Abstract
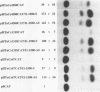
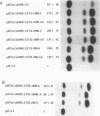
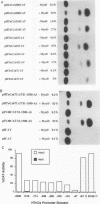
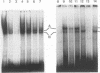
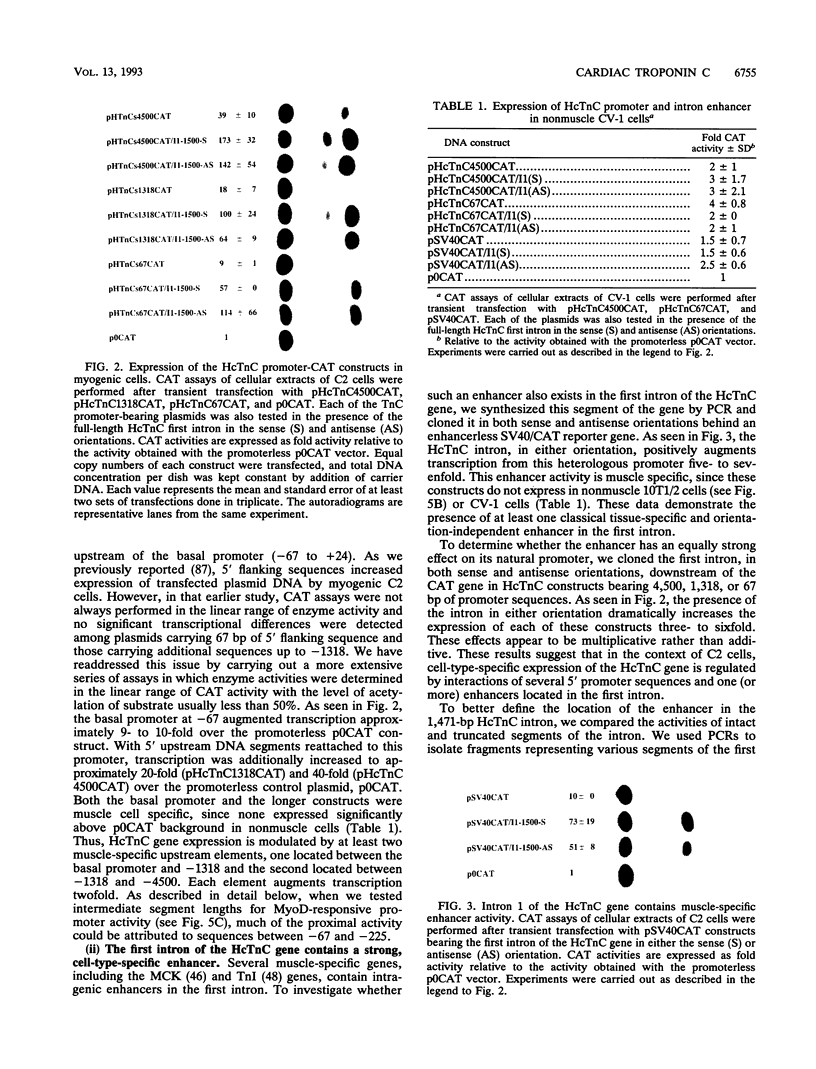
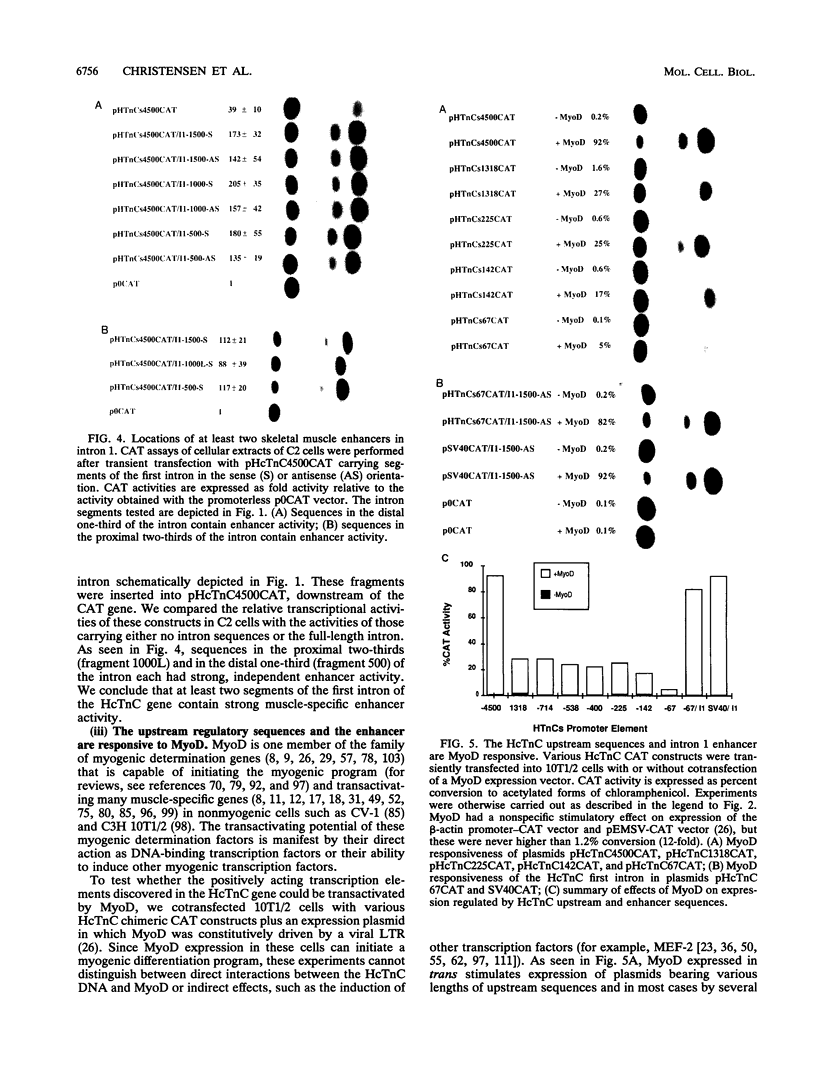
The cardiac troponin C (cTnC) gene produces identical transcripts in slow-twitch skeletal muscle and in heart muscle (R. Gahlmann, R. Wade, P. Gunning, and L. Kedes, J. Mol. Biol. 201:379-391, 1988). A separate gene encodes the fast-twitch skeletal muscle troponin C and is not expressed in heart muscle. We have used transient transfection to characterize the regulatory elements responsible for skeletal and cardiac cell-type-specific expression of the human cTnC (HcTnC) gene. At least four separate elements cooperate to confer tissue-specific expression of this gene in differentiated myotubes; a basal promoter (between -61 and -13) augments transcription 9-fold, upstream major regulatory sequences (between -68 and -142 and between -1319 and -4500) augment transcription as much as 39-fold, and at least two enhancer-like elements in the first intron (between +58 and +1028 and between +1029 and +1523) independently augment transcription 4- to 5-fold. These enhancers in the first intron increase myotube-specific chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity when linked to their own promoter elements or to the heterologous simian virus 40 promoter, and the effects are multiplicative rather than additive. Each of the major myotube regulatory regions is capable of responding directly or indirectly to the myogenic determination factor, MyoD.A MyoD expression vector in 10T1/2 cells induced constructs carrying either the upstream HcTnC promoter elements or the first intron of the gene 300- to 500-fold. Expression was inhibited by cotransfection with Id, a negative regulator of basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors. The basal promoter contains five tandem TGGGC repeats that interact with Sp1 or an Sp1-like factor in nuclear extracts. Mutational analysis of this element demonstrated that two of the five repeat sequences were sufficient to support basal level muscle cell-specific transcription. Whereas the basal promoter is also critical for expression in cardiac myocytes, the elements upstream of -67 appear to play little or no role. Major augmentation of expression in cardiomyocytes is also provided by sequences in the first intron, but these are upstream (between +58 and +1028). The downstream segment of the first intron has no enhancer activity in cardiomyocytes. A specific DNA-protein complex is formed by this C2 cell enhancer with extracts from C2 cells but not cardiomyocytes. These observations suggest that tissue-specific expression of the HcTnC gene is cooperatively regulated by the complex interactions of multiple regulatory elements and that different elements are used to regulate expression in myogenic and cardiac cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adolph E. A., Subramaniam A., Cserjesi P., Olson E. N., Robbins J. Role of myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor (MEF-2) in transcriptional regulation of the alpha-cardiac myosin heavy chain gene. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5349–5352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold H. H., Tannich E., Paterson B. M. The promoter of the chicken cardiac myosin light chain 2 gene shows cell-specific expression in transfected primary cultures of chicken muscle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2411–2429. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babu A., Sonnenblick E., Gulati J. Molecular basis for the influence of muscle length on myocardial performance. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):74–76. doi: 10.1126/science.3353709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassel-Duby R., Hernandez M. D., Gonzalez M. A., Krueger J. K., Williams R. S. A 40-kilodalton protein binds specifically to an upstream sequence element essential for muscle-specific transcription of the human myoglobin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5024–5032. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. M., Miwa T., Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. Identification and characterization of a factor that binds to two human sarcomeric actin promoters. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1284–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boxer L. M., Prywes R., Roeder R. G., Kedes L. The sarcomeric actin CArG-binding factor is indistinguishable from the c-fos serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):515–522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Winter B., Rosenthal N., Arnold H. H. Myf-6, a new member of the human gene family of myogenic determination factors: evidence for a gene cluster on chromosome 12. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):821–831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Tannich E., Buschhausen-Denker G., Arnold H. H. Promoter upstream elements of the chicken cardiac myosin light-chain 2-A gene interact with trans-acting regulatory factors for muscle-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2513–2525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T. J., Edmondson D. G., Li L., Olson E. N. Transforming growth factor beta represses the actions of myogenin through a mechanism independent of DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3822–3826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T. J., Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. Aberrant regulation of MyoD1 contributes to the partially defective myogenic phenotype of BC3H1 cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):929–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher E. A., Maisonpierre P. C., Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr Expression of the troponin complex genes: transcriptional coactivation during myoblast differentiation and independent control in heart and skeletal muscles. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4134–4142. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham M. E. Actin and myosin multigene families: their expression during the formation of skeletal muscle. Essays Biochem. 1985;20:77–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D. Identification of a myocyte nuclear factor that binds to the muscle-specific enhancer of the mouse muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2627–2640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Brennan T. J., Li L., Edmondson D., Olson E. N. Inefficient homooligomerization contributes to the dependence of myogenin on E2A products for efficient DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3633–3641. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty T., Brennan T., Olson E. Differential trans-activation of a muscle-specific enhancer by myogenic helix-loop-helix proteins is separable from DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2878–2882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. A., Ordahl C. P. A single cardiac troponin T gene generates embryonic and adult isoforms via developmentally regulated alternate splicing. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11140–11148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. A., Ordahl C. P. A single troponin T gene regulated by different programs in cardiac and skeletal muscle development. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.6095446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserjesi P., Olson E. N. Myogenin induces the myocyte-specific enhancer binding factor MEF-2 independently of other muscle-specific gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Rosales R., Staub A., Chambon P. The HeLa cell protein TEF-1 binds specifically and cooperatively to two SV40 enhancer motifs of unrelated sequence. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):931–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhoot G. K., Perry S. V. The effect of denervation on the distribution of the polymorphic forms of troponin components in fast and slow muscles of the adult rat. Cell Tissue Res. 1982;225(1):201–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00216229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frampton J., Walker M., Plumb M., Harrison P. R. Synergy between the NF-E1 erythroid-specific transcription factor and the CACCC factor in the erythroid-specific promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3838–3842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French B. A., Chow K. L., Olson E. N., Schwartz R. J. Heterodimers of myogenic helix-loop-helix regulatory factors and E12 bind a complex element governing myogenic induction of the avian cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2439–2450. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahlmann R., Kedes L. Cloning, structural analysis, and expression of the human fast twitch skeletal muscle troponin C gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12520–12528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahlmann R., Kedes L. Cloning, structural analysis, and expression of the human fast twitch skeletal muscle troponin C gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12520–12528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahlmann R., Kedes L. Tissue-specific restriction of skeletal muscle troponin C gene expression. Gene Expr. 1993;3(1):11–25. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahlmann R., Wade R., Gunning P., Kedes L. Differential expression of slow and fast skeletal muscle troponin C. Slow skeletal muscle troponin C is expressed in human fibroblasts. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 20;201(2):379–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray H. B., Jr, Ostrander D. A., Hodnett J. L., Legerski R. J., Robberson D. L. Extracellular nucleases of Pseudomonas BAL 31. I. Characterization of single strand-specific deoxyriboendonuclease and double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Sep;2(9):1459–1492. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.9.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Leavitt J., Muscat G., Ng S. Y., Kedes L. A human beta-actin expression vector system directs high-level accumulation of antisense transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4831–4835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. Identification of multiple proteins that interact with functional regions of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3269–3283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R., Weintraub H. Translation of mRNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is specifically inhibited by antisense RNA. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1094–1099. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood N. D., Pluck A., Gurdon J. B. MyoD expression in the forming somites is an early response to mesoderm induction in Xenopus embryos. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3409–3417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENSEN F. C., GIRARDI A. J., GILDEN R. V., KOPROWSKI H. INFECTION OF HUMAN AND SIMIAN TISSUE CULTURES WITH ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:53–59. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson P. D., Evans T., Nickol J. M., Felsenfeld G. Developmental modulation of protein binding to beta-globin gene regulatory sites within chicken erythrocyte nuclei. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1860–1873. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., Johnson J. E., Buskin J. N., Gartside C. L., Hauschka S. D. The muscle creatine kinase gene is regulated by multiple upstream elements, including a muscle-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):62–70. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. E., Wold B. J., Hauschka S. D. Muscle creatine kinase sequence elements regulating skeletal and cardiac muscle expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3393–3399. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr Complex regulation of the muscle-specific contractile protein (troponin I) gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3065–3075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Buskin J. N., Lockshon D., Davis R. L., Apone S., Hauschka S. D., Weintraub H. MyoD is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein requiring a region of myc homology to bind to the muscle creatine kinase enhancer. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):823–831. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90935-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Davis R. L., Wright W. E., Kadesch T., Murre C., Voronova A., Baltimore D., Weintraub H. Functional activity of myogenic HLH proteins requires hetero-oligomerization with E12/E47-like proteins in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90620-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. R., Henderson S. A., Reynolds R., Dunnmon P., Yuan D., Chien K. R. Alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation of cardiac gene transcription in neonatal rat myocardial cells. Effects on myosin light chain-2 gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 25;263(15):7352–7358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Yutzey K. E., Konieczny S. F. Muscle-specific expression of the troponin I gene requires interactions between helix-loop-helix muscle regulatory factors and ubiquitous transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):267–280. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Antin P. B., Cooper T. A., Ordahl C. P. Analysis of the upstream regions governing expression of the chicken cardiac troponin T gene in embryonic cardiac and skeletal muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):573–585. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar J. H., Ordahl C. P. A conserved CATTCCT motif is required for skeletal muscle-specific activity of the cardiac troponin T gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6404–6408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. F., Schwarz J. J., Olson E. N. Myocyte enhancer factor (MEF) 2C: a tissue-restricted member of the MEF-2 family of transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5282–5286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott J. C., Cardoso M. C., Yu Y. T., Andres V., Leifer D., Krainc D., Lipton S. A., Nadal-Ginard B. hMEF2C gene encodes skeletal muscle- and brain-specific transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2564–2577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. Herculin, a fourth member of the MyoD family of myogenic regulatory genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. Upstream sequences required for tissue-specific activation of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus laevis embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3185–3193. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Taylor M. V., Garrett N., Gurdon J. B. The CArG promoter sequence is necessary for muscle-specific transcription of the cardiac actin gene in Xenopus embryos. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1153–1161. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. L., Lauer M. R., Giulian G. G., Greaser M. L. Altered Ca2+ dependence of tension development in skinned skeletal muscle fibers following modification of troponin by partial substitution with cardiac troponin C. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):6096–6099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Wold B. In vivo footprinting of a muscle specific enhancer by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):780–786. doi: 10.1126/science.2814500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K., Faloona F., Scharf S., Saiki R., Horn G., Erlich H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: the polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):263–273. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat G. E., Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. A common factor regulates skeletal and cardiac alpha-actin gene transcription in muscle. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4120–4133. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat G. E., Perry S., Prentice H., Kedes L. The human skeletal alpha-actin gene is regulated by a muscle-specific enhancer that binds three nuclear factors. Gene Expr. 1992;2(2):111–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatsuji Y., Hidaka K., Tsujino S., Yamamoto Y., Mukai T., Yanagihara T., Kishimoto T., Sakoda S. A single MEF-2 site is a major positive regulatory element required for transcription of the muscle-specific subunit of the human phosphoglycerate mutase gene in skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4384–4390. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navankasattusas S., Zhu H., Garcia A. V., Evans S. M., Chien K. R. A ubiquitous factor (HF-1a) and a distinct muscle factor (HF-1b/MEF-2) form an E-box-independent pathway for cardiac muscle gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1469–1479. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. MyoD family: a paradigm for development? Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1454–1461. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmacek M. S., Leiden J. M. Structure and expression of the murine slow/cardiac troponin C gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13217–13225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmacek M. S., Leiden J. M. Structure, function, and regulation of troponin C. Circulation. 1991 Sep;84(3):991–1003. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.3.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmacek M. S., Vora A. J., Shen T., Barr E., Jung F., Leiden J. M. Identification and characterization of a cardiac-specific transcriptional regulatory element in the slow/cardiac troponin C gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):1967–1976. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Bessereau J. L., Huchet M., Changeux J. P. Two adjacent MyoD1-binding sites regulate expression of the acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit gene. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):353–355. doi: 10.1038/345353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quitschke W. W., DePonti-Zilli L., Lin Z. Y., Paterson B. M. Identification of two nuclear factor-binding domains on the chicken cardiac actin promoter: implications for regulation of the gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3218–3230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff C. A., Brankow D. W., Heidelberger C. Establishment and characterization of a cloned line of C3H mouse embryo cells sensitive to postconfluence inhibition of division. Cancer Res. 1973 Dec;33(12):3231–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Identification of MRF4: a new member of the muscle regulatory factor gene family. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2050–2061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N., Berglund E. B., Wentworth B. M., Donoghue M., Winter B., Bober E., Braun T., Arnold H. H. A highly conserved enhancer downstream of the human MLC1/3 locus is a target for multiple myogenic determination factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6239–6246. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. Muscle cell differentiation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;1(6):1094–1101. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli V., Hong N. A., Bishopric N. H., Kedes L. Myocardial activation of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter by helix-loop-helix proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4047–4051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli V., Kurabayashi M., Kedes L. Muscle-specific gene expression. A comparison of cardiac and skeletal muscle transcription strategies. Circ Res. 1993 May;72(5):925–931. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.5.925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorelli V., Webster K. A., Kedes L. Muscle-specific expression of the cardiac alpha-actin gene requires MyoD1, CArG-box binding factor, and Sp1. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1811–1822. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D., Lyons G., Wright W. E., Lin V., Lassar A., Weintraub H., Buckingham M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoD1 during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):303–307. doi: 10.1038/341303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Otsuka-Murakami H., Renkawitz R. Cooperativity of the glucocorticoid receptor and the CACCC-box binding factor. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):87–90. doi: 10.1038/332087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakata M., Nabeshima Y., Konishi K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Upstream regulatory region for inducible expression of the chicken skeletal myosin alkali light-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2581–2588. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P., Savion S. Differentiation of rat myocytes in single cell cultures with and without proliferating nonmyocardial cells. Cross-striations, ultrastructure, and chronotropic response to isoproterenol. Circ Res. 1982 Jan;50(1):101–116. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Weintraub H. MyoD and the regulation of myogenesis by helix-loop-helix proteins. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1133–1138. doi: 10.1172/JCI115109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Erba H. P., Muscat G. E., Kedes L. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the human skeletal alpha-actin gene: evolution of functional regulatory domains. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):323–336. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification and purification of a polypeptide that binds to the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2711–2717. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02564.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade R., Kedes L. Developmental regulation of contractile protein genes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:179–188. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Lockshon D., Lassar A. MyoD binds cooperatively to two sites in a target enhancer sequence: occupancy of two sites is required for activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5623–5627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Davis R., Tapscott S., Thayer M., Krause M., Benezra R., Blackwell T. K., Turner D., Rupp R., Hollenberg S. The myoD gene family: nodal point during specification of the muscle cell lineage. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):761–766. doi: 10.1126/science.1846704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Tapscott S. J., Davis R. L., Thayer M. J., Adam M. A., Lassar A. B., Miller A. D. Activation of muscle-specific genes in pigment, nerve, fat, liver, and fibroblast cell lines by forced expression of MyoD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth B. M., Donoghue M., Engert J. C., Berglund E. B., Rosenthal N. Paired MyoD-binding sites regulate myosin light chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1242–1246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. J., Arnheim N., Erlich H. A. The polymerase chain reaction. Trends Genet. 1989 Jun;5(6):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson J. M. Troponin C from rabbit slow skeletal and cardiac muscle is the product of a single gene. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(1):179–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04302.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Admon A., Lüscher B., Tjian R. Cloning and expression of AP-2, a cell-type-specific transcription factor that activates inducible enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12A):1557–1569. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12a.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Ferrandon D., Rosales R., Vigneron M., Macchi M., Ruffenach F., Chambon P. One cell-specific and three ubiquitous nuclear proteins bind in vitro to overlapping motifs in the domain B1 of the SV40 enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3005–3013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Macchi M., Rosales R., Vigneron M., Staub A., Chambon P. In vitro binding of several cell-specific and ubiquitous nuclear proteins to the GT-I motif of the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Oct;1(8):794–807. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.8.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Matthes H., Garnier J. M., Chambon P. Cloning, expression, and transcriptional properties of the human enhancer factor TEF-1. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):551–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90088-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. A myogenic cell line with altered serum requirements for differentiation. Differentiation. 1977;7(3):159–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1977.tb01507.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Breitbart R. E., Smoot L. B., Lee Y., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Human myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2 comprises a group of tissue-restricted MADS box transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Sep;6(9):1783–1798. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.9.1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu H., Garcia A. V., Ross R. S., Evans S. M., Chien K. R. A conserved 28-base-pair element (HF-1) in the rat cardiac myosin light-chain-2 gene confers cardiac-specific and alpha-adrenergic-inducible expression in cultured neonatal rat myocardial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2273–2281. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu H., Nguyen V. T., Brown A. B., Pourhosseini A., Garcia A. V., van Bilsen M., Chien K. R. A novel, tissue-restricted zinc finger protein (HF-1b) binds to the cardiac regulatory element (HF-1b/MEF-2) in the rat myosin light-chain 2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4432–4444. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]