Abstract
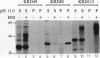
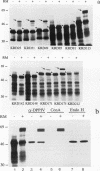
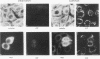
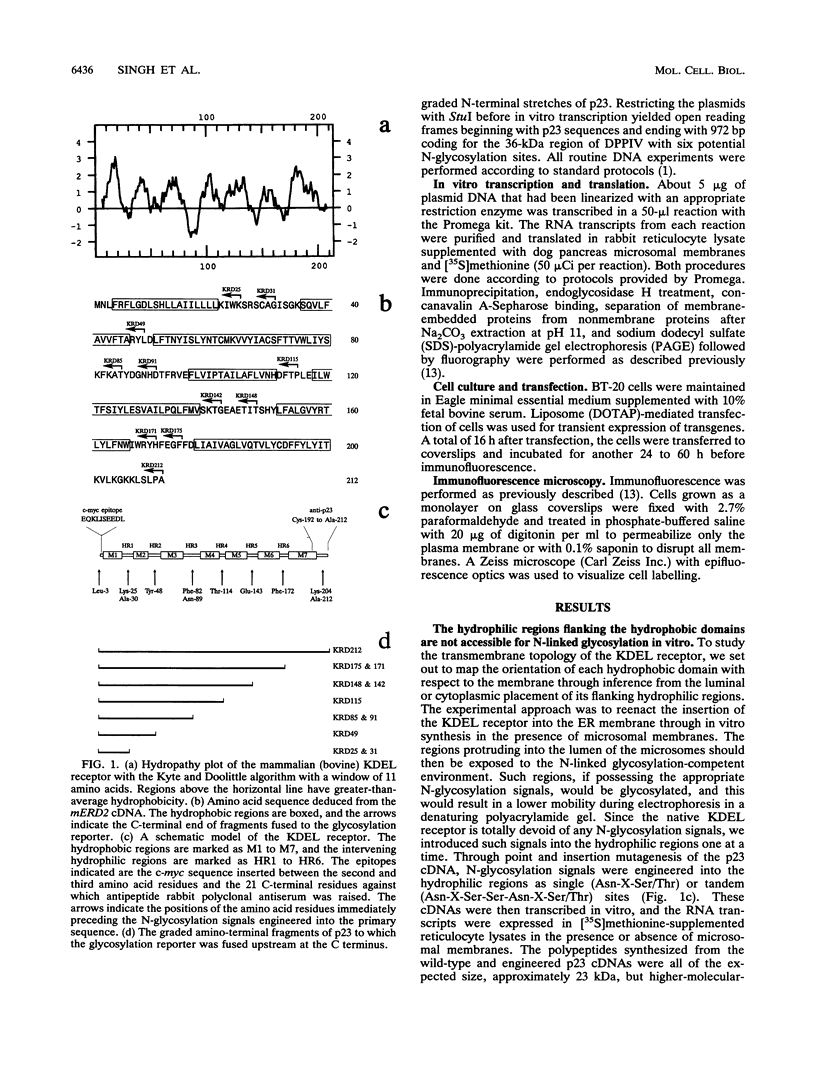
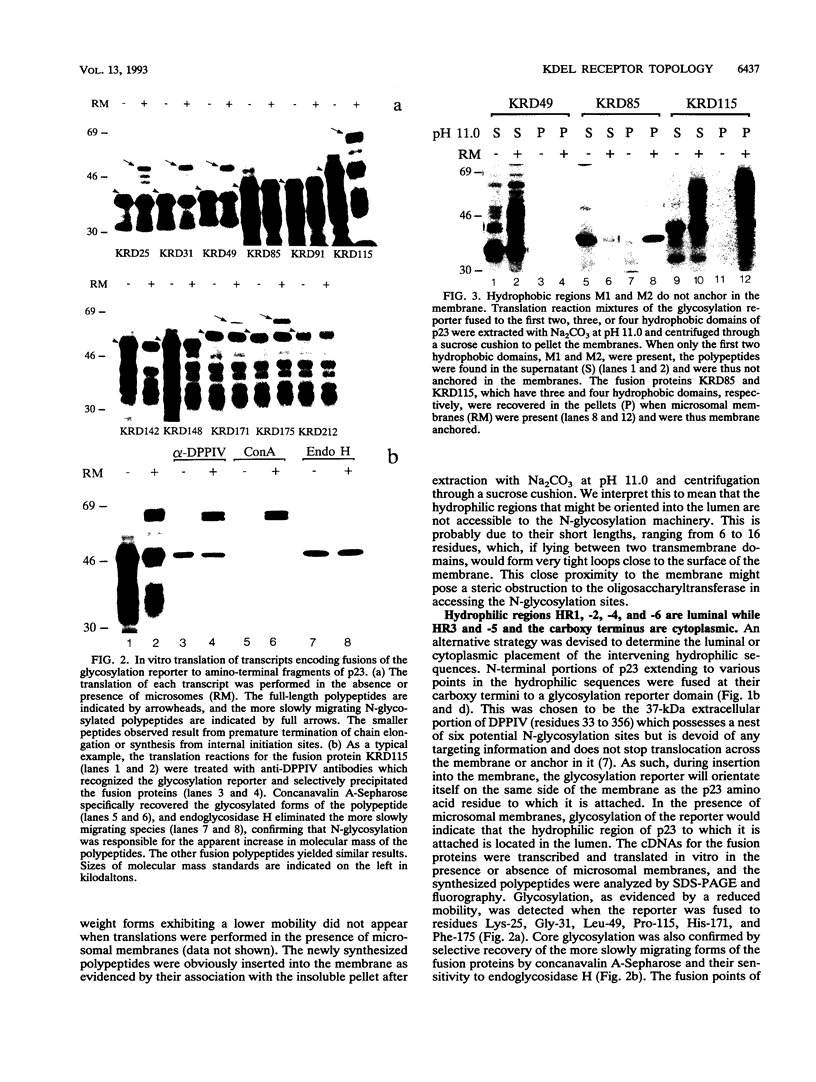
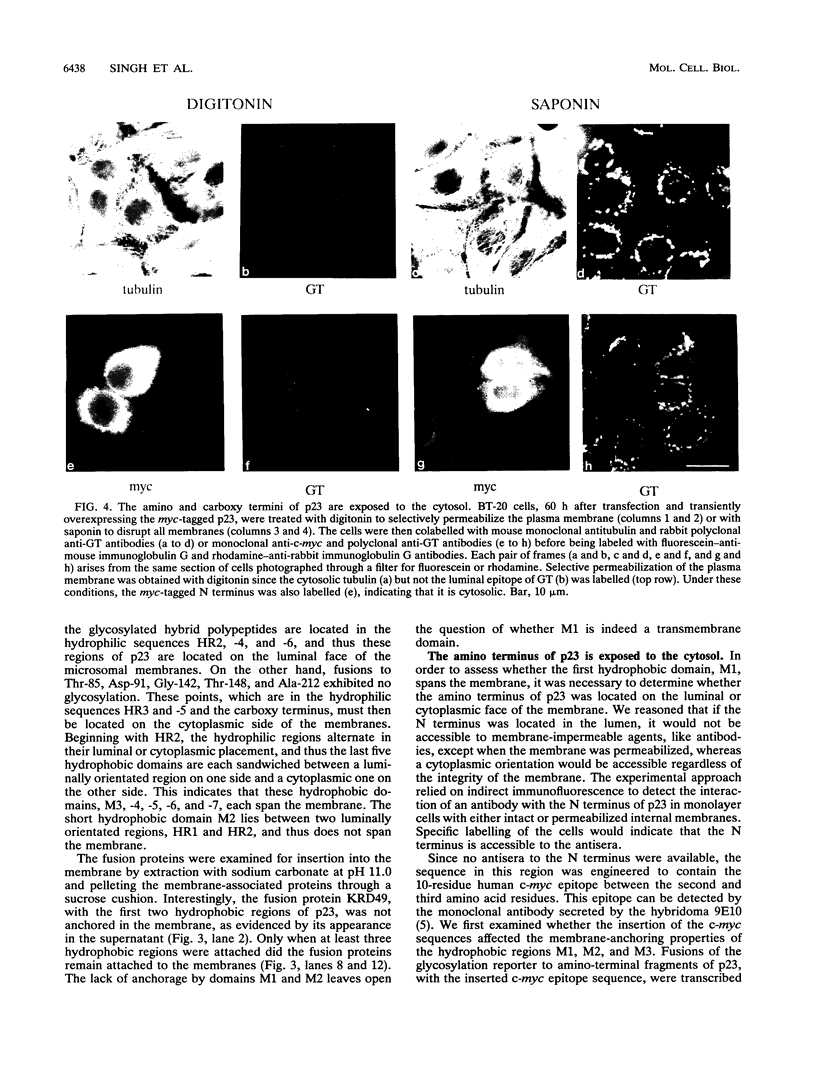
The mammalian KDEL receptor is an integral membrane protein with seven hydrophobic regions. Fusion proteins comprising a 37-kDa N-glycosylation reporter fused downstream of amino-terminal fragments of the KDEL receptor with varying numbers of hydrophobic regions were synthesized in an in vitro translation system containing canine pancreatic microsomes. The luminal or cytosolic orientation of the reporter, and hence of the hydrophilic region to which it is fused, was inferred from the presence or absence of glycosylation, which occurs only in the lumen of the microsomes. The cytosolic orientation of the N and C termini was also confirmed immunocytochemically. Our results suggest that the KDEL receptor is inserted into the membrane with only six transmembrane domains and that both the amino and carboxy termini are located in the cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bomsel M., Mostov K. Role of heterotrimeric G proteins in membrane traffic. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Dec;3(12):1317–1328. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.12.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Agostaro G., Bendiak B., Tropak M. Cloning of cDNA encoding the membrane-bound form of bovine beta 1,4-galactosyltransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jul 15;183(1):211–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Thorner J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Model systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:653–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Lewis G. K., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies specific for human c-myc proto-oncogene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3610–3616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick K. G., Boothroyd J. C., Rudner A. D., Pelham H. R. Genes that allow yeast cells to grow in the absence of the HDEL receptor. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4187–4195. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong W. J., Doyle D. Membrane orientation of rat gp110 as studied by in vitro translation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16892–16898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong W., Tang B. L. Protein trafficking along the exocytotic pathway. Bioessays. 1993 Apr;15(4):231–238. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu V. W., Shah N., Klausner R. D. A brefeldin A-like phenotype is induced by the overexpression of a human ERD-2-like protein, ELP-1. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):625–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90226-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. A human homologue of the yeast HDEL receptor. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):162–163. doi: 10.1038/348162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. Ligand-induced redistribution of a human KDEL receptor from the Golgi complex to the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1992 Jan 24;68(2):353–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90476-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Sweet D. J., Pelham H. R. The ERD2 gene determines the specificity of the luminal ER protein retention system. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1359–1363. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90699-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low S. H., Wong S. H., Tang B. L., Hong W. J. Involvement of both vectorial and transcytotic pathways in the preferential apical cell surface localization of rat dipeptidyl peptidase IV in transfected LLC-PK1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19710–19716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikaelian I., Sergeant A. A general and fast method to generate multiple site directed mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):376–376. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I. M., von Heijne G. Determination of the distance between the oligosaccharyltransferase active site and the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5798–5801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Control of protein exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Evidence that luminal ER proteins are sorted from secreted proteins in a post-ER compartment. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):913–918. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. The retention signal for soluble proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):483–486. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90303-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Agre P. Isolation of the cDNA for erythrocyte integral membrane protein of 28 kilodaltons: member of an ancient channel family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11110–11114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato C., Matsumoto G. Primary structure of squid sodium channel deduced from the complementary DNA sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jul 15;186(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80775-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenza J. C., Hardwick K. G., Dean N., Pelham H. R. ERD2, a yeast gene required for the receptor-mediated retrieval of luminal ER proteins from the secretory pathway. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1349–1357. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90698-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramaniam V. N., bin Mohd Yusoff A. R., Wong S. H., Lim G. B., Chew M., Hong W. Biochemical fractionation and characterization of proteins from Golgi-enriched membranes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):12016–12021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet D. J., Pelham H. R. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae SEC20 gene encodes a membrane glycoprotein which is sorted by the HDEL retrieval system. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):423–432. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05071.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang B. L., Wong S. H., Low S. H., Hong W. Retention of a type II surface membrane protein in the endoplasmic reticulum by the Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu sequence. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7072–7076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang B. L., Wong S. H., Qi X. L., Low S. H., Hong W. Molecular cloning, characterization, subcellular localization and dynamics of p23, the mammalian KDEL receptor. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(2):325–338. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. W., Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. pH-dependent binding of KDEL to its receptor in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7465–7468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng X. M., Wang Y., Pallen C. J. Cell transformation and activation of pp60c-src by overexpression of a protein tyrosine phosphatase. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):336–339. doi: 10.1038/359336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]