Abstract
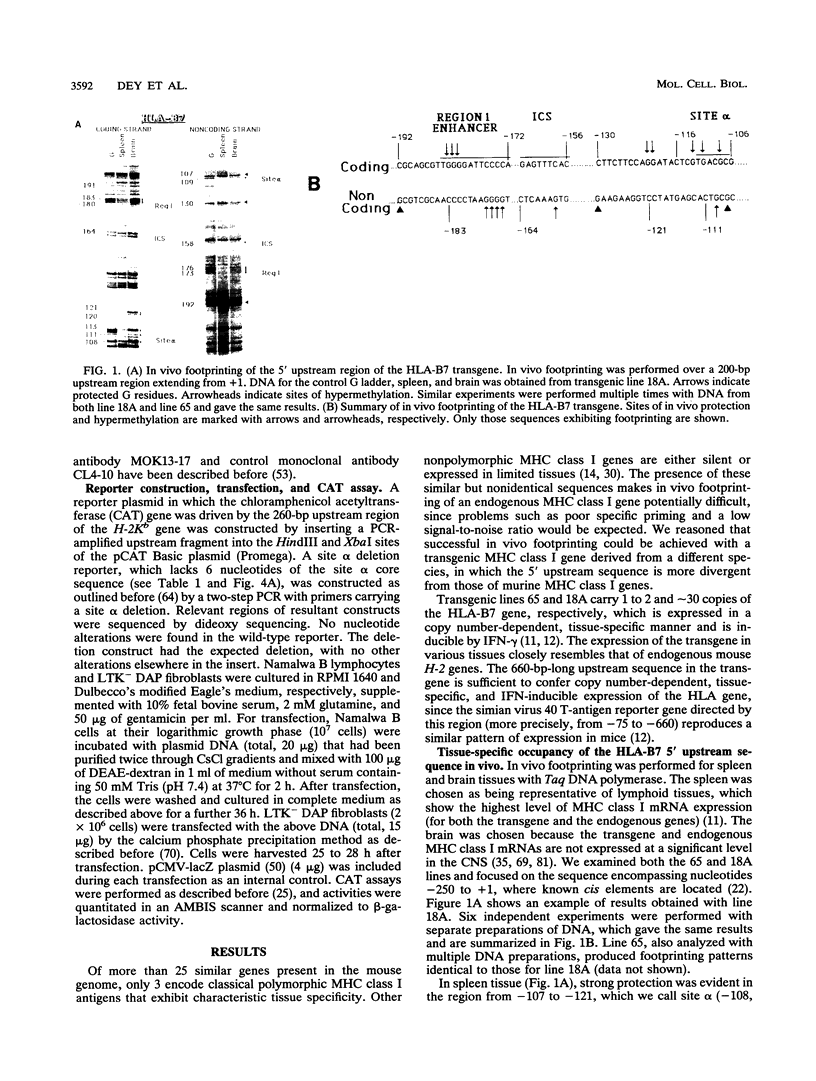
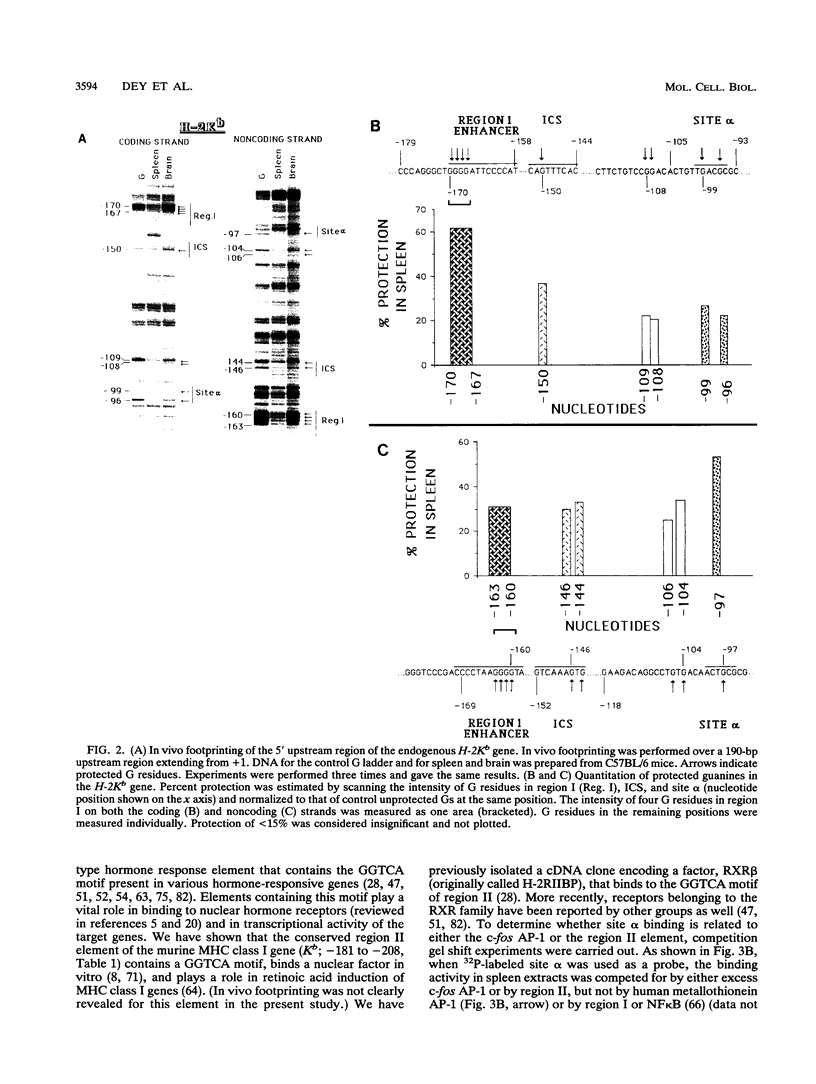
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I HLA-B7 transgene carrying a 660-bp upstream sequence is expressed in the mouse with tissue specificity that parallels that of the expression of endogenous mouse MHC class I (H-2) genes. We have performed in vivo genomic footprinting for the HLA-B7 transgene and the endogenous H-2Kb gene. We show that the upstream region of both the transgene and the endogenous gene was extensively occupied in spleen tissue, where these genes are expressed at high levels. In contrast, no occupancy was detected in brain tissue, where expression of these genes is virtually absent. Sites exhibiting in vivo protection correspond to cis elements previously shown to bind to nuclear factors in vitro, including the constitutive enhancer region I and the interferon response element. The strongest tissue-specific protection was detected at site alpha, located downstream from the interferon response element. Site alpha bound a constitutively expressed nuclear factor(s) in vitro that exhibited an overlapping specificity which may involve a nuclear hormone receptor, RXR, and an AP-1-related factor. Site alpha was functional in vivo, as it enhanced MHC class I transcription in lymphocytes. These results show that the tissue-specific occupancy of the MHC class I regulatory sequences in vivo correlates with their expression and suggest that in vivo occupancy is controlled by a mechanism other than the mere presence of factors capable of binding to these sites. Our results suggest that a sequence present in the 660-bp upstream region in a human leukocyte antigen gene directs tissue-specific occupancy of MHC class I genes in vivo, independently of their position and copy number, illustrating a potential advantage of using a transgene for delimitation of the sequence requirement for in vivo occupancy.
Full text
PDF


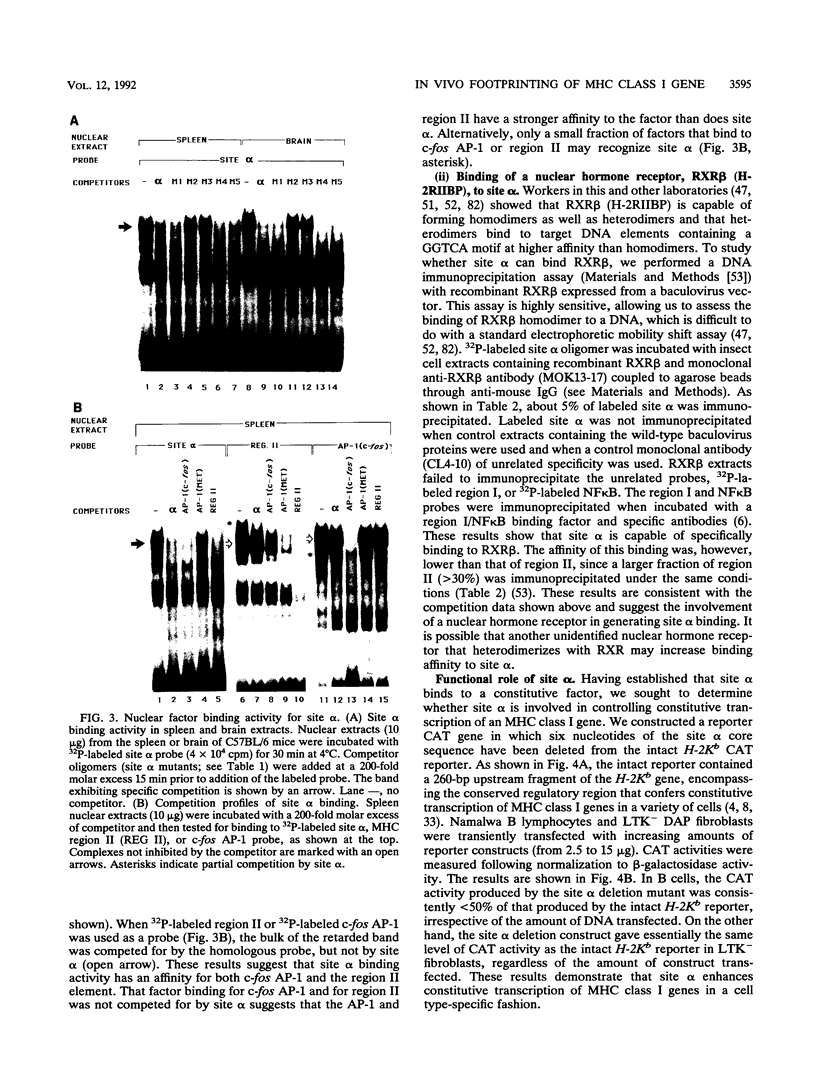
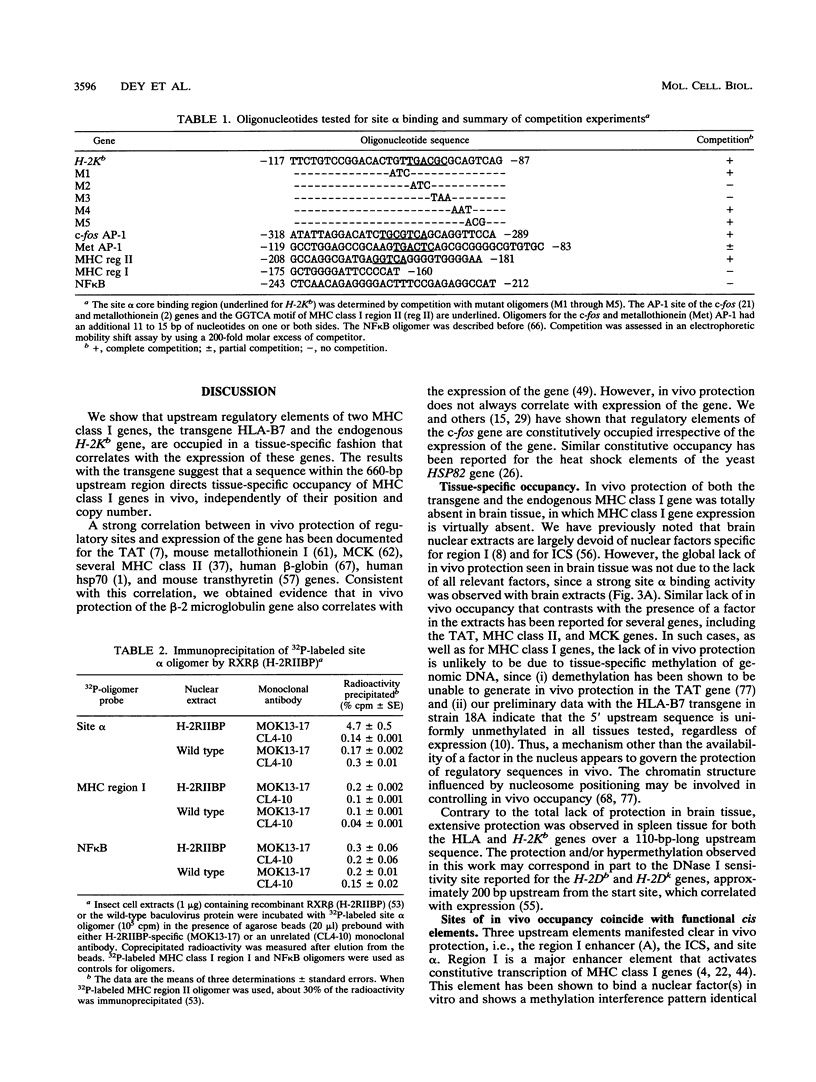
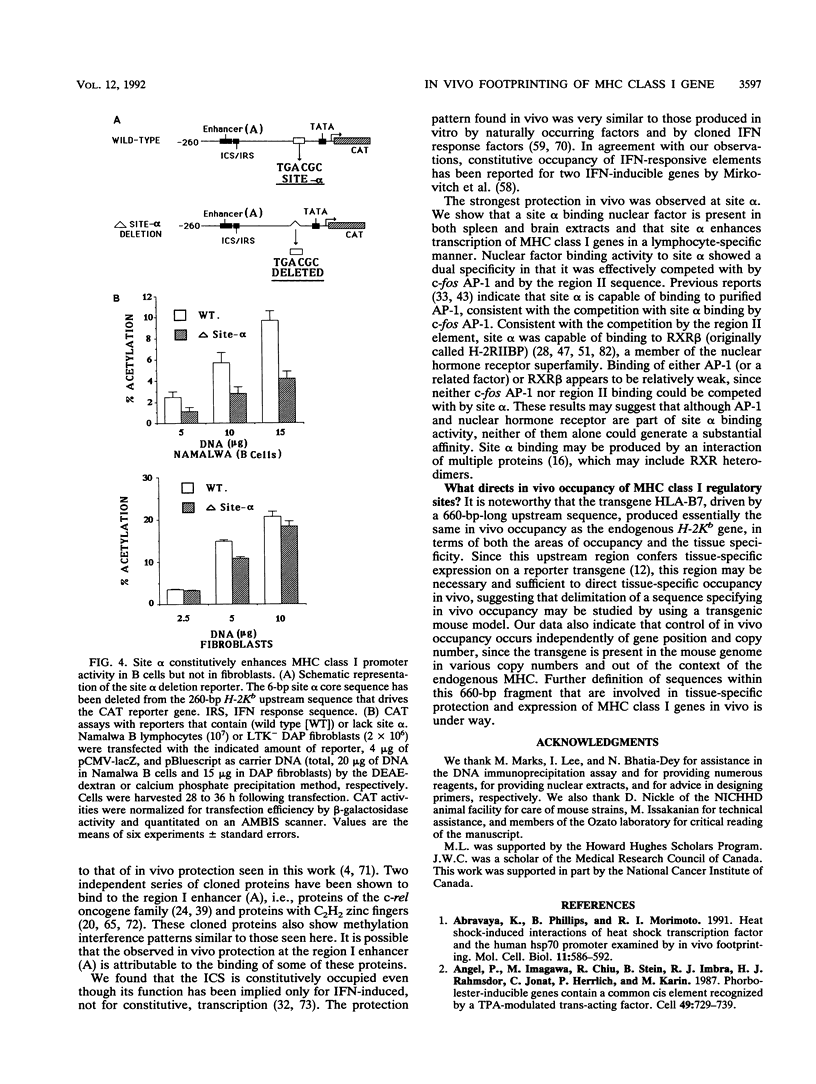


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abravaya K., Phillips B., Morimoto R. I. Heat shock-induced interactions of heat shock transcription factor and the human hsp70 promoter examined by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):586–592. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold B., Burgert H. G., Archibald A. L., Kvist S. Complete nucleotide sequence of the murine H-2Kk gene. Comparison of three H-2K locus alleles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9473–9487. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Binding of a nuclear factor to a regulatory sequence in the promoter of the mouse H-2Kb class I major histocompatibility gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):305–313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Ruppert S., Schütz G. Genomic footprinting reveals cell type-specific DNA binding of ubiquitous factors. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke P. A., Hirschfeld S., Shirayoshi Y., Kasik J. W., Hamada K., Appella E., Ozato K. Developmental and tissue-specific expression of nuclear proteins that bind the regulatory element of the major histocompatibility complex class I gene. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1309–1321. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke P. A., Ozato K. Regulation of major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Year Immunol. 1989;4:23–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. W., Nolan J. A., Conrad P. J., Vasavada H. A., Vasavada H. H., Ploegh H. L., Ganguly S., Janeway C. A., Jr, Weissman S. M. Tissue-specific and cell surface expression of human major histocompatibility complex class I heavy (HLA-B7) and light (beta 2-microglobulin) chain genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7690–7694. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. W., Vasavada H. A., Ganguly S., Weissman S. M. Identification of cis sequences controlling efficient position-independent tissue-specific expression of human major histocompatibility complex class I genes in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3564–3572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Baldwin A. S., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. Human CCAAT-binding proteins have heterologous subunits. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90483-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David-Watine B., Israël A., Kourilsky P. The regulation and expression of MHC class I genes. Immunol Today. 1990 Aug;11(8):286–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90114-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dey A., Nebert D. W., Ozato K. The AP-1 site and the cAMP- and serum response elements of the c-fos gene are constitutively occupied in vivo. DNA Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;10(7):537–544. doi: 10.1089/dna.1991.10.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich R., Maguire J. E., Singer D. S. Identification of negative and positive regulatory elements associated with a class I major histocompatibility complex gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):695–703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich R., Sharrow S. O., Maguire J. E., Singer D. S. Expression of a class I MHC transgene: effects of in vivo alpha/beta-interferon treatment. Immunogenetics. 1989;30(1):18–26. doi: 10.1007/BF02421465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. A DNA-binding protein containing two widely separated zinc finger motifs that recognize the same DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–42. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch T. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G. An AP1-binding site in the c-fos gene can mediate induction by epidermal growth factor and 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1327–1331. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly S., Vasavada H. A., Weissman S. M. Multiple enhancer-like sequences in the HLA-B7 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5247–5251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrity P. A., Wold B. J. Effects of different DNA polymerases in ligation-mediated PCR: enhanced genomic sequencing and in vivo footprinting. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):1021–1025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., English K. E., Collins K. W., Lee S. W. Genomic footprinting of the yeast HSP82 promoter reveals marked distortion of the DNA helix and constitutive occupancy of heat shock and TATA elements. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):611–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90387-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güssow D., Rein R. S., Meijer I., de Hoog W., Seemann G. H., Hochstenbach F. M., Ploegh H. L. Isolation, expression, and the primary structure of HLA-Cw1 and HLA-Cw2 genes: evolutionary aspects. Immunogenetics. 1987;25(5):313–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00404424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada K., Gleason S. L., Levi B. Z., Hirschfeld S., Appella E., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP, a member of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily that binds to both the regulatory element of major histocompatibility class I genes and the estrogen response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8289–8293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R. E., Shaw P. E., Nordheim A. Occupation of the c-fos serum response element in vivo by a multi-protein complex is unaltered by growth factor induction. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):68–70. doi: 10.1038/340068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Malissen B. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:529–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isamat M., Girdlestone J., Milstein C. Nucleotide sequence of an HLA-Bw57 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6702–6702. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Kimura A., Fournier A., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. Interferon response sequence potentiates activity of an enhancer in the promoter region of a mouse H-2 gene. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):743–746. doi: 10.1038/322743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Le Bail O., Hatat D., Piette J., Kieran M., Logeat F., Wallach D., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. TNF stimulates expression of mouse MHC class I genes by inducing an NF kappa B-like enhancer binding activity which displaces constitutive factors. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3793–3800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. D., Evans T., Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. Developmental modulation of protein binding to beta-globin gene regulatory sites within chicken erythrocyte nuclei. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1860–1873. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly E., Mucke L., Oldstone M. B. Viral persistence in neurons explained by lack of major histocompatibility class I expression. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1283–1285. doi: 10.1126/science.1891717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones-Youngblood S. L., Wieties K., Forman J., Hammer R. E. Effect of the expression of a hepatocyte-specific MHC molecule in transgenic mice on T cell tolerance. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1187–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara C. J., Glimcher L. H. In vivo footprinting of MHC class II genes: bare promoters in the bare lymphocyte syndrome. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):709–712. doi: 10.1126/science.1902592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh S., Ozawa K., Kondoh S., Soeda E., Israel A., Shiroki K., Fujinaga K., Itakura K., Gachelin G., Yokoyama K. Identification of sequences responsible for positive and negative regulation by E1A in the promoter of H-2Kbm1 class I MHC gene. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):127–135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Israël A., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. Detailed analysis of the mouse H-2Kb promoter: enhancer-like sequences and their role in the regulation of class I gene expression. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korber B., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Regulation of murine class I genes by interferons is controlled by regions located both 5' and 3' to the transcription initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3380–3384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korber B., Mermod N., Hood L., Stroynowski I. Regulation of gene expression by interferons: control of H-2 promoter responses. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1302–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.3125612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Roberts L., Dobberstein B. Mouse histocompatibility genes: structure and organisation of a Kd gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):245–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leid M., Kastner P., Lyons R., Nakshatri H., Saunders M., Zacharewski T., Chen J. Y., Staub A., Garnier J. M., Mader S. Purification, cloning, and RXR identity of the HeLa cell factor with which RAR or TR heterodimerizes to bind target sequences efficiently. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):377–395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90478-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Rustgi A. K., Schievella A. R., Bernards R. Suppression of MHC class I gene expression by N-myc through enhancer inactivation. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3351–3355. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08497.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. R., Caskey C. T. Construction of plasmids that express E. coli beta-galactosidase in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2365–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Borgmeyer U., Heyman R. A., Zhou J. Y., Ong E. S., Oro A. E., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):329–344. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Hallenbeck P. L., Nagata T., Segars J. H., Appella E., Nikodem V. M., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP (RXR beta) heterodimerization provides a mechanism for combinatorial diversity in the regulation of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone responsive genes. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1419–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks M. S., Levi B. Z., Segars J. H., Driggers P. H., Hirschfeld S., Nagata T., Appella E., Ozato K. H-2RIIBP expressed from a baculovirus vector binds to multiple hormone response elements. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Feb;6(2):219–230. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.2.1569965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maschek U., Pülm W., Hämmerling G. J. Altered regulation of MHC class I genes in different tumor cell lines is reflected by distinct sets of DNase I hypersensitive sites. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2297–2304. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Darnell J. E., Jr Rapid in vivo footprinting technique identifies proteins bound to the TTR gene in the mouse liver. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):83–93. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Decker T., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon induction of gene transcription analyzed by in vivo footprinting. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki J., Appella E., Ozato K. Negative regulation of the major histocompatibility class I gene in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9537–9541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Salser S. J., Wold B. Constitutive and metal-inducible protein:DNA interactions at the mouse metallothionein I promoter examined by in vivo and in vitro footprinting. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):412–427. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Wold B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):780–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2814500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata T., Segars J. H., Levi B. Z., Ozato K. Retinoic acid-dependent transactivation of major histocompatibility complex class I promoters by the nuclear hormone receptor H-2RIIBP in undifferentiated embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):937–941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Donovan D. M., Hamada K., Sax C. M., Norman B., Flanagan J. R., Ozato K., Westphal H., Piatigorsky J. Regulation of the mouse alpha A-crystallin gene: isolation of a cDNA encoding a protein that binds to a cis sequence motif shared with the major histocompatibility complex class I gene and other genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3700–3708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- När A. M., Boutin J. M., Lipkin S. M., Yu V. C., Holloway J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. The orientation and spacing of core DNA-binding motifs dictate selective transcriptional responses to three nuclear receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1267–1279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90021-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P. M., Shen C. K. Protein-DNA interactions in vivo of an erythroid-specific, human beta-globin locus enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8676–8680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik A., Schütz G., Stewart A. F. Glucocorticoids are required for establishment and maintenance of an alteration in chromatin structure: induction leads to a reversible disruption of nucleosomes over an enhancer. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2569–2576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J., Schachner M. Expression of Thy-1, H-2, and NS-4 cell surface antigens and tetanus toxin receptors in early postnatal and adult mouse cerebellum. J Neuroimmunol. 1981 Dec;1(4):429–456. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(81)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirayoshi Y., Burke P. A., Appella E., Ozato K. Interferon-induced transcription of a major histocompatibility class I gene accompanies binding of inducible nuclear factors to the interferon consensus sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5884–5888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirayoshi Y., Miyazaki J., Burke P. A., Hamada K., Appella E., Ozato K. Binding of multiple nuclear factors to the 5' upstream regulatory element of the murine major histocompatibility class I gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4542–4548. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita K., Miyazaki J., Appella E., Ozato K. Interferons increase transcription of a major histocompatibility class I gene via a 5' interferon consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2625–2630. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibensky D., Delovitch T. L. Promoter region of HLA-C genes: regulatory elements common to and different from those of HLA-A and HLA-B genes. Immunogenetics. 1990;32(3):210–213. doi: 10.1007/BF02114976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Giguere V., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):262–265. doi: 10.1038/336262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts S., Vogel J. M., Harriman W. D., Itoh T., Stauss H. J., Goodenow R. S. DNA sequence analysis of the C3H H-2Kk and H-2Dk loci. Evolutionary relationships to H-2 genes from four other mouse strains. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3878–3885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weih F., Nitsch D., Reik A., Schütz G., Becker P. B. Analysis of CpG methylation and genomic footprinting at the tyrosine aminotransferase gene: DNA methylation alone is not sufficient to prevent protein binding in vivo. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2559–2567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Golden L., Fahrner K., Mellor A. L., Devlin J. J., Bullman H., Tiddens H., Bud H., Flavell R. A. Organization and evolution of the class I gene family in the major histocompatibility complex of the C57BL/10 mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):650–655. doi: 10.1038/310650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. H., Kuon W., Dörner C., Lang M., Riethmüller G. Organization, sequence and expression of the HLA-B27 gene: a molecular approach to analyze HLA and disease associations. Immunobiology. 1985 Dec;170(5):367–380. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(85)80061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnholds J., Muller E., Ab G. Oestrogen facilitates the binding of ubiquitous and liver-enriched nuclear proteins to the apoVLDL II promoter in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):33–41. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Bartlett P. F., Clark-Lewis I., McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Schrader J. W. Interferon-gamma induces the expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on brain cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Feb-Mar;7(5-6):255–278. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(84)80026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu V. C., Delsert C., Andersen B., Holloway J. M., Devary O. V., När A. M., Kim S. Y., Boutin J. M., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G. RXR beta: a coregulator that enhances binding of retinoic acid, thyroid hormone, and vitamin D receptors to their cognate response elements. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1251–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90301-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]