Abstract
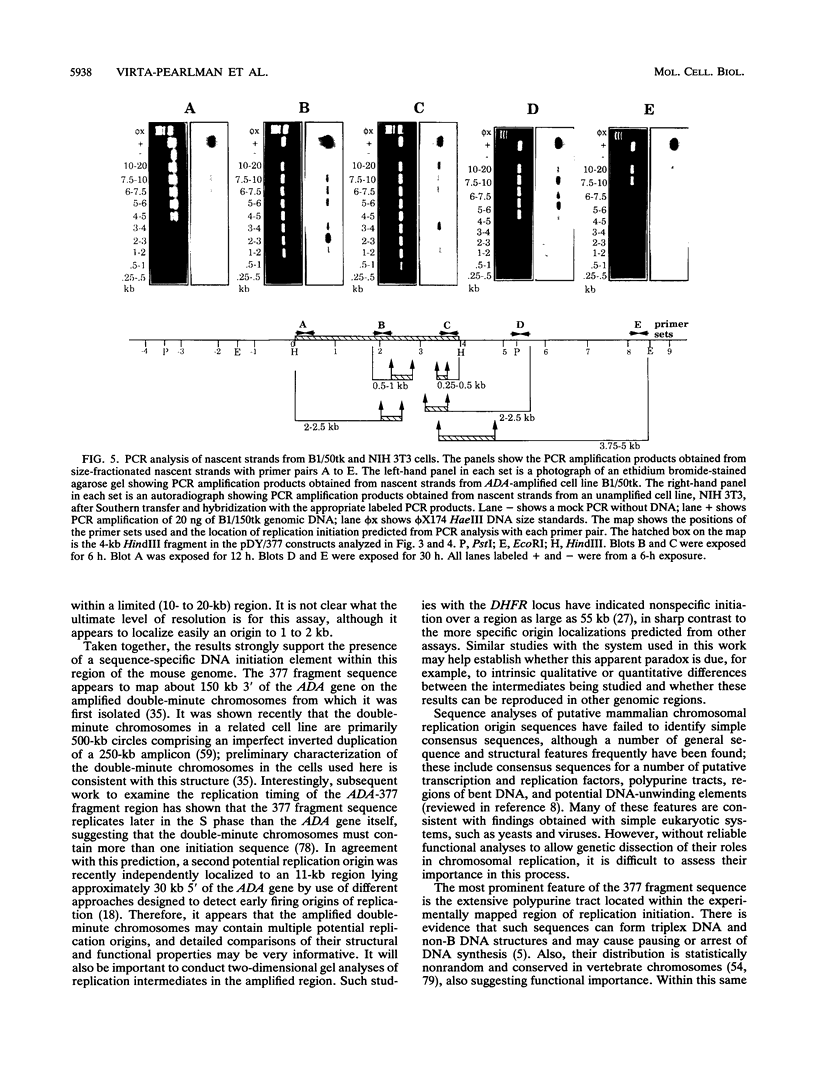
A 4-kb HindIII fragment that supported the efficient autonomous replication of plasmid vector pDY-, a replication-defective construct based on Epstein-Barr virus sequences, in human K562 cells was rescued from amplified double-minute chromosomes containing the murine adenosine deaminase locus. Polymerase chain reaction assays of size-fractionated nascent strands demonstrated that replication initiation occurred within the same 1- to 2-kb region of this fragment in autonomously replicating plasmids containing the sequence in either orientation, in double-minute chromosomes, and in the single-copy locus at its normal chromosomal location. The complete sequence of this fragment was determined; it contains a 248-bp polypurine tract and consensus binding site sequences for several putative transcription and replication factors.
Full text
PDF



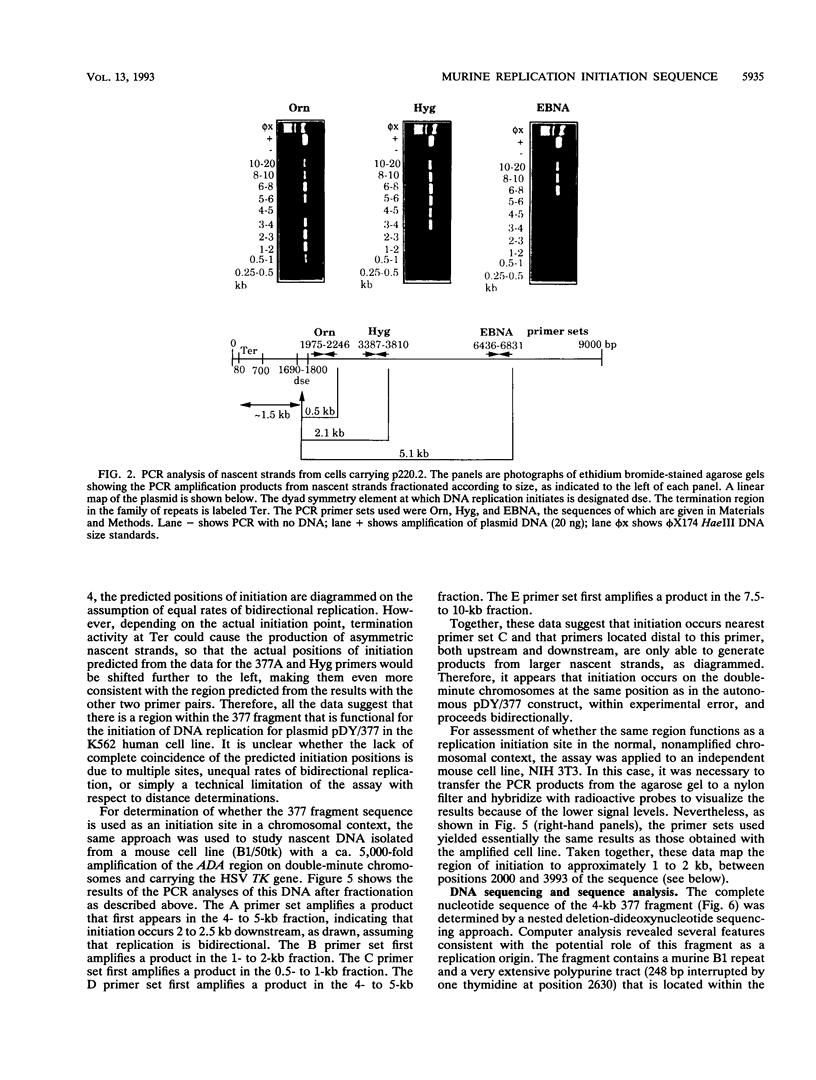
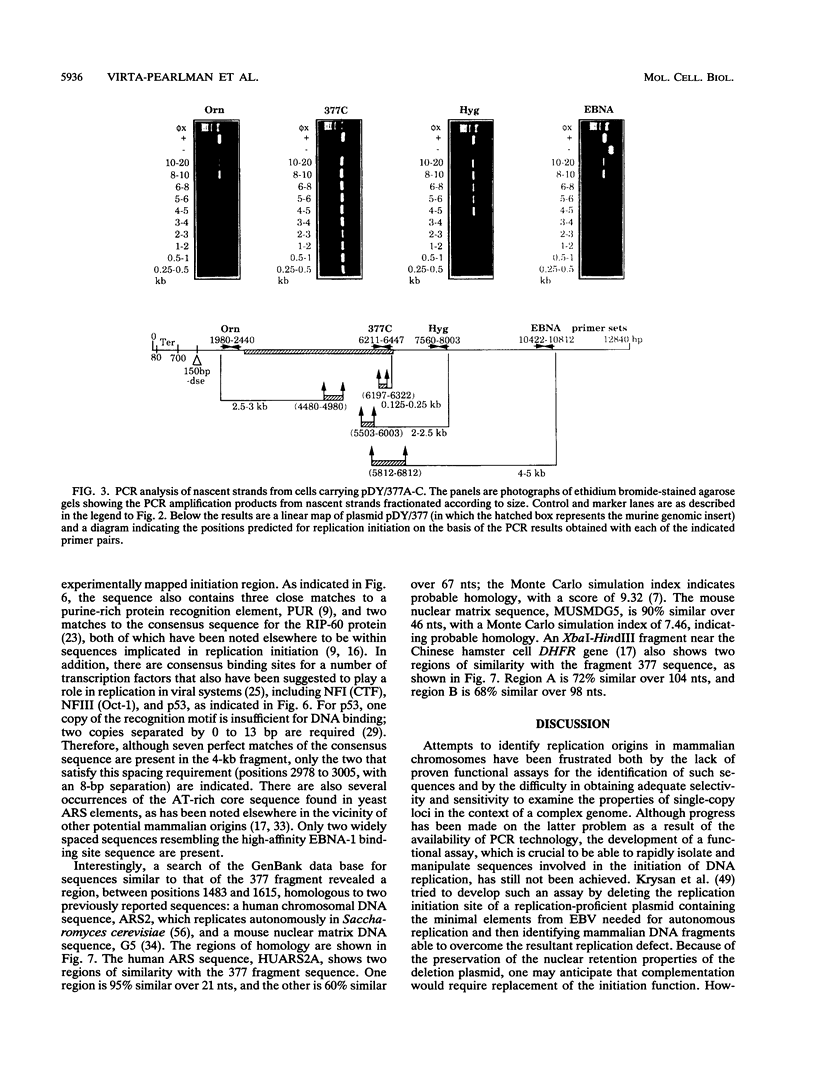
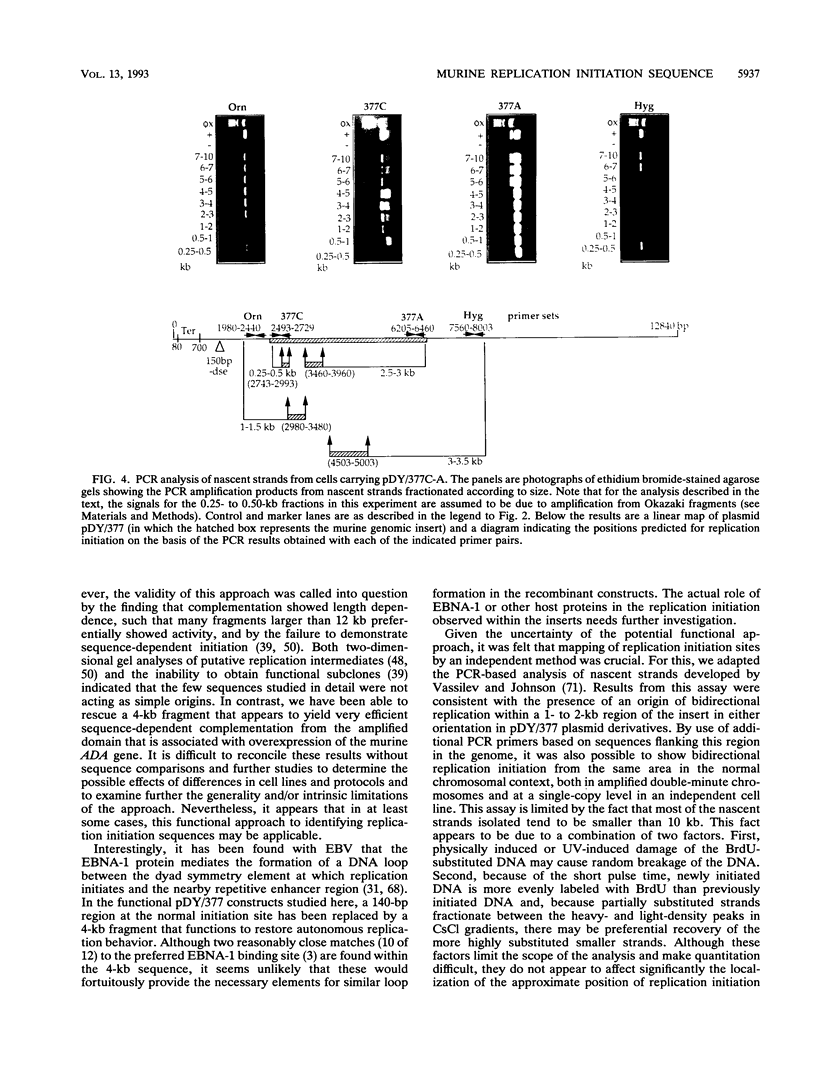




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Shneidman P. S., Hurwitz J. Reconstruction of adenovirus replication origins with a human nuclear factor I binding site. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3339–3346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambinder R. F., Shah W. A., Rawlins D. R., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. Definition of the sequence requirements for binding of the EBNA-1 protein to its palindromic target sites in Epstein-Barr virus DNA. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2369–2379. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2369-2379.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anachkova B., Hamlin J. L. Replication in the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain in CHO cells may initiate at two distinct sites, one of which is a repetitive sequence element. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):532–540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baran N., Lapidot A., Manor H. Formation of DNA triplexes accounts for arrests of DNA synthesis at d(TC)n and d(GA)n tracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):507–511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbow R. M., Zhao J., Larson D. D. On the nature of origins of DNA replication in eukaryotes. Bioessays. 1992 Oct;14(10):661–670. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergemann A. D., Johnson E. M. The HeLa Pur factor binds single-stranded DNA at a specific element conserved in gene flanking regions and origins of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1257–1265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. A replication fork barrier at the 3' end of yeast ribosomal RNA genes. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):637–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Selegue J. E., Heintz N. H. Isolation of the origin of replication associated with the amplified Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7790–7794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Selegue J. E., Heintz N. H. Replication intermediates formed during initiation of DNA synthesis in methotrexate-resistant CHOC 400 cells are enriched for sequences derived from a specific, amplified restriction fragment. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):441–449. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Vassilev L. T., Caddle M. S., Heintz N. H., DePamphilis M. L. Identification of an origin of bidirectional DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):955–965. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90270-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Vassilev L. T., Wu J., Sogo J. M., Nallaseth F. S., DePamphilis M. L. Emetine allows identification of origins of mammalian DNA replication by imbalanced DNA synthesis, not through conservative nucleosome segregation. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4351–4360. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caddle M. S., Dailey L., Heintz N. H. RIP60, a mammalian origin-binding protein, enhances DNA bending near the dihydrofolate reductase origin of replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6236–6243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caddle M. S., Lussier R. H., Heintz N. H. Intramolecular DNA triplexes, bent DNA and DNA unwinding elements in the initiation region of an amplified dihydrofolate reductase replicon. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90008-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., DeRose M. L., Kolman J. L., Nonet G. H., Kelly R. E., Wahl G. M. Localization of a bidirectional DNA replication origin in the native locus and in episomally amplified murine adenosine deaminase loci. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2971–2981. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleat P. H., Hay R. T. Co-operative interactions between NFI and the adenovirus DNA binding protein at the adenovirus origin of replication. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1841–1848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coenjaerts F. E., De Vries E., Pruijn G. J., Van Driel W., Bloemers S. M., Van der Lugt N. M., Van der Vliet P. C. Enhancement of DNA replication by transcription factors NFI and NFIII/Oct-1 depends critically on the positions of their binding sites in the adenovirus origin of replication. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Aug 27;1090(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90037-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A. Nomenclature for incompletely specified bases in nucleic acid sequences: recommendations 1984. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3021–3030. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey L., Caddle M. S., Heintz N., Heintz N. H. Purification of RIP60 and RIP100, mammalian proteins with origin-specific DNA-binding and ATP-dependent DNA helicase activities. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6225–6235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danna K. J., Nathans D. Bidirectional replication of Simian Virus 40 DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3097–3100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Origins of DNA replication in metazoan chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Initiation of DNA replication in the dihydrofolate reductase locus is confined to the early S period in CHO cells synchronized with the plant amino acid mimosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3715–3722. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBridge R. B., Tang P., Hsia H. C., Leong P. M., Miller J. H., Calos M. P. Analysis of mutation in human cells by using an Epstein-Barr virus shuttle system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):379–387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epner E., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Replication of alpha and beta globin DNA sequences occurs during early S phase in murine erythroleukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3058–3062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frappier L., O'Donnell M. Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 mediates a DNA loop within the latent replication origin of Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10875–10879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahn T. A., Schildkraut C. L. The Epstein-Barr virus origin of plasmid replication, oriP, contains both the initiation and termination sites of DNA replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale J. M., Tobey R. A., D'Anna J. A. Localization and DNA sequence of a replication origin in the rhodopsin gene locus of Chinese hamster cells. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 20;224(2):343–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90999-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg G. I., Collier I., Cassel A. Specific DNA sequences associated with the nuclear matrix in synchronized mouse 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6887–6891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z. S., DePamphilis M. L. Specific transcription factors stimulate simian virus 40 and polyomavirus origins of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2514–2524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handeli S., Klar A., Meuth M., Cedar H. Mapping replication units in animal cells. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Hamlin J. L. An amplified chromosomal sequence that includes the gene for dihydrofolate reductase initiates replication within specific restriction fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4083–4087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel S. S., Krysan P. J., Tran C. T., Calos M. P. Autonomous DNA replication in human cells is affected by the size and the source of the DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2263–2272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Yamada M., Nishimura A., Oka A., Sugimoto K., Asada K., Takanami M. The DNA replication origin (ori) of Escherichia coli: structure and function of the ori-containing DNA fragment. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1981;26:33–48. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60393-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Spotila L. D., Nawotka K. A., el-Assouli S. M., Davis L. R. The in vivo replication origin of the yeast 2 microns plasmid. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Zhu J. G., Davis L. R., Newlon C. S. Close association of a DNA replication origin and an ARS element on chromosome III of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6373–6384. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni J. M., Kornberg A. Replication initiated at the origin (oriC) of the E. coli chromosome reconstituted with purified enzymes. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearsey S. Structural requirements for the function of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krysan P. J., Calos M. P. Replication initiates at multiple locations on an autonomously replicating plasmid in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1464–1472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krysan P. J., Haase S. B., Calos M. P. Isolation of human sequences that replicate autonomously in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1026–1033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krysan P. J., Smith J. G., Calos M. P. Autonomous replication in human cells of multimers of specific human and bacterial DNA sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2688–2696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. Organization of replication of ribosomal DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4927–4935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. The two faces of higher eukaryotic DNA replication origins. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):845–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90258-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma C., Leu T. H., Hamlin J. L. Multiple origins of replication in the dihydrofolate reductase amplicons of a methotrexate-resistant chinese hamster cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1338–1346. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manor H., Rao B. S., Martin R. G. Abundance and degree of dispersion of genomic d(GA)n.d(TC)n sequences. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(2):96–101. doi: 10.1007/BF02138367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhinney C., Leffak M. Autonomous replication of a DNA fragment containing the chromosomal replication origin of the human c-myc gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1233–1242. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montiel J. F., Norbury C. J., Tuite M. F., Dobson M. J., Mills J. S., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Characterization of human chromosomal DNA sequences which replicate autonomously in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):1049–1068. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mul Y. M., Verrijzer C. P., van der Vliet P. C. Transcription factors NFI and NFIII/oct-1 function independently, employing different mechanisms to enhance adenovirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5510–5518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5510-5518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet G. H., Carroll S. M., DeRose M. L., Wahl G. M. Molecular dissection of an extrachromosomal amplicon reveals a circular structure consisting of an imperfect inverted duplication. Genomics. 1993 Mar;15(3):543–558. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palzkill T. G., Newlon C. S. A yeast replication origin consists of multiple copies of a small conserved sequence. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):441–450. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Nuclear factor III, a novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):656–659. doi: 10.1038/322656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Sugden B. trans activation of an Epstein-Barr viral transcriptional enhancer by the Epstein-Barr viral nuclear antigen 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3838–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Yates J., Sugden B. A putative origin of replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus is composed of two cis-acting components. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1822–1832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland P., 3rd, Pfeilsticker J., Hoffee P. A. Adenosine deaminase gene amplification in deoxycoformycin-resistant mammalian cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jun;239(2):396–403. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90705-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Middleton T., Sugden B., Echols H. DNA looping between the origin of replication of Epstein-Barr virus and its enhancer site: stabilization of an origin complex with Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10870–10874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Marsh K., Yates J. A vector that replicates as a plasmid and can be efficiently selected in B-lymphoblasts transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):410–413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symington B. E. Fibronectin receptor overexpression and loss of transformed phenotype in a stable variant of the K562 cell line. Cell Regul. 1990 Aug;1(9):637–648. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.9.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L. T., Burhans W. C., DePamphilis M. L. Mapping an origin of DNA replication at a single-copy locus in exponentially proliferating mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4685–4689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L. T., DePamphilis M. L. Guide to identification of origins of DNA replication in eukaryotic cell chromosomes. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;27(6):445–472. doi: 10.3109/10409239209082569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L., Johnson E. M. An initiation zone of chromosomal DNA replication located upstream of the c-myc gene in proliferating HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4899–4904. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L., Johnson E. M. Mapping initiation sites of DNA replication in vivo using polymerase chain reaction amplification of nascent strand segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7693–7705. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. P., Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Replication initiates in a broad zone in the amplified CHO dihydrofolate reductase domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1075–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90071-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., Kal A. J., Van der Vliet P. C. The DNA binding domain (POU domain) of transcription factor oct-1 suffices for stimulation of DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1883–1888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08314.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal M., Wrighton C., Eccles S., Burke J., Grosveld F. Differences in human cell lines to support stable replication of Epstein-Barr virus-based vectors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 6;1048(2-3):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90053-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong A. K., Yee H. A., van de Sande J. H., Rattner J. B. Distribution of CT-rich tracts is conserved in vertebrate chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1990 Sep;99(5):344–351. doi: 10.1007/BF01731722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J., Warren N., Reisman D., Sugden B. A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung C. Y., Ingolia D. E., Bobonis C., Dunbar B. S., Riser M. E., Siciliano M. J., Kellems R. E. Selective overproduction of adenosine deaminase in cultured mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8338–8345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Definition of a consensus binding site for p53. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):45–49. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]