Abstract
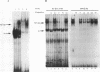
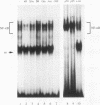
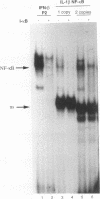
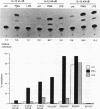
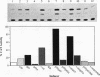
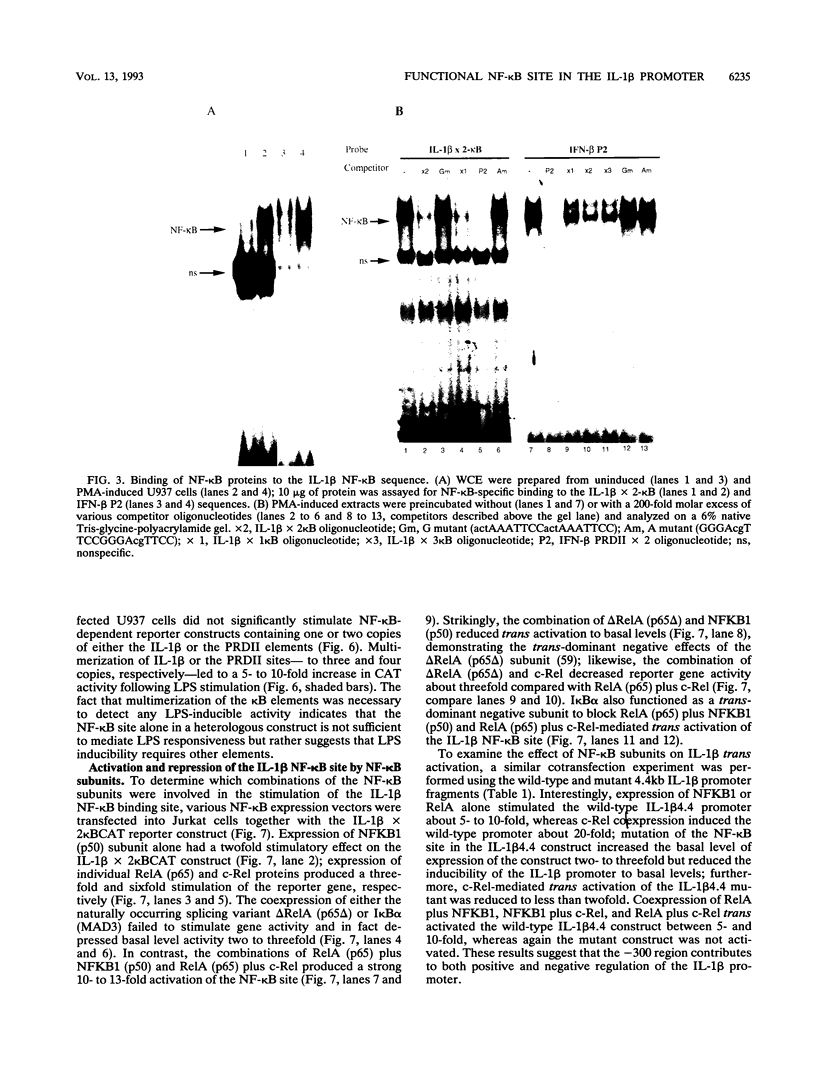
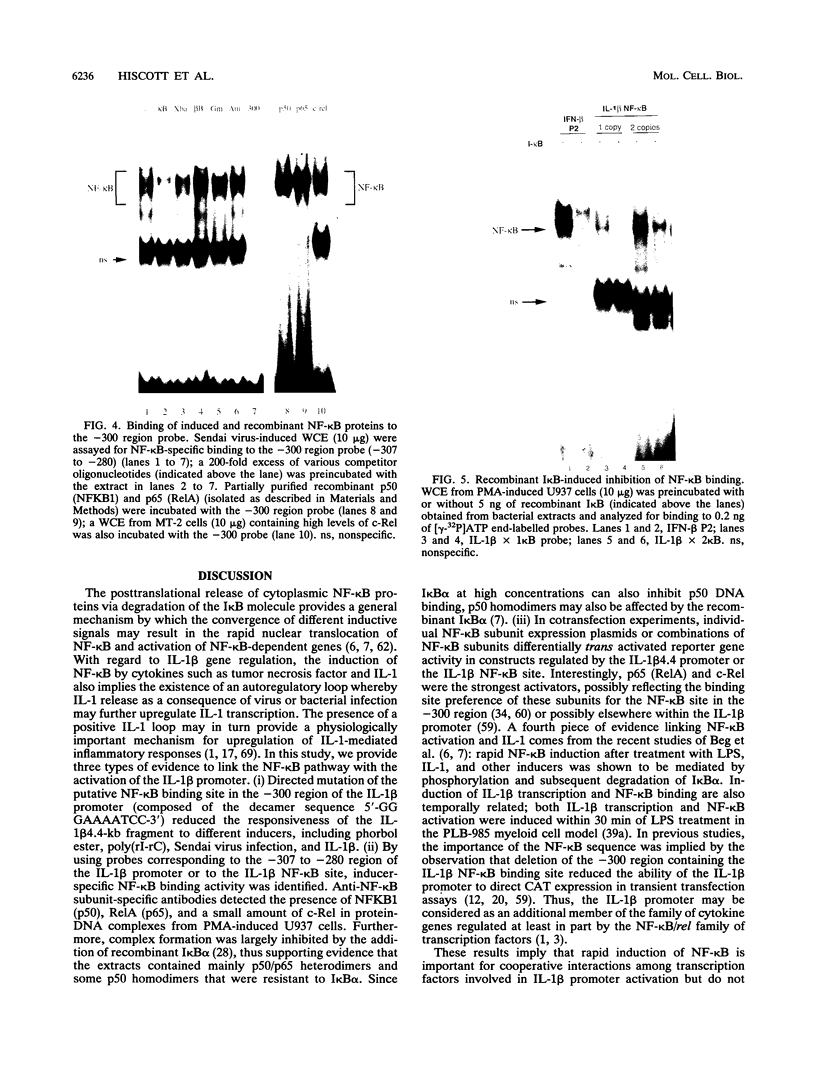
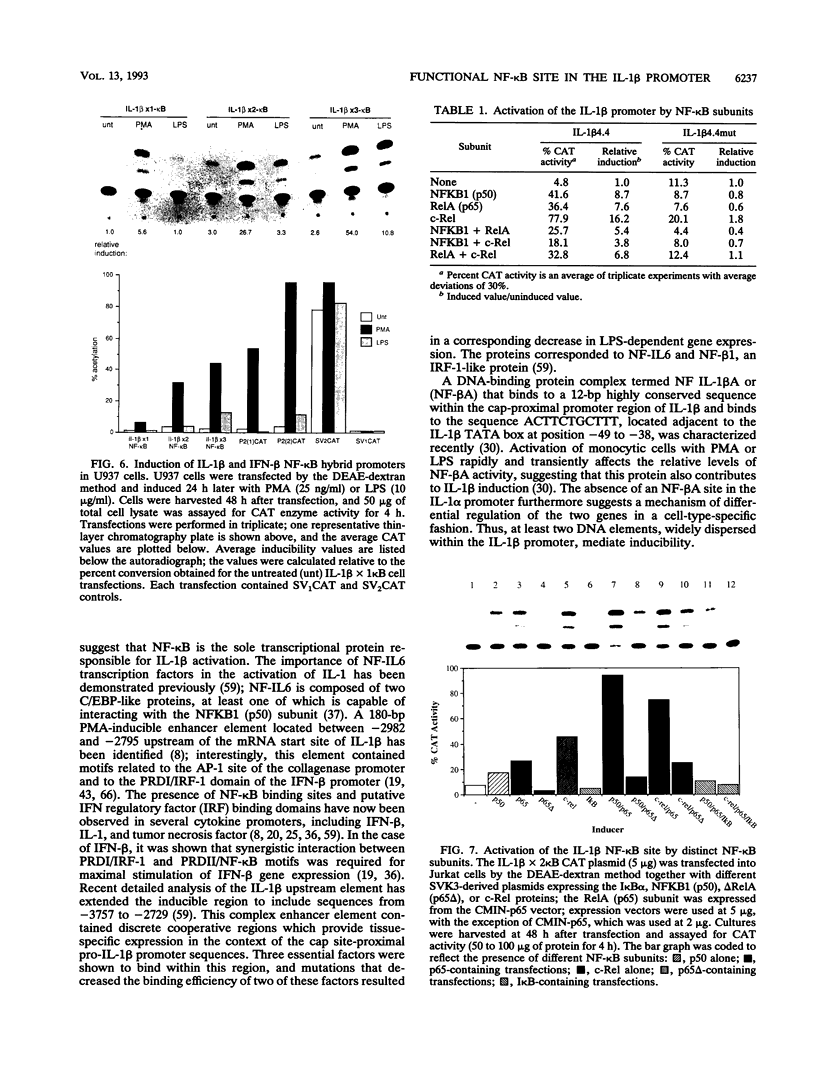
The -300 region of the interleukin 1 beta (IL-1 beta) promoter contains a functional NF-kappa B binding site composed of the decamer sequence 5'-GGGAAAATCC-3'. Probes representing the -300 region or the NF-kappa B site alone interacted with NF-kappa B proteins present in phorbol myristate acetate-, lipopolysaccharide-, or Sendai virus-induced myeloid cell extracts as well as recombinant NFKB1 (p50) and RelA (p65); furthermore, NF-kappa B protein-DNA complex formation was dissociated in vitro by the addition of recombinant I kappa B alpha. Mutation of the NF-kappa B site in the context of the IL-1 beta promoter reduced the responsiveness of the IL-1 beta promoter to various inducers, including phorbol ester, Sendai virus, poly(rI-rC), and IL-1 beta. A 4.4-kb IL-1 beta promoter fragment linked to a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene was also preferentially inducible by coexpression of individual NF-kappa B subunits compared with a mutated IL-1 beta promoter fragment. When multiple copies of the IL-1 beta NF-kappa B site were linked to an enhancerless simian virus 40 promoter, this element was able to mediate phorbol ester- or lipopolysaccharide-inducible gene expression. In cotransfection experiments, RelA (p65) and c-Rel (p85) were identified as the main subunits responsible for the activation of the IL-1 beta NF-kappa B site; also, combinations of NFKB1 (p50) and RelA (p65) or c-Rel and RelA were strong transcriptional activators of reporter gene activity. The presence of a functional NF-kappa B binding site in the IL-1 beta promoter suggests that IL-1 positively autoregulates its own synthesis, since IL-1 is a strong inducer of NF-kappa B binding activity. Thus, the IL-1 beta gene may be considered as an important additional member of the family of cytokine genes regulated in part by the NF-kappa B/rel family of transcription factors.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K. I., Lee F., Miyajima A., Miyatake S., Arai N., Yokota T. Cytokines: coordinators of immune and inflammatory responses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:783–836. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. A 65-kappaD subunit of active NF-kappaB is required for inhibition of NF-kappaB by I kappaB. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1689–1698. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Bogerd H., Doerre S., Stein B., Greene W. C. The 65-kDa subunit of human NF-kappa B functions as a potent transcriptional activator and a target for v-Rel-mediated repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1875–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Finco T. S., Nantermet P. V., Baldwin A. S., Jr Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: a mechanism for NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3301–3310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Ruben S. M., Scheinman R. I., Haskill S., Rosen C. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr I kappa B interacts with the nuclear localization sequences of the subunits of NF-kappa B: a mechanism for cytoplasmic retention. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1899–1913. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensi G., Mora M., Raugei G., Buonamassa D. T., Rossini M., Melli M. An inducible enhancer controls the expression of the human interleukin 1 beta gene. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Oct;1(10):491–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Villalobos J., Burd P. R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. Cloning of a mitogen-inducible gene encoding a kappa B DNA-binding protein with homology to the rel oncogene and to cell-cycle motifs. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):76–80. doi: 10.1038/348076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell E., Mittereder N., Rice N. R. A human rel proto-oncogene cDNA containing an Alu fragment as a potential coding exon. Oncogene. 1989 Jul;4(7):935–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. D., Collins K. L., Gandy M. S., Webb A. C., Auron P. E. Genomic sequence for human prointerleukin 1 beta: possible evolution from a reverse transcribed prointerleukin 1 alpha gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):7897–7914. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.7897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouse K. A., Cosentino L. M., Weih K. A., Pyle S. W., Robbins P. B., Hochstein H. D., Natarajan V., Farrar W. L. The HIV-1 gp120 envelope protein has the intrinsic capacity to stimulate monokine secretion. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):2892–2901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L., Hiscott J. Heterodimerization and transcriptional activation in vitro by NF-kappa B proteins. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Jul;152(1):10–18. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041520103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Addario M., Roulston A., Wainberg M. A., Hiscott J. Coordinate enhancement of cytokine gene expression in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected promonocytic cells. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6080–6089. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6080-6089.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Addario M., Wainberg M. A., Hiscott J. Activation of cytokine genes in HIV-1 infected myelomonoblastic cells by phorbol ester and tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 15;148(4):1222–1229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood. 1991 Apr 15;77(8):1627–1652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil M., Sportza L., D'Addario M., Lacoste J., Rooke R., Wainberg M. A., Hiscott J. Inhibition of HIV-1 transmission by interferon and 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine during de novo infection of promonocytic cells. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):388–394. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90306-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. Two different virus-inducible elements are required for human beta-interferon gene regulation. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):101–110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton M. J. Review: transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of interleukin 1 gene expression. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1992 Apr;14(3):401–411. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(92)90170-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Clouse K. A., Justement J., Rabson A., Duh E., Kehrl J. H., Fauci A. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces expression of human immunodeficiency virus in a chronically infected T-cell clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2365–2368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. Malignant transformation by mutant Rel proteins. Trends Genet. 1991 Oct;7(10):318–322. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90421-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfeld A. E., Doyle C., Maniatis T. Human tumor necrosis factor alpha gene regulation by virus and lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9769–9773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin G. E., Leung K., Folks T. M., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Activation of HIV gene expression during monocyte differentiation by induction of NF-kappa B. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):70–73. doi: 10.1038/339070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Beg A. A., Tompkins S. M., Morris J. S., Yurochko A. D., Sampson-Johannes A., Mondal K., Ralph P., Baldwin A. S., Jr Characterization of an immediate-early gene induced in adherent monocytes that encodes I kappa B-like activity. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiscott J., Alper D., Cohen L., Leblanc J. F., Sportza L., Wong A., Xanthoudakis S. Induction of human interferon gene expression is associated with a nuclear factor that interacts with the NF-kappa B site of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2557–2566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2557-2566.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Monks B. G., Geist L. J., Monick M. M., Monroy M. A., Stinski M. F., Webb A. C., Dayer J. M., Auron P. E., Fenton M. J. The functional importance of a cap site-proximal region of the human prointerleukin 1 beta gene is defined by viral protein trans-activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3439–3448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Kakizuka A., Verma I. M. I kappa B gamma, a 70 kd protein identical to the C-terminal half of p110 NF-kappa B: a new member of the I kappa B family. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1109–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90082-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Inoue J., Davis N., Link E., Baeuerle P. A., Bose H. R., Jr, Verma I. M. The rel-associated pp40 protein prevents DNA binding of Rel and NF-kappa B: relationship with I kappa B beta and regulation by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1464–1476. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Ruben S. M., Rosen C. A. Selection of optimal kappa B/Rel DNA-binding motifs: interaction of both subunits of NF-kappa B with DNA is required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4412–4421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacoste J., D'Addario M., Roulston A., Wainberg M. A., Hiscott J. Cell-specific differences in activation of NF-kappa B regulatory elements of human immunodeficiency virus and beta interferon promoters by tumor necrosis factor. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4726–4734. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4726-4734.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeClair K. P., Blanar M. A., Sharp P. A. The p50 subunit of NF-kappa B associates with the NF-IL6 transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8145–8149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc J. F., Cohen L., Rodrigues M., Hiscott J. Synergism between distinct enhanson domains in viral induction of the human beta interferon gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3987–3993. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Gubler U., Hellmann C. P., Dukovich M., Giri J. G., Pan Y. C., Collier K., Semionow R., Chua A. O., Mizel S. B. Cloning and expression of murine interleukin-1 cDNA in Escherichia coli. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):458–462. doi: 10.1038/312458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Skillman D. R., Gomatos P. J., Kalter D. C., Gendelman H. E. Role of mononuclear phagocytes in the pathogenesis of human immunodeficiency virus infection. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:169–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E., Koyanagi Y., Chen I. S. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha can be induced from mononuclear phagocytes by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 binding to the CD4 receptor. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4404–4408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4404-4408.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R., Hatada E. N., Hohmann H. P., Haiker M., Bartsch C., Röthlisberger U., Lahm H. W., Schlaeger E. J., van Loon A. P., Scheidereit C. Cloning of the DNA-binding subunit of human nuclear factor kappa B: the level of its mRNA is strongly regulated by phorbol ester or tumor necrosis factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):966–970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto M., Fujita T., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Harada H., Sudo Y., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Regulated expression of a gene encoding a nuclear factor, IRF-1, that specifically binds to IFN-beta gene regulatory elements. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):903–913. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor J. A., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B: a family of inducible and differentially expressed enhancer-binding proteins in human T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10028–10032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri A., Chang C. C., Lombardi L., Salina M., Corradini P., Maiolo A. T., Chaganti R. S., Dalla-Favera R. B cell lymphoma-associated chromosomal translocation involves candidate oncogene lyt-10, homologous to NF-kappa B p50. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1075–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno H., Takimoto G., McKeithan T. W. The candidate proto-oncogene bcl-3 is related to genes implicated in cell lineage determination and cell cycle control. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):991–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90347-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Kinter A., Justement J. S., Kehrl J. H., Bressler P., Stanley S., Fauci A. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha functions in an autocrine manner in the induction of human immunodeficiency virus expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):782–785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg Z. F., Fauci A. S. The immunopathogenesis of HIV infection. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:377–431. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60665-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roulston A., D'Addario M., Boulerice F., Caplan S., Wainberg M. A., Hiscott J. Induction of monocytic differentiation and NF-kappa B-like activities by human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection of myelomonoblastic cells. J Exp Med. 1992 Mar 1;175(3):751–763. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Klement J. F., Coleman T. A., Maher M., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. I-Rel: a novel rel-related protein that inhibits NF-kappa B transcriptional activity. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):745–760. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Narayanan R., Klement J. F., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Functional characterization of the NF-kappa B p65 transcriptional activator and an alternatively spliced derivative. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):444–454. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bull P., Takamiya M., Bours V., Siebenlist U., Dobrzanski P., Bravo R. RelB, a new Rel family transcription activator that can interact with p50-NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):674–684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R. M., Perkins N. D., Duckett C. S., Andrews P. C., Nabel G. J. Cloning of an NF-kappa B subunit which stimulates HIV transcription in synergy with p65. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):733–736. doi: 10.1038/352733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Saito K., Bonagura C. A., Galson D. L., Fenton M. J., Webb A. C., Auron P. E. The human prointerleukin 1 beta gene requires DNA sequences both proximal and distal to the transcription start site for tissue-specific induction. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1332–1344. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sica A., Tan T. H., Rice N., Kretzschmar M., Ghosh P., Young H. A. The c-rel protooncogene product c-Rel but not NF-kappa B binds to the intronic region of the human interferon-gamma gene at a site related to an interferon-stimulable response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1740–1744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Ganchi P. A., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B controls expression of inhibitor I kappa B alpha: evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1912–1915. doi: 10.1126/science.8096091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Baeuerle P. A. The 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B is a receptor for I kappa B and a modulator of DNA-binding specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1975–1984. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voth R., Rossol S., Klein K., Hess G., Schütt K. H., Schröder H. C., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Müller W. E. Differential gene expression of IFN-alpha and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with AIDS related complex and AIDS. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):970–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl L. M., Corcoran M. L., Pyle S. W., Arthur L. O., Harel-Bellan A., Farrar W. L. Human immunodeficiency virus glycoprotein (gp120) induction of monocyte arachidonic acid metabolites and interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):621–625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthoudakis S., Cohen L., Hiscott J. Multiple protein-DNA interactions within the human interferon-beta regulatory element. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1139–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamato K., el-Hajjaoui Z., Simon K., Koeffler H. P. Modulation of interleukin-1 beta RNA in monocytic cells infected with human immunodeficiency virus-1. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1109–1114. doi: 10.1172/JCI114815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabel U., Baeuerle P. A. Purified human I kappa B can rapidly dissociate the complex of the NF-kappa B transcription factor with its cognate DNA. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90806-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Lin J. X., Vilcek J. Interleukin-6 induction by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in human fibroblasts involves activation of a nuclear factor binding to a kappa B-like sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3818–3823. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]