties of a particular family of nerve endings.
In a typical experiment for measuring the release of endogenous amino acids such as glutamate or GABA, synaptosomes are layered in a thermostated superfusion chamber, the sample is continuously superfused for 36 min with isotonic buffered solution to reach stabilization of basal release; then collection of samples begins, with first 3 min representing basal release of neurotransmitter. At 39 min a stimulus, such as depolarizing concentrations of KCl (15–25 mM), a calcium ionophore (ionomycin), or a receptor agonist is applied for 90 sec. Collection of samples is protracted up to 48 min, with the evoked release-containing sample followed by one more 3-min basal release sample (see the figure, part C). Concentrations of released amino acids in the perfusate samples are successively measured by HPLC.
Over the years this method has been used by many authors to distinguish exocytotic release from release that is due to inversion of neurotransmitter transporters, and to measure changes in release induced by presynaptic receptors. Recently, this method revealed that antidepressant drugs reduce the release of glutamate in the hippocampus (in rats kept under basal conditions), and prevent the increase induced by acute stress in prefrontal/frontal cortex51,212.
The method of synaptosomes in superfusion involves using synaptic terminals detached from whole tissue. Measuring release of endogenous glutamate can also be performed in slices of whole PFC tissue, in which the neural circuitry is preserved. Patch-clamp recordings from PFC slices from rats subjected to footshock-stress showed that exposure to stress increased the amplitude of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic potentials in pyramidal neurons, an effect abolished by pretreating the rats with the antidepressant desipramine52. Moreover, PPF and its calcium-dependence were decreased in PFC slices from stressed rats. Combined, these results are consistent with increased glutamate release, as well as with increased activation of postsynaptic ionotropic glutamate receptors, in the PFC of stressed rats.
In principle, the acute-stress-induced enhancement of stimulus-evoked release of glutamate may be achieved by increasing the number of synaptic vesicles that are already docked to the membrane and ready for release — the readily releasable pool of vesicles (RRP) — or by increasing the probability of release of synaptic vesicles, or both55–58. At the level of presynaptic machinery, footshock-stress induced an increase in the number of SNARE complexes bound to the presynaptic membrane from PFC neurons 52 (Figure 2), suggesting that at least the first mechanism is involved. Indeed, inducing glutamate release with hyperosmotic sucrose from synaptosomes in superfusion from the prefrontal and frontal cortex of rats exposed to footshock-stress revealed that the RRP was about 2-fold that of control rats59. Preliminary data obtained using Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Microscopy to measure the recruitment of FM1-43-labeled synaptic vesicles to the membrane also suggest a greater RRP after in vitro application of corticosterone to prefrontal and frontal cortex synaptosomes59.
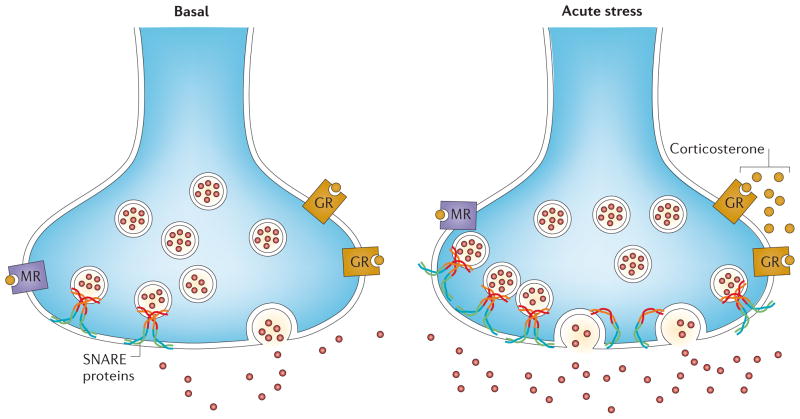
Figure 2. Acute stress rapidly enhances glutamate release in prefrontal/frontal cortex.
Acute footshock stress enhances depolarization-evoked release of glutamate from presynaptic terminals of rat prefrontal/frontal cortex52. The acute stress response involves a rapid increase of circulating levels of corticosterone, which binds to membrane-located glucocorticoid receptors (GRs). This induces a rapid GR-mediated increase of presynaptic SNARE protein complexes (which mediate fusion of synaptic vesicles) in the presynaptic membrane52. Because the number of SNARE complexes per vesicle is reputed to be constant, this suggests that acute stress induces an increase of the readily releasable pool of glutamate vesicles. The signalling pathways downstream of glucocorticoid receptor activation that induce the increase of the readily releasable pool are unknown.
Interestingly, the effect of acute stress on depolarization-evoked glutamate release in the PFC could be prevented by treating the rats with various classes of antidepressant drugs, endowed with different primary mechanisms of action, for two weeks prior to the stress exposure52. The mechanism whereby antidepressant drugs block the presynaptic effect of stress on depolarization-evoked glutamate release is unknown at present. Stress-induced serum corticosterone levels were similar in antidepressant-treated and untreated rats, suggesting that the drugs do not alter corticosterone release. Instead, they might affect intracellular signalling downstream of glucocorticoid receptor activation by corticosterone or act directly on the glutamate release machinery. However, the number of SNARE complexes was increased in all stressed rats, regardless of whether they had been previously treated with antidepressants or not. This suggests that the antidepressant drugs acted downstream from the assembly of SNARE complex. For example, they could act at the level of interaction of regulatory and fusogenic proteins with the SNARE complex, modulating the function of the complex itself60–63. It has been argued 64 that the effect of antidepressants on glutamate release in the PFC could be involved in the long-term anxiolytic and antidepressant action of these drugs, because they are able to dampen glutamate release in response to acute stress52.
Chronic stress and glutamate release
As discussed above, stress acutely enhances glutamate release in the PFC and hippocampus. However, the effects of chronic stress on glutamate release are still mostly unknown. It has been shown that three repeated tail-pinch stressors (at 2.5 hr intervals) in rats produce transient glutamate effluxes in the hippocampus that remain constant in duration and magnitude, whereas in the PFC they decrease upon subsequent applications65. These results suggest a selective adaptation of glutamate release to stress in the PFC. A different study tested the response to an acute stressor in rats subjected to 21-day chronic restraint stress. After a subsequent single stress challenge extracellular glutamate levels (measured by microdialysis) in CA366 remained elevated in chronically stressed rats, compared to naïve rats subjected to the same acute stressor, suggesting an altered regulation of the termination of glutamate release after chronic exposure to stressful stimuli.
Effects on ionotropic glutamate receptors
Stress and glucocorticoid effects on glutamatergic transmission
In addition to the rapid and transient increase in presynaptic glutamate release in the PFC after acute stress44,45,52, acute stress also has a delayed and sustained impact on PFC postsynaptic glutamate receptor-mediated responses67,68. Electrophysiological recordings have shown that both NMDAR- and AMPAR-mediated synaptic currents are markedly increased in PFC pyramidal neurons in various models of acute stress67. This effect is observed >1 hr post-stress, is sustained for 24 hrs after the cessation of stress and can be mimicked by short-term corticosterone treatment in vitro67–69. The acute stress- and corticosterone-induced enhancement of basal glutamatergic transmission is caused by an increased surface expression of NMDA and AMPA receptors at the postsynaptic plasma membrane67,68.
The delayed effect of acute stress or corticosterone treatment on basal PFC glutamatergic transmission is mediated by intracellular glucocorticoid receptors67,68, in contrast to the fast, increase of glutamate release in CA1 hippocampus, which is mediated by membrane-bound mineralocorticoid receptors49,70; this difference could be due to the low expression of mineralocorticoid receptors in the PFC71. There are other regional differences in the effects of stress on glutamate transmission. For example, acute stress or corticosterone treatment increases AMPAR and NMDAR responses to a similar extent in the PFC67,68 but selectively enhances AMPAR-mediated currents in CA1 neurons72,68, midbrain dopamine neurons73 and nucleus accumbens shell neurons73,74. Furthermore, the potentiating effects of acute stress on AMPAR and NMDAR responses in the PFC are independent of each other68, which is different from the classic NMDAR-dependent long-term potentiation (LTP) of AMPAR responses in the hippocampus.
The impact of chronic stress on basal PFC glutamatergic transmission is less well understood. A recent study showed that one week of repeated restraint or unpredictable stress leads to a marked reduction of AMPAR- and NMDAR-mediated synaptic currents in PFC pyramidal neurons from juvenile male rats, which sustains for a few days after stress extinction75. No change in basal synaptic currents was observed in striatal neurons, CA1 pyramidal neurons75 or dentate gyrus neurons76. This suggests that the PFC is more sensitive to chronic stress compared to the striatum or hippocampus, perhaps especially during the adolescent period, when this region is still undergoing significant development8.
Stress also affects synaptic plasticity — the ability to potentiate (LTP) or depress (long-term depression (LTD)) the efficacy of glutamatergic transmission — in the hippocampus9,71 and PFC. Acute stress inhibits LTP in the amygdala–PFC pathway, in parallel with the suppression of hippocampal LTP77. The acute stress-induced impairment of LTP in the hippocampus–PFC pathway is prevented by antidepressant treatment78 or GR blockade79. Moreover, prior stress exposure prevents the ability of a second episode of stress to suppress LTP in the prefrontal cortex80 — a form of emotional metaplasticity that forms the neural basis of stress experience-dependent fear memory81. Acute stress has divergent effects on LTD: it enhances mGluR-dependent LTD in the hippocampus82, but prevents serotonin-facilitated LTD induction in the PFC83. Chronic stress impairs LTP in the thalamus–PFC pathway84 and LTP in the hippocampus–PFC connection85, and these effects are associated with the disruption of PFC-dependent tasks, such as working memory and behavioural flexibility85. Catecholaminergic facilitation of LTP in the infralimbic region of the medial PFC is also impaired by chronic stress and restored by post-stress recovery86. These changes in synaptic plasticity could be due to the altered structure of glutamatergic synapses — such as atrophy, dendritic retraction or spine loss — which have been associated with chronic stress85,86 (Box 3). Alternatively, they could be due to chronic-stress-induced loss of glutamate receptors and diminished glutamatergic transmission in PFC neurons. In line with this view, the synaptic inhibition in the medial PFC and the fear extinction deficit that have been observed in rats with repeated early stress exposure are ameliorated by the NMDA receptor agonist D-cycloserine87.
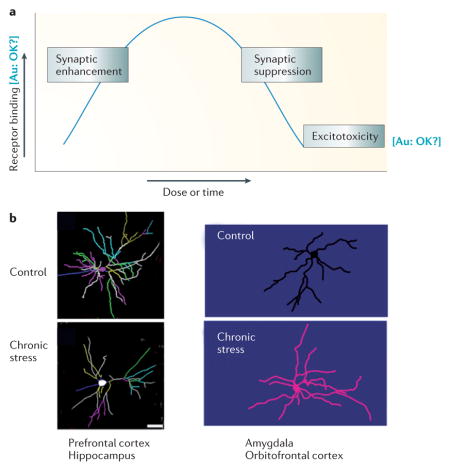
Box 3. Structural changes induced by stress.
Until recently, much of our information on stress, excitatory amino acids (EAA) and synaptic function has come from studies on the hippocampus, which expresses both mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors. In the hippocampus, EAAs and glucocorticoids mediate biphasic effects on structure and function (see the figure, part A). Acutely (that is, over hours), low to moderate physiological levels of adrenal steroids and EAA enhance synaptic function and certain types of memory, whereas higher levels of both mediators have the opposite effect213. More chronically (that is, over days to weeks), adrenal steroids and EAAs mediate adaptive plasticity involving spine synapse turnover, dendritic shrinkage and suppression of adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus 7. However, when there is a sudden insult such as a seizure, stroke or other head trauma, EAAs and glucocorticoids induce permanent, irreversible hippocampal damage214.
Acute and chronic stress also induce structural changes in other brain areas. Chronic stress causes neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex (medial PFC) to undergo shrinkage and simplification of dendrites and reduction of spine synapse density, whereas the same stress regimen causes neurons in the basolateral amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) to grow (see the figure, part B)5,6. With the cessation of stress, these alterations are reversible215,216, except possibly in the basolateral amygdala, where changes persisted for at least 30 d after chronic stress217. Moreover, age is a factor in recovery, as the aging medial prefrontal cortex fails to show recovery in the same time frame as occurs in younger animals218.
Structural plasticity can also occur after acute stress. A single traumatic stressor causes basolateral amygdala neurons to grow new spines over the next 10 days, but there is no growth of dendrites 219. And a single, high dose of injected corticosterone causes delayed dendritic growth over the next 10d220, mimicking the effects of chronic stress, although we do not know what happens to spines on those dendrites.
As to the mechanism underlying these effects, we know most about the hippocampus. Here, EAAs and glucocorticoids synergize to produce the effects summarized in Figure A221. EAA transporters in astrocytes and neurons play an important part in this160,222. In addition, chronic stress effects on shrinkage of dendrites in the CA3 region of the hippocampus are mediated in part by brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)223, whereas loss of spines in the CA1 region of the hippocampus are mediated in part by tissue plasminogen activator secretion by EAA-releasing neurons224 and by BDNF223. Effects of chronic stress on dendrite shrinkage in CA3 are blocked by NMDA blockers221 and NMDA blockade also prevents chronic stress induced shrinkage of medial prefrontal cortex neurons225.
Stress and glucocorticoid effects on glutamate receptor trafficking and mobility
Emerging evidence shows that AMPARs and NMDARs undergo dynamic exocytosis–endocytosis and lateral diffusion — processes that play a key role in controlling excitatory synaptic efficacy88,89. This suggests that stress and glucocorticoids may affect glutamatergic transmission through altering glutamate receptor trafficking and mobility. A glucocorticoid receptor-mediated, slowly-developing increase in the surface mobility of GluR2-containing AMPARs has been found in cultured hippocampal neurons after corticosterone treatment, which may underlie the facilitating effect of glucocorticoids on the recruitment or endocytosis of AMPA receptors during bi-directional synaptic plasticity90,91. Consistent with this possibility, mice trained in the spatial water maze task under stressful conditions show enhanced synaptic expression of AMPAR GluR2 subunits in the hippocampus than those trained under non-stressed conditions. This enhanced expression may underlie the facilitation of spatial learning and memory by stress in these mice92. In the rat PFC, the surface expression of NMDAR and AMPAR subunits, as well as the density of synaptic NMDAR and AMPAR clusters, is substantially elevated by acute stress or a short corticosterone treatment67,68. This suggests that the acute stress-induced synaptic potentiation in the PFC may be attributed to the increased delivery of glutamate receptors from intracellular or extrasynaptic surface pools to the synaptic membrane.
The impact of chronic stress on postsynaptic glutamate receptors in the PFC (and other brain areas) is less well understood (see supplementary online information S1 (table)). A history of chronic corticosterone exposure has been found to impair fear extinction in rats, with an associated reduction of NR2B and GluR2 and/or 3 subunit expression selectively in the ventromedial PFC93. Recently, it was shown that repeated restraint or unpredictable stress in rats causes a loss of surface AMPAR and NMDAR subunits in PFC neurons75, which contrasts with the facilitating effect of acute stress on glutamate receptor surface expression67,68. The level of total GluR1 and NR1 subunits in the PFC is also markedly reduced by exposure to repeated stress.75 Thus, disrupted membrane trafficking and/or altered degradation or synthesis of glutamate receptors may contribute to the loss of PFC glutamatergic transmission in chronically stressed animals.
Intracellular signalling underlying stress and glucocorticoid effects on glutamate receptors
The classical glucocorticoid receptor is a ligand-inducible nuclear transcription factor94. The delayed potentiating effect of short-term corticosterone treatment on excitatory postsynaptic responses in the PFC is abolished by glucocorticoid receptor antagonists and inhibitors of gene transcription or protein translation68, suggesting that it is a glucocorticoid receptor-mediated genomic effect. Serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinases (SGKs), a family of immediate early genes activated by glucocorticoid receptors, have been found to control the enhancing effect of acute stress on glutamate receptor trafficking and function in the PFC68 (Figure 3). The transcription, subcellular localization and enzymatic activity of SGKs are under the stringent regulation of various stimuli, such as oxidative stress or hormones95. SGKs participate in a wide variety of physiological functions, including activation of ion channels and carriers, regulation of transport, gene transcription, neuroexcitability, cell proliferation, and apoptosis96. Interestingly, SGK1 exhibits a fourfold higher expression in the hippocampus of fast-learning than slow-learning rats in the water maze learning task, and enhanced SGK expression in CA1 facilitates memory consolidation of spatial learning in rats97. Thus, SGK potentially plays a crucial role in glucocorticoid-induced memory facilitation by increasing the abundance of glutamate receptors in the synaptic membrane of neurons in limbic regions controlling cognition 67,68,92.
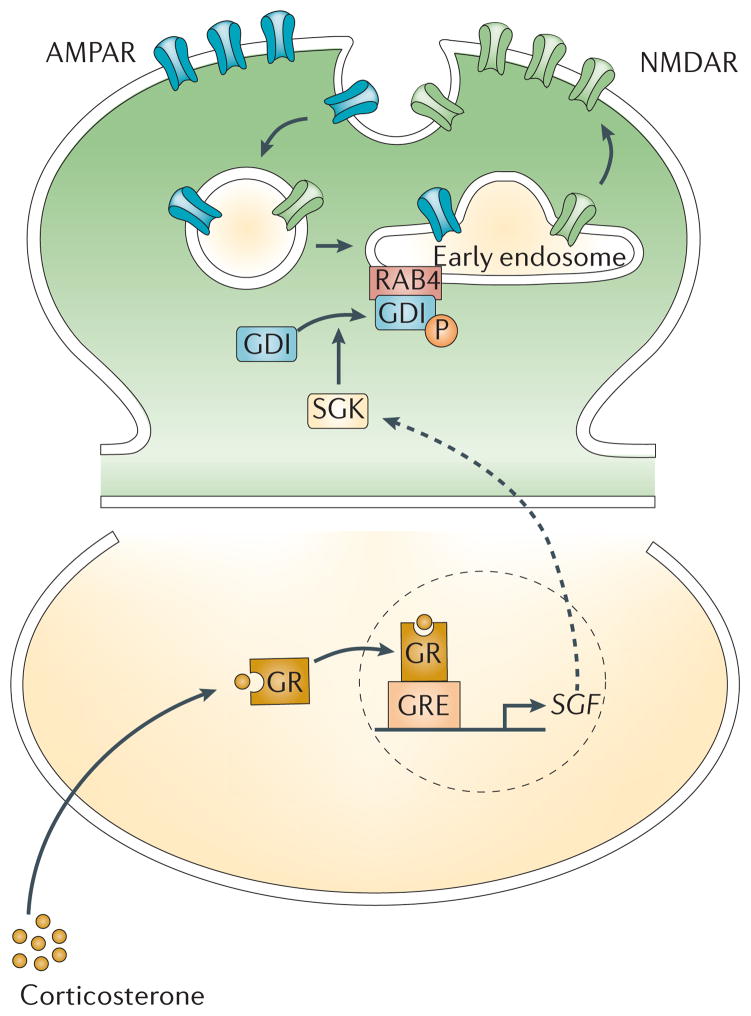
Figure 3. Stress induces changes in glutamate receptor trafficking and function in the prefrontal cortex.
In response to acute stress, activation of glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) triggers the upregulation of transcription of the gene encoding serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK) 1/368. SGK1/3 phosphorylates GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) and thereby increases the formation of GDI-Rab4 complexes69. Consequently, Rab4-mediated recycling of NMDARs and AMPARs from early endosomes (EE) to the plasma membrane is enhanced, and this results in increased glutamate receptor expression at the synaptic membrane and potentiated glutamatergic transmission67,68.
The key molecule linking glucocorticoid receptors and SGK activation to the increased surface expression of NMDARs and AMPARs following acute stress is Rab468,69, a member of the Rab family that mediates receptor recycling between early endosomes and the plasma membrane98. Rab proteins coordinate all the intracellular transport steps in the exocytic and endocytic pathways99. Many Rab proteins are regulated by the GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI)100, which functions as a cytosolic chaperone of Rab101. SGK phosphorylates GDI and thereby promotes the formation of GDI–Rab4 complex, thus facilitating the functional cycle of Rab4 and Rab4-mediated recycling of AMPARs to the synaptic membrane69 (Fig 3).
Whether other signalling pathways are also involved in effects of stress and glucocorticoids on glutamate receptors awaits investigation. In the hippocampus, a single corticosterone injection fails to upregulate Sgk1 mRNA102. However, acute stress has been found to trigger the activation of MAPK–EGR1 pathway via a glucocorticoid receptor-mediated genomic mechanism103, and inhibition of the hippocampal MAPK pathway abolishes the glucocorticoid-induced increase in contextual fear conditioning103. Moreover, in the PFC, but not the hippocampus, of mice, acute restraint stress causes an increase in the expression of Arc (activity-regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein)104, an immediate early gene that plays a key role in activity-dependent synaptic modification105,106. In addition, changes in adhesion molecules could potentially be involved in the effect of short-term glucocorticoids on excitatory synapses92.
The intracellular signalling pathway that mediates the effect of chronic stress on glutamate receptors remains largely unknown. One key mechanism for remodelling synaptic networks and altering synaptic transmission is post-translational modification of glutamate receptors and their interacting proteins through the ubiquitin pathway at the postsynaptic membrane107. Recently it was found that the loss of glutamate receptors in rat PFC neurons after repeated stress is attributable to increased ubiquitin–proteasome-dependent degradation of GluR1 and NR1 subunits75.
Implications for cognitive function
Given the role of glutamate receptor trafficking in learning, memory and other behaviours108,109, it is plausible that glucocorticoids regulate PFC-mediated cognitive processes by influencing postsynaptic glutamate receptor channels. Indeed, the GR–SGK-induced enhancement of PFC glutamatergic transmission may underlie the facilitated working memory induced by acute stress: exposing rodents to an acute stressor improves their performance in a working memory task, and this effect is abolished by blocking glucocorticoid receptor or SGK function in the PFC67,68. This finding fits well with acute stress- or glucocorticoid-induced facilitation of working memory (which involves the PFC) or declarative memory (which involves the hippocampus) observed in humans110–112. By contrast, chronic stress or glucocorticoid treatment impairs PFC-dependent cognitive functions in rats5,113 and humans114,115, similar to the stress-induced deficits in hippocampus-dependent cognitive processes116. It awaits investigation whether the suppression of PFC glutamatergic transmission by repeated stress underlies the working memory impairment and other cognitive symptoms often observed in stress-related mental disorders.
Effects on clearance and metabolism
Most studies examining the effects of stress on brain structure and physiology focus on neurons. However, emerging data suggest that stress may also affect glial cell function, including glutamate clearance and metabolism in these cells. These data are discussed below.
Glutamate transporters on glial and, to a lesser extent, neuronal, membranes rapidly bind synaptic glutamate, thereby influencing synaptic transmission and plasticity117. The locations of the transporters within the tripartite synapse are optimized for preventing glutamate spillover and activation of extrasynaptic glutamate receptors. Consistent with this function, in the hippocampus, glial glutamate transporter activity influences the level of stimulation of peri- and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors and mGluRs, but has little direct effect on synaptic AMPA-mediated excitatory postsynaptic potentials118. The effects of astrocytic remodelling on glutamatergic neurotransmission in the hypothalamus of lactating rats provides a clear example of how reduced astrocytic coverage of synapses can have dramatic effects on extrasynaptic glutamatergic neurotransmission119. Modulation of EAAT2 (the major glutamate transporter, expressed predominantly in glia) expression and function can affect neuronal vulnerability to excitotoxic events39, which is thought to be mediated by the relative activation of extrasynaptic to synaptic NMDA receptors120–125. Moreover, modulation of EAAT2 expression affects hippocampal LTD126. As the transporters are generally highly efficient in clearing glutamate from the extracellular space39,127, any effects of altered EAAT function are likely to be most pronounced under conditions of elevated glutamate release, such as under stress. Considering that individual astrocytes serve large numbers of synapses, with minimal overlap in the synapses served by neighbouring astrocytes128,129, the failure of a single astrocyte could impair glutamate removal at thousands of synapses118.
Effects of stress and glucocorticoids on glial cell number
Studies published over a decade ago revealed the potential contributions of glial cell pathology to stress-related psychiatric disorders such as major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder. For example, PFC regions of post-mortem brain samples from individuals suffering from mood disorders showed markedly reduced glial cell numbers and density 130–132. Depressed subjects also show reduced immuno-staining of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) — the main intermediate filament protein in mature astrocyte — in the PFC and other brain regions including the amygdala and cerebellum 133–137. Classically, GFAP has been used as a marker for mature astrocytes, but more recent studies that highlight the complex relationship between GFAP expression and a variety of astrocytic functions suggest that the expression may be heavily physiologically regulated138. It is therefore unclear if the findings in postmortem brain tissue from patients reflect a loss of GFAP expressing cells or a reduction in the amount of GFAP expressed by the cells. Considering the central role of astrocytes in amino acid neurotransmitter metabolism, these findings, which are suggestive of glial cell pathology, were rapidly associated with emerging reports of abnormal GABA and glutamate content in the brains of patients with mood disorders139,140 that appeared around the same time.
Rodent models assessing the impact of stress on glial cells have largely focused on the effects of chronic stress. Chronic unpredictable stress was associated with reduced proliferation of glial progenitor cells141, decreased numbers of GFAP-positive cells and reduced expression of GFAP in the prelimbic cortex141,142 (Figure 4). Rats exposed to early life stress had a reduced density of GFAP-immunoreactive astrocytes in the frontal cortex in adulthood, demonstrating the potential long-term effects of stress on glial cells143. Chronic stress-induced reductions in GFAP-immunoreactive astrocyte levels were also found in the hippocampus in rats and tree shrews 144,145. Another recent study employing a shorter-term repeated stress exposure accompanied by a blast-induced traumatic brain injury found inflammation and increased GFAP immunoreactivity in the PFC and hippocampus from the animals that had experienced both the chronic stress and the trauma but not in animals that had been exposed to the stress alone146. This finding suggests that physical injury or inflammation may stimulate a region of reactive gliosis that can be associated with an increased GFAP expression138. This reactive gliosis-associated increase in GFAP expression could provide an explanation for the increased GFAP expression observed under certain stress conditions, such as those involving repeated restraint stress147.
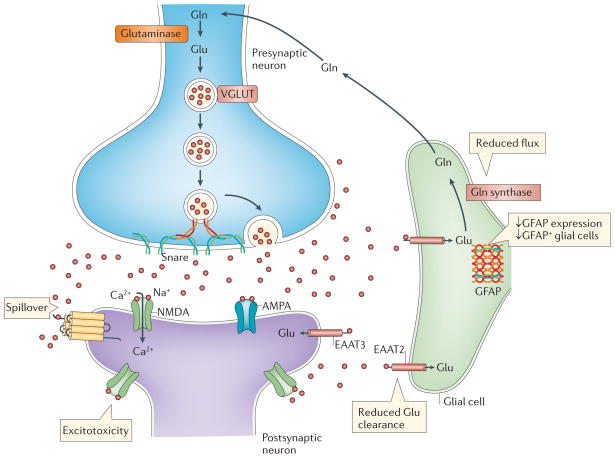
Figure 4. Chronic stress affects glial cells and glutamate metabolism.
Accumulating evidence suggests that chronic stress has significant effects on glial cell function. Several studies have demonstrated decreases in the expression of glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP) and in the number of GFAP-expressing glial cells in the hippocampus and PFC following exposure to chronic stress142. Chronic stress may also impair the ability to effectively clear synaptic glutamate through glial excitatory amino acid transporters (EAATs). This may lead to glutamate spillover and, ultimately, increased activation of extrasynaptic glutamate receptors resulting in excitotoxicity, a process that has been proposed to occur in several neurodegenerative disorders127,226 and possibly after exposure to chronic stress171. Finally, chronic stress may decrease the rates of flux through the glutamate–glutamine cycle, resulting in reduced glutamate metabolism171.
Glucocorticoids can alter the level and expression of GFAP in the PFC and other regions in rat brain, with both short and long term corticosterone treatments resulting in > 20% reduction in GFAP levels148,149. These changes were paralleled by changes in GFAP mRNA expression, indicating a genomic effect. This effect of glucocorticoids was not generalized to other astrocytic proteins or major structural neuronal proteins148. However, later studies that reported increased levels of GFAP expression in the hippocampus after chronic glucocorticoid treatment150,151 suggest that the effects are diverse and complex, with glucocorticoids potentially having regional and dose-related effects on GFAP expression.
Effects of stress and glucocorticoids on glial cell glutamate uptake
Changes in GFAP expression in the brains of stressed animals of course do not provide direct evidence of altered glutamate clearance (and, by extension, glutamate neurotransmission). However, there is evidence to suggest GFAP can modulate glutamate uptake activity through effects on transporter trafficking and surface expression152. A few studies have provided more direct measures of the effect of stress on glutamate uptake. An early study employing synaptosomal preparations from acutely restrained rats suggested that acute stress increases glutamate uptake in the frontal cortex and hippocampus153. Later studies have yielded mixed results in the hippocampus following acute stress exposure, showing either a glucocorticoid-mediated suppression of glutamate uptake154 or no effect on uptake155.
In relation to chronic stress, one study showed a decrease in cortical glutamate uptake following 21 days of restraint stress exposure156. A recent study also found a reduction in hippocampal glutamate clearance in hippocampal slice preparations from chronically stressed rats as well as evidence of increased glutamate release from hippocampal synaptosomes157. Another recent study using slice preparations from hippocampal, striatal and PFC regions reported no change in glutamate clearance immediately or 24 hours following various types of footshock exposure. However, increased glutamate uptake from hippocampal slices of helpless animals was observed immediately after exposure, and reduced rates of glutamate uptake in all three regions of the helpless animals 21 days later was reported158. This suggests a potential biphasic time course of the regulation of glutamate uptake following stress exposure. Yet another study, demonstrating a negative correlation between EAAT2-expression levels in the hippocampus, occipital and retrosplenial granular cortex of rats and the level of helplessness 5 weeks after exposure to foot shock stress159, provides evidence that the stress-related effects on EAAT2 function are long-lasting and associated with behavioural changes. Together with the findings discussed above, these data suggest that chronic stress impairs both the mechanisms that regulate glutamate release and the mechanisms that regulate glutamate clearance. These longer-term effects on the balance of glutamate release and uptake following chronic stress could contribute to the finding of sustained elevations of extracellular glutamate concentrations in the hippocampus of rats subjected to chronic stress, discussed above66.
Emerging evidence suggests that glucocorticoids may have a role in mediating the effects of stress on EAAT2 regulation. Rats chronically exposed to high levels of glucocorticoids exhibited increases in GLT-1b (an isoform of GLT-1 (EAAT2)) expression in the hippocampus160. In addition, activation of glucocorticoid receptors increased EAAT2 expression and enhanced glutamate uptake in primary astrocytes derived from cortical tissue161. However, the complex and seemingly biphasic regulation of EAAT2 by glucocorticoids is highlighted by the fact that EAAT2 mRNA expression was increased by adrenalectomy and inhibited by subsequent glucocorticoid replacement, whereas chronically elevated levels of glucocorticoids increased EAAT2 protein expression throughout the hippocampus160.
Other processes could also mediate the stress-induced effects on glutamate uptake. Highly conserved promoter sequences, including those for epithelial growth factor (EGF), transforming growth factor α (TGF α), and tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), have been identified in the regulatory region of EAAT2 in rodents and humans162. Circulating TNFα levels in particular, increase with chronic stress163 and have been shown to downregulate astrocyte-mediated glutamate transport through the direct downregulation of GLT-1164,165. In vitro studies also show that neuronal activity is linked to genomic and non-genomic regulation of astrocyte-specific synaptic functions such as trafficking and membrane stabilization or clustering of EAAT2 protein166,167. Thus, extracellular levels of glutamate itself can act to rapidly increase the function of glutamate transporters, to limit excitotoxicity following excessive glutamate release. Interestingly, post-mortem studies showed lower mRNA expression levels of SCL1A2 and SCL1A3 (the genes encoding the glial glutamate transporters) in the PFC168 and locus coeruleus169 of patients with major depressive disorder and lower EAAT2 immunoreactivity in the orbitofrontal cortex of depressed individuals compared with controls136.
Effects of stress on glutamate metabolism
Postmortem studies of the PFC of depressed individuals have shown reduced levels of the glutamate-ammonia ligase gene (GLUL) that encodes glutamine synthethase (which converts glutamate into glutamine) in glia168,170, and a trend for reduced glutamine synthethase-immunoreactivity in the orbitofrontal cortex of patients with major depressive disorder compared to controls136. However, few studies have examined the effects of stress on glutamine synthethase regulation. Rats exposed to chronic unpredictable stress showed reductions in glutamate–glutamine cycling in the PFC171. However, there was no evidence of reduced glutamine synthethase expression, suggesting that other, non-transcriptional regulatory factors may mediate the stress-induced changes. It is also possible that other steps in the metabolic cycle, such as the decreased uptake of glutamate into the glial cell, as discussed above, may contribute to the stress effect on glutamate metabolism.
In sum, the evidence suggests that acute stress and acute glucocorticoid treatments induce adaptive changes that lead to increased glutamate clearance, thereby preventing spillover of the excessive release of presynaptic glutamate into the extrasynaptic space. However, chronic stress, and possibly chronic glucocorticoids treatment, seem to result in sustained glial cell alterations and reduced rates of amino acid neurotransmitter cycling in the PFC, suggesting that chronic stress causes a reduced glutamate clearance capacity relative to the levels of glutamate release. Increased levels of extrasynaptic glutamate could lead to cellular damage through activation of extrasynaptic glutamate receptors, resulting in disruption of cellular functions and neurodegeneration120. This process could be involved in the cellular changes130,131,133,134,136,172,173 and volume reductions that are commonly observed in the PFC and hippocampus of patients with stress-related disorders, such as mood and anxiety disorders174,175. In a preliminary report, extracellular hippocampal glutamate content, measured by in vivo microdialysis, were correlated with reduced hippocampal volume in individuals with seizure disorders176, lending support to this hypothesis outlined above, although it does not prove that the relationship between extracellular glutamate levels and hippocampal volumes is causal.
Conclusions and future directions
Stress has been shown to induce complex structural changes in various brain regions (Box 3). With regard to the glutamatergic synapse, stress can have either plasticity-enhancing effects that are associated with improved cognition and function or noxious effects that are associated with impaired function, depending on the type, intensity and duration of the event, and this may contribute to the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders (see supplementary online information S1 (table)). Recent studies are beginning to elucidate how stress-induced changes in various aspects of glutamate neurotransmission are causally linked to each other and to the glucocorticoid responses to stress.
Acute stress seems to have the general effect of increasing glutamatergic neurotransmission in the PFC and other regions associated with memory, learning and affect, by inducing both genomic and non-genomic changes at various sites within the tripartite synapse. The presynaptic release of glutamate is rapidly increased by mineralocorticoid or glucocorticoid receptor-mediated effects on the machinery that regulates glutamate release. At the postsynaptic site, acute stress seems to increase the surface expression and density of ionotropic glutamate receptors, resulting in synaptic potentiation, with the mechanism and timing of these effects varying between brain regions. Although few studies have adequately examined the effects of acute stress on glutamate clearance and metabolism, there seems to be an increased expression of EAAT2 and possibly other glutamate transporters, matching the increased synaptic release of glutamate following acute stress exposure. Together, these changes could contribute to the adaptive stress response on cognitive functions, demonstrated by findings that moderate acute stress facilitates classical conditioning177, associative learning92,178 and working memory 67,68.
Emerging studies now suggest that chronic stress exposure has different effects on the glutamate synapse. Data from early studies suggest that chronic stress causes prolonged periods of stimulated glutamate release following acute stress exposure, at least in the hippocampus. Possibly as a compensatory response to elevated synaptic glutamate activity, there are changes in the surface expression of AMPAR and NMDAR subunits that seem to be associated with a decreased transmission efficiency and potentially impaired synaptic plasticity. Initial rodent studies suggest that the PFC may be specifically sensitive to the stress-induced effects on postsynaptic receptor function. Lastly, there is growing evidence from animal studies that chronic stress has effects on glial cell morphology, metabolism and function in the PFC and possibly also the hippocampus. These long-lasting chronic stress-induced changes in glutamatergic transmission may be linked to the impairments in spatial and contextual memory performance and attentional control5,7, and the impaired synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus–PFC connection that have been observed in rats after chronic stress85. The decreased ability to clear extracellular glutamate as a result of impaired glial cell uptake and metabolism, combined with stress-induced changes in glutamate release and glutamate receptor function, could provide a pathophysiological mechanism leading to many of the structural changes (Box 3) observed in brain regions of individuals with stress-associated psychiatric disorders, such as mood and anxiety disorders.
These findings suggest a new line of drug development that should be aimed at minimizing the effects of chronic stress exposure on the function of the glutamatergic neurotransmitter system64,179 (Figure 5). Findings from animal studies that chronic administration of classical antidepressant drugs such as SSRIs, SNRIs, tricyclics and atypical antidepressants reduce the stress-induced up-regulation of glutamate release in superfused synaptosomes from prefrontal/frontal cortex52 support the hypothesis that pharmacological modulation of presynaptic release of glutamate may provide a means of preventing the effects of stress. Other studies have demonstrated that drugs such as riluzole180–182 and ceftriaxone183, which increase glutamate clearance, can prevent or reverse the effects of chronic stress and chronic glucocorticoid exposure on amino acid neurotransmitter cycling; on glial expression within the PFC; and on despair and anhedonia in animal models of depression171,184,185. This points to glutamate clearance mechanisms as potential new targets for novel drug development. Positive and negative allosteric modulators of metabotropic glutamate receptors, which can influence glutamate release and extracellular glutamate levels, have also been shown to have antidepressant-like actions186 and are now being investigated for use in various psychiatric indications. Further, drugs that directly target ionotropic receptors have become targets for psychiatric drug development179. Specifically, NMDA receptor antagonists such as ketamine have been shown to produce a rapid and sustained antidepressant response in both preclinical animal models and small controlled clinical trials187. The results of recent studies suggest that this NMDAR antagonist antidepressant effect may be related to a rapid increase in glutamate release, resulting in activation of AMPA receptors and downstream changes in synaptic protein synthesis and dendritic spine formation188–190. The antidepressant effect of the NMDA receptor antagonist-induced glutamate surge may at first seem contradictory to the model presented above. However, it is possible that the rapid increase in glutamate release following ketamine treatment can transiently compensate for the decreased transmission efficiency and impaired synaptic plasticity associated with chronic stress and stress-related disorders. A recent study that demonstrated that acute treatment with NMDA channel blockers rapidly ameliorates chronic unpredictable stress-induced decreases in the expression levels of synaptic proteins and spine number and the frequency and amplitude of synaptic currents in the PFC191, further supports this line of reasoning. Additional support for this hypothesis comes from studies showing that positive allosteric modulators of AMPA-type glutamate receptors have antidepressant-like properties in rodent models of depression192.
Figure 5. Pharmacological targets.
Observations of stress-induced effects on the glutamate synapse have suggested several unique forms of pharmacological interventions for stress related disorders such as mood and anxiety disorders179. Drugs that modify glutamate release (a), such as lamotrigine and rilzuole, have been shown to have antidepressant-like actions in rodent models and in clinical trials171,227,228. In addition, negative and positive allosteric modulators of group II mGluRs that also modulate presynaptic glutamate release (not shown), have been shown to have antidepressant-like actions in rodent models186. Drugs targeting NMDA receptors (b), especially NMDA antagonists (ketamine, RO 25-6981, and CP101,606) have demonstrated rapid and robust antidepressant-like effects in both rodent models and clinical trials187,188. Positive and negative allosteric modulators of the mGlu 5 receptor (c) have been shown to possess antidepressant and anxiolytic properties in preclinical studies186 Drugs targeting AMPA receptors (d), especially agents that potentiate the activation of AMPA receptors, have both nootropic (cognition-enhancing) properties and antidepressant-like effects in rodent models192. Various agents that regulate glucocorticoid signalling have effects on memory and possess mood and anxiety modifying properties229 (e). Drugs such as riluzole and ceftriaxone that indirectly facilitate glutamate transport into glia (f), possess both neuroprotective and antidepressant-like effects171,184,185. Considering endocannabinoids are reduced in the PFC and hippocampus in animal models of depression, and CB1 receptor stimulation in the PFC and hippocampus is anxiolytic and antidepressant, targeted pharmacological augmentation of endocannabinoid signalling (g) has recently been proposed as a promising therapeutic strategy for the treatment of mood and anxiety disorders230.
In conclusion, recent studies are beginning to show that acute stress and glucocorticoids can facilitate learning and memory in both the PFC and hippocampus and that chronic stress may contribute to the pathophysiology of several psychiatric disorders through effects on the glutamatergic synapse, especially within the PFC. The identification and characterization of the physiological mechanisms that regulate the presynaptic release, post-synaptic receptor expression and trafficking, and clearance and metabolism of glutamate allows the opportunity to use novel pharmacological interventions to improve and retain memory function and to treat and possibly prevent some psychiatric disorders.
Acknowledgments
MP support: Ministry of University and Research (MIUR-PRIN), NARSAD, European Union (FP6 – GENDEP Project). ZY support: MH85774 and MH84233. BMc support: MH 41256 to BMc and 5 P50 MH58911 (Conte Center Grant: Joe Ledoux, PI) and MacArthur Foundation Research Newtwork on Socioeconomic Status and Health. GS Support: NIMH R01 MH081211, 5 R01 MH071676-05, NARSAD, Department of Veterans Affairs National Center for PTSD, Clinical Neuroscience Division West Haven CT, State of Connecticut Department of Mental Health and Addiction Services
Glossary
- FM1-43
FM1-43 is an amphiphilic fluorescent dye, that can intercalate into the phospholipid bilayer of biological membranes, allowing to stain presynaptic vesicles
Footnotes
Further information
MP websites: http://users.unimi.it/DPS/
GS website: http://psychiatry.yale.edu/research/programs/clinical_people/trials/sanacora1.aspx
BMc: http://www.rockefeller.edu/research/faculty/labheads/BruceMcEwen/
Competing financial interests
MP: Dr. Popoli received support and/or has consulted for Abiogen, GlaxoSmith-Kline, MerckSharp and Dohme, Servier and Fidia
ZY: Reports no competing financial interests
BMc: Reports no competing financial interests
GS: Dr. Sanacora has received consulting fees form AstraZeneca, Avanier Pharmaceuticals, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Evotec, Eli Lilly & Co., Hoffman La-Roche, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, and Novum Pharmaceuticals over the last 24 months. He has also received additional grant support from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Hoffman La-Roche, Merck & Co., and Sepracor Inc over the last 24 months. In addition he is a co-inventor on filed patent application by Yale University (PCTWO06108055A1).
References
- 1.Selye H. A syndrome produced by diverse nocuous agents. Nature. 1936;138:32. doi: 10.1176/jnp.10.2.230a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lazarus RS, Folkman S. Stress, Appraisal and Coping. Springer Verlag; New York: 1984. [Google Scholar]
- 3.McEwen BS. Protective and damaging effects of stress mediators. New England Journal of Medicine. 1998;338:171–179. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199801153380307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McEwen BS, Gianaros PJ. Stress- and allostasis-induced brain plasticity. Annu Rev Med. 2011;62:431–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-052209-100430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liston C, et al. Stress-induced alterations in prefrontal cortical dendritic morphology predict selective impairments in perceptual attentional set-shifting. J Neurosci. 2006;26:7870–7874. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1184-06.2006. 26/30/7870 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vyas A, Mitra R, Shankaranarayana Rao BS, Chattarji S. Chronic stress induces contrasting patterns of dendritic remodeling in hippocampal and amygdaloid neurons. J Neurosci. 2002;22:6810–6818. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-15-06810.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McEwen BS. Stress and hippocampal plasticity. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 1999;22:105–122. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.22.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lupien SJ, McEwen BS, Gunnar MR, Heim C. Effects of stress throughout the lifespan on the brain, behaviour and cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:434–445. doi: 10.1038/nrn2639. nrn2639 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Diamond DM, Campbell AM, Park CR, Halonen J, Zoladz PR. The temporal dynamics model of emotional memory processing: a synthesis on the neurobiological basis of stress-induced amnesia, flashbulb and traumatic memories, and the Yerkes-Dodson law. Neural Plast. 2007:60803. doi: 10.1155/2007/60803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Arnsten AF. Stress signalling pathways that impair prefrontal cortex structure and function. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:410–422. doi: 10.1038/nrn2648. nrn2648 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Goldman-Rakic PS. Cellular basis of working memory. Neuron. 1995;14:477–485. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90304-6. 0896-6273(95)90304-6 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lisman JE, Fellous JM, Wang XJ. A role for NMDA-receptor channels in working memory. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:273–275. doi: 10.1038/1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Milad MR, et al. Recall of fear extinction in humans activates the ventromedial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus in concert. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;62:446–454. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.10.011. S0006-3223(06)01298-4 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Milad MR, Quirk GJ. Neurons in medial prefrontal cortex signal memory for fear extinction. Nature. 2002;420:70–74. doi: 10.1038/nature01138. nature01138 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Goto Y, Yang CR, Otani S. Functional and dysfunctional synaptic plasticity in prefrontal cortex: roles in psychiatric disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67:199–207. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.08.026. S0006-3223(09)01046-4 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hains AB, Arnsten AF. Molecular mechanisms of stress-induced prefrontal cortical impairment: implications for mental illness. Learn Mem. 2008;15:551–564. doi: 10.1101/lm.921708. 15/8/551 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Moghaddam B. Bringing order to the glutamate chaos in schizophrenia. Neuron. 2003;40:881–884. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00757-8. S0896627303007578 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Joels M, Baram TZ. The neuro-symphony of stress. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:459–466. doi: 10.1038/nrn2632. nrn2632 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Roozendaal B, McEwen BS, Chattarji S. Stress, memory and the amygdala. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10:423–433. doi: 10.1038/nrn2651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Joiner ML, et al. Assembly of a beta2-adrenergic receptor--GluR1 signalling complex for localized cAMP signalling. EMBO J. 2010;29:482–495. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.344. emboj2009344 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Erecinska M, Silver IA. Metabolism and role of glutamate in mammalian brain. Prog Neurobiol. 1990;35:245–296. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(90)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lang T, Jahn R. Core proteins of the secretory machinery. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008:107–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-74805-2_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rizo J, Rosenmund C. Synaptic vesicle fusion. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008;15:665–674. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sudhof TC, Rothman JE. Membrane fusion: grappling with SNARE and SM proteins. Science. 2009;323:474–477. doi: 10.1126/science.1161748. 323/5913/474 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Roche KW, et al. Molecular determinants of NMDA receptor internalization. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:794–802. doi: 10.1038/9049890498. [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hayashi Y, et al. Driving AMPA receptors into synapses by LTP and CaMKII: requirement for GluR1 and PDZ domain interaction. Science. 2000;287:2262–2267. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5461.2262. 8357 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Elias GM, et al. Synapse-specific and developmentally regulated targeting of AMPA receptors by a family of MAGUK scaffolding proteins. Neuron. 2006;52:307–320. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.09.012. S0896-6273(06)00717-3 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee SH, Liu L, Wang YT, Sheng M. Clathrin adaptor AP2 and NSF interact with overlapping sites of GluR2 and play distinct roles in AMPA receptor trafficking and hippocampal LTD. Neuron. 2002;36:661–674. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)01024-3. S0896627302010243 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Prybylowski K, et al. The synaptic localization of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors is controlled by interactions with PDZ proteins and AP-2. Neuron. 2005;47:845–857. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.08.016. S0896-6273(05)00691-4 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Bhattacharyya S, Biou V, Xu W, Schluter O, Malenka RC. A critical role for PSD-95/AKAP interactions in endocytosis of synaptic AMPA receptors. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:172–181. doi: 10.1038/nn.2249. nn.2249 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Setou M, Nakagawa T, Seog DH, Hirokawa N. Kinesin superfamily motor protein KIF17 and mLin-10 in NMDA receptor-containing vesicle transport. Science. 2000;288:1796–1802. doi: 10.1126/science.288.5472.1796. 8578 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Setou M, et al. Glutamate-receptor-interacting protein GRIP1 directly steers kinesin to dendrites. Nature. 2002;417:83–87. doi: 10.1038/nature743. nature743 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang Z, et al. Myosin Vb mobilizes recycling endosomes and AMPA receptors for postsynaptic plasticity. Cell. 2008;135:535–548. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.057. S0092-8674(08)01253-1 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pfeffer S, Aivazian D. Targeting Rab GTPases to distinct membrane compartments. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:886–896. doi: 10.1038/nrm1500. nrm1500 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brown TC, Tran IC, Backos DS, Esteban JA. NMDA receptor-dependent activation of the small GTPase Rab5 drives the removal of synaptic AMPA receptors during hippocampal LTD. Neuron. 2005;45:81–94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.12.023. S0896627304008359 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Park M, Penick EC, Edwards JG, Kauer JA, Ehlers MD. Recycling endosomes supply AMPA receptors for LTP. Science. 2004;305:1972–1975. doi: 10.1126/science.1102026305/5692/1972. [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Liu Y, et al. A single fear-inducing stimulus induces a transcription-dependent switch in synaptic AMPAR phenotype. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13:223–231. doi: 10.1038/nn.2474. nn.2474 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hawasli AH, et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 governs learning and synaptic plasticity via control of NMDAR degradation. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:880–886. doi: 10.1038/nn1914. nn1914 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.O’Shea RD. Roles and regulation of glutamate transporters in the central nervous system. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2002;29:1018–1023. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1681.2002.03770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lowy MT, Gault L, Yamamoto BK. Adrenalectomy attenuates stress-induced elevations in extracellular glutamate concentrations in the hippocampus. J Neurochem. 1993;61:1957–1960. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb09839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lowy MT, Wittenberg L, Yamamoto BK. Effect of acute stress on hippocampal glutamate levels and spectrin proteolysis in young and aged rats. Journal of Neurochemistry. 1995;65:268–274. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1995.65010268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Venero C, Borrell J. Rapid glucocorticoid effects on excitatory amino acid levels in the hippocampus: a microdialysis study in freely moving rats. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:2465–2473. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Reznikov LR, et al. Acute stress-mediated increases in extracellular glutamate levels in the rat amygdala: differential effects of antidepressant treatment. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25:3109–3114. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05560.x. EJN5560 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bagley J, Moghaddam B. Temporal dynamics of glutamate efflux in the prefrontal cortex and in the hippocampus following repeated stress: effects of pretreatment with saline or diazepam. Neuroscience. 1997;77:65–73. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(96)00435-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Moghaddam B. Stress preferentially increases extraneuronal levels of excitatory amino acids in the prefrontal cortex: comparison to hippocampus and basal ganglia. Journal of Neurochemistry. 1993;60:1650–1657. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb13387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Westerink BH. Brain microdialysis and its application for the study of animal behaviour. Behav Brain Res. 1995;70:103–124. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(95)80001-8. 0166-4328(95)80001-8 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Timmerman W, Westerink BH. Brain microdialysis of GABA and glutamate: what does it signify? Synapse. 1997;27:242–261. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(199711)27:3<242::AID-SYN9>3.0.CO;2-D. [pii]10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(199711)27:3<242::AID-SYN9>3.0.CO;2-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hascup ER, et al. Rapid microelectrode measurements and the origin and regulation of extracellular glutamate in rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurochem. 2010;115:1608–1620. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Karst H, et al. Mineralocorticoid receptors are indispensable for nongenomic modulation of hippocampal glutamate transmission by corticosterone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:19204–19207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507572102. 0507572102 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.de Kloet ER, Karst H, Joels M. Corticosteroid hormones in the central stress response: quick-and-slow. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2008;29:268–272. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2007.10.002. S0091-3022(07)00057-X [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mallei A, et al. Synaptoproteomics of learned helpless rats involve energy metabolism and cellular remodeling pathways in depressive-like behavior and antidepressant response. Neuropharmacology. 2010 doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.12.012. S0028-3908(10)00347-3 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Musazzi L, et al. Acute stress increases depolarization-evoked glutamate release in the rat prefrontal/frontal cortex: the dampening action of antidepressants. PLoS One. 2010;5:e8566. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wang CC, Wang SJ. Modulation of presynaptic glucocorticoid receptors on glutamate release from rat hippocampal nerve terminals. Synapse. 2009;63:745–751. doi: 10.1002/syn.20654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hill MN, et al. Recruitment of prefrontal cortical endocannabinoid signaling by glucocorticoids contributes to termination of the stress response. J Neurosci. 2011;31:10506–10515. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0496-11.2011. 31/29/10506 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Rizzoli SO, Betz WJ. Synaptic vesicle pools. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:57–69. doi: 10.1038/nrn1583. nrn1583 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sorensen JB. Formation, stabilisation and fusion of the readily releasable pool of secretory vesicles. Pflugers Arch. 2004;448:347–362. doi: 10.1007/s00424-004-1247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Matz J, Gilyan A, Kolar A, McCarvill T, Krueger SR. Rapid structural alterations of the active zone lead to sustained changes in neurotransmitter release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:8836–8841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906087107. 0906087107 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Lonart G, Sudhof TC. Assembly of SNARE core complexes prior to neurotransmitter release sets the readily releasable pool of synaptic vesicles. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:27703–27707. 275/36/27703 [pii] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Popoli M, et al. Acute behavioural stress affects the readily releasable pool of vesicles in prefrontal/frontal cortex. Society for Neuroscience Abs. 2010:667.667. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Martens S, Kozlov MM, McMahon HT. How synaptotagmin promotes membrane fusion. Science. 2007;316:1205–1208. doi: 10.1126/science.1142614. 1142614 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Chicka MC, Hui E, Liu H, Chapman ER. Synaptotagmin arrests the SNARE complex before triggering fast, efficient membrane fusion in response to Ca2+ Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008;15:827–835. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1463. nsmb.1463 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Xue M, et al. Complexins facilitate neurotransmitter release at excitatory and inhibitory synapses in mammalian central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:7875–7880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803012105. 0803012105 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Giraudo CG, et al. Alternative zippering as an on-off switch for SNARE-mediated fusion. Science. 2009;323:512–516. doi: 10.1126/science.1166500. 323/5913/512 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Sanacora G, Treccani G, Popoli M. Towards a glutamate hypothesis of depression An emerging frontier of neuropsychopharmacology for mood disorders. Neuropharmacology. 2012;62:63–77. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.07.036. S0028-3908(11)00324-8 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Moghaddam B. Stress activation of glutamate neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex: implications for dopamine-associated psychiatric disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2002;51:775–787. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(01)01362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Yamamoto BK, Reagan LP. The glutamatergic system in neuronal plasticity and vulnerability in mood disorders. Neuropsychiatric Dis Treatment. 2006;2:7–14. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Yuen EY, et al. Acute stress enhances glutamatergic transmission in prefrontal cortex and facilitates working memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:14075–14079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906791106. 0906791106 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Yuen EY, et al. Mechanisms for acute stress-induced enhancement of glutamatergic transmission and working memory. Mol Psychiatry. 2011;16:156–170. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.50. mp201050 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Liu W, Yuen EY, Yan Z. The stress hormone corticosterone increases synaptic alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors via serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK) regulation of the GDI-Rab4 complex. J Biol Chem. 285:6101–6108. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.050229. M109.050229 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Olijslagers JE, et al. Rapid changes in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell function via pre- as well as postsynaptic membrane mineralocorticoid receptors. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;27:2542–2550. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06220.x. EJN6220 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.de Kloet ER, Joels M, Holsboer F. Stress and the brain: from adaptation to disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:463–475. doi: 10.1038/nrn1683. nrn1683 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Karst H, Joels M. Corticosterone slowly enhances miniature excitatory postsynaptic current amplitude in mice CA1 hippocampal cells. J Neurophysiol. 2005;94:3479–3486. doi: 10.1152/jn.00143.2005. 00143.2005 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Saal D, Dong Y, Bonci A, Malenka RC. Drugs of abuse and stress trigger a common synaptic adaptation in dopamine neurons. Neuron. 2003;37:577–582. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00021-7. S0896627303000217 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Campioni MR, Xu M, McGehee DS. Stress-induced changes in nucleus accumbens glutamate synaptic plasticity. J Neurophysiol. 2009;101:3192–3198. doi: 10.1152/jn.91111.2008. 91111.2008 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Yuen EY, Wei J, Yan Z. Soc Neurosci Abstr. Vol. 389.21. San Diego, California: Nov 13–17, 2010. Repeated stress suppresses glutamate receptor expression and function in prefrontal cortex and impairs object recognition memory. [Google Scholar]
- 76.Karst H, Joels M. Effect of chronic stress on synaptic currents in rat hippocampal dentate gyrus neurons. J Neurophysiol. 2003;89:625–633. doi: 10.1152/jn.00691.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Maroun M, Richter-Levin G. Exposure to acute stress blocks the induction of long-term potentiation of the amygdala-prefrontal cortex pathway in vivo. J Neurosci. 2003;23:4406–4409. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-11-04406.2003. 23/11/4406 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Rocher C, Spedding M, Munoz C, Jay TM. Acute stress-induced changes in hippocampal/prefrontal circuits in rats: effects of antidepressants. Cereb Cortex. 2004;14:224–229. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhg122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Mailliet F, et al. Protection of stress-induced impairment of hippocampal/prefrontal LTP through blockade of glucocorticoid receptors: implication of MEK signaling. Exp Neurol. 2008;211:593–596. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.02.030. S0014-4886(08)00100-3 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Richter-Levin G, Maroun M. Stress and amygdala suppression of metaplasticity in the medial prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2010;20:2433–2441. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhp311. bhp311 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hirata R, et al. Possible relationship between the stress-induced synaptic response and metaplasticity in the hippocampal CA1 field of freely moving rats. Synapse. 2009;63:549–556. doi: 10.1002/syn.20631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Chaouloff F, Hemar A, Manzoni O. Acute stress facilitates hippocampal CA1 metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression. J Neurosci. 2007;27:7130–7135. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1150-07.2007. 27/27/7130 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Zhong P, Liu W, Gu Z, Yan Z. Serotonin facilitates long-term depression induction in prefrontal cortex via p38 MAPK/Rab5-mediated enhancement of AMPA receptor internalization. J Physiol. 2008;586:4465–4479. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.155143. jphysiol.2008.155143 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Quan M, et al. Impairments of behavior, information flow between thalamus and cortex, and prefrontal cortical synaptic plasticity in an animal model of depression. Brain Res Bull. 2011;85:109–116. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.03.002. S0361-9230(11)00079-7 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Cerqueira JJ, Mailliet F, Almeida OF, Jay TM, Sousa N. The prefrontal cortex as a key target of the maladaptive response to stress. J Neurosci. 2007;27:2781–2787. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4372-06.2007. 27/11/2781 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Goldwater DS, et al. Structural and functional alterations to rat medial prefrontal cortex following chronic restraint stress and recovery. Neuroscience. 2009;164:798–808. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.08.053. S0306-4522(09)01404-3 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Judo C, et al. Early stress exposure impairs synaptic potentiation in the rat medial prefrontal cortex underlying contextual fear extinction. Neuroscience. 2010;169:1705–1714. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.06.035. S0306-4522(10)00882-1 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Malinow R, Malenka RC. AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2002;25:103–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.25.112701.142758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Wenthold RJ, Prybylowski K, Standley S, Sans N, Petralia RS. Trafficking of NMDA receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003;43:335–358. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.43.100901.135803100901.135803. [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Groc L, Choquet D, Chaouloff F. The stress hormone corticosterone conditions AMPAR surface trafficking and synaptic potentiation. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11:868–870. doi: 10.1038/nn.2150. nn.2150 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Martin S, et al. Corticosterone alters AMPAR mobility and facilitates bidirectional synaptic plasticity. PLoS One. 2009;4:e4714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Conboy L, Sandi C. Stress at learning facilitates memory formation by regulating AMPA receptor trafficking through a glucocorticoid action. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010;35:674–685. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.172. npp2009172 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Gourley SL, Kedves AT, Olausson P, Taylor JR. A history of corticosterone exposure regulates fear extinction and cortical NR2B, GluR2/3, and BDNF. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;34:707–716. doi: 10.1038/npp.2008.123. npp2008123 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Funder JW. Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors: biology and clinical relevance. Annu Rev Med. 1997;48:231–240. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.48.1.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Firestone GL, Giampaolo JR, O’Keeffe BA. Stimulus-dependent regulation of serum and glucocorticoid inducible protein kinase (SGK) transcription, subcellular localization and enzymatic activity. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2003;13:1–12. doi: 10.1159/000070244CPB13001. [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Lang F, et al. (Patho)physiological significance of the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase isoforms. Physiol Rev. 2006;86:1151–1178. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00050.2005. 86/4/1151 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Tsai KJ, Chen SK, Ma YL, Hsu WL, Lee EH. sgk, a primary glucocorticoid-induced gene, facilitates memory consolidation of spatial learning in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:3990–3995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.062405399062405399. [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.van der Sluijs P, et al. The small GTP-binding protein rab4 controls an early sorting event on the endocytic pathway. Cell. 1992;70:729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90307-x. 0092-8674(92)90307-X [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Zerial M, McBride H. Rab proteins as membrane organizers. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2:107–117. doi: 10.1038/35052055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Sasaki T, et al. Purification and characterization from bovine brain cytosol of a protein that inhibits the dissociation of GDP from and the subsequent binding of GTP to smg p25A, a ras p21-like GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:2333–2337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Wu YW, et al. Membrane targeting mechanism of Rab GTPases elucidated by semisynthetic protein probes. Nat Chem Biol. 6:534–540. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.386. nchembio.386 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.van Gemert NG, Meijer OC, Morsink MC, Joels M. Effect of brief corticosterone administration on SGK1 and RGS4 mRNA expression in rat hippocampus. Stress. 2006;9:165–170. doi: 10.1080/10253890600966169. T436X75727027277 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Revest JM, et al. The MAPK pathway and Egr-1 mediate stress-related behavioral effects of glucocorticoids. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:664–672. doi: 10.1038/nn1441. nn1441 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Fumagalli F, et al. AMPA GluR-A receptor subunit mediates hippocampal responsiveness in mice exposed to stress. Hippocampus. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Chowdhury S, et al. Arc/Arg3.1 interacts with the endocytic machinery to regulate AMPA receptor trafficking. Neuron. 2006;52:445–459. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.08.033. S0896-6273(06)00682-9 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Messaoudi E, et al. Sustained Arc/Arg3.1 synthesis controls long-term potentiation consolidation through regulation of local actin polymerization in the dentate gyrus in vivo. J Neurosci. 2007;27:10445–10455. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2883-07.2007. 27/39/10445 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Mabb AM, Ehlers MD. Ubiquitination in postsynaptic function and plasticity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 26:179–210. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100109-104129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Krugers HJ, Hoogenraad CC, Groc L. Stress hormones and AMPA receptor trafficking in synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Rev Neurosci. 11:675–681. doi: 10.1038/nrn2913. nrn2913 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Van den Oever MC, et al. Prefrontal cortex AMPA receptor plasticity is crucial for cue-induced relapse to heroin-seeking. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11:1053–1058. doi: 10.1038/nn.2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Lupien SJ, et al. The modulatory effects of corticosteroids on cognition: studies in young human populations. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2002;27:401–416. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4530(01)00061-0. S0306453001000610 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Henckens MJ, van Wingen GA, Joels M, Fernandez G. Time-dependent corticosteroid modulation of prefrontal working memory processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:5801–5806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019128108. 1019128108 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Smeets T, Giesbrecht T, Jelicic M, Merckelbach H. Context-dependent enhancement of declarative memory performance following acute psychosocial stress. Biol Psychol. 2007;76:116–123. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2007.07.001. S0301-0511(07)00114-7 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Cerqueira JJ, et al. Morphological correlates of corticosteroid-induced changes in prefrontal cortex-dependent behaviors. J Neurosci. 2005;25:7792–7800. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1598-05.2005. 25/34/7792 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Young AH, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW, Cowen PJ. The effects of chronic administration of hydrocortisone on cognitive function in normal male volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1999;145:260–266. doi: 10.1007/s002130051057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Liston C, McEwen BS, Casey BJ. Psychosocial stress reversibly disrupts prefrontal processing and attentional control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:912–917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807041106. 0807041106 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.McEwen BS. Physiology and neurobiology of stress and adaptation: central role of the brain. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:873–904. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00041.2006. 87/3/873 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Tzingounis AV, Wadiche JI. Glutamate transporters: confining runaway excitation by shaping synaptic transmission. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:935–947. doi: 10.1038/nrn2274. nrn2274 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Zheng K, Scimemi A, Rusakov DA. Receptor actions of synaptically released glutamate: the role of transporters on the scale from nanometers to microns. Biophys J. 2008;95:4584–4596. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.108.129874. S0006-3495(08)78599-0 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Piet R, Vargova L, Sykova E, Poulain DA, Oliet SH. Physiological contribution of the astrocytic environment of neurons to intersynaptic crosstalk. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:2151–2155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.03084081000308408100. [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Hardingham GE, Bading H. Synaptic versus extrasynaptic NMDA receptor signalling: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11:682–696. doi: 10.1038/nrn2911. nrn2911 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Hardingham GE, Fukunaga Y, Bading H. Extrasynaptic NMDARs oppose synaptic NMDARs by triggering CREB shut-off and cell death pathways.[see comment] Nature Neuroscience. 2002;5:405–414. doi: 10.1038/nn835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Vanhoutte P, Bading H. Opposing roles of synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors in neuronal calcium signalling and BDNF gene regulation. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 2003;13:366–371. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(03)00073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Ivanov A, et al. Opposing role of synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors in regulation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) activity in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J Physiol. 2006;572:789–798. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.105510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Leveille F, et al. Neuronal viability is controlled by a functional relation between synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors. FASEB J. 2008;22:4258–4271. doi: 10.1096/fj.08-107268. fj.08-107268 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Xu J, et al. Extrasynaptic NMDA receptors couple preferentially to excitotoxicity via calpain-mediated cleavage of STEP. J Neurosci. 2009;29:9330–9343. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2212-09.2009. 29/29/9330 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Omrani A, et al. Up-regulation of GLT-1 severely impairs LTD at mossy fibre--CA3 synapses. J Physiol. 2009;587:4575–4588. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.177881. jphysiol.2009.177881 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Beart PM, O’Shea RD. Transporters for L-glutamate: an update on their molecular pharmacology and pathological involvement. Br J Pharmacol. 2007;150:5–17. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Bushong EA, Martone ME, Jones YZ, Ellisman MH. Protoplasmic astrocytes in CA1 stratum radiatum occupy separate anatomical domains. J Neurosci. 2002;22:183–192. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-01-00183.2002. 22/1/183 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Ogata K, Kosaka T. Structural and quantitative analysis of astrocytes in the mouse hippocampus. Neuroscience. 2002;113:221–233. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00041-6. S0306452202000416 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Ongur D, Drevets WC, Price JL. Glial reduction in the subgenual prefrontal cortex in mood disorders. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1998;95:13290–13295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.13290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Cotter D, et al. Reduced neuronal size and glial cell density in area 9 of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in subjects with major depressive disorder. Cerebral Cortex. 2002;12:386–394. doi: 10.1093/cercor/12.4.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Rajkowska G, Miguel-Hidalgo JJ. Gliogenesis and glial pathology in depression. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2007;6:219–233. doi: 10.2174/187152707780619326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, et al. Glial fibrillary acidic protein immunoreactivity in the prefrontal cortex distinguishes younger from older adults in major depressive disorder. Biological Psychiatry. 2000;48:861–873. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(00)00999-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Webster MJ, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of phosphorylated glial fibrillary acidic protein in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus from patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression. Brain, Behavior, & Immunity. 2001;15:388–400. doi: 10.1006/brbi.2001.0646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Fatemi SH, et al. Glial fibrillary acidic protein is reduced in cerebellum of subjects with major depression, but not schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research. 2004;69:317–323. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2003.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Miguel-Hidalgo JJ, et al. Glial and glutamatergic markers in depression, alcoholism, and their comorbidity. J Affect Disord. 2010;127:230–240. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2010.06.003. S0165-0327(10)00416-7 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Altshuler LL, et al. Amygdala astrocyte reduction in subjects with major depressive disorder but not bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2010;12:541–549. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5618.2010.00838.x. BDI838 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Middeldorp J, Hol EM. GFAP in health and disease. Prog Neurobiol. 2011;93:421–443. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.01.005. S0301-0082(11)00006-2 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Sanacora G, et al. Reduced cortical gamma-aminobutyric acid levels in depressed patients determined by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1999;56:1043–1047. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.56.11.1043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Sanacora G, et al. Subtype-specific alterations of GABA and glutamate in major depression. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2004;61:705–713. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.61.7.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Banasr M, et al. Chronic Unpredictable Stress Decreases Cell Proliferation in the Cerebral Cortex of the Adult Rat. Biol Psychiatry. 2007 doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Banasr M, Duman RS. Glial Loss in the Prefrontal Cortex Is Sufficient to Induce Depressive-like Behaviors. Biol Psychiatry. 2008 doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.06.008. S0006-3223(08)00708-7 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Leventopoulos M, et al. Long-term effects of early life deprivation on brain glia in Fischer rats. Brain Res. 2007 doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Fuchs E. Social stress in tree shrews as an animal model of depression: an example of a behavioral model of a CNS disorder. CNS Spectr. 2005;10:182–190. doi: 10.1017/s1092852900010038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Liu Q, et al. Glia atrophy in the hippocampus of chronic unpredictable stress-induced depression model rats is reversed by electroacupuncture treatment. J Affect Disord. 2010 doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2010.07.007. S0165-0327(10)00475-1 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Kwon SK, et al. Stress and traumatic brain injury: a behavioral, proteomics, and histological study. Front Neurol. 2011;2:12. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2011.00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Jang S, Suh SH, Yoo HS, Lee YM, Oh S. Changes in iNOS, GFAP and NR1 expression in various brain regions and elevation of sphingosine-1-phosphate in serum after immobilized stress. Neurochem Res. 2008;33:842–851. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9523-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.O’Callaghan JP, Brinton RE, McEwen BS. Glucocorticoids regulate the synthesis of glial fibrillary acidic protein in intact and adrenalectomized rats but do not affect its expression following brain injury. J Neurochem. 1991;57:860–869. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Nichols NR, Osterburg HH, Masters JN, Millar SL, Finch CE. Messenger RNA for glial fibrillary acidic protein is decreased in rat brain following acute and chronic corticosterone treatment. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1990;7:1–7. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(90)90066-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Ramos-Remus C, Gonzalez-Castaneda RE, Gonzalez-Perez O, Luquin S, Garcia-Estrada J. Prednisone induces cognitive dysfunction, neuronal degeneration, and reactive gliosis in rats. J Investig Med. 2002;50:458–464. doi: 10.1136/jim-50-06-06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Bridges N, Slais K, Sykova E. The effects of chronic corticosterone on hippocampal astrocyte numbers: a comparison of male and female Wistar rats. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 2008;68:131–138. doi: 10.55782/ane-2008-1682. 6817 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Hughes EG, Maguire JL, McMinn MT, Scholz RE, Sutherland ML. Loss of glial fibrillary acidic protein results in decreased glutamate transport and inhibition of PKA-induced EAAT2 cell surface trafficking. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004;124:114–123. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.02.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Gilad GM, Gilad VH, Wyatt RJ, Tizabi Y. Region-selective stress-induced increase of glutamate uptake and release in rat forebrain. Brain Res. 1990;525:335–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90886-g. 0006-8993(90)90886-G [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Yang CH, Huang CC, Hsu KS. Behavioral stress enhances hippocampal CA1 long-term depression through the blockade of the glutamate uptake. J Neurosci. 2005;25:4288–4293. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0406-05.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Fontella FU, et al. Repeated restraint stress alters hippocampal glutamate uptake and release in the rat. Neurochem Res. 2004;29:1703–1709. doi: 10.1023/b:nere.0000035805.46592.6c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Olivenza R, et al. Chronic stress induces the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in rat brain cortex. J Neurochem. 2000;74:785–791. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.740785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.de Vasconcellos-Bittencourt AP, et al. Chronic stress and lithium treatments alter hippocampal glutamate uptake and release in the rat and potentiate necrotic cellular death after oxygen and glucose deprivation. Neurochem Res. 2011;36:793–800. doi: 10.1007/s11064-011-0404-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Almeida RF, et al. Effects of depressive-like behavior of rats on brain glutamate uptake. Neurochem Res. 2010;35:1164–1171. doi: 10.1007/s11064-010-0169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Zink M, Vollmayr B, Gebicke-Haerter PJ, Henn FA. Reduced expression of glutamate transporters vGluT1, EAAT2 and EAAT4 in learned helpless rats, an animal model of depression. Neuropharmacology. 2010;58:465–473. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2009.09.005. S0028-3908(09)00310-4 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Autry AE, et al. Glucocorticoid regulation of GLT-1 glutamate transporter isoform expression in the rat hippocampus. Neuroendocrinology. 2006;83:371–379. doi: 10.1159/000096092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Zschocke J, et al. Differential promotion of glutamate transporter expression and function by glucocorticoids in astrocytes from various brain regions. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:34924–34932. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502581200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Allritz C, Bette S, Figiel M, Engele J. Comparative structural and functional analysis of the GLT-1/EAAT-2 promoter from man and rat. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88:1234–1241. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Grippo AJ, Francis J, Beltz TG, Felder RB, Johnson AK. Neuroendocrine and cytokine profile of chronic mild stress-induced anhedonia. Physiol Behav. 2005;84:697–706. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.02.011. S0031-9384(05)00049-1 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Carmen J, Rothstein JD, Kerr DA. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha modulates glutamate transport in the CNS and is a critical determinant of outcome from viral encephalomyelitis. Brain Res. 2009;1263:143–154. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.01.040. S0006-8993(09)00171-1 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Tolosa L, Caraballo-Miralles V, Olmos G, Llado J. TNF-alpha potentiates glutamate-induced spinal cord motoneuron death via NF-kappaB. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011;46:176–186. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2010.09.001. S1044-7431(10)00221-6 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Nakagawa T, Otsubo Y, Yatani Y, Shirakawa H, Kaneko S. Mechanisms of substrate transport-induced clustering of a glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 in astroglial-neuronal cultures. Eur J Neurosci. 2008;28:1719–1730. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06494.x. EJN6494 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Zhou J, Sutherland ML. Glutamate transporter cluster formation in astrocytic processes regulates glutamate uptake activity. J Neurosci. 2004;24:6301–6306. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1404-04.200424/28/6301. [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Choudary PV, et al. Altered cortical glutamatergic and GABAergic signal transmission with glial involvement in depression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:15653–15658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507901102. Epub 12005 Oct 15617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Bernard R, et al. Altered expression of glutamate signaling, growth factor, and glia genes in the locus coeruleus of patients with major depression. Mol Psychiatry. 2010 doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.44. mp201044 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Sequeira A, et al. Global brain gene expression analysis links glutamatergic and GABAergic alterations to suicide and major depression. PLoS One. 2009;4:e6585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Banasr M, et al. Glial pathology in an animal model of depression: reversal of stress-induced cellular, metabolic and behavioral deficits by the glutamate-modulating drug riluzole. Mol Psychiatry. 2010;15:501–511. doi: 10.1038/mp.2008.106. mp2008106 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Rajkowska G. Postmortem studies in mood disorders indicate altered numbers of neurons and glial cells. Biological Psychiatry. 2000;48:766–777. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(00)00950-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Rajkowska G. Cell pathology in mood disorders. Seminars in Clinical Neuropsychiatry. 2002;7:281–292. doi: 10.1053/scnp.2002.35228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Musazzi L, Racagni G, Popoli M. Stress, glucocorticoids and glutamate release: effects of antidepressant drugs. Neurochem Int. 2011;59:138–149. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.05.002. S0197-0186(11)00169-0 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.van Tol MJ, et al. Regional brain volume in depression and anxiety disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010;67:1002–1011. doi: 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.121. 67/10/1002 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Cavus I, et al. Decreased hippocampal volume on MRI is associated with increased extracellular glutamate in epilepsy patients. Epilepsia. 2008;49:1358–1366. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01603.x. EPI1603 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Shors TJ, Weiss C, Thompson RF. Stress-induced facilitation of classical conditioning. Science. 1992;257:537–539. doi: 10.1126/science.1636089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Beylin AV, Shors TJ. Glucocorticoids are necessary for enhancing the acquisition of associative memories after acute stressful experience. Horm Behav. 2003;43:124–131. doi: 10.1016/s0018-506x(02)00025-9. S0018506X02000259 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Sanacora G, Zarate CA, Krystal JH, Manji HK. Targeting the glutamatergic system to develop novel, improved therapeutics for mood disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008;7:426–437. doi: 10.1038/nrd2462. nrd2462 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Fumagalli E, Funicello M, Rauen T, Gobbi M, Mennini T. Riluzole enhances the activity of glutamate transporters GLAST, GLT1 and EAAC1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;578:171–176. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.10.023. S0014-2999(07)01181-8 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Sung B, Lim G, Mao J. Altered expression and uptake activity of spinal glutamate transporters after nerve injury contribute to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain in rats. J Neurosci. 2003;23:2899–2910. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-02899.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Frizzo ME, Dall’Onder LP, Dalcin KB, Souza DO. Riluzole enhances glutamate uptake in rat astrocyte cultures. Cellular & Molecular Neurobiology. 2004;24:123–128. doi: 10.1023/B:CEMN.0000012717.37839.07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Rothstein JD, et al. Beta-lactam antibiotics offer neuroprotection by increasing glutamate transporter expression. Nature. 2005;433:73–77. doi: 10.1038/nature03180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Mineur YS, Picciotto MR, Sanacora G. Antidepressant-Like Effects of Ceftriaxone in Male C57BL/6J Mice. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;61:250–252. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.04.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Gourley SL, Espitia JW, Sanacora G, Taylor JR. Utility and antidepressant-like properties of oral riluzole in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2403-4. (In Press) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Krystal JH, et al. Potential psychiatric applications of metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists and antagonists. CNS Drugs. 2010;24:669–693. doi: 10.2165/11533230-000000000-000004. [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Machado-Vieira R, Salvadore G, Ibrahim LA, Diaz-Granados N, Zarate CA., Jr Targeting glutamatergic signaling for the development of novel therapeutics for mood disorders. Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15:1595–1611. doi: 10.2174/138161209788168010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Li N, et al. mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science. 329:959–964. doi: 10.1126/science.1190287. 329/5994/959 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Autry AE, et al. NMDA receptor blockade at rest triggers rapid behavioural antidepressant responses. Nature. 2011;475:91–95. doi: 10.1038/nature10130nature10130. [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Koike H, Iijima M, Chaki S. Involvement of AMPA receptor in both the rapid and sustained antidepressant-like effects of ketamine in animal models of depression. Behav Brain Res. 2011;224:107–111. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.05.035. S0166-4328(11)00440-2 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Li N, et al. Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists rapidly reverse behavioral and synaptic deficits caused by chronic stress exposure. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;69:754–761. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.12.015. S0006-3223(10)01306-5 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Farley S, Apazoglou K, Witkin JM, Giros B, Tzavara ET. Antidepressant-like effects of an AMPA receptor potentiator under a chronic mild stress paradigm. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;13:1207–1218. doi: 10.1017/S1461145709991076. S1461145709991076 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Haller J, Mikics E, Makara GB. The effects of non-genomic glucocorticoid mechanisms on bodily functions and the central neural system. A critical evaluation of findings. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2008;29:273–291. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2007.10.004. S0091-3022(07)00059-3 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Yamamoto KR. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Levin ER. Membrane oestrogen receptor alpha signalling to cell functions. J Physiol. 2009;587:5019–5023. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.177097. jphysiol.2009.177097 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Pietras RJ, Nemere I, Szego CM. Steroid hormone receptors in target cell membranes. Endocrine. 2001;14:417–427. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:14:3:417. ENDO:14:3:417 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Ahima R, Krozowski Z, Harlan R. Type I corticosteroid receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat CNS: distribution and regulation by corticosteroids. J Comp Neurol. 1991;313:522–538. doi: 10.1002/cne.903130312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Ahima RS, Harlan RE. Charting of type II glucocorticoid receptor-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1990;39:579–604. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90244-x. 0306-4522(90)90244-X [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Johnson LR, Farb C, Morrison JH, McEwen BS, LeDoux JE. Localization of glucocorticoid receptors at postsynaptic membranes in the lateral amygdala. Neuroscience. 2005;136:289–299. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.06.050. S0306-4522(05)00710-4 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Orchinik M, Murray TF, Franklin PH, Moore FL. Guanyl nucleotides modulate binding to steroid receptors in neuronal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:3830–3834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Tasker JG, Di S, Malcher-Lopes R. Minireview: rapid glucocorticoid signaling via membrane-associated receptors. Endocrinology. 2006;147:5549–5556. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-0981. en.2006-0981 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Du J, et al. Dynamic regulation of mitochondrial function by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:3543–3548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812671106. 0812671106 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Psarra AM, Sekeris CE. Glucocorticoid receptors and other nuclear transcription factors in mitochondria and possible functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1787:431–436. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.11.011. S0005-2728(08)00729-9 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Groeneweg FL, Karst H, de Kloet ER, Joels M. Rapid non-genomic effects of corticosteroids and their role in the central stress response. J Endocrinol. 2011;209:153–167. doi: 10.1530/JOE-10-0472. JOE-10-0472 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Katona I, Freund TF. Endocannabinoid signaling as a synaptic circuit breaker in neurological disease. Nat Med. 2008;14:923–930. doi: 10.1038/nm.f.1869. nm.f.1869 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Chavez AE, Chiu CQ, Castillo PE. TRPV1 activation by endogenous anandamide triggers postsynaptic long-term depression in dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13:1511–1518. doi: 10.1038/nn.2684. nn.2684 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Hill MN, et al. Endogenous cannabinoid signaling is essential for stress adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:9406–9411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914661107. 0914661107 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Di S, Maxson MM, Franco A, Tasker JG. Glucocorticoids regulate glutamate and GABA synapse-specific retrograde transmission via divergent nongenomic signaling pathways. J Neurosci. 2009;29:393–401. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4546-08.2009. 29/2/393 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Hill MN, et al. Functional interactions between stress and the endocannabinoid system: from synaptic signaling to behavioral output. J Neurosci. 2010;30:14980–14986. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4283-10.2010. 30/45/14980 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Raiteri M, Angelini F, Levi G. A simple apparatus for studying the release of neurotransmitters from synaptosomes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974;25:411–414. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Raiteri L, Raiteri M. Synaptosomes still viable after 25 years of superfusion. Neurochem Res. 2000;25:1265–1274. doi: 10.1023/a:1007648229795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Bonanno G, et al. Chronic antidepressants reduce depolarization-evoked glutamate release and protein interactions favoring formation of SNARE complex in hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2005;25:3270–3279. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5033-04.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Joels M. Corticosteroid effects in the brain: U-shape it. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2006;27:244–250. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2006.03.007. S0165-6147(06)00081-2 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Sapolsky RM. Stress, the Aging Brain and the Mechanisms of Neuron Death. MIT Press; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 215.Conrad CD, LeDoux JE, Magarinos AM, McEwen BS. Repeated restraint stress facilitates fear conditioning independently of causing hippocampal CA3 dendritic atrophy. Behav Neurosci. 1999;113:902–913. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.113.5.902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Radley JJ, et al. Reversibility of apical dendritic retraction in the rat medial prefrontal cortex following repeated stress. Exp Neurol. 2005;196:199–203. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.07.008. S0014-4886(05)00237-2 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Vyas A, Pillai AG, Chattarji S. Recovery after chronic stress fails to reverse amygdaloid neuronal hypertrophy and enhanced anxiety-like behavior. Neuroscience. 2004;128:667–673. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.07.013. S0306-4522(04)00613-X [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Bloss EB, Janssen WG, McEwen BS, Morrison JH. Interactive effects of stress and aging on structural plasticity in the prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci. 2010;30:6726–6731. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0759-10.2010. 30/19/6726 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Mitra R, Jadhav S, McEwen BS, Vyas A, Chattarji S. Stress duration modulates the spatiotemporal patterns of spine formation in the basolateral amygdala. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:9371–9376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504011102. 0504011102 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Mitra R, Sapolsky RM. Acute corticosterone treatment is sufficient to induce anxiety and amygdaloid dendritic hypertrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:5573–5578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705615105. 0705615105 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Magarinos AM, McEwen BS. Stress-induced atrophy of apical dendrites of hippocampal CA3c neurons: involvement of glucocorticoid secretion and excitatory amino acid receptors. Neuroscience. 1995;69:89–98. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(95)00259-l. 030645229500259L [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Reagan LP, et al. Chronic restraint stress up-regulates GLT-1 mRNA and protein expression in the rat hippocampus: reversal by tianeptine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:2179–2184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307294101. Epub 2004 Feb 2176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Magarinos AM, et al. Effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor haploinsufficiency on stress-induced remodeling of hippocampal neurons. Hippocampus. 2010 doi: 10.1002/hipo.20744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Pawlak R, et al. Tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen mediate stress-induced decline of neuronal and cognitive functions in the mouse hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:18201–18206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509232102. 0509232102 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Martin KP, Wellman CL. NMDA Receptor Blockade Alters Stress-Induced Dendritic Remodeling in Medial Prefrontal Cortex. Cereb Cortex. 2011 doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhr021. bhr021 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Kim K, et al. Role of excitatory amino acid transporter-2 (EAAT2) and glutamate in neurodegeneration: Opportunities for developing novel therapeutics. J Cell Physiol. 2010 doi: 10.1002/jcp.22609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Bowden CL, et al. A placebo-controlled 18-month trial of lamotrigine and lithium maintenance treatment in recently manic or hypomanic patients with bipolar I disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003;60:392–400. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.60.4.392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Brennan BP, et al. Rapid Enhancement of Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in Bipolar Depression Following Treatment with Riluzole. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009 doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.191. npp2009191 [pii] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.Gallagher P, et al. Antiglucocorticoid treatments for mood disorders. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008:CD005168. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005168.pub2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.McLaughlin RJ, Gobbi G. Cannabinoids and emotionality: a neuroanatomical perspective. Neuroscience. 2011 doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.07.052. S0306-4522(11)00877-3 [pii] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]