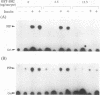
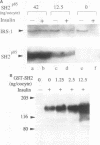
Abstract
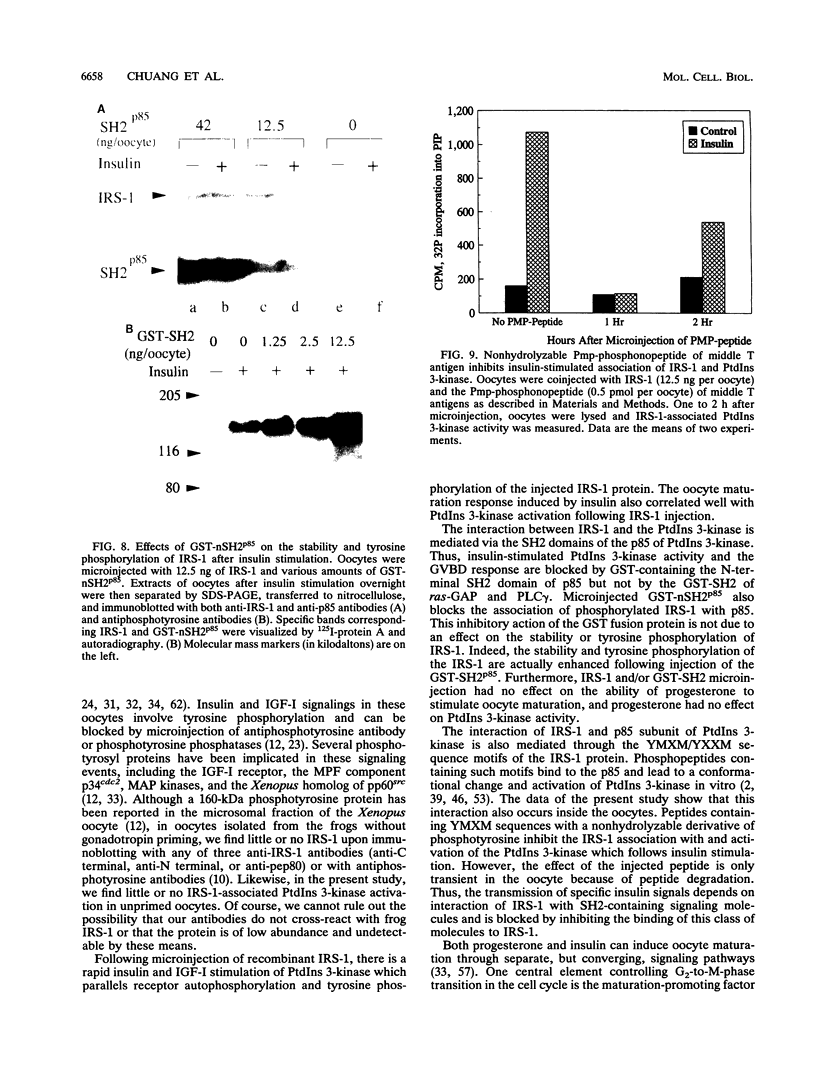
Xenopus oocytes from unprimed frogs possess insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) receptors but lack insulin and IGF-I receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1), the endogenous substrate of this kinase, and fail to show downstream responses to hormonal stimulation. Microinjection of recombinant IRS-1 protein enhances insulin-stimulated phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) 3-kinase activity and restores the germinal vesicle breakdown response. Activation of PtdIns 3-kinase results from formation of a complex between phosphorylated IRS-1 and the p85 subunit of PtdIns 3-kinase. Microinjection of a phosphonopeptide containing a pYMXM motif with high affinity for the src homology 2 (SH2) domain of PtdIns 3-kinase p85 inhibits IRS-1 association with and activation of the PtdIns 3-kinase. Formation of the IRS-1-PtdIns 3-kinase complex and insulin-stimulated PtdIns 3-kinase activation are also inhibited by microinjection of a glutathione S-transferase fusion protein containing the SH2 domain of p85. This effect occurs in a concentration-dependent fashion and results in a parallel loss of hormone-stimulated oocyte maturation. These inhibitory effects are specific and are not mimicked by glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins expressing the SH2 domains of ras-GAP or phospholipase C gamma. Moreover, injection of the SH2 domains of p85, ras-GAP, and phospholipase C gamma do not interfere with progesterone-induced oocyte maturation. These data demonstrate that phosphorylation of IRS-1 plays an essential role in IGF-I and insulin signaling in oocyte maturation and that this effect occurs through interactions of the phosphorylated YMXM/YXXM motifs of IRS-1 with SH2 domains of PtdIns 3-kinase or some related molecules.
Full text
PDF

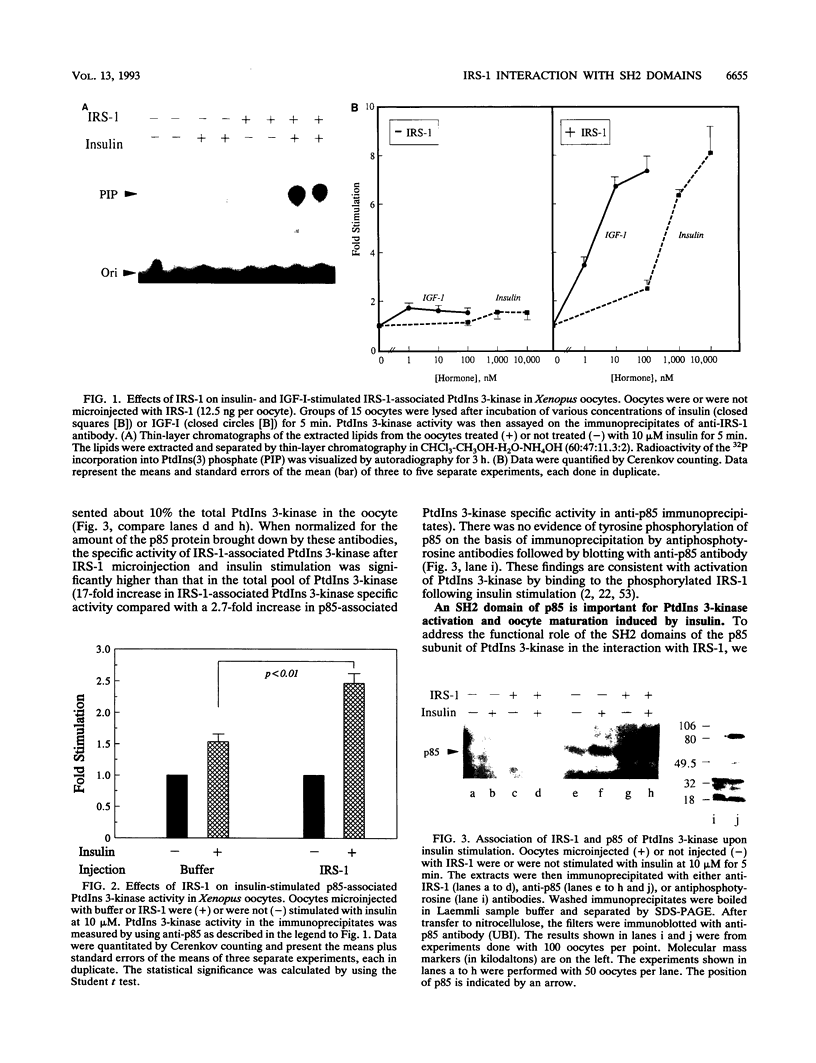

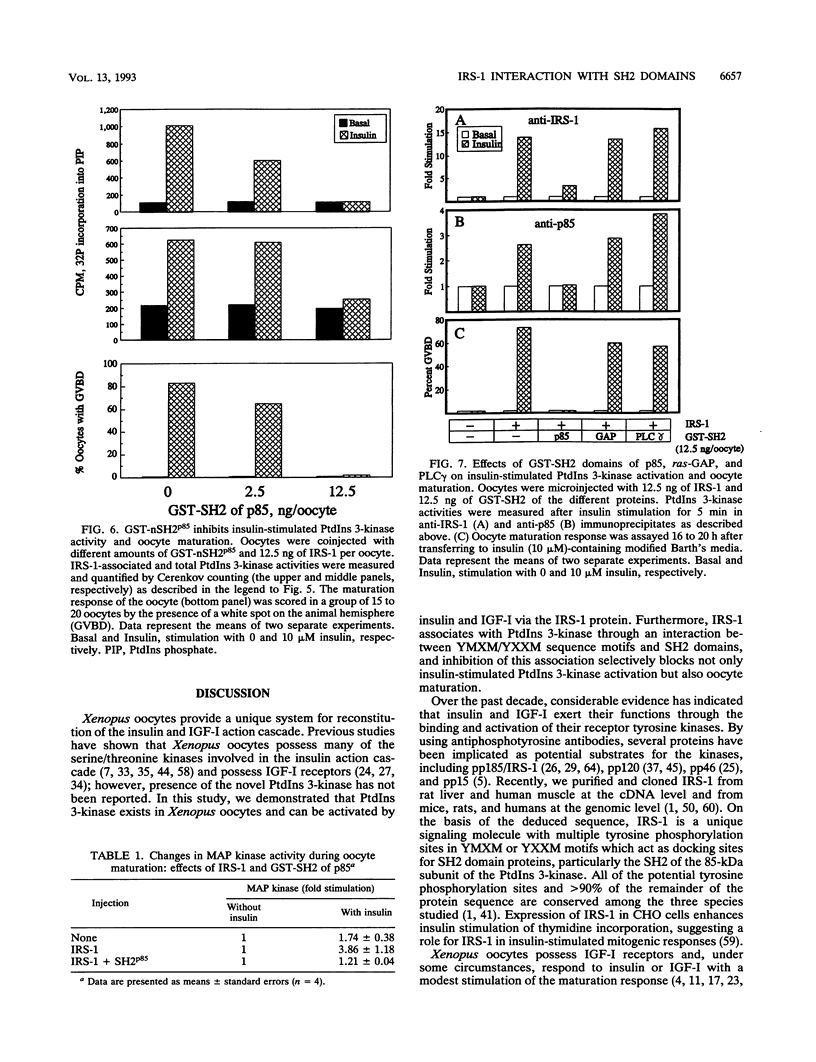


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki E., Sun X. J., Haag B. L., 3rd, Chuang L. M., Zhang Y., Yang-Feng T. L., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Human skeletal muscle insulin receptor substrate-1. Characterization of the cDNA, gene, and chromosomal localization. Diabetes. 1993 Jul;42(7):1041–1054. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.7.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Shoelson S. E., Chin D. J., Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3469–3479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Schroeder G. G., Kahn C. R., Myers M. G., Jr, Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., White M. F. Insulin stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity maps to insulin receptor regions required for endogenous substrate phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1367–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett C. B., Schroetke R. M., Van der Hoorn F. A., Nordeen S. K., Maller J. L. Ha-rasVal-12,Thr-59 activates S6 kinase and p34cdc2 kinase in Xenopus oocytes: evidence for c-mosxe-dependent and -independent pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):310–315. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernier M., Laird D. M., Lane M. D. Insulin-activated tyrosine phosphorylation of a 15-kilodalton protein in intact 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1844–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J. Identification of a novel gene encoding an insulin-responsive glucose transporter protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90968-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campa M. J., Glickman J. F., Yamamoto K., Chang K. J. The antibiotic azatyrosine suppresses progesterone or [Val12]p21 Ha-ras/insulin-like growth factor I-induced germinal vesicle breakdown and tyrosine phosphorylation of Xenopus mitogen-activated protein kinase in oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7654–7658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. K., Dull T. J., Russell D. S., Gherzi R., Lebwohl D., Ullrich A., Rosen O. M. Human insulin receptors mutated at the ATP-binding site lack protein tyrosine kinase activity and fail to mediate postreceptor effects of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang L. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Seidner G. A., Birnbaum M. J., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Insulin receptor substrate 1 mediates insulin and insulin-like growth factor I-stimulated maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5172–5175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Pelech S. L., Krebs E. G. Insulin and progesterone activate a common synthetic ribosomal protein S6 peptide kinase in Xenopus oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 5;241(1-2):195–201. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Weiel J. E., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. Microinjection of a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase inhibits insulin action in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5514–5518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Signal transmission by the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domchek S. M., Auger K. R., Chatterjee S., Burke T. R., Jr, Shoelson S. E. Inhibition of SH2 domain/phosphoprotein association by a nonhydrolyzable phosphonopeptide. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 20;31(41):9865–9870. doi: 10.1021/bi00156a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Araki E., Taira M., Shimada F., Mori M., Craik C. S., Siddle K., Pierce S. B., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of lysine residue 1030 in the putative ATP-binding region of the insulin receptor abolishes insulin- and antibody-stimulated glucose uptake and receptor kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Etr M., Schorderet-Slatkine S., Baulieu E. E. Meiotic maturation in Xenopus laevis oocytes initiated by insulin. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1397–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.472755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endemann G., Yonezawa K., Roth R. A. Phosphatidylinositol kinase or an associated protein is a substrate for the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):396–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Martin G. A., Turck C. W., del Rosario M., McCormick F., Williams L. T. Distinct phosphotyrosines on a growth factor receptor bind to specific molecules that mediate different signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90444-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folli F., Saad M. J., Backer J. M., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity and association with insulin receptor substrate 1 in liver and muscle of the intact rat. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22171–22177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainaut P., Giorgetti S., Kowalski A., Ballotti R., Van Obberghen E. Antibodies to phosphotyrosine injected in Xenopus laevis oocytes modulate maturation induced by insulin/IGF-I. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Jul;195(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90508-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainaut P., Kowalski A., Giorgetti S., Baron V., Van Obberghen E. Insulin and insulin-like-growth-factor-I (IGF-I) receptors in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Comparison with insulin receptors from liver and muscle. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):673–678. doi: 10.1042/bj2730673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H. SH2 domains: elements that control protein interactions during signal transduction. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):450–452. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90175-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi T., White M. F., Kadowaki T., Takaku F., Akanuma Y., Kasuga M. Insulin-like growth factor I rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a Mr 185,000 protein in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1282–1287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janicot M., Flores-Riveros J. R., Lane M. D. The insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) receptor is responsible for mediating the effects of insulin, IGF-1, and IGF-2 in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9382–9391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of the 95,000-dalton subunit of its own receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.7031900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller S. R., Kitagawa K., Aebersold R., Lienhard G. E., Garner C. W. Isolation and characterization of the 160,000-Da phosphotyrosyl protein, a putative participant in insulin signaling. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12817–12820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Siebel C. W., McCormick F., Roth R. A. Ras p21 as a potential mediator of insulin action in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):840–843. doi: 10.1126/science.3554510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Goascogne C., Hirai S., Baulieu E. E. Induction of germinal vesicle breakdown in Xenopus laevis oocytes: synergistic action of progesterone and insulin. J Endocrinol. 1984 Apr;101(1):7–12. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1010007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Koontz J. W. A study of the induction of cell division in amphibian oocytes by insulin. Dev Biol. 1981 Jul 30;85(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L., Pike L. J., Freidenberg G. R., Cordera R., Stith B. J., Olefsky J. M., Krebs E. G. Increased phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 following microinjection of insulin receptor-kinase into Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):459–461. doi: 10.1038/320459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J. L. Xenopus oocytes and the biochemistry of cell division. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3157–3166. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B. Proteins with SH2 domains: transducers in the tyrosine kinase signaling pathway. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Jan;3(1):73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. N., Schell M. J., Taylor S. I., Hubbard A. L. Hepatocyte plasma membrane ECTO-ATPase (pp120/HA4) is a substrate for tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 30;166(2):562–566. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90845-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Ho L., Korn L. J., Roth R. A. Insulin action is blocked by a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the insulin receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):328–332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, Backer J. M., Sun X. J., Shoelson S., Hu P., Schlessinger J., Yoakim M., Schaffhausen B., White M. F. IRS-1 activates phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase by associating with src homology 2 domains of p85. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10350–10354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, Sun X. J., Cheatham B., Jachna B. R., Glasheen E. M., Backer J. M., White M. F. IRS-1 is a common element in insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I signaling to the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase. Endocrinology. 1993 Apr;132(4):1421–1430. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.4.8384986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama M., Wands J. R. Cloning and increased expression of an insulin receptor substrate-1-like gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 28;183(1):280–285. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91640-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. MAP kinases: charting the regulatory pathways. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1355–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.1382311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrotti N., Accili D., Marcus-Samuels B., Rees-Jones R. W., Taylor S. I. Insulin stimulates phosphorylation of a 120-kDa glycoprotein substrate (pp120) for the receptor-associated protein kinase in intact H-35 hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3137–3140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccione E., Case R. D., Domchek S. M., Hu P., Chaudhuri M., Backer J. M., Schlessinger J., Shoelson S. E. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase p85 SH2 domain specificity defined by direct phosphopeptide/SH2 domain binding. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 6;32(13):3197–3202. doi: 10.1021/bi00064a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice K. M., Lienhard G. E., Garner C. W. Regulation of the expression of pp160, a putative insulin receptor signal protein, by insulin, dexamethasone, and 1-methyl-3-isobutylxanthine in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):10163–10167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M. Cell biology. A signal chain of events. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):534–535. doi: 10.1038/360534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M. After insulin binds. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1452–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2442814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg P. L., Lane W. S., Karasik A., Backer J., White M., Kahn C. R. Purification and partial sequence analysis of pp185, the major cellular substrate of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8302–8311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Kapeller R., White M. F., Cantley L. C. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad M. J., Araki E., Miralpeix M., Rothenberg P. L., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Regulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 in liver and muscle of animal models of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1839–1849. doi: 10.1172/JCI116060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoelson S. E., Sivaraja M., Williams K. P., Hu P., Schlessinger J., Weiss M. A. Specific phosphopeptide binding regulates a conformational change in the PI 3-kinase SH2 domain associated with enzyme activation. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):795–802. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjölander A., Yamamoto K., Huber B. E., Lapetina E. G. Association of p21ras with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):7908–7912. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.7908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. D. The induction of oocyte maturation: transmembrane signaling events and regulation of the cell cycle. Development. 1989 Dec;107(4):685–699. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Wu J. Recent progress in characterization of protein kinase cascades for phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 17;1092(3):350–357. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(97)90012-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Myers M. G., Jr, Glasheen E. M., Backer J. M., Kahn C. R., White M. F. Expression and function of IRS-1 in insulin signal transmission. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22662–22672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vera J. C., Rosen O. M. Reconstitution of an insulin signaling pathway in Xenopus laevis oocytes: coexpression of a mammalian insulin receptor and three different mammalian hexose transporters. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):743–751. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Maron R., Kahn C. R. Insulin rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a Mr-185,000 protein in intact cells. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):183–186. doi: 10.1038/318183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden P. A., Siddle K., Haring E., Backer J. M., White M. F., Kahn C. R. The role of insulin receptor kinase domain autophosphorylation in receptor-mediated activities. Analysis with insulin and anti-receptor antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13719–13727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries-Smits A. M., Burgering B. M., Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J., Bos J. L. Involvement of p21ras in activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):602–604. doi: 10.1038/357602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]