Abstract
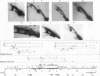
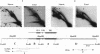
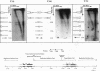
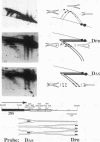
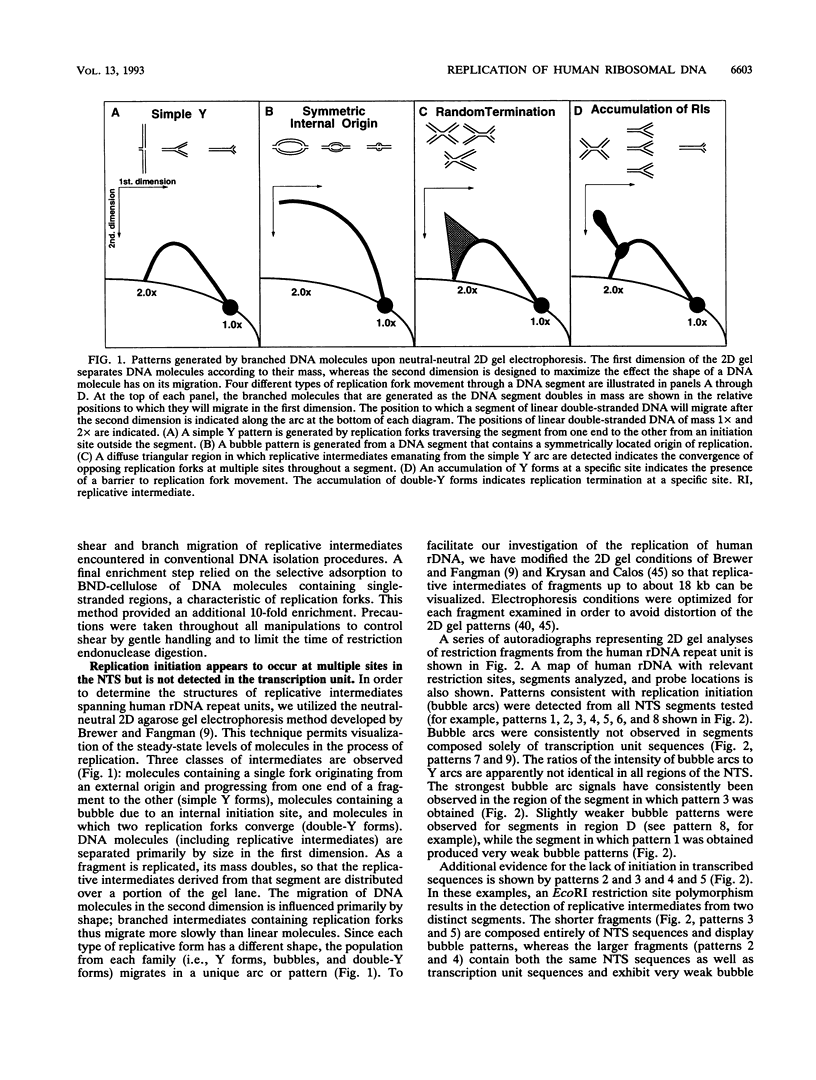
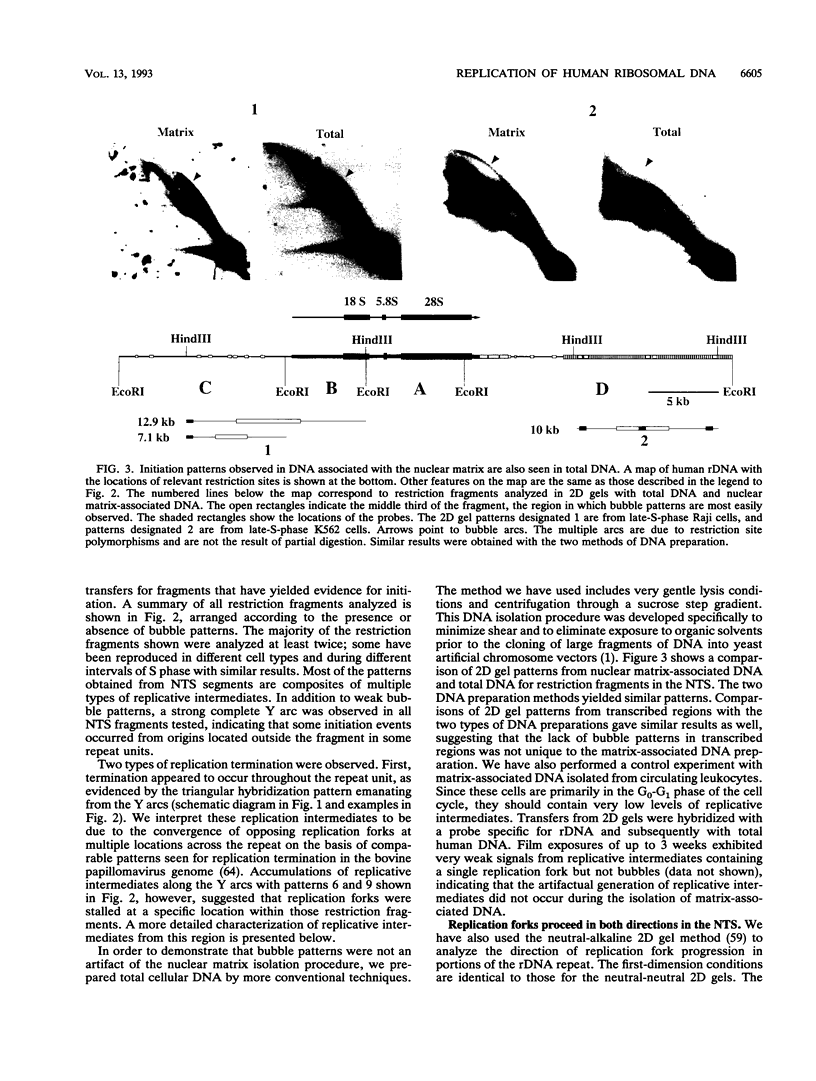
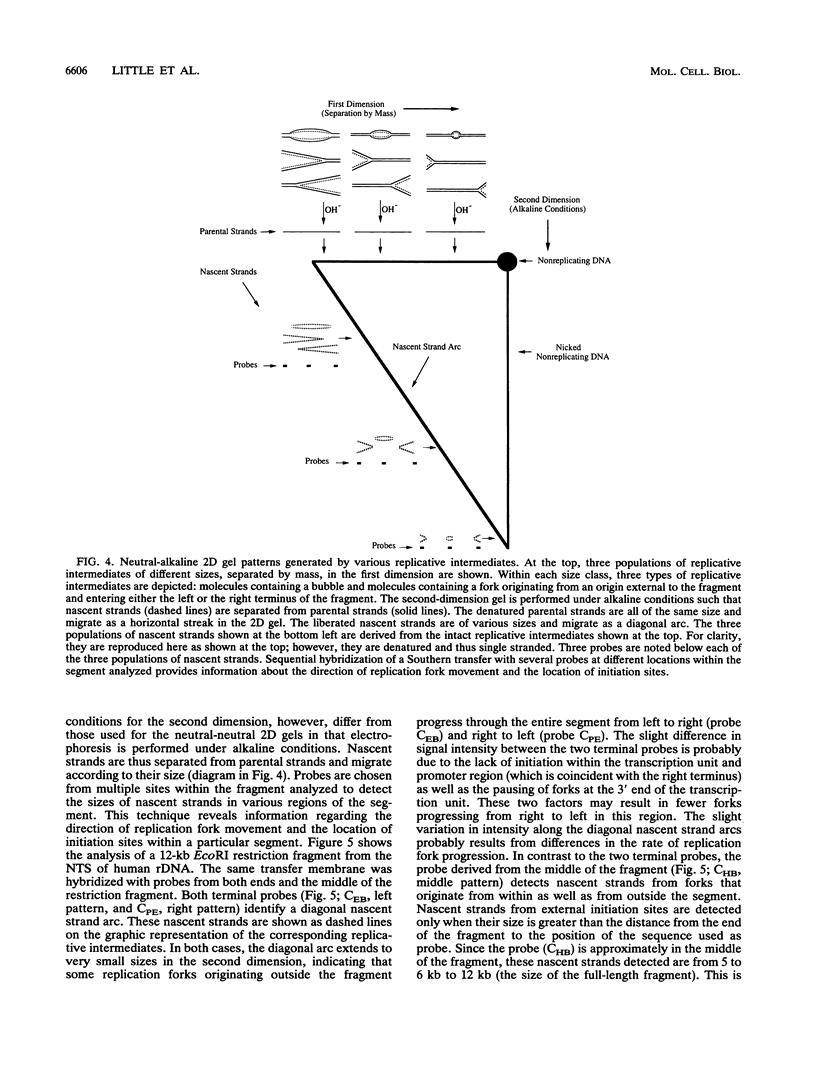
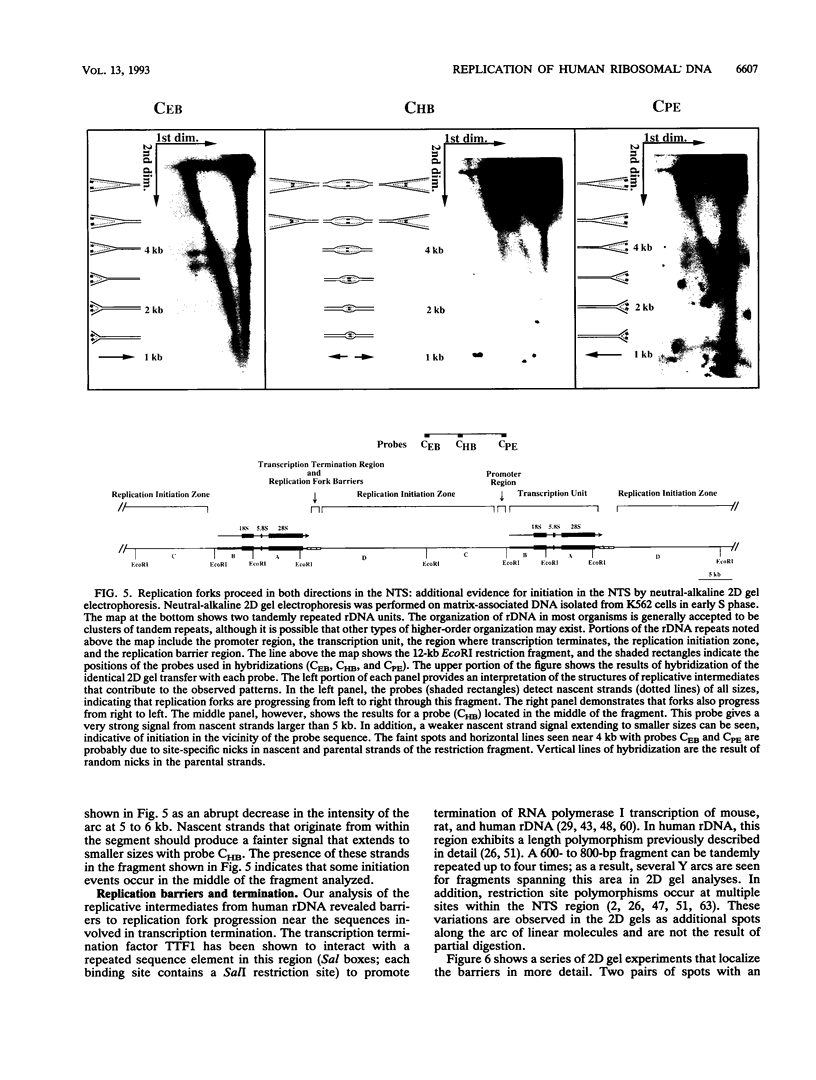
We have used the multicopy human rRNA genes as a model system to study replication initiation and termination in mammalian chromosomes. Enrichment for replicating molecules was achieved by isolating S-phase enriched populations of cells by centrifugal elutriation, purification of DNA associated with the nuclear matrix, and a chromatographic procedure that enriches for molecules containing single-stranded regions, a characteristic of replication forks. Two-dimensional agarose gel electrophoresis techniques were used to demonstrate that replication appears to initiate at multiple sites throughout most of the 31-kb nontranscribed spacer (NTS) of human ribosomal DNA but not within the 13-kb transcription unit or adjacent regulatory elements. Although initiation events were detected throughout the majority of the NTS, some regions may initiate more frequently than others. Termination of replication, the convergence of opposing replication forks, was found throughout the ribosomal DNA repeat units, and, in some repeats, specifically at the junction of the 3' end of the transcription unit and the NTS. This site-specific termination of replication is the result of pausing of replication forks near the sites of transcription termination. The naturally occurring multicopy rRNA gene family offers a unique system to study mammalian DNA replication without the use of chemical synchronization agents.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abidi F. E., Wada M., Little R. D., Schlessinger D. Yeast artificial chromosomes containing human Xq24-Xq28 DNA: library construction and representation of probe sequences. Genomics. 1990 Jul;7(3):363–376. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90170-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnheim N., Krystal M., Schmickel R., Wilson G., Ryder O., Zimmer E. Molecular evidence for genetic exchanges among ribosomal genes on nonhomologous chromosomes in man and apes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7323–7327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balazs L., Schildkraut C. L. DNA replication in synchronized cultured mammalian cells. II. Replication of ribosomal cistrons in thymidine-synchronized HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 14;57(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baran N., Lapidot A., Manor H. Formation of DNA triplexes accounts for arrests of DNA synthesis at d(TC)n and d(GA)n tracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):507–511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbow R. M., Zhao J., Larson D. D. On the nature of origins of DNA replication in eukaryotes. Bioessays. 1992 Oct;14(10):661–670. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P., Taggart M. H., Gehring C. A. Methylated and unmethylated ribosomal RNA genes in the mouse. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 15;152(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90092-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan P. M., Dayton A. I. A specific replication origin in the chromosomal rDNA of Lytechinus variegatus. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):453–456. doi: 10.1038/299453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzoni I., Baldari C. T., Amaldi F., Buongiorno-Nardelli M. Replication of ribosomal DNA in Xenopus laevis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;118(3):585–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. A replication fork barrier at the 3' end of yeast ribosomal RNA genes. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):637–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. The localization of replication origins on ARS plasmids in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):463–471. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Lockshon D., Fangman W. L. The arrest of replication forks in the rDNA of yeast occurs independently of transcription. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90355-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. H., Iqbal M. A., Stuart S., Hatton K. S., Valinsky J., Schildkraut C. L. Rate of replication of the murine immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus: evidence that the region is part of a single replicon. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):450–457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Vassilev L. T., Caddle M. S., Heintz N. H., DePamphilis M. L. Identification of an origin of bidirectional DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):955–965. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90270-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Vassilev L. T., Wu J., Sogo J. M., Nallaseth F. S., DePamphilis M. L. Emetine allows identification of origins of mammalian DNA replication by imbalanced DNA synthesis, not through conservative nucleosome segregation. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4351–4360. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conconi A., Widmer R. M., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Two different chromatin structures coexist in ribosomal RNA genes throughout the cell cycle. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90790-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dammann R., Lucchini R., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Chromatin structures and transcription of rDNA in yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2331–2338. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Origins of DNA replication in metazoan chromosomes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delidakis C., Kafatos F. C. Amplification enhancers and replication origins in the autosomal chorion gene cluster of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):891–901. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dershowitz A., Newlon C. S. The effect on chromosome stability of deleting replication origins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):391–398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Initiation of DNA replication in the dihydrofolate reductase locus is confined to the early S period in CHO cells synchronized with the plant amino acid mimosine. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3715–3722. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkwel P. A., Vaughn J. P., Hamlin J. L. Mapping of replication initiation sites in mammalian genomes by two-dimensional gel analysis: stabilization and enrichment of replication intermediates by isolation on the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3850–3859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenberg H. J., Huberman J. A. Eukaryotic chromosome replication. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:245–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. M., Schmickel R. D. A molecular basis for discrete size variation in human ribosomal DNA. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Mar;37(2):311–325. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fangman W. L., Brewer B. J. Activation of replication origins within yeast chromosomes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:375–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahn T. A., Schildkraut C. L. The Epstein-Barr virus origin of plasmid replication, oriP, contains both the initiation and termination sites of DNA replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Maier U., Ohrlein A., Hassouna N., Bachellerie J. P. Transcription of mouse rDNA terminates downstream of the 3' end of 28S RNA and involves interaction of factors with repeated sequences in the 3' spacer. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haaf T., Hayman D. L., Schmid M. Quantitative determination of rDNA transcription units in vertebrate cells. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Mar;193(1):78–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90540-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin J. L. Mammalian origins of replication. Bioessays. 1992 Oct;14(10):651–659. doi: 10.1002/bies.950141002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handeli S., Klar A., Meuth M., Cedar H. Mapping replication units in animal cells. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton K. S., Dhar V., Brown E. H., Iqbal M. A., Stuart S., Didamo V. T., Schildkraut C. L. Replication program of active and inactive multigene families in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2149–2158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Spradling A. C. Multiple replication origins are used during Drosophila chorion gene amplification. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):903–914. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel S. S., Krysan P. J., Tran C. T., Calos M. P. Autonomous DNA replication in human cells is affected by the size and the source of the DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2263–2272. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. M. Arrest of bacterial DNA replication. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:603–633. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.003131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyrien O., Méchali M. Plasmid replication in Xenopus eggs and egg extracts: a 2D gel electrophoretic analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1463–1469. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavathas P., Bach F. H., DeMars R. Gamma ray-induced loss of expression of HLA and glyoxalase I alleles in lymphoblastoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4251–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki K., Minoshima S., Kudoh J., Fukuyama R., Shimizu N. Methylation status of ribosomal RNA gene clusters in the flow-sorted human acrocentric chromosomes. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(3):173–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00352463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kermekchiev M. B., Grummt I. Natural point mutations within rat rDNA transcription terminator elements reveal the functional importance of single bases for factor binding and termination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4131–4143. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi T., Hidaka M., Nishizawa M., Horiuchi T. Identification of a site required for DNA replication fork blocking activity in the rRNA gene cluster in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jun;233(3):355–362. doi: 10.1007/BF00265431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krysan P. J., Calos M. P. Replication initiates at multiple locations on an autonomously replicating plasmid in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1464–1472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krysan P. J., Haase S. B., Calos M. P. Isolation of human sequences that replicate autonomously in human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1026–1033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal M., D'Eustachio P., Ruddle F. H., Arnheim N. Human nucleolus organizers on nonhomologous chromosomes can share the same ribosomal gene variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5744–5748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn A., Normann A., Bartsch I., Grummt I. The mouse ribosomal gene terminator consists of three functionally separable sequence elements. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1497–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02968.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunnath L., Locker J. Variable methylation of the ribosomal RNA genes of the rat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3877–3892. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Volpe A., Simeone A., D'Esposito M., Scotto L., Fidanza V., de Falco A., Boncinelli E. Molecular analysis of the heterogeneity region of the human ribosomal spacer. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90214-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidot A., Baran N., Manor H. (dT-dC)n and (dG-dA)n tracts arrest single stranded DNA replication in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):883–900. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leu T. H., Hamlin J. L. High-resolution mapping of replication fork movement through the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain in CHO cells by in-gel renaturation analysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):523–531. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang C., Spitzer J. D., Smith H. S., Gerbi S. A. Replication initiates at a confined region during DNA amplification in Sciara DNA puff II/9A. Genes Dev. 1993 Jun;7(6):1072–1084. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.6.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. Ambiguities in results obtained with 2D gel replicon mapping techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):647–652. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. Organization of replication of ribosomal DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4927–4935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linskens M. H., Huberman J. A. The two faces of higher eukaryotic DNA replication origins. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):845–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90258-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini R., Sogo J. M. Different chromatin structures along the spacers flanking active and inactive Xenopus rRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4288–4296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawotka K. A., Huberman J. A. Two-dimensional gel electrophoretic method for mapping DNA replicons. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1408–1413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. A STUDY OF MALIGNANT TUMOURS IN NIGERIA BY SHORT-TERM TISSUE CULTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:261–273. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfleiderer C., Smid A., Bartsch I., Grummt I. An undecamer DNA sequence directs termination of human ribosomal gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4727–4736. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer L. D., Miller O. L., Jr Electron microscopic study of Saccharomyces cerevisiae rDNA chromatin replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1148–1157. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safrany G., Hidvegi E. J. New tandem repeat region in the non-transcribed spacer of human ribosomal RNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3013–3022. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya T., Ina S. Analysis of chromosomal replicons in early embryos of Drosophila melanogaster by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3935–3941. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinomiya T., Ina S. DNA replication of histone gene repeats in Drosophila melanogaster tissue culture cells: multiple initiation sites and replication pause sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4098–4106. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett M. A., Gall J. G. The replication of ribosomal DNA in the macronucleus of Tetrahymena. Chromosoma. 1977 Dec 6;64(4):295–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00294937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustav M., Ustav E., Szymanski P., Stenlund A. Identification of the origin of replication of bovine papillomavirus and characterization of the viral origin recognition factor E1. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4321–4329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van 't Hof J., Lamm S. S. Site of initiation of replication of the ribosomal genes of pea (Pisum sativum) detected by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Nov;20(3):377–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00040597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L. T., Burhans W. C., DePamphilis M. L. Mapping an origin of DNA replication at a single-copy locus in exponentially proliferating mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4685–4689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. P., Dijkwel P. A., Hamlin J. L. Replication initiates in a broad zone in the amplified CHO dihydrofolate reductase domain. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1075–1087. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90071-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M., Braun R. The replication of ribosomal DNA in Physarum polycephalum. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Nov 1;80(2):557–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner M., Schwender S., Dinkl E., Grummt F. Interaction of a protein with a palindromic sequence from murine rDNA increases the occurrence of amplification-dependent transformation in mouse cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13925–13932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner M., Zastrow G., Klavinius A., Schwender S., Müller F., Luksza H., Hoppe J., Wienberg J., Grummt F. Cis-acting sequences from mouse rDNA promote plasmid DNA amplification and persistence in mouse cells: implication of HMG-I in their function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9909–9932. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worton R. G., Sutherland J., Sylvester J. E., Willard H. F., Bodrug S., Dubé I., Duff C., Kean V., Ray P. N., Schmickel R. D. Human ribosomal RNA genes: orientation of the tandem array and conservation of the 5' end. Science. 1988 Jan 1;239(4835):64–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3336775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Botchan M. Replication of bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA initiates within an E2-responsive enhancer element. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5903–5911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5903-5911.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Brun C., Kurooka H., Yanagida M., Huberman J. A. Identification and characterization of a complex chromosomal replication origin in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Chromosoma. 1992;102(1 Suppl):S7–16. doi: 10.1007/BF02451780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J., Newlon C. S., Huberman J. A. Localization of a DNA replication origin and termination zone on chromosome III of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4733–4741. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Capoa A., Aleixandre C., Felli M. P., Ravenna L., Costantino M. A., Giancotti P., Vicenti O., Poggesi I., Grappelli C., Miller D. A. Inheritance of ribosomal gene activity and level of DNA methylation of individual gene clusters in a three generation family. Hum Genet. 1991 Dec;88(2):146–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00206062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]