Abstract
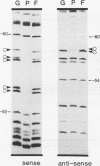
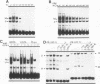
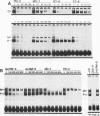
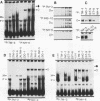
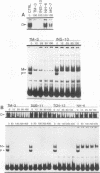
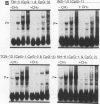
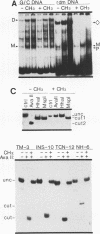
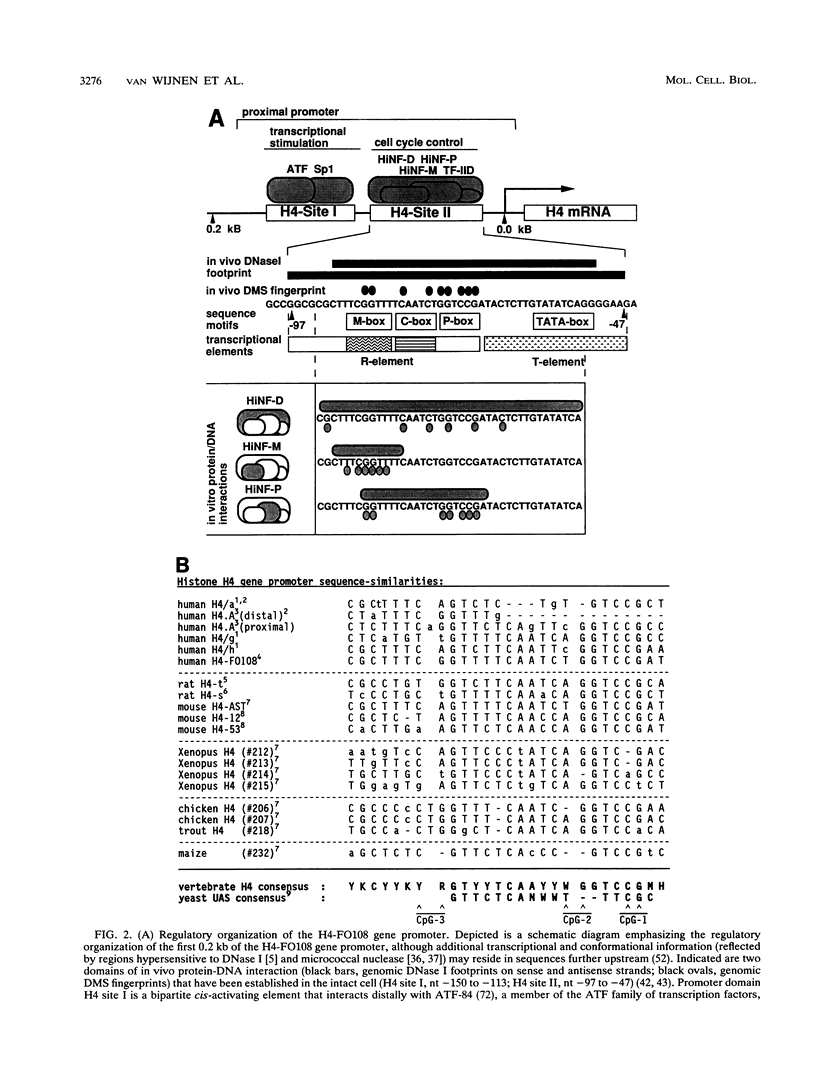
Transcriptional regulation of vertebrate histone genes during the cell cycle is mediated by several factors interacting with a series of cis-acting elements located in the 5' regions of these genes. The arrangement of these promoter elements is different for each gene. However, most histone H4 gene promoters contain a highly conserved sequence immediately upstream of the TATA box (H4 subtype consensus sequence), and this region in the human H4 gene FO108 is involved in cell cycle control. The sequence-specific interaction of nuclear factor HiNF-D with this key proximal promoter element of the H4-FO108 gene is cell cycle regulated in normal diploid cells (J. Holthuis, T.A. Owen, A.J. van Wijnen, K.L. Wright, A. Ramsey-Ewing, M.B. Kennedy, R. Carter, S.C. Cosenza, K.J. Soprano, J.B. Lian, J.L. Stein, and G.S. Stein, Science, 247:1454-1457, 1990). Here, we show that this region of the H4-FO108 gene represents a composite protein-DNA interaction domain for several distinct sequence-specific DNA-binding activities, including HiNF-D, HiNF-M, and HiNF-P. Factor HiNF-P is similar to H4TF-2, a DNA-binding activity that is not cell cycle regulated and that interacts with the analogous region of the H4 gene H4.A (F. LaBella and N. Heintz, Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:5825-5831, 1991). The H4.A gene fails to interact with factors HiNF-M and HiNF-D owing to two independent sets of specific nucleotide variants, indicating differences in protein-DNA interactions between these H4 genes. Cytosine methylation of a highly conserved CpG dinucleotide interferes with binding of HiNF-P/H4TF-2 to both the H4-FO108 and H4.A promoters, but no effect is observed for either HiNF-M or HiNF-D binding to the H4-FO108 gene. Thus, strong evolutionary conservation of the H4 consensus sequence may be related to combinatorial interactions involving overlapping and interdigitated recognition nucleotides for several proteins, whose activities are regulated independently. Our results also suggest molecular complexity in the transcriptional regulation of distinct human H4 genes.
Full text
PDF




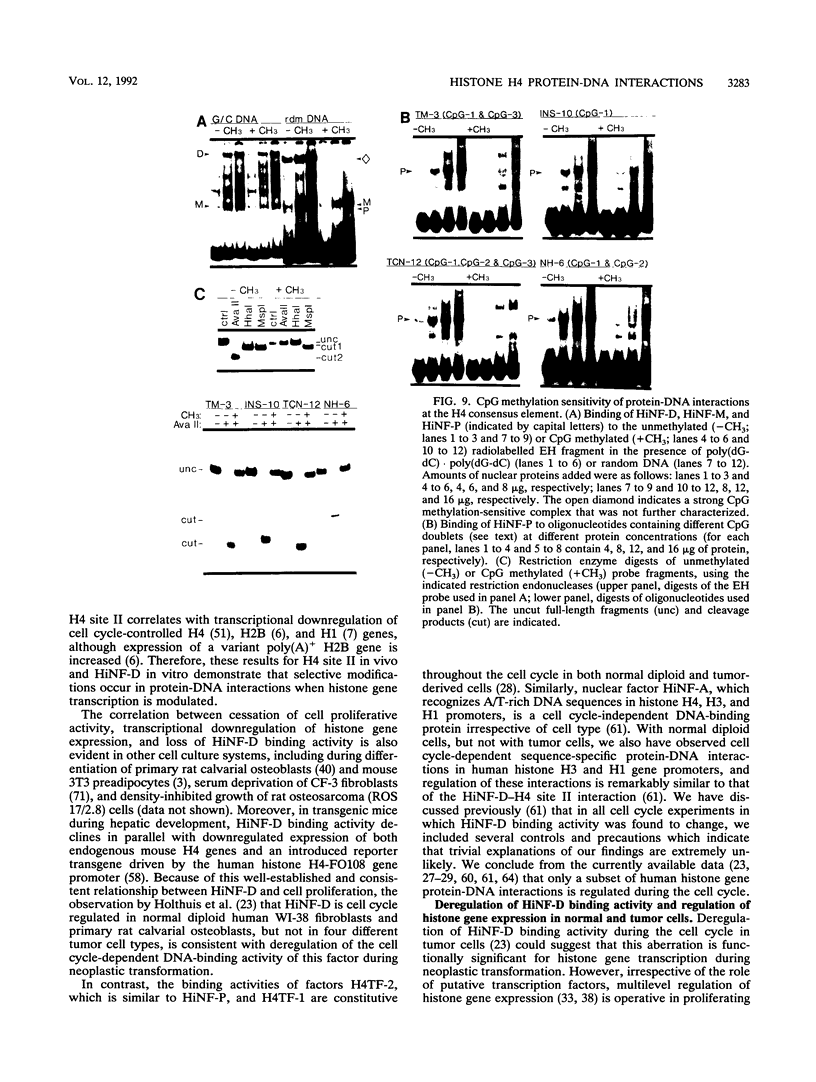
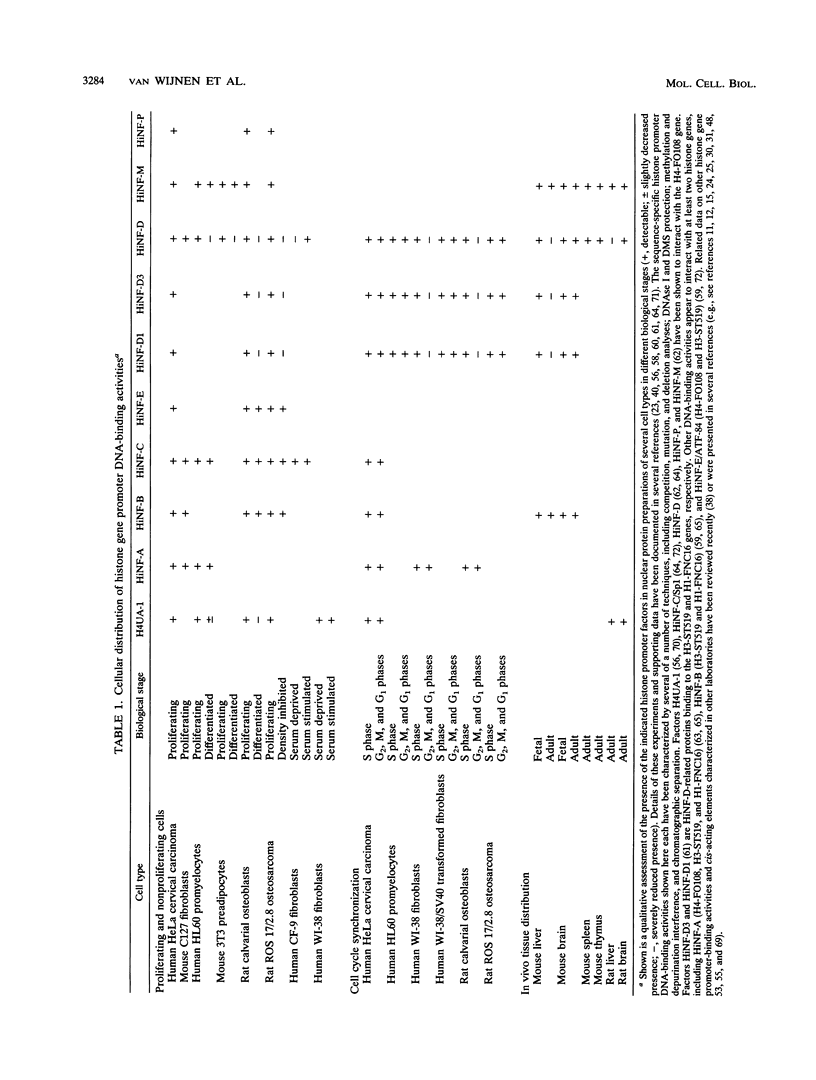



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen B. S., Stein J. L., Stein G. S., Ostrer H. Single-copy flanking sequences in human histone gene clusters map to chromosomes 1 and 6. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):486–488. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90337-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. W., Dou Q. P., Fridovich-Keil J. L., Pardee A. B. Transformed and nontransformed cells differ in stability and cell cycle regulation of a binding activity to the murine thymidine kinase promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9310–9314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collar D. G., Wright K. L., van Wijnen A. J., Ramsey A. L., Lian J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. The human H1 histone gene FNC16 is functionally expressed in proliferating HeLa S3 cells and is down-regulated during terminal differentiation in HL60 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15860–15863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart D., Ramsey-Ewing A., Bortell R., Lian J., Stein J., Stein G. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA from a human histone H2B gene which is reciprocally expressed in relation to replication-dependent H2B histone genes during HL60 cell differentiation. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 12;30(6):1610–1617. doi: 10.1021/bi00220a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Hanly S. M., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Distinct transcription factors bind specifically to two regions of the human histone H4 promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7241–7245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. Purification of the human histone H4 gene-specific transcription factors H4TF-1 and H4TF-2. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1700–1712. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. RNA polymerase II transcription factors H4TF-1 and H4TF-2 require metal to bind specific DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4582–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Wells J. R. A gene-specific promoter element is required for optimal expression of the histone H1 gene in S-phase. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):49–56. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02782.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Wells J. R. Maximal binding levels of an H1 histone gene-specific factor in S-phase correlate with maximal H1 gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4576–4578. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dou Q. P., Fridovich-Keil J. L., Pardee A. B. Inducible proteins binding to the murine thymidine kinase promoter in late G1/S phase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1157–1161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallinari P., La Bella F., Heintz N. Characterization and purification of H1TF2, a novel CCAAT-binding protein that interacts with a histone H1 subtype-specific consensus element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1566–1575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L., Schlaffer I., Wright K., Moreno M. L., Berand D., Hager G., Stein J., Stein G. Cell cycle-dependent expression of a stable episomal human histone gene in a mouse cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2315–2319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes S., Weisz-Carrington P., Daum H., 3rd, Smith J., Green L., Wright K., Stein G., Stein J. A rat histone H4 gene closely associated with the testis-specific H1t gene. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Dec;173(2):534–545. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanly S. M., Bleecker G. C., Heintz N. Identification of promoter elements necessary for transcriptional regulation of a human histone H4 gene in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):380–389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. The regulation of histone gene expression during the cell cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 26;1088(3):327–339. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms S. R., van Wijnen A. J., Kroeger P., Shiels A., Stewart C., Hirshman J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Identification of an enhancer-like element upstream from a cell cycle dependent human H4 histone gene. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Sep;132(3):552–558. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041320319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofbauer R., Denhardt D. T. Cell cycle-regulated and proliferation stimulus-responsive genes. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1991;1(4):247–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthuis J., Owen T. A., van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Ramsey-Ewing A., Kennedy M. B., Carter R., Cosenza S. C., Soprano K. J., Lian J. B. Tumor cells exhibit deregulation of the cell cycle histone gene promoter factor HiNF-D. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1454–1457. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang I., Chae C. B. S-phase-specific transcription regulatory elements are present in a replication-independent testis-specific H2B histone gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1005–1013. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Sharma A., Lee A. S., Maxson R. Cell cycle regulation of H2b histone octamer DNA-binding activity in Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):869–873. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger P., Stewart C., Schaap T., van Wijnen A., Hirshman J., Helms S., Stein G., Stein J. Proximal and distal regulatory elements that influence in vivo expression of a cell cycle-dependent human H4 histone gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):3982–3986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Bella F., Gallinari P., McKinney J., Heintz N. Histone H1 subtype-specific consensus elements mediate cell cycle-regulated transcription in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1982–1990. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Bella F., Heintz N. Histone gene transcription factor binding in extracts of normal human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5825–5831. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBella F., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Cell-cycle regulation of a human histone H2b gene is mediated by the H2b subtype-specific consensus element. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):32–39. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., Maxson R., Childs G. Both basal and ontogenic promoter elements affect the timing and level of expression of a sea urchin H1 gene during early embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):173–183. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee I. J., Tung L., Bumcrot D. A., Weinberg E. S. UHF-1, a factor required for maximal transcription of early and late sea urchin histone H4 genes: analysis of promoter-binding sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1048–1061. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtler A. C., Sierra F., Clark S., Wells J. R., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Multiple H4 histone mRNAs of HeLa cells are encoded in different genes. Nature. 1982 Jul 8;298(5870):195–198. doi: 10.1038/298195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Pandey N. B. Multiple regulatory steps control histone mRNA concentrations. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier V. S., Böhni R., Schümperli D. Nucleotide sequence of two mouse histone H4 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):795–795. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno M. L., Chrysogelos S. A., Stein G. S., Stein J. L. Reversible changes in the nucleosomal organization of a human H4 histone gene during the cell cycle. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 23;25(19):5364–5370. doi: 10.1021/bi00367a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno M. L., Pauli U., Chrysogelos S., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Persistence of a micrococcal nuclease sensitive region spanning the promoter-coding region junction of a cell cycle regulated human H4 histone gene throughout the cell cycle. Biochem Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;66(2):132–137. doi: 10.1139/o88-017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Gould J., Kim S., Kane M. Y., Hereford L. Identification of sequences in a yeast histone promoter involved in periodic transcription. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A. The regulation of histone synthesis in the cell cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:827–861. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.004143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen T. A., Holthuis J., Markose E., van Wijnen A. J., Wolfe S. A., Grimes S. R., Lian J. B., Stein G. S. Modifications of protein-DNA interactions in the proximal promoter of a cell-growth-regulated histone gene during onset and progression of osteoblast differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5129–5133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. G1 events and regulation of cell proliferation. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):603–608. doi: 10.1126/science.2683075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli U., Chrysogelos S., Stein G., Stein J., Nick H. Protein-DNA interactions in vivo upstream of a cell cycle-regulated human H4 histone gene. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1308–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.3035717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segil N., Roberts S. B., Heintz N. Mitotic phosphorylation of the Oct-1 homeodomain and regulation of Oct-1 DNA binding activity. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1814–1816. doi: 10.1126/science.1684878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Paterson B. M. Cell cycle regulation of a mouse histone H4 gene requires the H4 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1048–1054. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma A., Bos T. J., Pekkala-Flagan A., Vogt P. K., Lee A. S. Interaction of cellular factors related to the Jun oncoprotein with the promoter of a replication-dependent hamster histone H3.2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):491–495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra F., Lichtler A., Marashi F., Rickles R., Van Dyke T., Clark S., Wells J., Stein G., Stein J. Organization of human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1795–1799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierra F., Stein G., Stein J. Structure and in vitro transcription of a human H4 histone gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):7069–7086. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.7069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. S., Stein J. L., van Wijnen A. J., Lian J. B. Regulation of histone gene expression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;4(2):166–173. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90028-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G., Lian J., Stein J., Briggs R., Shalhoub V., Wright K., Pauli U., van Wijnen A. Altered binding of human histone gene transcription factors during the shutdown of proliferation and onset of differentiation in HL-60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1865–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata T., Takase H., Takayama S., Mikami K., Nakatsuka A., Kawata T., Nakayama T., Iwabuchi M. A protein that binds to a cis-acting element of wheat histone genes has a leucine zipper motif. Science. 1989 Sep 1;245(4921):965–967. doi: 10.1126/science.2772648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripputi P., Emanuel B. S., Croce C. M., Green L. G., Stein G. S., Stein J. L. Human histone genes map to multiple chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3185–3188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung L., Lee I. J., Rice H. L., Weinberg E. S. Positive and negative transcriptional regulatory elements in the early H4 histone gene of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7339–7348. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells D., McBride C. A comprehensive compilation and alignment of histones and histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989;17 (Suppl):r311–r346. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.suppl.r311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender E. Transcription regulating proteins and their recognition sequences. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1990;1(1):11–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. A., Anderson J. V., Grimes S. R., Stein G. S., Stein J. S. Comparison of the structural organization and expression of germinal and somatic rat histone H4 genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 1;1007(2):140–150. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90032-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe S. A., Grimes S. R. Protein-DNA interactions within the rat histone H4t promoter. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6637–6643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright K. L., Dell'Orco R. T., van Wijnen A. J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Multiple mechanisms regulate the proliferation-specific histone gene transcription factor HiNF-D in normal human diploid fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 17;31(10):2812–2818. doi: 10.1021/bi00125a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Choi T. K., Owen T. A., Wright K. L., Lian J. B., Jaenisch R., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Involvement of the cell cycle-regulated nuclear factor HiNF-D in cell growth control of a human H4 histone gene during hepatic development in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2573–2577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Protein/DNA interactions involving ATF/AP1-, CCAAT-, and HiNF-D-related factors in the human H3-ST519 histone promoter: cross-competition with transcription regulatory sites in cell cycle controlled H4 and H1 histone genes. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Dec;47(4):337–351. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240470408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Massung R. F., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Human H1 histone gene promoter CCAAT box binding protein HiNF-B is a mosaic factor. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6534–6541. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Owen T. A., Holthuis J., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Coordination of protein-DNA interactions in the promoters of human H4, H3, and H1 histone genes during the cell cycle, tumorigenesis, and development. J Cell Physiol. 1991 Jul;148(1):174–189. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041480120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Ramsey-Ewing A. L., Bortell R., Owen T. A., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Transcriptional element H4-site II of cell cycle regulated human H4 histone genes is a multipartite protein/DNA interaction site for factors HiNF-D, HiNF-M, and HiNF-P: involvement of phosphorylation. J Cell Biochem. 1991 Jun;46(2):174–189. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240460211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. A nuclear protein with affinity for the 5' flanking region of a cell cycle dependent human H4 histone gene in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1679–1698. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Lian J. B., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Human H4 histone gene transcription requires the proliferation-specific nuclear factor HiNF-D. Auxiliary roles for HiNF-C (Sp1-like) and HiNF-A (high mobility group-like). J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):15034–15042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wijnen A. J., Wright K. L., Massung R. F., Gerretsen M., Stein J. L., Stein G. S. Two target sites for protein binding in the promoter region of a cell cycle regulated human H1 histone gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):571–592. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]