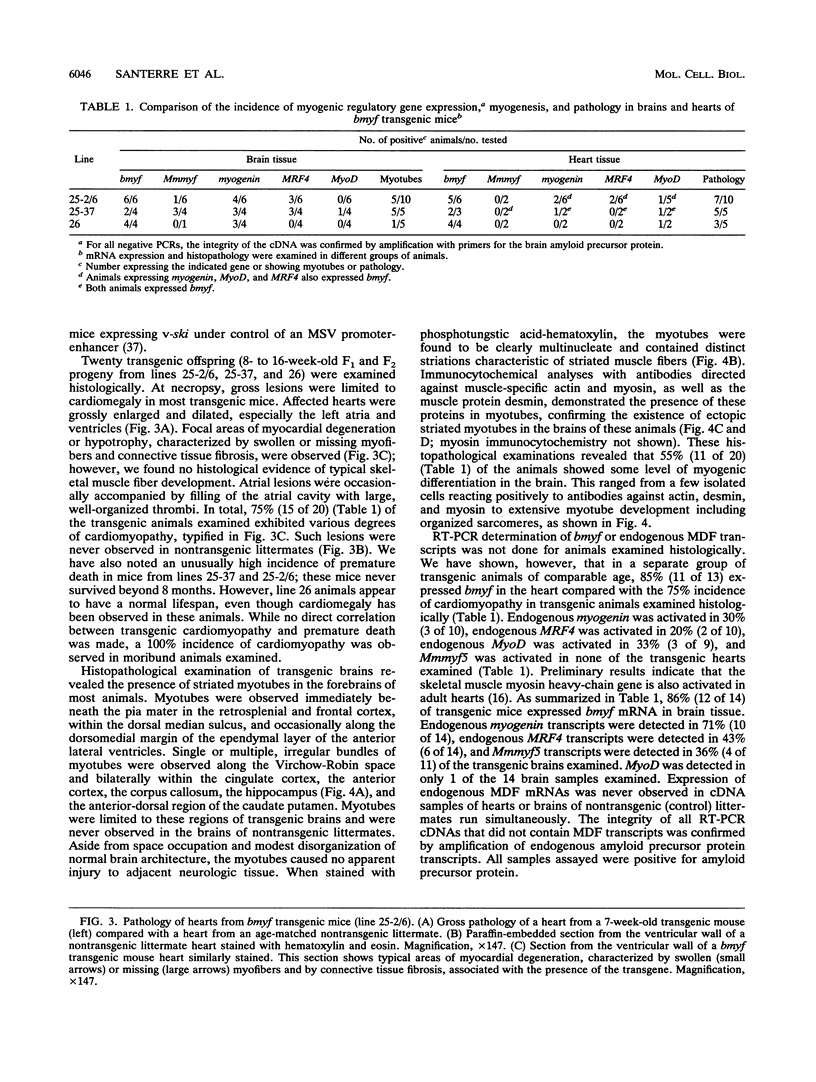
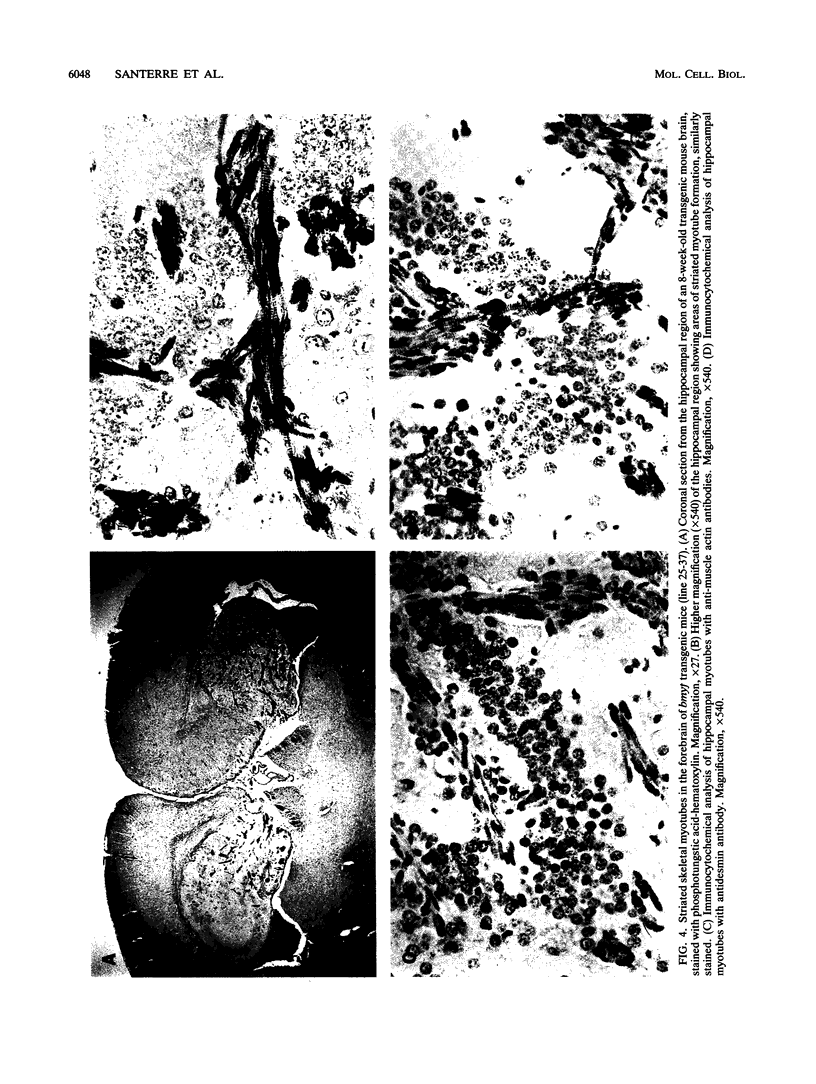
Abstract
myf5 is one of a family of four myogenic determination genes that control skeletal muscle differentiation. To study the role of myf5 in vivo, we generated transgenic mice harboring the bovine homolog, bmyf, under control of the murine sarcoma virus promoter. Ectopic expression of the full-length bmyf transgene was detected in brain and heart tissue samples of F1 progeny from transgenic founder mice. Ectopic bmyf expression activated endogenous skeletal myogenic determination genes in the hearts and brains of transgenic animals. Incomplete skeletal myogenesis in most hearts gave rise to cardiomegaly and focal areas of cardiomyopathy. In brains in which ectopic expression led to a more complete myogenesis, focal areas of multinucleated, striated myotubes containing actin, desmin, and myosin were observed. These unexpected results show that myf5 can initiate myogenic differentiation in vivo, supporting the hypothesis that myf5 is responsible for determination of cells to the myogenic lineage in normal embryogenesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benezra R., Davis R. L., Lockshon D., Turner D. L., Weintraub H. The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90214-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bober E., Lyons G. E., Braun T., Cossu G., Buckingham M., Arnold H. H. The muscle regulatory gene, Myf-6, has a biphasic pattern of expression during early mouse development. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1255–1265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Arnold H. H. Inhibition of muscle differentiation by the adenovirus E1a protein: repression of the transcriptional activating function of the HLH protein Myf-5. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):888–902. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Winter B., Rosenthal N., Arnold H. H. Myf-6, a new member of the human gene family of myogenic determination factors: evidence for a gene cluster on chromosome 12. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):821–831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Rudnicki M. A., Arnold H. H., Jaenisch R. Targeted inactivation of the muscle regulatory gene Myf-5 results in abnormal rib development and perinatal death. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):369–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buonanno A., Apone L., Morasso M. I., Beers R., Brenner H. R., Eftimie R. The MyoD family of myogenic factors is regulated by electrical activity: isolation and characterization of a mouse Myf-5 cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 11;20(3):539–544. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D. Identification of a myocyte nuclear factor that binds to the muscle-specific enhancer of the mouse muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2627–2640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi J., Costa M. L., Mermelstein C. S., Chagas C., Holtzer S., Holtzer H. MyoD converts primary dermal fibroblasts, chondroblasts, smooth muscle, and retinal pigmented epithelial cells into striated mononucleated myoblasts and multinucleated myotubes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7988–7992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark T. G., Morris J., Akamatsu M., McGraw R., Ivarie R. A bovine homolog to the human myogenic determination factor myf-5: sequence conservation and 3' processing of transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3147–3153. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J. A., Lewis B. A., Cole M. D. Increased retinoblastoma gene expression is associated with late stages of differentiation in many different cell types. Oncogene. 1990 Nov;5(11):1731–1733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner L., de Lanerolle P., Costa J. Immunoreactivity of paraffin-embedded normal tissues and mesenchymal tumors for smooth muscle myosin. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Nov;80(5):677–681. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.5.677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon K., Smith C. K., 2nd, Bales K. R., Santerre R. F. Temporal and quantitative analysis of myogenic regulatory and growth factor gene expression in the developing mouse embryo. Dev Biol. 1992 May;151(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R., Weintraub H. Translation of mRNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is specifically inhibited by antisense RNA. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1094–1099. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinterberger T. J., Sassoon D. A., Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Expression of the muscle regulatory factor MRF4 during somite and skeletal myofiber development. Dev Biol. 1991 Sep;147(1):144–156. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(05)80014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Thayer M. J., Overell R. W., Weintraub H. Transformation by activated ras or fos prevents myogenesis by inhibiting expression of MyoD1. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Z. Y., Dechesne C. A., Eldridge J., Paterson B. M. An avian muscle factor related to MyoD1 activates muscle-specific promoters in nonmuscle cells of different germ-layer origin and in BrdU-treated myoblasts. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):986–996. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Miller J. B., Wold B. J. Skeletal muscle phenotypes initiated by ectopic MyoD in transgenic mouse heart. Development. 1992 Apr;114(4):853–860. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.4.853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. Herculin, a fourth member of the MyoD family of myogenic regulatory genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro M. J., Hoffman P. N., Gearhart J. D., Cleveland D. W. Expression of NF-L in both neuronal and nonneuronal cells of transgenic mice: increased neurofilament density in axons without affecting caliber. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1543–1557. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. Interplay between proliferation and differentiation within the myogenic lineage. Dev Biol. 1992 Dec;154(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90066-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Bober E., Lyons G., Arnold H., Buckingham M. Early expression of the myogenic regulatory gene, myf-5, in precursor cells of skeletal muscle in the mouse embryo. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):1097–1107. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Bessereau J. L., Huchet M., Changeux J. P. Two adjacent MyoD1-binding sites regulate expression of the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit gene. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):353–355. doi: 10.1038/345353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Rosenberg M. P., Cork L. C., Kovatch R. M., Rauch S., Westphal H., Khillan J., Schulz N. T., Vande Woude G. F., Neumann P. E. Neuropathological changes in transgenic mice carrying copies of a transcriptionally activated Mos protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9703–9707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Identification of MRF4: a new member of the muscle regulatory factor gene family. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2050–2061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N., Berglund E. B., Wentworth B. M., Donoghue M., Winter B., Bober E., Braun T., Arnold H. H. A highly conserved enhancer downstream of the human MLC1/3 locus is a target for multiple myogenic determination factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6239–6246. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnicki M. A., Braun T., Hinuma S., Jaenisch R. Inactivation of MyoD in mice leads to up-regulation of the myogenic HLH gene Myf-5 and results in apparently normal muscle development. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90508-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D., Lyons G., Wright W. E., Lin V., Lassar A., Weintraub H., Buckingham M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoD1 during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):303–307. doi: 10.1038/341303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer B. W., Blakely B. T., Darlington G. J., Blau H. M. Effect of cell history on response to helix-loop-helix family of myogenic regulators. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):454–458. doi: 10.1038/344454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. A., Spizz G., Perry W. M., Vizard D., Weil T., Olson E. N. Identification of upstream and intragenic regulatory elements that confer cell-type-restricted and differentiation-specific expression on the muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2896–2909. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutrave P., Kelly A. M., Hughes S. H. ski can cause selective growth of skeletal muscle in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1462–1472. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Simmons D. M., Arriza J., Hammer R., Brinster R., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Novel developmental specificity in the nervous system of transgenic animals expressing growth hormone fusion genes. 1985 Sep 26-Oct 2Nature. 317(6035):363–366. doi: 10.1038/317363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Cheng P. F., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. MyoD1: a nuclear phosphoprotein requiring a Myc homology region to convert fibroblasts to myoblasts. Science. 1988 Oct 21;242(4877):405–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3175662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer M. J., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. Positive autoregulation of the myogenic determination gene MyoD1. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90838-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theuring F., Götz W., Balling R., Korf H. W., Schulze F., Herken R., Gruss P. Tumorigenesis and eye abnormalities in transgenic mice expressing MSV-SV40 large T-antigen. Oncogene. 1990 Feb;5(2):225–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., McNutt M. A., Ross R., Gown A. M. HHF35, a muscle actin-specific monoclonal antibody. II. Reactivity in normal, reactive, and neoplastic human tissues. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):389–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Adam M. A., Lassar A. B., Miller A. D. Activation of muscle-specific genes in pigment, nerve, fat, liver, and fibroblast cell lines by forced expression of MyoD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]