Abstract
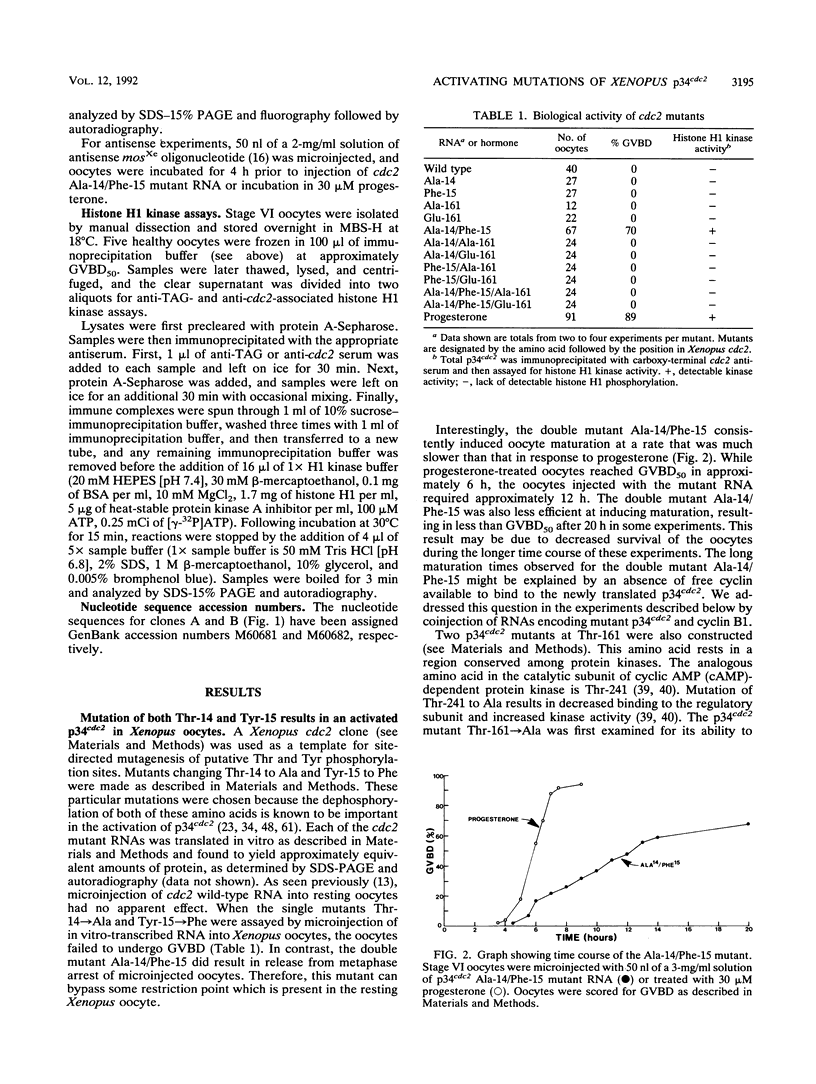
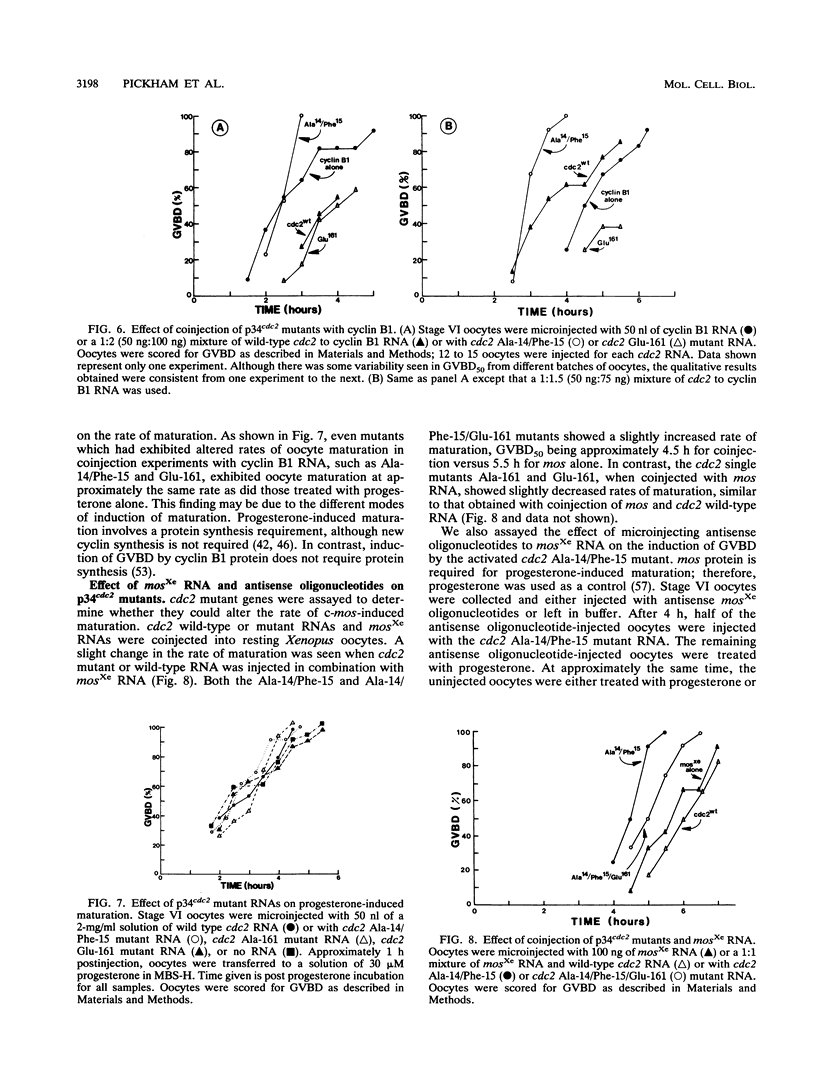
The p34cdc2 protein kinase is a component of maturation-promoting factor, the master regulator of the cell cycle in all eukaryotes. The activity of p34cdc2 is itself tightly regulated by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Predicted regulatory phosphorylation sites of Xenopus p34cdc2 were mutated in vitro, and in vitro-transcribed RNAs were injected into Xenopus oocytes. The cdc2 single mutants Thr-14----Ala and Tyr-15----Phe did not induce germinal vesicle breakdown (BVBD) upon microinjection into oocytes. In contrast, the cdc2 double mutant Ala-14/Phe-15 did induce GVBD. Both the Ala-14 and Ala-14/Phe-15p34cdc2 mutants were shown to coimmunoprecipitate cyclin B1 and to phosphorylate histone H1 in immune complex kinase assays. Microinjection of antisense oligonucleotides to c-mosXe was used to demonstrate the role of mos protein synthesis in the induction of GVBD by the Ala-14/Phe-15 cdc2 mutant. Thr-161 was also mutated. p34cdc2 single mutants Ala-161 and Glu-161 and triple mutants Ala-14/Phe-15/Ala-161 and Ala-14/Phe-15/Glu-161 failed to induce GVBD in oocytes and showed a decreased binding to cyclin B1 in coimmunoprecipitations. Each of the cdc2 mutants was also assayed by coinjection with cyclin B1 or c-mosXe RNA into oocytes. Several of the cdc2 mutants were found to affect the kinetics of cyclin B1 and/or mos-induced GVBD upon coinjection, although none affected the rate of progesterone-induced maturation. We demonstrate here the significance of Thr-14, Tyr-15, and Thr-161 of p34cdc2 in Xenopus oocyte maturation. In addition, these results suggest a regulatory role for mosXe in induction of oocyte maturation by the cdc2 mutant Ala-14/Phe-15.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amon A., Surana U., Muroff I., Nasmyth K. Regulation of p34CDC28 tyrosine phosphorylation is not required for entry into mitosis in S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):368–371. doi: 10.1038/355368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R., Beach D. Site-specific mutagenesis of cdc2+, a cell cycle control gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3523–3530. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I., Paules R. S., Vande Woude G. F. A characterization of cytostatic factor activity from Xenopus eggs and c-mos-transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):329–335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Brambilla P., Félix M. A., Franza B. R., Jr, Karsenti E., Draetta G. cdc2 phosphorylation is required for its interaction with cyclin. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3311–3319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Kumagai A. The cdc25 protein contains an intrinsic phosphatase activity. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90582-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Fission yeast p13 blocks mitotic activation and tyrosine dephosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc2 protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Russell P. Fission yeast p107wee1 mitotic inhibitor is a tyrosine/serine kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):808–811. doi: 10.1038/349808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Wu M., Gerhart J. C., Martin G. S. Cell cycle tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 and a microtubule-associated protein kinase homolog in Xenopus oocytes and eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1965–1971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Ballantyne S. M., Donoghue D. J. Meiotic induction by Xenopus cyclin B is accelerated by coexpression with mosXe. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1713–1717. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Donoghue D. J. Protein kinases and protooncogenes: biochemical regulators of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 5;30(9):2293–2302. doi: 10.1021/bi00223a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Kanki J. P., Ballantyne S. M., Pickham K. M., Donoghue D. J. Effects of the v-mos oncogene on Xenopus development: meiotic induction in oocytes and mitotic arrest in cleaving embryos. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):533–541. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. S., Pickham K. M., Kanki J. P., Lee B. A., Pena S. V., Donoghue D. J. Xenopus homolog of the mos protooncogene transforms mammalian fibroblasts and induces maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5805–5809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Félix M. A., Cohen P., Karsenti E. Cdc2 H1 kinase is negatively regulated by a type 2A phosphatase in the Xenopus early embryonic cell cycle: evidence from the effects of okadaic acid. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):675–683. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galaktionov K., Beach D. Specific activation of cdc25 tyrosine phosphatases by B-type cyclins: evidence for multiple roles of mitotic cyclins. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1181–1194. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90294-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Maller J. L. Cyclin B in Xenopus oocytes: implications for the mechanism of pre-MPF activation. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):177–182. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Minshull J., Lohka M., Glotzer M., Hunt T., Maller J. L. Cyclin is a component of maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90599-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Solomon M. J., Booher R. N., Bazan J. F., Kirschner M. W. cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90583-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J., Wu M., Kirschner M. Cell cycle dynamics of an M-phase-specific cytoplasmic factor in Xenopus laevis oocytes and eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1247–1255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Owen D. J., Sazer S., Nurse P. Phosphorylation at Thr167 is required for Schizosaccharomyces pombe p34cdc2 function. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3297–3309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04894.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto N., Kishimoto T. Regulation of meiotic metaphase by a cytoplasmic maturation-promoting factor during mouse oocyte maturation. Dev Biol. 1988 Apr;126(2):242–252. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Embryology. Under arrest in the cell cycle. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):483–484. doi: 10.1038/342483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi T., Maller J. L. Phosphorylation of Xenopus cyclins B1 and B2 is not required for cell cycle transitions. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3860–3867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessus C., Beach D. Oscillation of MPF is accompanied by periodic association between cdc25 and cdc2-cyclin B. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):323–332. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90473-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessus C., Rime H., Haccard O., Van Lint J., Goris J., Merlevede W., Ozon R. Tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 and p42 during meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocyte. Antagonistic action of okadaic acid and 6-DMAP. Development. 1991 Mar;111(3):813–820. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.3.813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanki J. P., Donoghue D. J. Progression from meiosis I to meiosis II in Xenopus oocytes requires de novo translation of the mosxe protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Minshull J., Ford C., Golsteyn R., Poon R., Hunt T. On the synthesis and destruction of A- and B-type cyclins during oogenesis and meiotic maturation in Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):755–765. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Differential phosphorylation of vertebrate p34cdc2 kinase at the G1/S and G2/M transitions of the cell cycle: identification of major phosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):305–316. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07951.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Mutations of p34cdc2 phosphorylation sites induce premature mitotic events in HeLa cells: evidence for a double block to p34cdc2 kinase activation in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3331–3341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. The cdc25 protein controls tyrosine dephosphorylation of the cdc2 protein in a cell-free system. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):903–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90315-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Ogg S., Xu M., Parker L. L., Donoghue D. J., Maller J. L., Piwnica-Worms H. cdc25+ encodes a protein phosphatase that dephosphorylates p34cdc2. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):73–84. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Solomon M. J., Mumby M. C., Kirschner M. W. INH, a negative regulator of MPF, is a form of protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90649-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin L. R., Kuret J., Johnson K. E., Powers S., Cameron S., Michaeli T., Wigler M., Zoller M. J. A mutation in the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase that disrupts regulation. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):68–70. doi: 10.1126/science.2832943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin L. R., Zoller M. J. Association of catalytic and regulatory subunits of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase requires a negatively charged side group at a conserved threonine. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1066–1075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Walworth N., Booher R., Dembski M., Kirschner M., Beach D. mik1 and wee1 cooperate in the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1111–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui Y., Markert C. L. Cytoplasmic control of nuclear behavior during meiotic maturation of frog oocytes. J Exp Zool. 1971 Jun;177(2):129–145. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401770202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Azzi L., Wang J. Y. Cyclin B targets p34cdc2 for tyrosine phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1545–1554. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A. Translation of messenger RNA in injected frog oocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:288–296. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. B., McGowan C. H., Lenaers G., Jones R., Russell P. p80cdc25 mitotic inducer is the tyrosine phosphatase that activates p34cdc2 kinase in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4301–4309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Murray A., Colman A., Hunt T. Xenopus oocyte maturation does not require new cyclin synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):767–772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Blow J., Nurse P. Regulatory phosphorylation of the p34cdc2 protein kinase in vertebrates. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3321–3329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe S. J., Kiessling A. A., Cooper G. M. The c-mos gene product is required for cyclin B accumulation during meiosis of mouse eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7869–7872. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. L., Atherton-Fessler S., Lee M. S., Ogg S., Falk J. L., Swenson K. I., Piwnica-Worms H. Cyclin promotes the tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 in a wee1+ dependent manner. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1255–1263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pondaven P., Meijer L., Beach D. Activation of M-phase-specific histone H1 kinase by modification of the phosphorylation of its p34cdc2 and cyclin components. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):9–17. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy L. M., Singh B., Gautier J., Arlinghaus R. B., Nordeen S. K., Maller J. L. The cyclin B2 component of MPF is a substrate for the c-mos(xe) proto-oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):825–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90192-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy L. M., Swenson K. I., Walker D. H., Gabrielli B. G., Li R. S., Piwnica-Worms H., Maller J. L. Activation of p34cdc2 kinase by cyclin A. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):507–514. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Daar I., Oskarsson M., Showalter S. D., Vande Woude G. F. The product of the mos proto-oncogene as a candidate "initiator" for oocyte maturation. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):643–646. doi: 10.1126/science.2474853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Oskarsson M., Copeland T., Brumbaugh J., Vande Woude G. F. Function of c-mos proto-oncogene product in meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):519–525. doi: 10.1038/335519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Watanabe N., Vande Woude G. F., Ikawa Y. The c-mos proto-oncogene product is a cytostatic factor responsible for meiotic arrest in vertebrate eggs. Nature. 1989 Nov 30;342(6249):512–518. doi: 10.1038/342512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Lee T., Kirschner M. W. Role of phosphorylation in p34cdc2 activation: identification of an activating kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):13–27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Murray A. W. S-phase feedback control in budding yeast independent of tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc28. Nature. 1992 Jan 23;355(6358):365–368. doi: 10.1038/355365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wandosell F., Serrano L., Hernández M. A., Avila J. Phosphorylation of tubulin by a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10332–10339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yew N., Mellini M. L., Vande Woude G. F. Meiotic initiation by the mos protein in Xenopus. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):649–652. doi: 10.1038/355649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou R. P., Oskarsson M., Paules R. S., Schulz N., Cleveland D., Vande Woude G. F. Ability of the c-mos product to associate with and phosphorylate tubulin. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):671–675. doi: 10.1126/science.1825142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]