Abstract
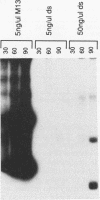
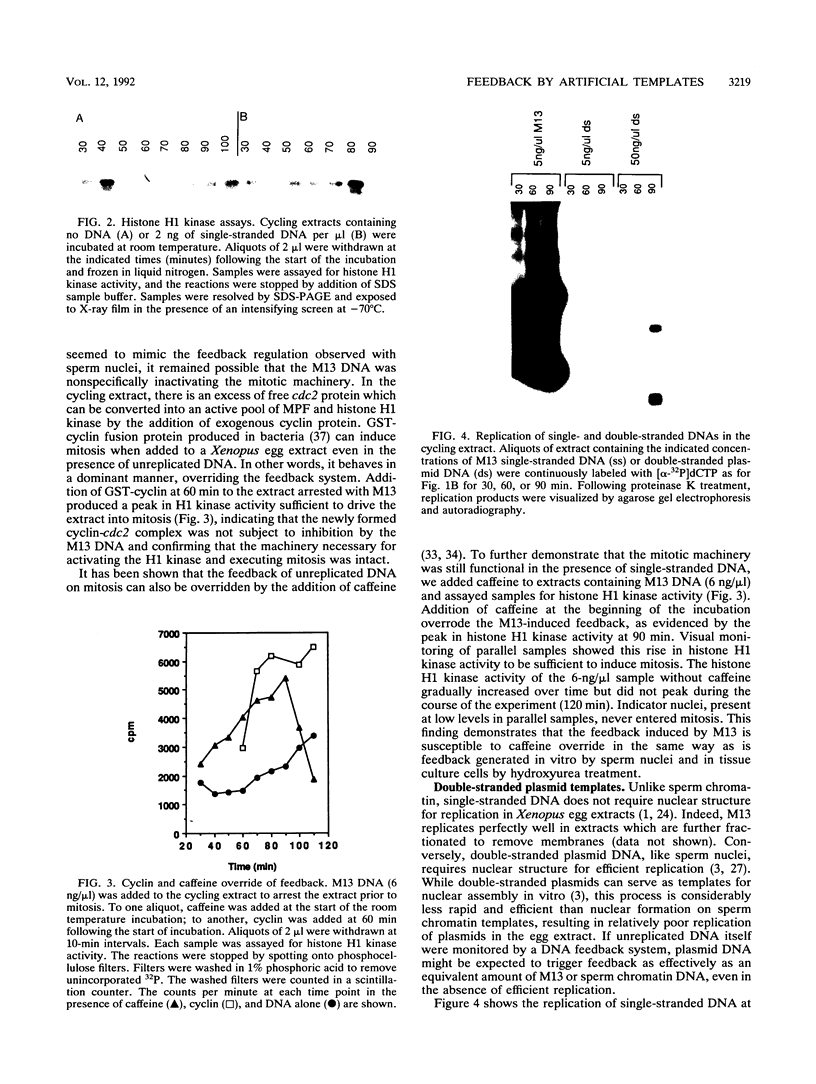
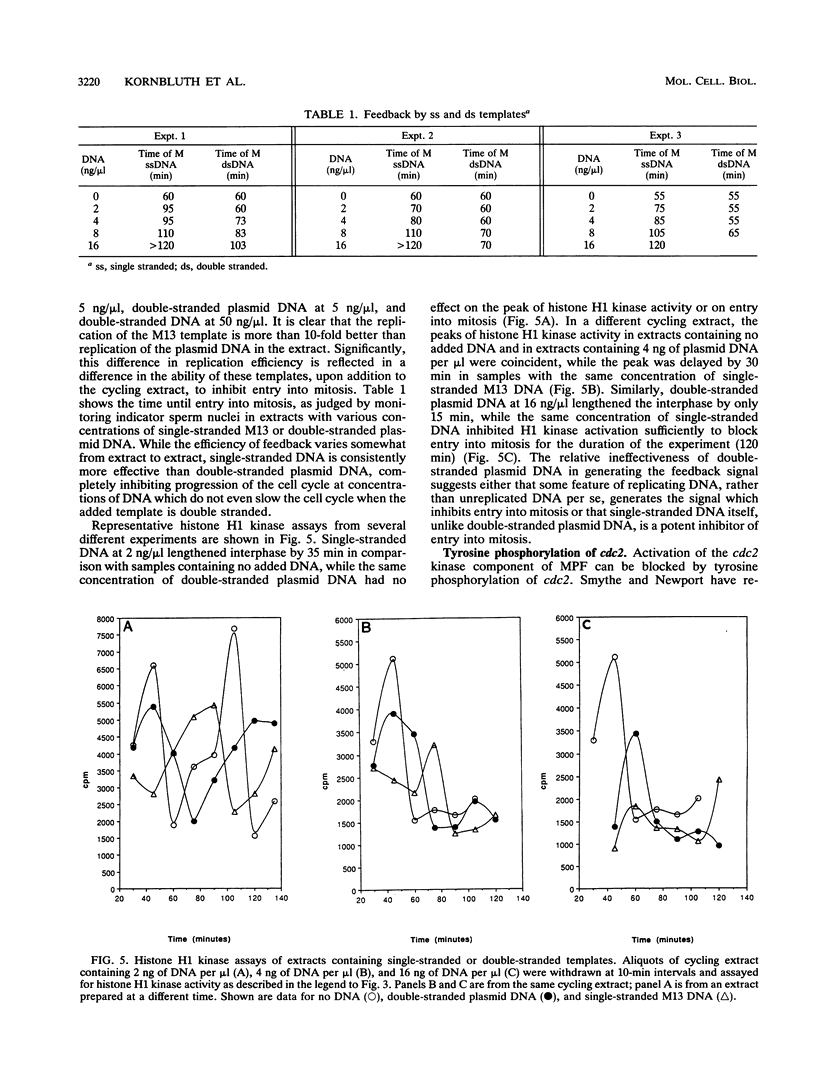
In cell extracts of Xenopus eggs which oscillate between S and M phases of the cell cycle, the onset of mitosis is blocked by the presence of incompletely replicated DNA. In this report, we show that several artificial DNA templates (M13 single-stranded DNA and double-stranded plasmid DNA) can trigger this feedback pathway, which inhibits mitosis. Single-stranded M13 DNA is much more effective than double-stranded plasmid DNA at inhibiting the onset of mitosis. Furthermore, we have shown that low levels of M13 single-stranded DNA and high levels of double-stranded plasmid DNA can elevate the tyrosine kinase activity responsible for phosphorylating p34cdc2, thereby inactivating maturation-promoting factor and inhibiting entry into mitosis. This constitutes a simplified system with which to study the signal transduction pathway from the DNA template to the tyrosine kinase responsible for inhibiting p34cdc2 activity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almouzni G., Méchali M. Assembly of spaced chromatin promoted by DNA synthesis in extracts from Xenopus eggs. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):665–672. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02861.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arion D., Meijer L., Brizuela L., Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase-specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blow J. J., Laskey R. A. Initiation of DNA replication in nuclei and purified DNA by a cell-free extract of Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90622-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callan H. G. Replication of DNA in the chromosomes of eukaryotes. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1972 Apr 18;181(1062):19–41. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1972.0039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M., Newport J. W. Completion of DNA replication is monitored by a feedback system that controls the initiation of mitosis in vitro: studies in Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):811–823. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90191-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Fission yeast p13 blocks mitotic activation and tyrosine dephosphorylation of the Xenopus cdc2 protein kinase. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):181–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90414-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Nurse P. Mutation of fission yeast cell cycle control genes abolishes dependence of mitosis on DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):665–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90669-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Russell P. Fission yeast p107wee1 mitotic inhibitor is a tyrosine/serine kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):808–811. doi: 10.1038/349808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Matsukawa T., Nurse P., Maller J. Dephosphorylation and activation of Xenopus p34cdc2 protein kinase during the cell cycle. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):626–629. doi: 10.1038/339626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Weinert T. A. Checkpoints: controls that ensure the order of cell cycle events. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):629–634. doi: 10.1126/science.2683079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C., Kill I. Changes in the nuclear distribution of DNA polymerase alpha and PCNA/cyclin during the progress of the cell cycle, in a cell-free extract of Xenopus eggs. J Cell Sci. 1989 Aug;93(Pt 4):605–613. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.4.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. The cdc25 protein controls tyrosine dephosphorylation of the cdc2 protein in a cell-free system. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):903–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90315-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Picard A., Peaucellier G., Cavadore J. C., Nurse P., Doree M. Purification of MPF from starfish: identification as the H1 histone kinase p34cdc2 and a possible mechanism for its periodic activation. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90963-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Solomon M. J., Mumby M. C., Kirschner M. W. INH, a negative regulator of MPF, is a form of protein phosphatase 2A. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90649-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Driving the cell cycle: M phase kinase, its partners, and substrates. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90181-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Masui Y. Formation in vitro of sperm pronuclei and mitotic chromosomes induced by amphibian ooplasmic components. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):719–721. doi: 10.1126/science.6601299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Walworth N., Booher R., Dembski M., Kirschner M., Beach D. mik1 and wee1 cooperate in the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1111–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Blow J. J., Hunt T. Translation of cyclin mRNA is necessary for extracts of activated xenopus eggs to enter mitosis. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):947–956. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90628-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méchali M., Harland R. M. DNA synthesis in a cell-free system from Xenopus eggs: priming and elongation on single-stranded DNA in vitro. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. Nuclear reconstitution in vitro: stages of assembly around protein-free DNA. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):205–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto T., Eilen E., Basilico C. Premature of chromosome condensation in a ts DNA- mutant of BHK cells. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):475–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Kai R., Furuno N., Sekiguchi T., Sekiguchi M., Hayashida H., Kuma K., Miyata T., Fukushige S., Murotsu T. Isolation and characterization of the active cDNA of the human cell cycle gene (RCC1) involved in the regulation of onset of chromosome condensation. Genes Dev. 1987 Aug;1(6):585–593. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.6.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani S. A., Engle D. B., Doonan J. H., Morris N. R. Spindle formation and chromatin condensation in cells blocked at interphase by mutation of a negative cell cycle control gene. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90513-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90546-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Pardee A. B. Caffeine-induced uncoupling of mitosis from the completion of DNA replication in mammalian cells. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1264–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.2422760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Pardee A. B. Periodic mitotic events induced in the absence of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9025–9029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Nurse P. The cell cycle control gene cdc2+ of fission yeast encodes a protein kinase potentially regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe C., Newport J. W. Coupling of mitosis to the completion of S phase in Xenopus occurs via modulation of the tyrosine kinase that phosphorylates p34cdc2. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):787–797. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausfeld U., Labbé J. C., Fesquet D., Cavadore J. C., Picard A., Sadhu K., Russell P., Dorée M. Dephosphorylation and activation of a p34cdc2/cyclin B complex in vitro by human CDC25 protein. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):242–245. doi: 10.1038/351242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinert T. A., Hartwell L. H. The RAD9 gene controls the cell cycle response to DNA damage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):317–322. doi: 10.1126/science.3291120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]