Abstract
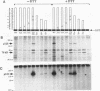
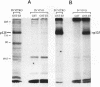
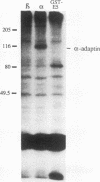
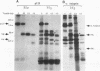
The bovine papillomavirus E5 gene encodes an oncoprotein that can independently transform rodent fibroblasts. This small 44-amino-acid protein is thought to function through the activation of growth factor receptors. E5 activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor results in an increase in the number of activated receptors at the cell surface. This finding suggests that E5 may act by inhibiting the normal down regulation of activated epidermal growth factor receptor via coated pit-mediated endocytosis. We have constructed a fusion protein consisting of glutathione S-transferase and the conserved C-terminal domain of E5 (GST-E5) in order to identify E5-associated cellular proteins that may be involved in its transforming activity. We have identified a 125-kDa cellular protein with a strong associated serine kinase activity that specifically associated with GST-E5 in the reduced form but not with GST-E5 fusions that contained changes in several conserved amino acids. Microsequence and biochemical analyses suggest that p125 is a novel member of the alpha-adaptin family. Since alpha-adaptins have previously been shown to be involved in coated pit-mediated cell surface receptor endocytosis and down regulation, these results suggest that p125 may be an alpha-adaptin-like molecule involved in growth factor receptor down regulation and that E5 may act by inhibiting its activity.
Full text
PDF

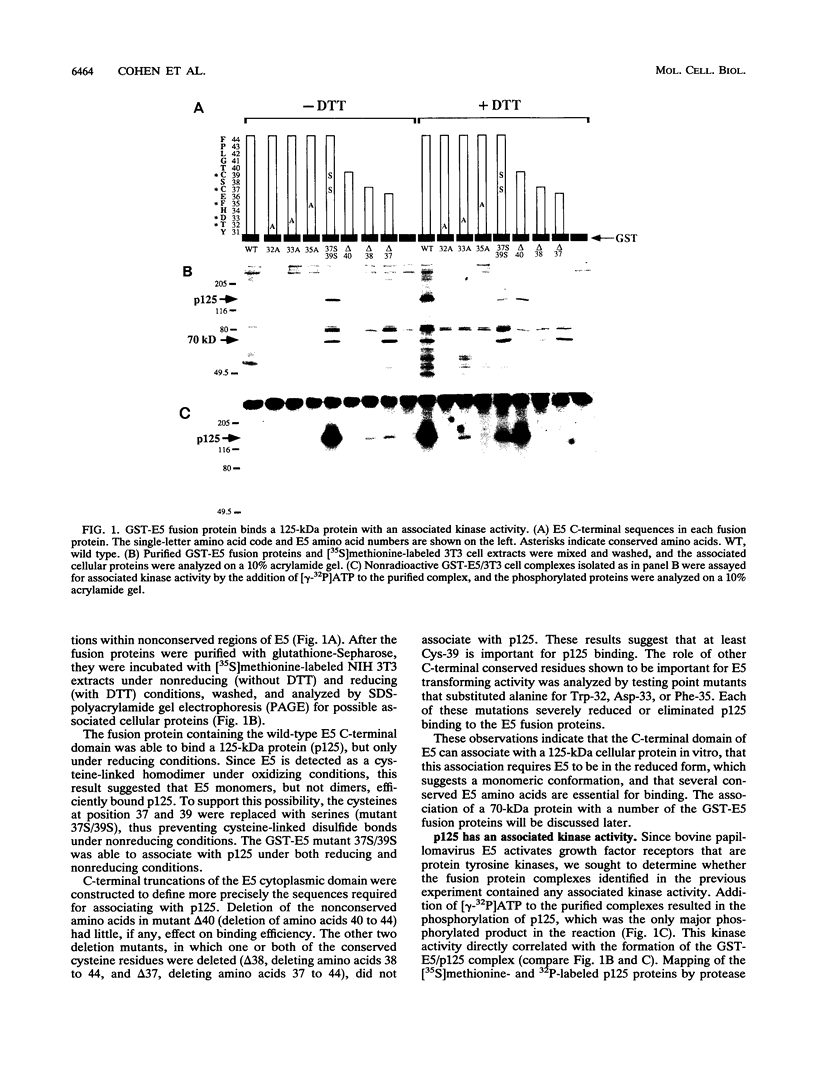
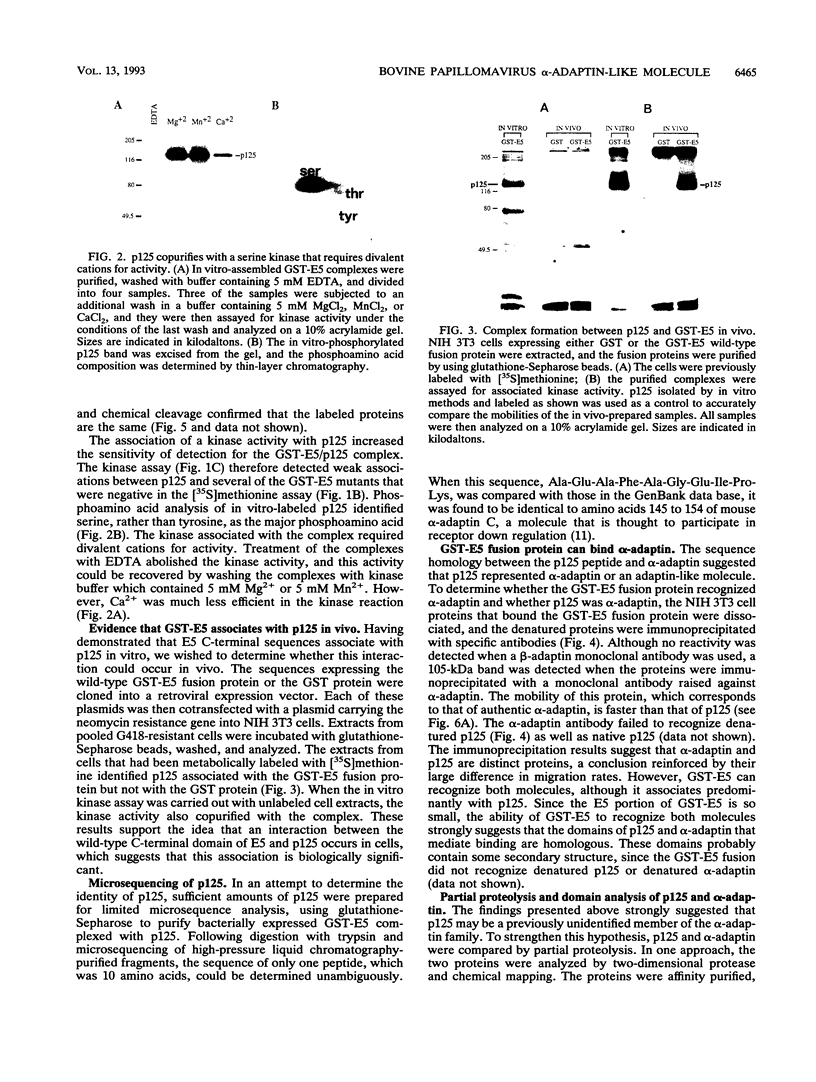
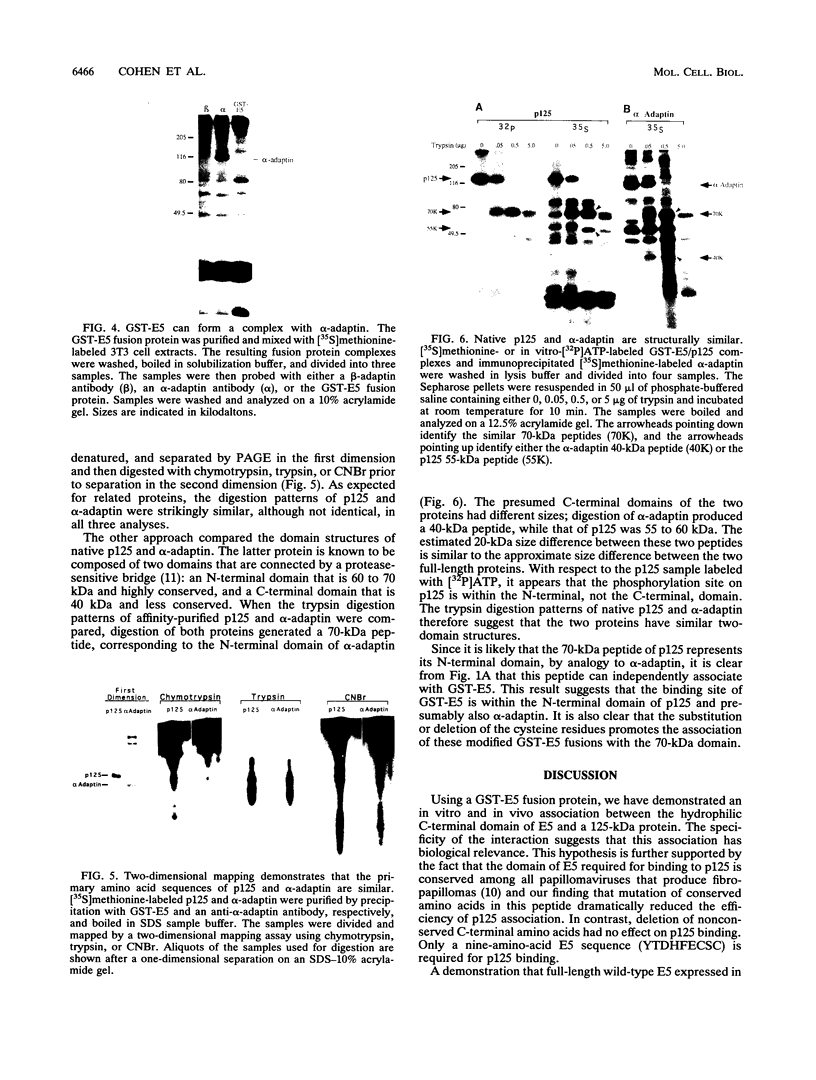


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A., DiMaio D., Schlegel R. Genetic and biochemical definition of the bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2381–2385. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02515.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A., Willingham M., Gay C., Jeang K. T., Schlegel R. The E5 oncoprotein of bovine papillomavirus is oriented asymmetrically in Golgi and plasma membranes. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):334–339. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90391-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Lund K. A., Welsh J. B., Chang C. P., Walton G. M., Der C. J., Wiley H. S., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Functional independence of the epidermal growth factor receptor from a domain required for ligand-induced internalization and calcium regulation. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):33–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90867-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin D. J., Straubinger R. M., Acton S., Näthke I., Brodsky F. M. 100-kDa polypeptides in peripheral clathrin-coated vesicles are required for receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9289–9293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. D., Goldstein D. J., Rutledge L., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R., Schlegel R., Schiller J. T. Transformation-specific interaction of the bovine papillomavirus E5 oncoprotein with the platelet-derived growth factor receptor transmembrane domain and the epidermal growth factor receptor cytoplasmic domain. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5303–5311. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5303-5311.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Andresson T., Sparkowski J. J., Schlegel R. The BPV-1 E5 protein, the 16 kDa membrane pore-forming protein and the PDGF receptor exist in a complex that is dependent on hydrophobic transmembrane interactions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4851–4859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Schlegel R. The E5 oncoprotein of bovine papillomavirus binds to a 16 kd cellular protein. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):137–145. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08089.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Beguinot L. Internalization and down-regulation of the human epidermal growth factor receptor are regulated by the carboxyl-terminal tyrosines. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8363–8368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B. H., Burkhardt A. L., Schlegel R., DiMaio D. 44-amino-acid E5 transforming protein of bovine papillomavirus requires a hydrophobic core and specific carboxyl-terminal amino acids. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4071–4078. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. H., Black M. M. The phosphorylation of coated membrane proteins in intact neurons. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1325–1333. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. H., Chestnut M. H., Beck K. A. The clathrin coat assembly polypeptide complex. Autophosphorylation and assembly activities. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3864–3871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen J. H. Clathrin and associated assembly and disassembly proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:415–438. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.002215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Vass W. C., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R., Velu T. J. The bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein can stimulate the transforming activity of EGF and CSF-1 receptors. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90866-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse B. M. Receptors compete for adaptors found in plasma membrane coated pits. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3331–3336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03204.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeler J. S., Donzell W. C., Anderson R. G. The appendage domain of the AP-2 subunit is not required for assembly or invagination of clathrin-coated pits. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):47–54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Nilson L. A., DiMaio D. Activation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor by the bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):845–855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Mayer B. J., Cicchetti P., Baltimore D. Identification of a ten-amino acid proline-rich SH3 binding site. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.8438166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. S. 100-kD coated vesicle proteins: molecular heterogeneity and intracellular distribution studied with monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):887–895. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M. S. Cloning of cDNAs encoding two related 100-kD coated vesicle proteins (alpha-adaptins). J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):833–842. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Silver J. E., Benjamin T. L. Tumor antigen(s) in cell productively infected by wild-type polyoma virus and mutant NG-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):79–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Vousden K. H., Lowy D. R. E5 open reading frame of bovine papillomavirus type 1 encodes a transforming gene. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.1-6.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Wade-Glass M., Rabson M. S., Yang Y. C. The E5 transforming gene of bovine papillomavirus encodes a small, hydrophobic polypeptide. Science. 1986 Jul 25;233(4762):464–467. doi: 10.1126/science.3014660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Schaffhausen B., Benjamin T. Tumor antigens induced by nontransforming mutants of polyoma virus. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):485–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velu T. J., Beguinot L., Vass W. C., Zhang K., Pastan I., Lowy D. R. Retroviruses expressing different levels of the normal epidermal growth factor receptor: biological properties and new bioassay. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Feb;39(2):153–166. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters C. M., Overholser K. A., Sorkin A., Carpenter G. Analysis of the influences of the E5 transforming protein on kinetic parameters of epidermal growth factor binding and metabolism. J Cell Physiol. 1992 Aug;152(2):253–263. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041520206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]