Abstract
Mutations were targeted to the Hprt locus of mouse embryo-derived stem cells by using 22 different sequence replacement and sequence insertion vectors. The targeting frequency was examined at two sites within the Hprt locus as a function of the extent of homology between the targeting vector and the target locus. The targeting frequency was also compared by using vectors prepared from isogenic and nonisogenic DNA sources. With one exception, all of the vectors showed the same exponential dependence of targeting efficiency on the extent of homology between the targeting vector and the target locus. This was true regardless of whether they were sequence replacement or sequence insertion vectors, whether they were directed toward either of the two different sites within the Hprt locus, or whether they were prepared from isogenic or nonisogenic DNA sources. Vectors prepared from isogenic DNA targeted four to five times more efficiently than did the corresponding vectors prepared from nonisogenic DNA. The single case of unexpectedly low targeting efficiency involved one of the vectors prepared from nonisogenic DNA and could be attributed to an unfavorable distribution of heterology between the Hprt sequences present in the targeting vector and the endogenous Hprt gene.
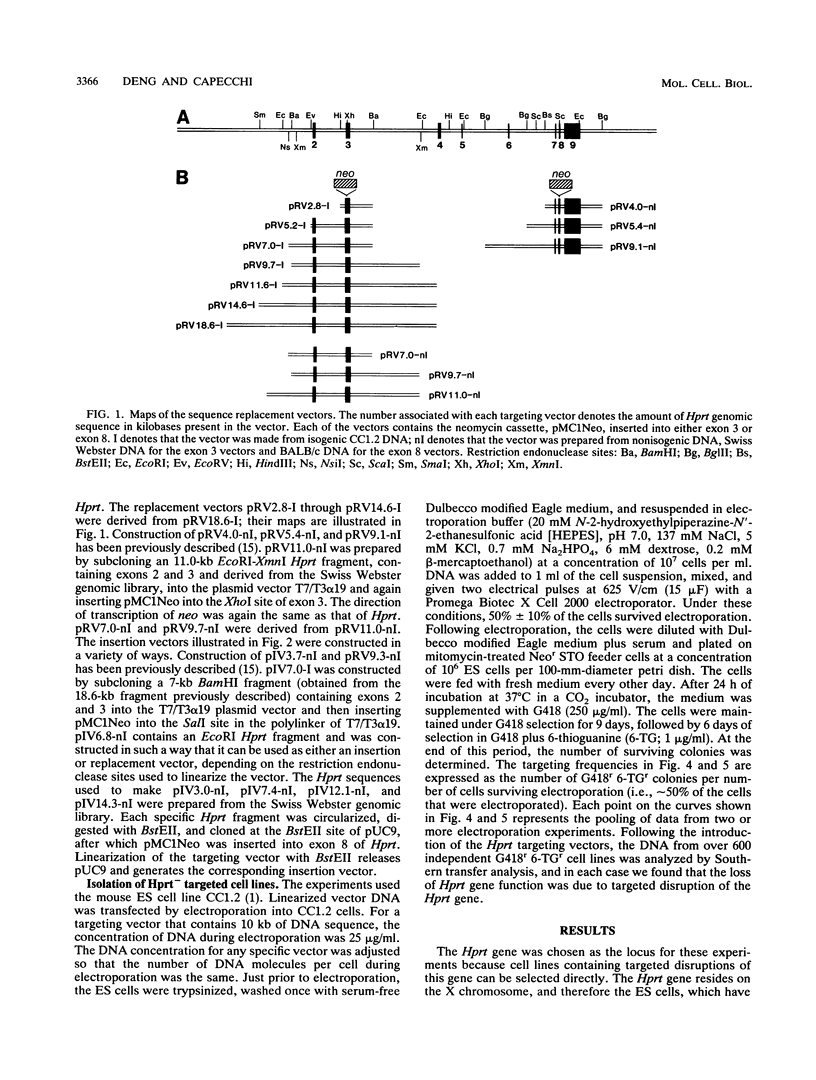
Full text
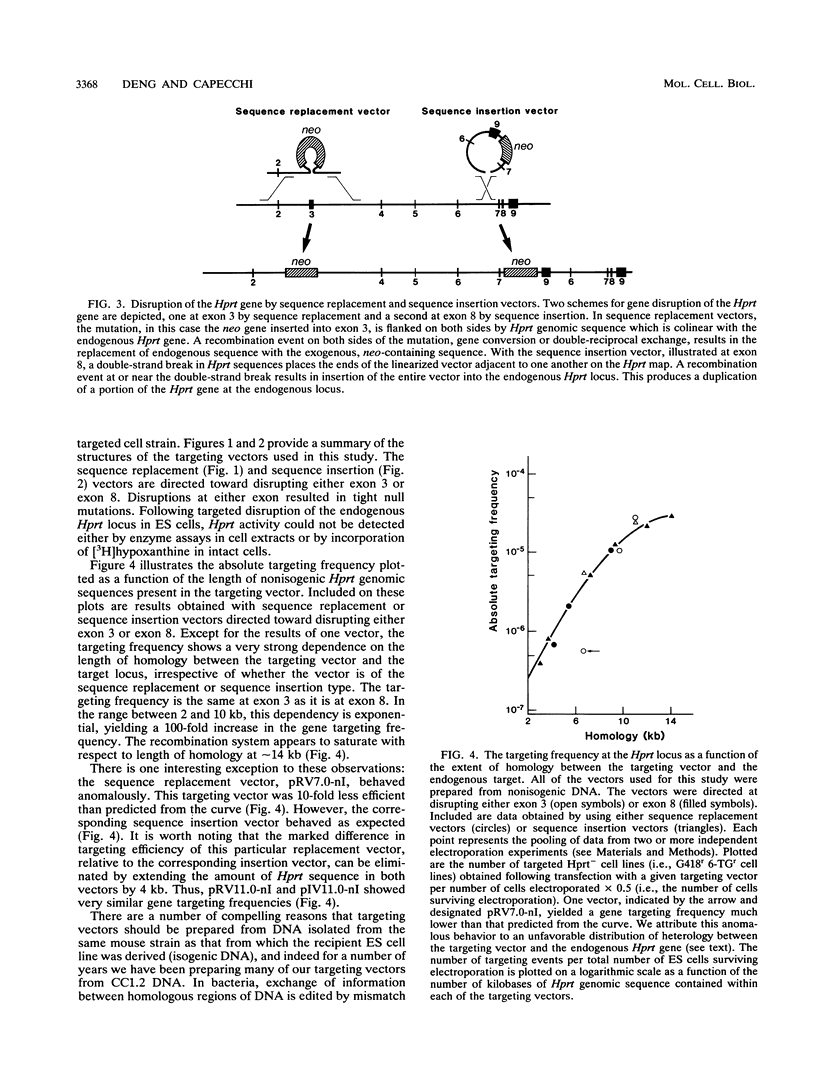
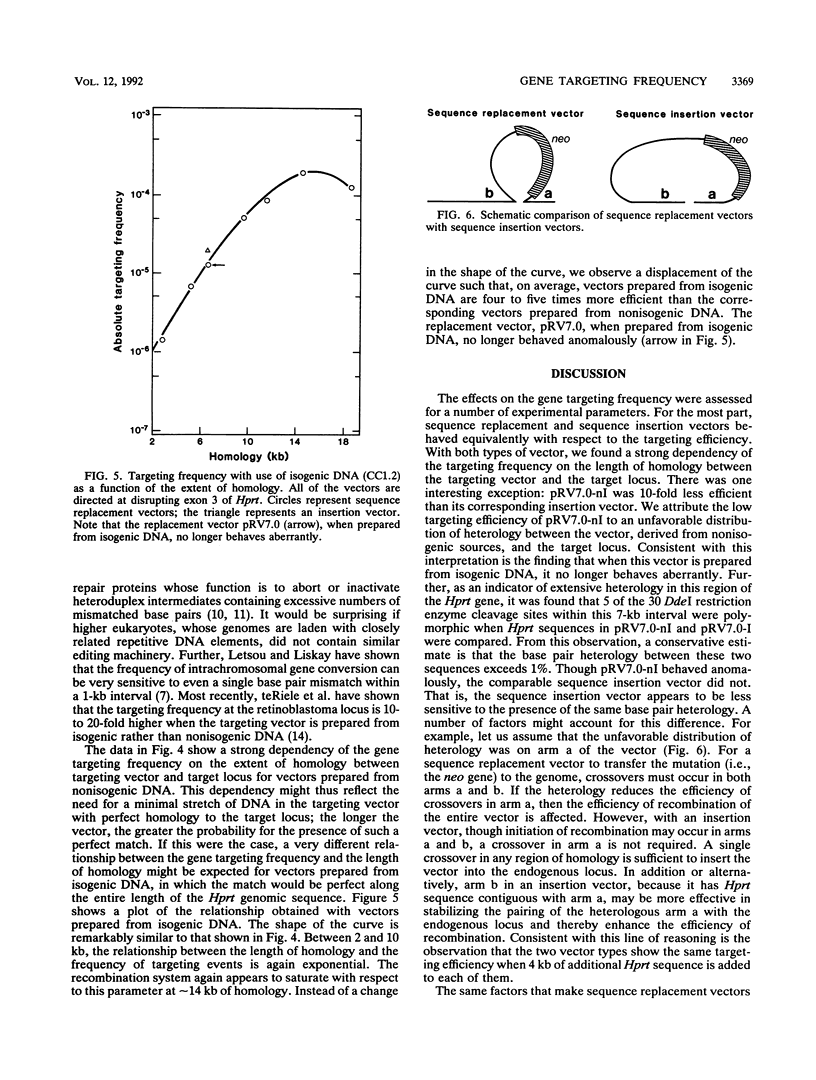
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley A., Evans M., Kaufman M. H., Robertson E. Formation of germ-line chimaeras from embryo-derived teratocarcinoma cell lines. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):255–256. doi: 10.1038/309255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2660260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. R. The new mouse genetics: altering the genome by gene targeting. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty P., Rivera-Pérez J., Bradley A. The length of homology required for gene targeting in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5586–5591. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty P., Rivera-Pérez J., Chang C., Bradley A. Target frequency and integration pattern for insertion and replacement vectors in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4509–4517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H. S., Smithies O. Recombinant fragment assay for gene targetting based on the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8887–8903. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letsou A., Liskay R. M. Effect of the molecular nature of mutation on the efficiency of intrachromosomal gene conversion in mouse cells. Genetics. 1987 Dec;117(4):759–769. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.4.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayssiguier C., Thaler D. S., Radman M. The barrier to recombination between Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium is disrupted in mismatch-repair mutants. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):396–401. doi: 10.1038/342396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen P., Huang H. V. Effect of base pair mismatches on recombination via the RecBCD pathway. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Aug;218(2):358–360. doi: 10.1007/BF00331291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolik-Utlaut S., Petes T. D. Recombination of plasmids into the Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome is reduced by small amounts of sequence heterogeneity. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1204–1211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szostak J. W., Wu R. Insertion of a genetic marker into the ribosomal DNA of yeast. Plasmid. 1979 Oct;2(4):536–554. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Deng C., Capecchi M. R. High-fidelity gene targeting in embryonic stem cells by using sequence replacement vectors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):2919–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.2919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



