Abstract
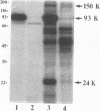
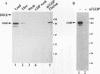
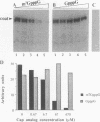
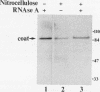
The eukaryotic mRNA 5' cap structure m7GpppX (where X is any nucleotide) interacts with a number of cellular proteins. Several of these proteins were studied in mammalian, yeast, and drosophila cells and found to be involved in translation initiation. Here we describe a novel cap-binding protein, the coat protein of L-A, a double-stranded RNA virus that is persistently maintained in many Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. The results also suggest that the coat protein of a related double-stranded RNA virus (L-BC) is likewise a cap-binding protein. Strikingly, in contrast to the cellular cap-binding proteins, the interaction between the L-A virus coat protein and the cap structure is through a covalent bond.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmann M., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Trachsel H. Purification and characterization of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-4E from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6085–6089. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann M., Handschin C., Trachsel H. mRNA cap-binding protein: cloning of the gene encoding protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-4E from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):998–1003. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambros V., Baltimore D. Protein is linked to the 5' end of poliovirus RNA by a phosphodiester linkage to tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5263–5266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braam-Markson J., Jaudon C., Krug R. M. Expression of a functional influenza viral cap-recognizing protein by using a bovine papilloma virus vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4326–4330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner C., Nakayama N., Goebl M., Tanaka K., Toh-e A., Matsumoto K. CDC33 encodes mRNA cap-binding protein eIF-4E of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3556–3559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruenn J. A. Virus-like particles of yeast. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:49–68. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.000405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruenn J., Keitz B. The 5' ends of yeast killer factor RNAs are pppGp. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Oct;3(10):2427–2436. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.10.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey H. K1 killer toxin, a pore-forming protein from yeast. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Oct;5(10):2339–2343. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. E., Dowhanick J. J., Nemeroff M. E., Pietras D. F., Tu C. L., Bruenn J. A. Overlapping genes in a yeast double-stranded RNA virus. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3983–3990. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3983-3990.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinman J. D., Icho T., Wickner R. B. A -1 ribosomal frameshift in a double-stranded RNA virus of yeast forms a gag-pol fusion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):174–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Altmann M., Sonenberg N. High-level synthesis in Escherichia coli of functional cap-binding eukaryotic initiation factor eIF-4E and affinity purification using a simplified cap-analog resin. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90184-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Hümbelin M., Darveau A., Lee K. A., Milburn S., Hershey J. W., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Involvement of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A in the cap recognition process. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Sonenberg N. Cap-dependent RNA splicing in a HeLa nuclear extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7590–7594. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Sherbeini M., Tipper D. J., Mitchell D. J., Bostian K. A. Virus-like particle capsid proteins encoded by different L double-stranded RNAs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: their roles in maintenance of M double-stranded killer plasmids. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2818–2827. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura T., Wickner R. B. Replicase of L-A virus-like particles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In vitro conversion of exogenous L-A and M1 single-stranded RNAs to double-stranded form. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):454–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., LaFiandra A., Shatkin A. J. 5'-Terminal structure and mRNA stability. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):235–239. doi: 10.1038/266235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyer C., Altmann M., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Identification and characterization of cap-binding proteins from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7603–7610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. New initiation factor activity required for globin mRNA translation. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5804–5810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Mattaj I. W. Monomethylated cap structures facilitate RNA export from the nucleus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90292-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site cleavage in a HeLa nuclear extract is dependent on downstream sequences. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Icho T., Wickner R. B. The double-stranded RNA genome of yeast virus L-A encodes its own putative RNA polymerase by fusing two open reading frames. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6716–6723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo M., Pelletier J., Edery I., Nielsen P. J., Sonenberg N. Multiple mRNAs encode the murine translation initiation factor eIF-4E. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10446–10451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Prat A. Baker's yeast, the new work horse in protein synthesis studies: analyzing eukaryotic translation initiation. Bioessays. 1990 Nov;12(11):519–526. doi: 10.1002/bies.950121103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K., Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Transfer of proteins to membranes facilitates both cyanogen bromide cleavage and two-dimensional proteolytic mapping. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):921–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P. P., Trachsel H. Translation and regulation of translation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 31;191(2):257–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeroff M. E., Bruenn J. A. Initiation by the yeast viral transcriptase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6785–6787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno M., Kataoka N., Shimura Y. A nuclear cap binding protein from HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6989–6995. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzelt E., Blaas D., Kuechler E. CAP binding proteins associated with the nucleus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5821–5835. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Photochemical cross-linking of cap binding proteins to eucaryotic mRNAs: effect of mRNA 5' secondary structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3222–3230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. K., Icho T., Wickner R. B. Structure and nuclear localization signal of the SKI3 antiviral protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1989 May-Jun;5(3):149–158. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley S. P., Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Superkiller mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae suppress exclusion of M2 double-stranded RNA by L-A-HN and confer cold sensitivity in the presence of M and L-A-HN. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):761–770. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe T. C., Tewey K. M., Liu L. F. Identification of the breakage-reunion subunit of T4 DNA topoisomerase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9177–9181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Sonenberg N. Identification of nuclear cap specific proteins in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6489–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rychlik W., Domier L. L., Gardner P. R., Hellmann G. M., Rhoads R. E. Amino acid sequence of the mRNA cap-binding protein from human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):945–949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samad A., Carroll R. B. The tumor suppressor p53 is bound to RNA by a stable covalent linkage. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1598–1606. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanhueza S., Eisenberg S. Bacteriophage phi X174 A protein cleaves single-stranded DNA and binds to it covalently through a tyrosyl-dAMP phosphodiester bond. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):695–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.695-697.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz P., Stucka R., Feldmann H., Combriato G., Klobeck H. G., Fittler F. Sequence of a cDNA clone encompassing the complete mature human prostate specific antigen (PSA) and an unspliced leader sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6226–6226. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Hurwitz J. Mechanism of mRNA capping by vaccinia virus guanylyltransferase: characterization of an enzyme--guanylate intermediate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):187–191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Gene disruption indicates that the only essential function of the SKI8 chromosomal gene is to protect Saccharomyces cerevisiae from viral cytopathology. Virology. 1987 Mar;157(1):252–256. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Yeast L dsRNA consists of at least three distinct RNAs; evidence that the non-Mendelian genes [HOK], [NEX] and [EXL] are on one of these dsRNAs. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):429–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Cap-binding proteins of eukaryotic messenger RNA: functions in initiation and control of translation. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:173–207. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J. Two forms of purified m7G-cap binding protein with different effects on capped mRNA translation in extracts of uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7691–7694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin G. J., Young D. C., Flanegan J. B. Self-catalyzed linkage of poliovirus terminal protein VPg to poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyama R., Mizumoto K., Nakahara Y., Tatsuno T., Kaziro Y. Mechanism of the mRNA guanylyltransferase reaction: isolation of N epsilon-phospholysine and GMP (5' leads to N epsilon) lysine from the guanylyl-enzyme intermediate. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2195–2201. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01723.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. Double-stranded RNA replication in yeast: the killer system. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:373–395. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Icho T., Fujimura T., Widner W. R. Expression of yeast L-A double-stranded RNA virus proteins produces derepressed replication: a ski- phenocopy. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.155-161.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. Yeast virology. FASEB J. 1989 Sep;3(11):2257–2265. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.11.2550303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]