Abstract
Nutraceuticals are food or part of food that provides medical or health benefits including the prevention and/or treatment of a disease. Nutraceutical has advantage over the medicine because they avoid side effect, have naturally dietary supplement, etc. Nutraceutical; on the basis of their natural source, chemical grouping, categories into three key terms -nutrients, herbals, dietary supplements, dietary fiber, etc. The most rapidly growing segments of the industry were dietary supplements (19.5 percent per year) and natural/herbal products (11.6 percent per year). Global nutraceutical market is estimated as USD 117 billion. FDA regulated dietary supplements as foods to ensure that they were safe. In 2006, the Indian government passed Food Safety and Standard Act to regulate the nutraceutical industry. Herbal nutraceutical is used as a powerful instrument in maintaining health and to act against nutritionally induced acute and chronic diseases, thereby promoting optimal health, longevity, and quality of life.
Keywords: Dietary supplement, global market, nutraceutical, regulation
INTRODUCTION
The term nutraceuticals was coined from “nutrition” and “pharmaceutical” by Stephen Defelice MD, founder and chairman of the foundation for innovation in medicine (FIM) Cranford, New Jersy, in 1989.[1] According to Defelice “nutracetuicals are food or part of a food that provides medical or health benefits including the prevention and/or treatment of a disease.”[2] Greek physician HIPPOCRATES (known as father of medicines) said “let food be your medicine” The philosophy behind is “focus on prevention” Other words used in the context are Dietary supplements, functional food, multi-functional food, etc. Functional foods are ordinary foods that have components, ingredients that incorporated into give them a specific medicinal or health benefit moreover nutritional effect.[3]
According to dietary supplement, health and education act (DSHEA) dietary supplements are products intended to supplement the diet that bears or contains one or more of the following dietary ingredients: a vitamin, a mineral, an herb or other botanical, an amino acid, a dietary substance for use by man to supplement the diet by increasing the total daily intake, or a concentrate, metabolite, constituent, extract, or combinations of these ingredients.[4] It may be taken in the form of pill capsule, tablet, or liquid form. It is not represented for use as a conventional food or as the sole item of a meal or diet. It is labeled as a “dietary supplement.”[5] Under the DSHEA (1994), the manufacturer of a dietary supplement is responsible for ensuring that the dietary supplement is safe before it is marketed.[6]
Simply, Nutraceuticals means, NUTRITIVE + PHARMACEUTICAL: A food stuff (as a fortified food or dietary supplement) that provides health benefits.
The functional food concept can be defined as “Food products to be taken as part of the usual diet in order to have beneficial effects that go beyond basic nutritional function” [Tables 1–4].
Table 1.
As per chemical classification[9]
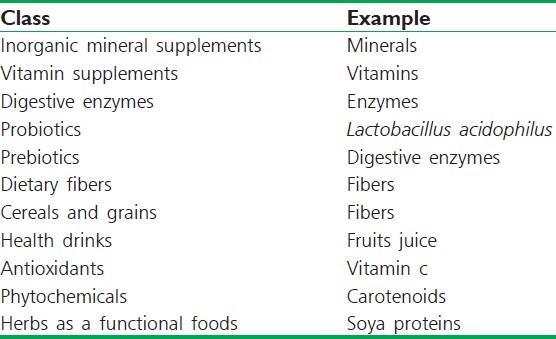
Table 4.
List of marketed nutraceutical products

Table 2.
Various vitamins and their health benefits
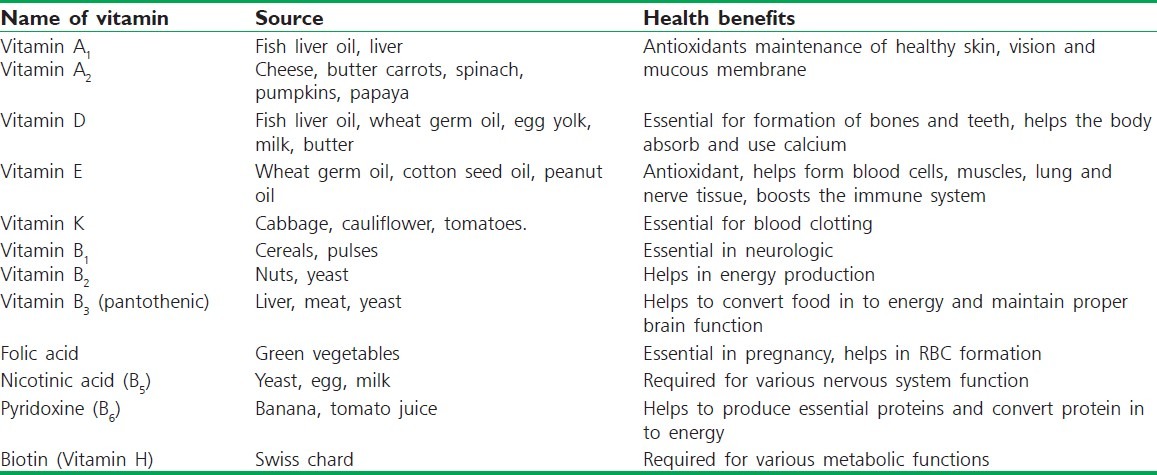
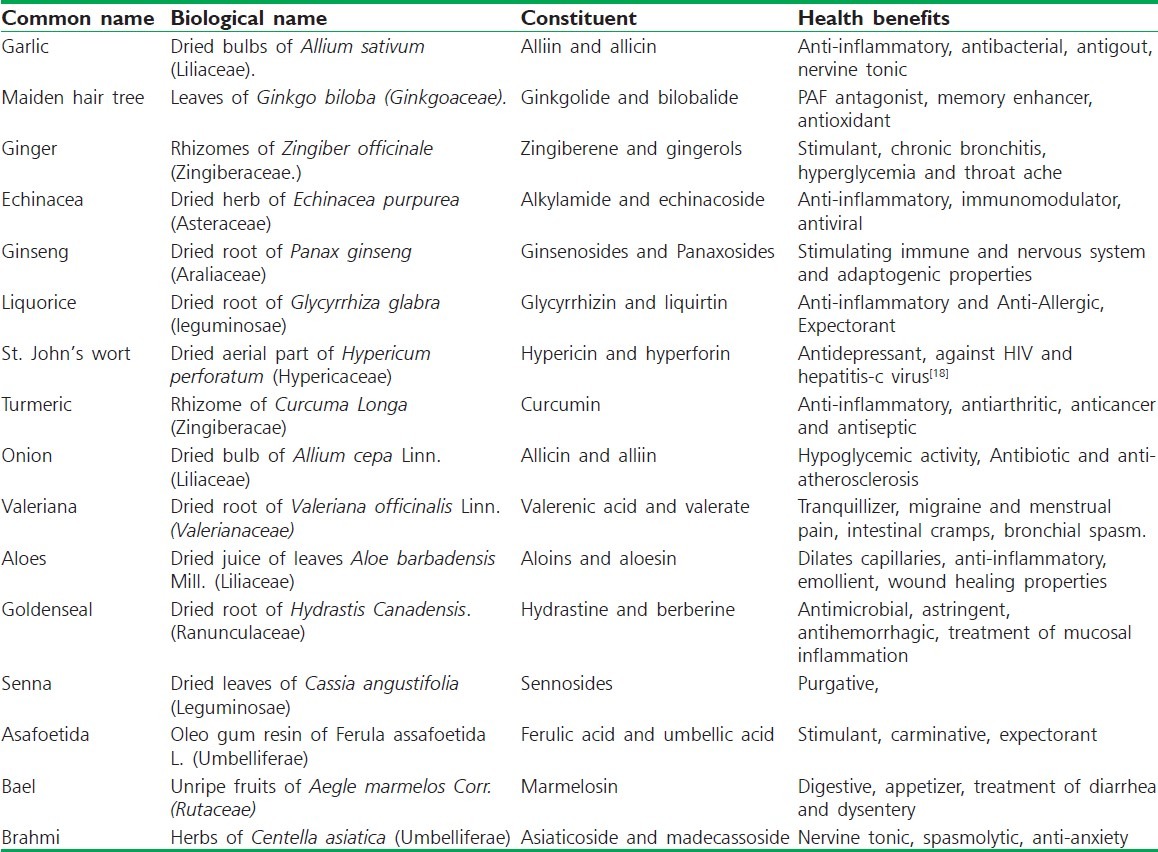
Table 3.
Common herbals as nutraceuticals
HEALTH BENEFITS
Avoid the side effect.
May increase the health beneficial effect.
May have naturally dietary supplement, so do not have unpleasant side effect.
May increase the health value, our diet and improve medical condition of human.
May easily be available and economically affordable.
Nutritional therapy is a healing system using dietary therapeutics or nutraceuticals as a complementary therapy. This therapy is based on the belief that foods can not only be sources of nutrients and energy but could also provide medicinal benefits.
According to nutraceutical and nutritional therapy theory, it achieves this goal by using efficacy of such nutraceuticals in detoxifying the body, avoiding vitamin and mineral deficiencies, and restoring healthy digestion and dietary habit. Phytonutrients basically is plant nutrients with particular biological activities in supporting human health.[7]
The phytochemical work by following way:
Substrate for biochemical reactions.
Cofactors of enzymatic reactions.
Inhibitors of enzymatic reactions.
Absorbents that bind to and eliminate undesirable constituent in the intestine.
Enhance the absorption and/or stability of essential nutrients.
Selective growth factor for beneficial bacteria.
Fermentation substrate for beneficial bacteria.
Selective inhibitors of deleterious intestinal bacteria.
Scavengers of reactive or toxic chemicals.
Ligands that agonize or antagonize cell surface or intracellular receptors.[8]
CLASSIFICATION
Nutraceuticals or functional foods can be classified on the basis of their natural sources, pharmacological conditions, or as per chemical constitution of the products.
On the basis of natural source, it can be classified as the products obtained from plants, animals, minerals, or microbial sources.
Nutraceuticals as per the chemical groupings.
Category of Nutraceutical
Substances with established nutritional functions, such as vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and fatty acids–Nutrients.
Herbs or botanical products as concentrates or extracts–Herbals.
Reagents derived from other sources (e.g., pyruvate, chondroitin sulfate, steroid hormone precursors) serving specific functions, such as sports nutrition, weight-loss supplements, fortified conventional foods, and meal replacements–Dietary supplements.
Dietary supplements are not intended to treat or cure disease,[10] whereas nutraceuticals more emphasize the expected results of these products, such as prevention or treatment of diseases.[11]
Some of the most common ways of classifying nutraceuticals can be based on food sources, mechanism of action, chemical nature, etc. The food sources used as nutraceuticals are all natural and can be categorized as
Dietary Fiber.
Probiotics.
Prebiotics.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Antioxidant vitamins.
Polyphenols.
Spices[12]
Nutraceutical can be broadly classified into the following 2 groups:
-
i)
Potential nutraceuticals.
-
ii)
Established nutraceuticals.
A potential nutraceutical could become an established one only after efficient clinical data of its health and medical benefits are obtained.[13,14]
GLOBAL DEMAND OF NUTRACEUTICAL
The nutraceutical industry lies under three main segments which include functional foods, dietary supplements, and herbal/natural products.[15] Global nutraceutical market is estimated as USD 117 billion (INR 5148 billion).[16] In 2007, nutraceuticals sale is projected to reach $74.7 billion at an AAGR of 9.9%. This assumes a world economic recovery in 2003 and an end to price competition [Figure 1].[17]
Figure 1.
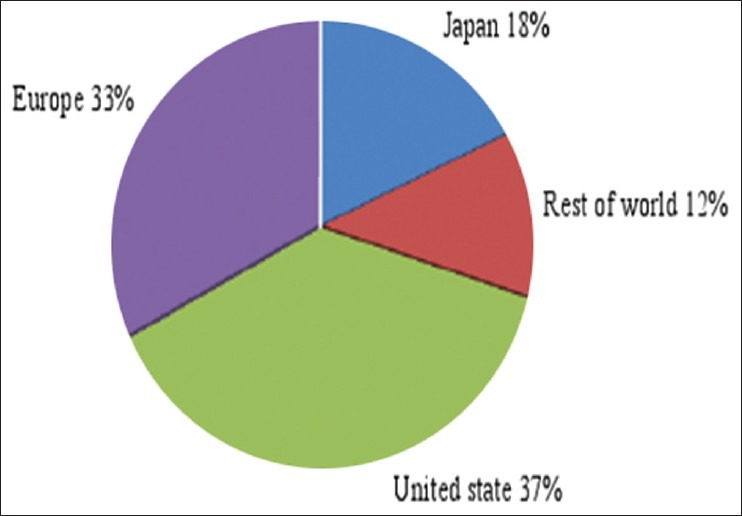
Nutraceutical market in different countries
According to a recent report, the total market for nutraceuticals in India is growing at 21 percent per annum. It is currently valued at INR 44bn (€621 m), but could be worth more than INR 95bn in four years.[19]
As a concept, “Nutraceuticals” is still in its stage of infancy in India. But it has been growing much faster than global rates at CAGR of 18% for the last 3 years driven by functional food and beverages categories.[20] The most rapidly growing segments of the industry were dietary supplements (19.5 percent per year) and natural/herbal products (11.6 percent per year).
REGULATIONS
A food stuff (as a fortified food or a dietary supplement) that provides health benefits, if indeed a claim was made that implied medicinal benefit regarding a nutraceutical product, the product would be required to comply with the regulatory requirements for medicinal products, in respect of safety, efficacy, and quality testing and marketing authorization procedures.[14] For decades, FDA regulated dietary supplements as foods to ensure that they were safe and wholesome and that their labeling was truthful and not misleading. In 2006, the Indian government passed Food Safety and Standard Act to integrate and streamline the many regulations covering nutraceuticals, foods, and dietary supplements. The act calls for the creation of the Food Safety and Standards Authority (FSSA).[21]
BENEFITS OF IMPLEMENTATION OF FSSA ACTS
Unification of eight laws, i.e, steps to Harmonization.
Alignment of international regulations.
Science-based standards.
Clarity and uniformity on novel food areas.
Help curb corruptions.
Unlike the US, where the DSHEA is in place to regulate these products, in India the Government is in the process of drafting a law to regulate manufacturing, importing, and marketing of health foods, dietary supplements, and other nutraceuticals[22] and finally Indian food safety standard bill 2005 signed into law, promising a major impact on Indian food processing industry. The Indian Food Safety and Standard Act came into enforcement in 2006 with the following two main objectives:
To introduce a single statute relating to food, and
To provide for scientific development of the food processing 2009 industry.[21]
GOVERNMENT REGULATIONS - NLEA 1990
Nutrition Labeling and Education Act of 1990 (NLEA) defines how food is labeled, including nutrition labeling, in accordance with definitions established by FDA, and providing for the use of claims about the relationship between nutrients and diseases or health-related condition.
Benefits of Regulation
Allows greater legal security and more predicable environment.
Supports innovation (food and drink products).
Prevents unfair competition from manufactures using false or misleading claims.
If positive claims cannot be made, the regulation does not oblige anyone to make negative claims about the product.[26]
CONCLUSION
Nutraceuticals have proven health benefits and their consumption (within their acceptable Recommended Dietary Intakes) will keep diseases at bay and allow humans to maintain an overall good health. Although nutraceuticals have significant promise in the promotion of human health and disease prevention, health professional, nutritionists, and regulatory toxicologist should strategically work together to plan appropriate regulation to provide the ultimate health and therapeutic benefit to mankind. That is why implementation of regulatory body is necessary to standardize the nutraceutical industry. It is also necessary to review this topic because the nutraceutical industry is growing at a rate far exceeding expansion in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Herbal nutraceutical is a powerful instrument in maintaining health and to act against nutritionally induced acute and chronic diseases, thereby promoting optimal health, longevity, and quality of life.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors wish to thank Jamia Hamdard.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: Nil.
REFERENCES
- 1.Brower V. Nutraceuticals: Poised for a healthy slice of the healthcare market? Nat Biotechnol. 1998;16:728–31. doi: 10.1038/nbt0898-728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Trottier G, Boström PJ, Lawrentschuk N, Fleshner NE. Nutraceuticals and prostate cancer prevention: A current review. Nat Rev Urol. 2010;7:21–30. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2009.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kalra EK. Nutraceutical - Definition and introduction. AAPS PharmSci. 2003;5:E25. doi: 10.1208/ps050325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zeisel SH. Regulation of “Nutraceuticals”. Science. 1999;285:1853–5. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5435.1853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.FDA/CFSAN resources page. Food and Drug Administration website. Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994. [Last accessed on 2012 Mar 24]. Available from: http://vm.cfsan.fda.gov/~dms/dietsupp.html .
- 6.United State Pharmacopeia USP2006, The regulation of Dietary Supplements. [Last accessed on 2012 Mar 24]. Available from: http://www.usp.org/pdf/EN/USPVerified/dietarySupplementRegulation.pdf .
- 7.Zhao J. Nutraceuticals, Nutritional Therapy, Phytonutrients, and Phytotherapy for Improvement of Human Health: A Perspective on Plant Biotechnology Application, 2007. Bentham Science Publishers. [Last accessed on 2012 Mar 24]. Available from: http://www.benthamscience.com/biot/samples/biot1-1/Zhao.pdf . [DOI] [PubMed]
- 8.Dillard CJ, German JB. Phytochemicals: Nutraceuticals and human health. J Sci Food Agric. 2000;80:1744–56. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Faisal N, Varma KS. Nutraceuticals and its impact on health care. [Last accessed on 2012 Mar 24]. Available from: http://farmacists.blogspot.in/2009/05/nutraceuticals-and-itsimpact-on-health.html .
- 10.Ross S. Functional foods: The food and drug administration perspective. Am J Clin Nut. 2000;71:1735–8. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/71.6.1735S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bagchi D. Nutraceuticals and functional foods regulations in the United States and around the world. Toxicology. 2006;221:1–3. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kalia AN. New Delhi: CBS Publisher and Distributor; 2005. Textbook of industrial pharmacognocy; pp. 204–8. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kokate CK, Purohit AP, Gokhale SB. Pharmacognosy. 21st ed. Pune, India: Nirali Prakashan; 2002. Nutraceutical and cosmaceutical; pp. 542–9. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pandey M, Verma RK, Saraf SA. Nutraceuticals: New era of medicine and health. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2010;3:11–5. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Das L, Bhaumik E, Raychaudhuri U, Chakraborty R. Role of nutraceuticals in human health. J Food Sci Technol. 2011 doi: 10.1007/s13197-011-0269-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rishi RK. Nutraceutical: Borderline between food and drug. Pharma Review. 2006. [Last accessed on [Last accessed on 2012 Mar 24]]. Available from: http://www.kppub.com/articles/herbal-safety-pharmareview-004/nutraceuticalsborderlinebetween-food-anddrugs.html .
- 17.Nutrition business journal estimates (NBJ data) [Google Scholar]
- 18.Joanne B, linda AA, Phillipson DJ. 3rd ed. RPS Publishing; Herbal medicines; p. 48. 263. [Google Scholar]
- 19. [Last accessed on 2012 Mar 24]. Available from: http://www.horiba.com/scientific/products/particlecharacterization/applications/nutraceuticals .
- 20.FICCI study on Implementation of Food Safety and Standard Act 2006: An Industry Perspective. [Last accessed on 2009 Mar 1]. Available from: http://www.Indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/Files/food_safety_study.pdf .
- 21.Nutraceutical Market and its Regulation. [Last accessed on 2012 Mar 24]. Available from: http://www.agrifoodgateway.com/articles/nutraceutical-market-anditsregulation .
- 22.Regulation of functional food in Indian Subcontinent, food and beverages news. [Last accessed on 2008 Nov 1]. Available from: http://www.efenbeonline.com/view_story.asp? type=story and id=880 .
- 23.Dureja H, Kaushik D, Kumar V. Developments in nutraceuticals. Indian J Pharmacol. 2003;35:363–72. [Google Scholar]
- 24. [Last accessed on 2012 Mar 24]. Available from: http://www.indiamart.com/hindustanbiosynth/nutraceuticalsupplements.html .
- 25. [Last accessed on 2012 Mar 24]. Available from: http://www.tradeindia.com/fp348658/Amiriprash-Gold-.html .
- 26. [Last accessed on 2012 Mar 24]. Available from: http://www.nutraceutical.com/educate/pdf/garlic.pdf .


