Abstract
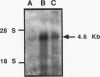
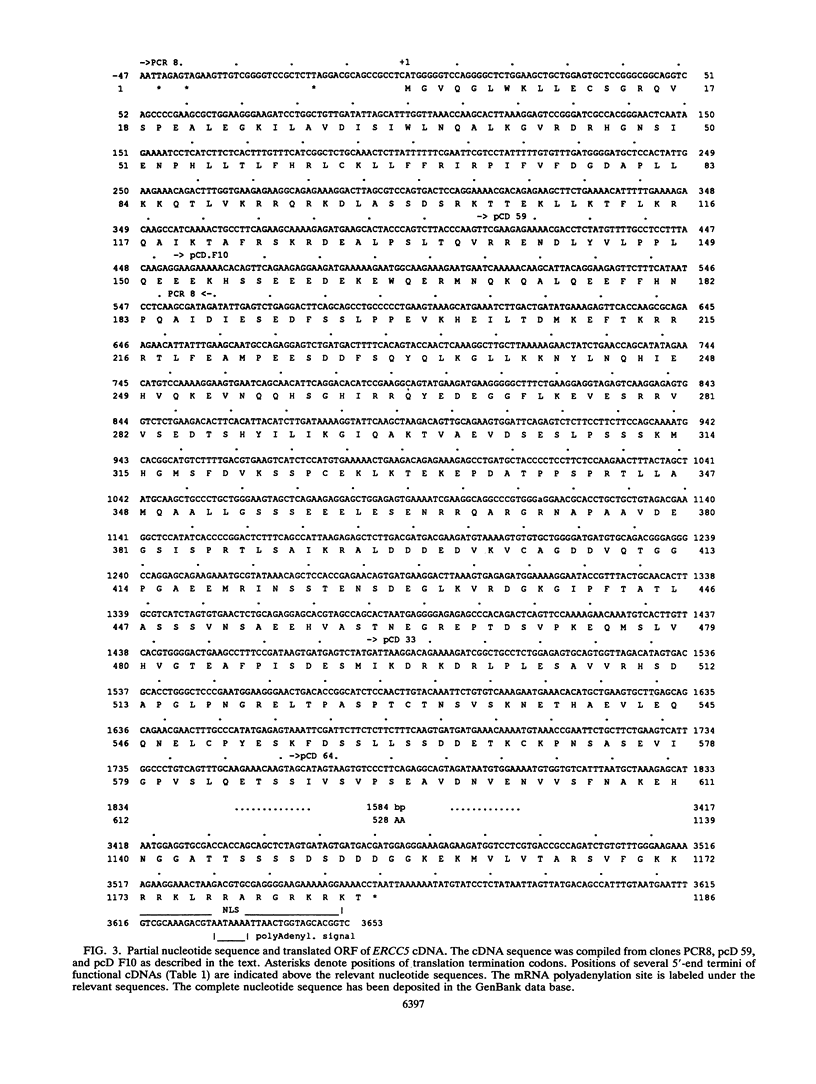
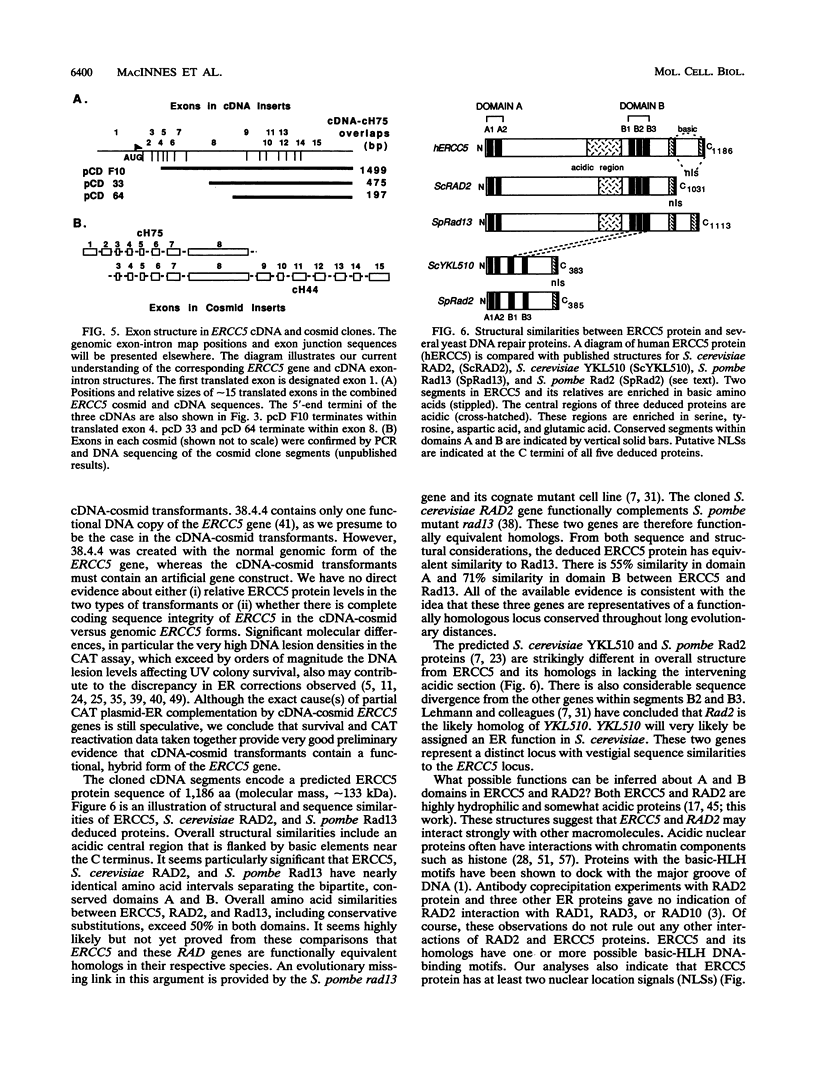
Several human genes related to DNA excision repair (ER) have been isolated via ER cross-species complementation (ERCC) of UV-sensitive CHO cells. We have now isolated and characterized cDNAs for the human ERCC5 gene that complement CHO UV135 cells. The ERCC5 mRNA size is about 4.6 kb. Our available cDNA clones are partial length, and no single clone was active for UV135 complementation. When cDNAs were mixed pairwise with a cosmid clone containing an overlapping 5'-end segment of the ERCC5 gene, DNA transfer produced UV-resistant colonies with 60 to 95% correction of UV resistance relative to either a genomic ERCC5 DNA transformant or the CHO AA8 progenitor cells. cDNA-cosmid transformants regained intermediate levels (20 to 45%) of ER-dependent reactivation of a UV-damaged pSVCATgpt reporter plasmid. Our evidence strongly implicates an in situ recombination mechanism in cDNA-cosmid complementation for ER. The complete deduced amino acid sequence of ERCC5 was reconstructed from several cDNA clones encoding a predicted protein of 1,186 amino acids. The ERCC5 protein has extensive sequence similarities, in bipartite domains A and B, to products of RAD repair genes of two yeasts, Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD2 and Schizosaccharomyces pombe rad13. Sequence, structural, and functional data taken together indicate that ERCC5 and its relatives are probable functional homologs. A second locus represented by S. cerevisiae YKL510 and S. pombe rad2 genes is structurally distinct from the ERCC5 locus but retains vestigial A and B domain similarities. Our analyses suggest that ERCC5 is a nuclear-localized protein with one or more highly conserved helix-loop-helix segments within domains A and B.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony-Cahill S. J., Benfield P. A., Fairman R., Wasserman Z. R., Brenner S. L., Stafford W. F., 3rd, Altenbach C., Hubbell W. L., DeGrado W. F. Molecular characterization of helix-loop-helix peptides. Science. 1992 Feb 21;255(5047):979–983. doi: 10.1126/science.1312255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly V., Sommers C. H., Sung P., Prakash L., Prakash S. Specific complex formation between proteins encoded by the yeast DNA repair and recombination genes RAD1 and RAD10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8273–8277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Evans M. K., Fornace A. J., Jr DNA repair and its pathogenetic implications. Lab Invest. 1989 Aug;61(2):143–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr V. A., Okumoto D. S., Hanawalt P. C. Survival of UV-irradiated mammalian cells correlates with efficient DNA repair in an essential gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3830–3833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch D., Greiner C., Lewis K., Ford R., Adair G., Thompson L. Summary of complementation groups of UV-sensitive CHO cell mutants isolated by large-scale screening. Mutagenesis. 1989 Sep;4(5):349–354. doi: 10.1093/mutage/4.5.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr A. M., Sheldrick K. S., Murray J. M., al-Harithy R., Watts F. Z., Lehmann A. R. Evolutionary conservation of excision repair in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: evidence for a family of sequences related to the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 25;21(6):1345–1349. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.6.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E., Cortés F., Lutze L. H., Morgan W. F., Player A. N., Mitchell D. L. Unique DNA repair properties of a xeroderma pigmentosum revertant. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3353–3357. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Defective repair replication of DNA in xeroderma pigmentosum. Nature. 1968 May 18;218(5142):652–656. doi: 10.1038/218652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flejter W. L., McDaniel L. D., Johns D., Friedberg E. C., Schultz R. A. Correction of xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group D mutant cell phenotypes by chromosome and gene transfer: involvement of the human ERCC2 DNA repair gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):261–265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Hanson I. M., Trowsdale J. A novel cysteine-rich sequence motif. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):483–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90229-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C. Eukaryotic DNA repair: glimpses through the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioessays. 1991 Jun;13(6):295–302. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C. Nuclear targeting sequences. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Sep;17(9):347–347. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90312-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C. Xeroderma pigmentosum, Cockayne's syndrome, helicases, and DNA repair: what's the relationship? Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):887–889. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90384-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman L., Yeung A. T. The UvrABC endonuclease of Escherichia coli. Photochem Photobiol. 1990 Jun;51(6):749–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Legrain P., Dujon B. Sequence of a 10.7 kb segment of yeast chromosome XI identifies the APN1 and the BAF1 loci and reveals one tRNA gene and several new open reading frames including homologs to RAD2 and kinases. Yeast. 1992 Feb;8(2):121–132. doi: 10.1002/yea.320080207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. J., Cleaver J. E., Wood R. D. Repair of damaged DNA by extracts from a xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group A revertant and expression of a protein absent in its parental cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 11;20(5):991–995. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.5.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klocker H., Schneider R., Burtscher H. J., Auer B., Hirsch-Kauffmann M., Schweiger M. Transient expression of a plasmid gene, a tool to study DNA repair in human cells: defect of DNA repair in Cockayne syndrome; one thymine cyclobutane dimer is sufficient to block transcription. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;39(2):346–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer K. H., Lee M. M., Scotto J. Xeroderma pigmentosum. Cutaneous, ocular, and neurologic abnormalities in 830 published cases. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Feb;123(2):241–250. doi: 10.1001/archderm.123.2.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapeyre B., Bourbon H., Amalric F. Nucleolin, the major nucleolar protein of growing eukaryotic cells: an unusual protein structure revealed by the nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1472–1476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R., Carr A. M., Watts F. Z., Murray J. M. DNA repair in the fission yeast, Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mutat Res. 1991 Sep-Oct;250(1-2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(91)90177-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R. Three complementation groups in Cockayne syndrome. Mutat Res. 1982 Dec;106(2):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(82)90115-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Lasko P. F., Ashburner M., Leroy P., Nielsen P. J., Nishi K., Schnier J., Slonimski P. P. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):121–122. doi: 10.1038/337121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh E. Y., Elliott J. F., Cwirla S., Lanier L. L., Davis M. M. Polymerase chain reaction with single-sided specificity: analysis of T cell receptor delta chain. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):217–220. doi: 10.1126/science.2463672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lommel L., Hanawalt P. C. Increased UV resistance of a xeroderma pigmentosum revertant cell line is correlated with selective repair of the transcribed strand of an expressed gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):970–976. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacInnes M. A., Bingham J. M., Thompson L. H., Strniste G. F. DNA-mediated cotransfer of excision repair capacity and drug resistance into chinese hamster ovary mutant cell line UV-135. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1152–1158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madura K., Prakash S. Nucleotide sequence, transcript mapping, and regulation of the RAD2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):914–923. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.914-923.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCready S. J., Burkill H., Evans S., Cox B. S. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD2 gene complements a Schizosaccharomyces pombe repair mutation. Curr Genet. 1989 Jan;15(1):27–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00445748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon I., Spivak G., Hanawalt P. C. Selective removal of transcription-blocking DNA damage from the transcribed strand of the mammalian DHFR gene. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):241–249. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. L., Vaughan J. E., Nairn R. S. Inhibition of transient gene expression in Chinese hamster ovary cells by cyclobutane dimers and (6-4) photoproducts in transfected ultraviolet-irradiated plasmid DNA. Plasmid. 1989 Jan;21(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(89)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudgett J. S., MacInnes M. A. Isolation of the functional human excision repair gene ERCC5 by intercosmid recombination. Genomics. 1990 Dec;8(4):623–633. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90248-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nance M. A., Berry S. A. Cockayne syndrome: review of 140 cases. Am J Med Genet. 1992 Jan 1;42(1):68–84. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320420115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff J. A., Reynolds R. J. Transcription stimulates homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4837–4845. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet C. M., Chenevert J. M., Friedberg E. C. The RAD2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence and transcript mapping. Gene. 1985;36(3):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolet C. M., Friedberg E. C. Overexpression of the RAD2 gene of S. cerevisiae: identification and preliminary characterization of Rad2 protein. Yeast. 1987 Sep;3(3):149–160. doi: 10.1002/yea.320030303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donovan A., Wood R. D. Identical defects in DNA repair in xeroderma pigmentosum group G and rodent ERCC group 5. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):185–188. doi: 10.1038/363185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orren D. K., Selby C. P., Hearst J. E., Sancar A. Post-incision steps of nucleotide excision repair in Escherichia coli. Disassembly of the UvrBC-DNA complex by helicase II and DNA polymerase I. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):780–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E., Guzder S. N., Koken M. H., Jaspers-Dekker I., Weeda G., Hoeijmakers J. H., Prakash S., Prakash L. RAD25 (SSL2), the yeast homolog of the human xeroderma pigmentosum group B DNA repair gene, is essential for viability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11416–11420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C., Legerski R. High-frequency transformation of human repair-deficient cell lines by an Epstein-Barr virus-based cDNA expression vector. Gene. 1991 Nov 15;107(2):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90328-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protić-Sabljić M., Kraemer K. H. Host cell reactivation by human cells of DNA expression vectors damaged by ultraviolet radiation or by acid-heat treatment. Carcinogenesis. 1986 Oct;7(10):1765–1770. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.10.1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protić-Sabljić M., Kraemer K. H. One pyrimidine dimer inactivates expression of a transfected gene in xeroderma pigmentosum cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Dilworth S. M., Laskey R. A., Dingwall C. Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):615–623. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90245-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Nouspikel T., Corlet J., Ucla C., Bairoch A., Clarkson S. G. Complementation of the DNA repair defect in xeroderma pigmentosum group G cells by a human cDNA related to yeast RAD2. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):182–185. doi: 10.1038/363182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby C. P., Sancar A. Structure and function of the (A)BC excinuclease of Escherichia coli. Mutat Res. 1990 Sep-Nov;236(2-3):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(90)90005-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini M., Lagomarsini P., Arlett C. F., Marinoni S., Borrone C., Crovato F., Trevisan G., Cordone G., Nuzzo F. Xeroderma pigmentosum (complementation group D) mutation is present in patients affected by trichothiodystrophy with photosensitivity. Hum Genet. 1986 Oct;74(2):107–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00282072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash S., Prakash L. The RAD6 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae polyubiquitinates histones, and its acidic domain mediates this activity. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1476–1485. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Miura N., Satokata I., Miyamoto I., Yoshida M. C., Satoh Y., Kondo S., Yasui A., Okayama H., Okada Y. Analysis of a human DNA excision repair gene involved in group A xeroderma pigmentosum and containing a zinc-finger domain. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):73–76. doi: 10.1038/348073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Satokata I., Ogita Z., Uchida T., Okada Y. Molecular cloning of a mouse DNA repair gene that complements the defect of group-A xeroderma pigmentosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5512–5516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Brookman K. W., Dillehay L. E., Mooney C. L., Carrano A. V. Hypersensitivity to mutation and sister-chromatid-exchange induction in CHO cell mutants defective in incising DNA containing UV lesions. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Nov;8(6):759–773. doi: 10.1007/BF01543017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Glynn S., Levi E., Mjolsness S., Hayday A. Use of a chemically modified T7 DNA polymerase for manual and automated sequencing of supercoiled DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):460–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troelstra C., van Gool A., de Wit J., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., Hoeijmakers J. H. ERCC6, a member of a subfamily of putative helicases, is involved in Cockayne's syndrome and preferential repair of active genes. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):939–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90390-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten B. Nucleotide excision repair in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Mar;54(1):18–51. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.1.18-51.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber C. A., Salazar E. P., Stewart S. A., Thompson L. H. ERCC2: cDNA cloning and molecular characterization of a human nucleotide excision repair gene with high homology to yeast RAD3. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1437–1447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08260.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeda G., van Ham R. C., Vermeulen W., Bootsma D., van der Eb A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. A presumed DNA helicase encoded by ERCC-3 is involved in the human repair disorders xeroderma pigmentosum and Cockayne's syndrome. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):777–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90122-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei Q., Matanoski G. M., Farmer E. R., Hedayati M. A., Grossman L. DNA repair and aging in basal cell carcinoma: a molecular epidemiology study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1614–1618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelle B., Lohman P. H. Repair of UV-endonuclease-susceptible sites in the 7 complementation groups of xeroderma pigmentosum A through G. Mutat Res. 1979 Sep;62(2):363–368. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(79)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., Vredeveldt G., Mayne L. V., Odijk H., Vermeulen W., Klein B., Weeda G., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D., Westerveld A. The cloned human DNA excision repair gene ERCC-1 fails to correct xeroderma pigmentosum complementation groups A through I. Mutat Res. 1989 Mar;217(2):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(89)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]