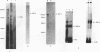Abstract
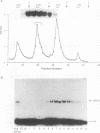
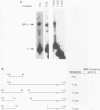
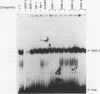
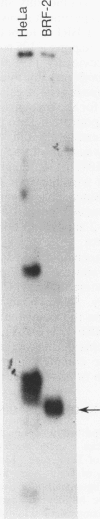
Apolipoprotein B100 (apoB), the only protein of low-density lipoprotein, is produced primarily in the liver and serves as a ligand for the low-density lipoprotein receptor. Hepatic cell-specific expression of the human apoB gene is controlled by at least two cis-acting positive elements located between positions-128 and -70 (H. K. Das, T. Leff, and J.L. Breslow, J. Biol. Chem. 263:11452-11458, 1988). The distal element (-128 to -85) appears to be liver specific since it shows positive activity in HepG2 cells and negative activity in HeLa cells. The proximal element (-84 to -70) acts as a positive element in both these cell lines, and two rat liver nuclear proteins, BRF-1 and C/EBP, bind to two overlapping sites (-84 to -60 and -70 to -50, respectively). By gel mobility shift assay, we have identified a rat liver nuclear protein (BRF-2) which binds to the distal element (-128 to -85) of the apoB gene. This putative trans-acting factor has been purified to apparent homogeneity by DEAE-cellulose, heparin-agarose, and DNA-specific affinity chromatography. The purified BRF-2 has an apparent molecular mass of 120 kDa and was found to specifically recognize sequence -128 to -85; BRF-2 also produced a strong hypersensitive site at nucleotide position -95 with copper-orthophenanthroline reagent. A double-stranded oligonucleotide (-128 to -85) containing a 3-nucleotide (TTC) insertion between position -95 and -94 was found to abolish DNA binding by BRF-2. This result suggests that the region surrounding the hypersensitive site -95 is important for protein-DNA interaction. By using apoB promoter fragments containing various internal deletions as templates for gel mobility shift assay, the region between -104 and -85 was identified to be crucial for binding by BRF-2. We propose that BRF-2 may play an important role in the tissue-specific regulation of apoB gene transcription.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borgmeyer U., Nowock J., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA-binding protein: a eukaryotic nuclear protein recognizing a symmetrical sequence on double-stranded linear DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4295–4311. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks A. R., Blackhart B. D., Haubold K., Levy-Wilson B. Characterization of tissue-specific enhancer elements in the second intron of the human apolipoprotein B gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7848–7859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson P., Bjursell G. Negative and positive promoter elements contribute to tissue specificity of apolipoprotein B expression. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90365-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson P., Eriksson P., Bjursell G. Two nuclear proteins bind to the major positive element of the apolipoprotein B gene promoter. Gene. 1990 Oct 15;94(2):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90401-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins D. R., Knott T. J., Pease R. J., Powell L. M., Wallis S. C., Robertson S., Pullinger C. R., Milne R. W., Marcel Y. L., Humphries S. E. Truncated variants of apolipoprotein B cause hypobetalipoproteinaemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8361–8375. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Morgan J. G., Campbell L. A., Fourel G., Crabtree G. R. Interaction of a liver-specific nuclear factor with the fibrinogen and alpha 1-antitrypsin promoters. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):688–692. doi: 10.1126/science.3499668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Cell type-specific expression of the human apoB gene is controlled by two cis-acting regulatory regions. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11452–11458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frain M., Swart G., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Stämpfli S., Frank R., Cortese R. The liver-specific transcription factor LF-B1 contains a highly diverged homeobox DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayson D. R., Costa R. H., Xanthopoulos K. G., Darnell J. E. One factor recognizes the liver-specific enhancers in alpha 1-antitrypsin and transthyretin genes. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):786–788. doi: 10.1126/science.3257586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannel W. B., Castelli W. P., Gordon T. Cholesterol in the prediction of atherosclerotic disease. New perspectives based on the Framingham study. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jan;90(1):85–91. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardassis D., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Ramji D. P., Cortese R., Zannis V. I., Cladaras C. Characterization of the promoter elements required for hepatic and intestinal transcription of the human apoB gene: definition of the DNA-binding site of a tissue-specific transcriptional factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2653–2659. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kardassis D., Zannis V. I., Cladaras C. Purification and characterization of the nuclear factor BA1. A transcriptional activator of the human apoB gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21733–21740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwabara M. D., Sigman D. S. Footprinting DNA-protein complexes in situ following gel retardation assays using 1,10-phenanthroline-copper ion: Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-lac promoter complexes. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 17;26(23):7234–7238. doi: 10.1021/bi00397a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladias J. A., Karathanasis S. K. Regulation of the apolipoprotein AI gene by ARP-1, a novel member of the steroid receptor superfamily. Science. 1991 Feb 1;251(4993):561–565. doi: 10.1126/science.1899293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Smith E., Litvin O., Costa R. H., Darnell J. E., Jr HNF-3A, a hepatocyte-enriched transcription factor of novel structure is regulated transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1427–1436. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Prezioso V. R., Tao W. F., Chen W. S., Darnell J. E., Jr Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 alpha belongs to a gene family in mammals that is homologous to the Drosophila homeotic gene fork head. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):416–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Shen R. F., Tsai S. Y., Woo S. L. Multiple hepatic trans-acting factors are required for in vitro transcription of the human alpha-1-antitrypsin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4362–4369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1, a member of a novel class of dimerizing homeodomain proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):677–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger S., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Nuclear factors AF-1 and C/EBP bind to the human ApoB gene promoter and modulate its transcriptional activity in hepatic cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9978–9983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paonessa G., Gounari F., Frank R., Cortese R. Purification of a NF1-like DNA-binding protein from rat liver and cloning of the corresponding cDNA. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3115–3123. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymondjean M., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Several distinct "CCAAT" box binding proteins coexist in eukaryotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):757–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaul Y., Ben-Levy R., De-Medina T. High affinity binding site for nuclear factor I next to the hepatitis B virus S gene promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1967–1971. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04451.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siervogel R. M., Morrison J. A., Kelly K., Mellies M., Gartside P., Glueck C. J. Familial hyper-alpha-lipoproteinemia in 26 kindreds. Clin Genet. 1980 Jan;17(1):13–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1980.tb00107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek F. M., Zhong W. M., Lai E., Darnell J. E., Jr Liver-enriched transcription factor HNF-4 is a novel member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2353–2365. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Bertics S. J., Curtiss L. K., Dubois B. W., Witztum J. L. Genetic analysis of a kindred with familial hypobetalipoproteinemia. Evidence for two separate gene defects: one associated with an abnormal apolipoprotein B species, apolipoprotein B-37; and a second associated with low plasma concentrations of apolipoprotein B-100. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1842–1851. doi: 10.1172/JCI113026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Bertics S. J., Curtiss L. K., Witztum J. L. Characterization of an abnormal species of apolipoprotein B, apolipoprotein B-37, associated with familial hypobetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1831–1841. doi: 10.1172/JCI113025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. G., Northey S. T., McCarthy B. J. Low plasma cholesterol levels caused by a short deletion in the apolipoprotein B gene. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):591–593. doi: 10.1126/science.3399894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]