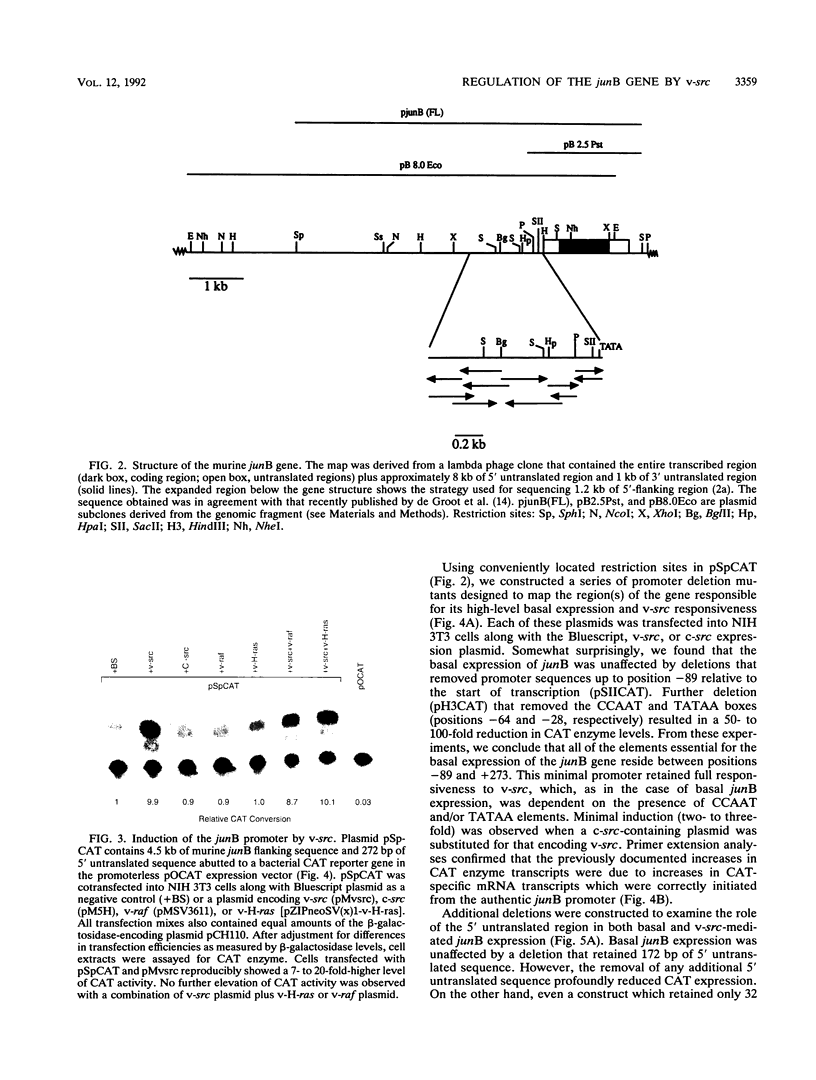
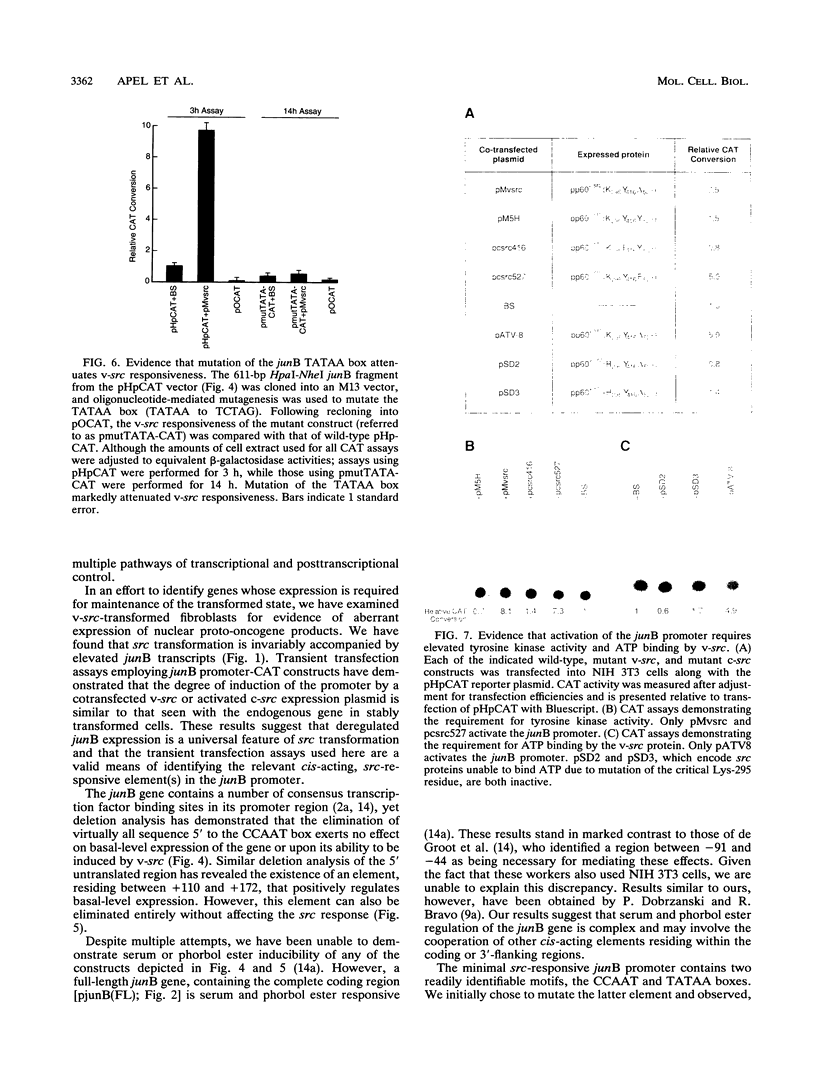
Abstract
The proteins encoded by cellular and viral src genes are believed to be involved in the transmission of mitogenic signals, the nuclear recipients of which are largely unknown. In this work, we report that four different v-src-transformed cell lines from three different species possess elevated levels of junB transcripts. Transient expression of junB promoter-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase constructs in NIH 3T3 cells was used to demonstrate that the increase in junB transcripts was specifically associated with v-src expression and could not be recapitulated with a c-src, v-H-ras, or v-raf expression vector. Deletion mutants were used to localize the v-src-responsive region in the junB promoter to a 121-nucleotide region encompassing the CCAAT and TATAA elements. This region is distinct from one in the 5' untranslated region of the junB gene which is required to maintain its high-level basal expression. Point mutagenesis of the junB TATAA box completely abolished v-src responsiveness, suggesting that proteins which bind to this element are modified by src transformation. Several v-src and c-src mutants were used to demonstrate that elevated tyrosine kinase activity of src proteins is required for the observed effects on junB expression. Finally, homology between the TATAA box regions of junB and the unrelated but src-responsive gene 9E3/CEF-4 suggests that modulation of gene activity through proteins which bind to this region may be a recurrent, although not exclusive, theme in src transforming action. Our results suggest that src proteins may modulate some nuclear effectors through pathways not involving cellular ras or raf gene products.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anisowicz A., Bardwell L., Sager R. Constitutive overexpression of a growth-regulated gene in transformed Chinese hamster and human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7188–7192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Park A., Tjian R. v-Src and EJ Ras alleviate repression of c-Jun by a cell-specific inhibitor. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):165–168. doi: 10.1038/352165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard P. A., Alcorta D., Simmons D. L., Luk K. C., Erikson R. L. Constitutive expression of a gene encoding a polypeptide homologous to biologically active human platelet protein in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6715–6719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binétruy B., Smeal T., Karin M. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):122–127. doi: 10.1038/351122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchenall-Roberts M. C., Ruscetti F. W., Kasper J., Lee H. D., Friedman R., Geiser A., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Kim S. J. Transcriptional regulation of the transforming growth factor beta 1 promoter by v-src gene products is mediated through the AP-1 complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4978–4983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. A., Hanafusa H. The v-src inducible gene 9E3/pCEF4 is regulated by both its promoter upstream sequence and its 3' untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1162–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brott B. K., Decker S., O'Brien M. C., Jove R. Molecular features of the viral and cellular Src kinases involved in interactions with the GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5059–5067. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brott B. K., Decker S., Shafer J., Gibbs J. B., Jove R. GTPase-activating protein interactions with the viral and cellular Src kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Zhang K., Redford P., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Suppression of src transformation by overexpression of full-length GTPase-activating protein (GAP) or of the GAP C terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2819–2825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutta A., Stoeckle M. Y., Hanafusa H. Serum and v-src increase the level of a CCAAT-binding factor required for transcription from a retroviral long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):243–254. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Hoey T., Tjian R. Isolation of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. B., Sobel M. E., Yamada K. M., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Effects of transformation on fibronectin gene expression using cloned fibronectin cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):520–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Shalloway D., Verma I. M. Gene regulation by tyrosine kinases: src protein activates various promoters, including c-fos. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2493–2499. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Hunter T. Platelet-derived growth factor induces multisite phosphorylation of pp60c-src and increases its protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3345–3356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J. Roles of TFIID in transcriptional initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1067–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90027-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Activation of cellular genes by avian RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5351–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendricks M., Weintraub H. Multiple tropomyosin polypeptides in chicken embryo fibroblasts: differential repression of transcription by Rous sarcoma virus transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1823–1833. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Dynlacht B. D., Peterson M. G., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Isolation and characterization of the Drosophila gene encoding the TATA box binding protein, TFIID. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1179–1186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90682-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A tail of two src's: mutatis mutandis. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90745-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inostroza J., Flores O., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of general transcription factor IIE. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9304–9308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Hanafusa H. Cell transformation by the viral src oncogene. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:31–56. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Neither arginine nor histidine can carry out the function of lysine-295 in the ATP-binding site of p60src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):751–757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledwith B. J., Manam S., Kraynak A. R., Nichols W. W., Bradley M. O. Antisense-fos RNA causes partial reversion of the transformed phenotypes induced by the c-Ha-ras oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1545–1555. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nori M., Vogel U. S., Gibbs J. B., Weber M. J. Inhibition of v-src-induced transformation by a GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2812–2818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma Y., Sumimoto H., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification and characterization of general transcription factor TFIIE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9163–9167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Weber M. J. Genetics of src: structure and functional organization of a protein tyrosine kinase. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;147:79–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74697-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Hunter T., Esch F. S., Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M. Analysis of the sequence of amino acids surrounding sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):973–977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Inostroza J., Maxon M. E., Flores O., Admon A., Reinberg D., Tjian R. Structure and functional properties of human general transcription factor IIE. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):369–373. doi: 10.1038/354369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prost E., Moore D. D. CAT vectors for analysis of eukaryotic promoters and enhancers. Gene. 1986;45(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Goldsborough M. D., Mark G. E., Bonner T. I., Groffen J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Structure and biological activity of v-raf, a unique oncogene transduced by a retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4218–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth C. W., Richert N. D., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Cyclic AMP treatment of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed Chinese hamster ovary cells increases phosphorylation of pp60src and increases pp60src kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10768–10773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönthal A., Herrlich P., Rahmsdorf H. J., Ponta H. Requirement for fos gene expression in the transcriptional activation of collagenase by other oncogenes and phorbol esters. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):325–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90195-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. L., Levy D. B., Yannoni Y., Erikson R. L. Identification of a phorbol ester-repressible v-src-inducible gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1178–1182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sistonen L., Hölttä E., Mäkelä T. P., Keski-Oja J., Alitalo K. The cellular response to induction of the p21 c-Ha-ras oncoprotein includes stimulation of jun gene expression. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):815–822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03442.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar M. D., Thompson E., Welsh M. J., Liebert M., Harney J., Grossman H. B., Smith M., Prochownik E. V. Depletion of c-myc with specific antisense sequences reverses the transformed phenotype in ras oncogene-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3699–3710. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Oppermann H., Czernilofsky A. P., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L., Bishop J. M. Characterization of sites for tyrosine phosphorylation in the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus (pp60v-src) and its normal cellular homologue (pp60c-src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6013–6017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., DeGudicibus S. J., Stacey D. W. Requirement for c-ras proteins during viral oncogene transformation. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):540–543. doi: 10.1038/320540a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugano S., Stoeckle M. Y., Hanafusa H. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus induces a novel gene with homology to a mitogenic platelet protein. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):321–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. L., Chipman J. G., Robertson D. L., Erikson R. L., Simmons D. L. Expression of a mitogen-responsive gene encoding prostaglandin synthase is regulated by mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2692–2696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K., DeClue J. E., Vass W. C., Papageorge A. G., McCormick F., Lowy D. R. Suppression of c-ras transformation by GTPase-activating protein. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):754–756. doi: 10.1038/346754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. P., Auwerx J., Karperien M., Staels B., Kruijer W. Activation of junB by PKC and PKA signal transduction through a novel cis-acting element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):775–781. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








