Abstract
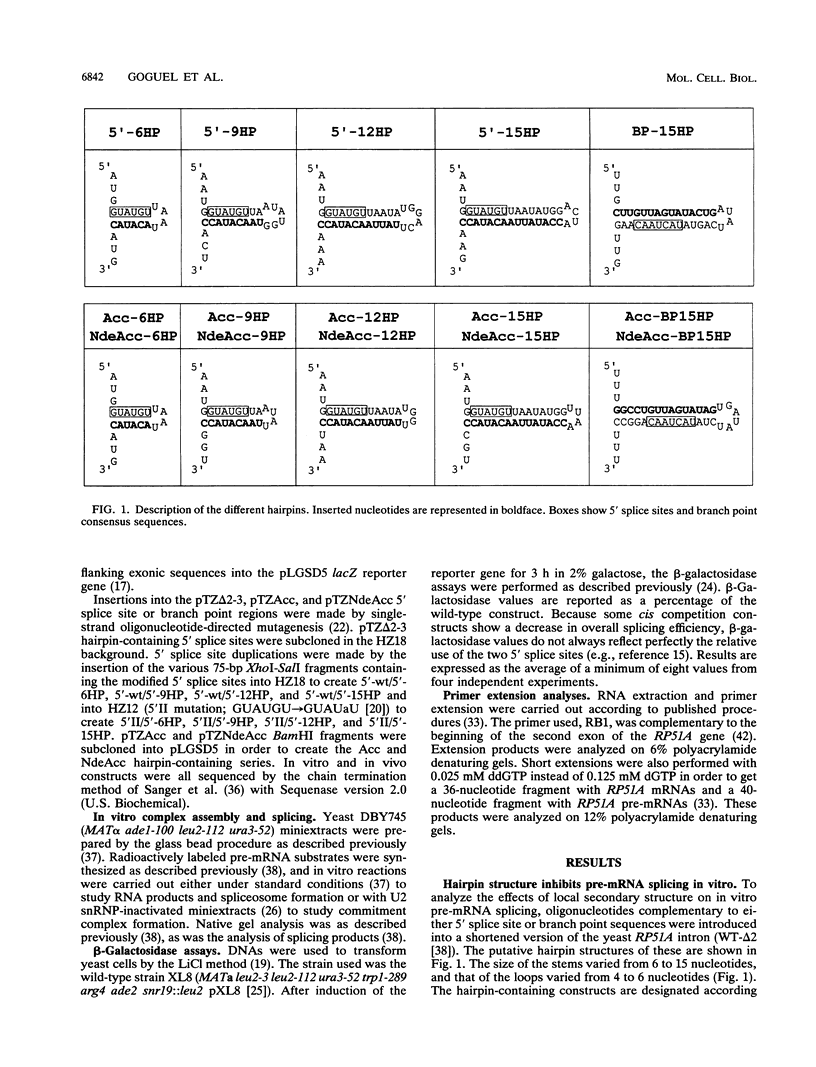
To examine the stability of yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) pre-mRNA structures, we inserted a series of small sequence elements that generated potential RNA hairpins at the 5' splice site and branch point regions. We analyzed spliceosome assembly and splicing in vitro as well as splicing and nuclear pre-mRNA retention in vivo. Surprisingly, the inhibition of in vivo splicing approximately paralleled that of in vitro splicing. Even a 6-nucleotide hairpin could be shown to inhibit splicing, and a 15-nucleotide hairpin gave rise to almost complete inhibition. The in vitro results indicate that hairpins that sequester the 5' splice site have a major effect on the early steps of spliceosome assembly, including U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein binding. The in vivo experiments lead to comparable conclusions as the sequestering hairpins apparently result in the transport of pre-mRNA to the cytoplasm. The observations are compared with previous data from both yeast and mammalian systems and suggest an important effect of pre-mRNA structure on in vivo splicing.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Padgett R. A., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Sequence requirements for splicing of higher eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The generality of self-splicing RNA: relationship to nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chebli K., Gattoni R., Schmitt P., Hildwein G., Stevenin J. The 216-nucleotide intron of the E1A pre-mRNA contains a hairpin structure that permits utilization of unusually distant branch acceptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4852–4861. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouet d'Orval B., d'Aubenton Carafa Y., Sirand-Pugnet P., Gallego M., Brody E., Marie J. RNA secondary structure repression of a muscle-specific exon in HeLa cell nuclear extracts. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1823–1828. doi: 10.1126/science.2063195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshler J. O., Rossi J. J. Unexpected point mutations activate cryptic 3' splice sites by perturbing a natural secondary structure within a yeast intron. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1252–1263. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domenjoud L., Gallinaro H., Kister L., Meyer S., Jacob M. Identification of a specific exon sequence that is a major determinant in the selection between a natural and a cryptic 5' splice site. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4581–4590. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Matunis M. J., Piñol-Roma S., Burd C. G. hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:289–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng F. J., Warner J. R. Structural basis for the regulation of splicing of a yeast messenger RNA. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):797–804. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90387-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon L. P., Estibeiro J. P., Eperon I. C. The role of nucleotide sequences in splice site selection in eukaryotic pre-messenger RNA. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):280–282. doi: 10.1038/324280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon L. P., Graham I. R., Griffiths A. D., Eperon I. C. Effects of RNA secondary structure on alternative splicing of pre-mRNA: is folding limited to a region behind the transcribing RNA polymerase? Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye G., Leung D. W., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Smith M. Deletion mapping of sequences essential for in vivo transcription of the iso-1-cytochrome c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. Y., Manley J. L. Factors influencing alternative splice site utilization in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):738–748. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furdon P. J., Kole R. The length of the downstream exon and the substitution of specific sequences affect pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):860–866. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego M. E., Nadal-Ginard B. Myosin light-chain 1/3 gene alternative splicing: cis regulation is based upon a hierarchical compatibility between splice sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2133–2144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguel V., Liao X. L., Rymond B. C., Rosbash M. U1 snRNP can influence 3'-splice site selection as well as 5'-splice site selection. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1430–1438. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguel V., Rosbash M. Splice site choice and splicing efficiency are positively influenced by pre-mRNA intramolecular base pairing in yeast. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):893–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90578-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Yocum R. R., Gifford P. A GAL10-CYC1 hybrid yeast promoter identifies the GAL4 regulatory region as an upstream site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfter H., Gallwitz D. Impairment of yeast pre-mRNA splicing by potential secondary structure-forming sequences near the conserved branchpoint sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10413–10423. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquier A., Rodriguez J. R., Rosbash M. A quantitative analysis of the effects of 5' junction and TACTAAC box mutants and mutant combinations on yeast mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):423–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühne T., Wieringa B., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Evidence against a scanning model of RNA splicing. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):727–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear A. L., Eperon L. P., Wheatley I. M., Eperon I. C. Hierarchy for 5' splice site preference determined in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 5;211(1):103–115. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90014-D. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrain P., Rosbash M. Some cis- and trans-acting mutants for splicing target pre-mRNA to the cytoplasm. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao X. L., Kretzner L., Seraphin B., Rosbash M. Universally conserved and yeast-specific U1 snRNA sequences are important but not essential for U1 snRNP function. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1766–1774. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libri D., Piseri A., Fiszman M. Y. Tissue-specific splicing in vivo of the beta-tropomyosin gene: dependence on an RNA secondary structure. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1842–1845. doi: 10.1126/science.2063196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Ohshima Y. Short donor site sequences inserted within the intron of beta-globin pre-mRNA serve for splicing in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4484–4491. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M. The yeast MATa1 gene contains two introns. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1061–1065. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. K., Green M. R. Splice site selection and ribonucleoprotein complex assembly during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):319–329. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. Specific accessory sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae introns control assembly of pre-mRNAs into spliceosomes. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3833–3839. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. mRNA splicing efficiency in yeast and the contribution of nonconserved sequences. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seraphin B., Rosbash M. Identification of functional U1 snRNA-pre-mRNA complexes committed to spliceosome assembly and splicing. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Alternative splicing caused by RNA secondary structure. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D., Lee S. I. Amount of RNA secondary structure required to induce an alternative splice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3194–3198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Splicing takes a holliday. Science. 1992 Aug 14;257(5072):888–889. doi: 10.1126/science.1386941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Rosbash M. The yeast branchpoint sequence is not required for the formation of a stable U1 snRNA-pre-mRNA complex and is recognized in the absence of U2 snRNA. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1209–1216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08062.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Expression of a beta-galactosidase gene containing the ribosomal protein 51 intron is sensitive to the rna2 mutation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4403–4407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gauss P., Thermes C., Groebe D. R., Gayle M., Guild N., Stormo G., d'Aubenton-Carafa Y., Uhlenbeck O. C., Tinoco I., Jr CUUCGG hairpins: extraordinarily stable RNA secondary structures associated with various biochemical processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1364–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulfendahl P. J., Kreivi J. P., Akusjärvi G. Role of the branch site/3'-splice site region in adenovirus-2 E1A pre-mRNA alternative splicing: evidence for 5'- and 3'-splice site co-operation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):925–938. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watakabe A., Inoue K., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. A secondary structure at the 3' splice site affects the in vitro splicing reaction of mouse immunoglobulin mu chain pre-mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8159–8169. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimatsu T., Nagawa F. Control of gene expression by artificial introns in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1346–1348. doi: 10.1126/science.2544026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]