Abstract
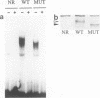
NGFI-A is an immediate-early gene that encodes a transcription factor whose DNA-binding domain is composed of three zinc fingers. To define the domains responsible for its transcriptional activity, a mutational analysis was conducted with an NGFI-A molecule in which the zinc fingers were replaced by the GAL4 DNA-binding domain. In a cotransfection assay, four activation domains were found within NGFI-A. Three of the activation domains are similar to those characterized previously: one contains a large number of acidic residues, another is enriched in proline and glutamine residues, and another has some sequence homology to a domain found in Krox-20. The fourth bears no resemblance to previously described activation domains. NGFI-A also contains an inhibitory domain whose removal resulted in a 15-fold increase in NGFI-A activity. This increase in activity occurred in all mammalian cell types tested but not in Drosophila S2 cells. Competition experiments in which increasing amounts of the inhibitory domain were cotransfected along with NGFI-A demonstrated a dose-dependent increase in NGFI-A activity. A point mutation within the inhibitory domain of the competitor (I293F) abolished this property. When the analogous mutation was introduced into native NGFI-A, a 17-fold increase in activity was observed. The inhibitory effect therefore appears to be the result of an interaction between this domain and a titratable cellular factor which is weakened by this mutation. Downmodulation of transcription factor activity through interaction with a cellular factor has been observed in several other systems, including the regulation of transcription factor E2F by retinoblastoma protein, and in studies of c-Jun.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. L., Minden A. G., Williams G. T., Bobonis C., Yeung C. Y. Functional significance of an overlapping consensus binding motif for Sp1 and Zif268 in the murine adenosine deaminase gene promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7523–7527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Park A., Tjian R. The cell-type-specific activator region of c-Jun juxtaposes constitutive and negatively regulated domains. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1493–1502. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Park A., Tjian R. v-Src and EJ Ras alleviate repression of c-Jun by a cell-specific inhibitor. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):165–168. doi: 10.1038/352165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Tjian R. Control of c-Jun activity by interaction of a cell-specific inhibitor with regulatory domain delta: differences between v- and c-Jun. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90147-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X. M., Koski R. A., Gashler A., McKiernan M., Morris C. F., Gaffney R., Hay R. V., Sukhatme V. P. Identification and characterization of the Egr-1 gene product, a DNA-binding zinc finger protein induced by differentiation and growth signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1931–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Vesque C., Galliot B., Vigneron M., Dollé P., Duboule D., Charnay P. The segment-specific gene Krox-20 encodes a transcription factor with binding sites in the promoter region of the Hox-1.4 gene. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1209–1218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. J., Klann E., Gower M. C., Powell C. M., Sessoms J. S., Sweatt J. D. Studies with synthetic peptide substrates derived from the neuronal protein neurogranin reveal structural determinants of potency and selectivity for protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 2;32(4):1032–1039. doi: 10.1021/bi00055a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B. A., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated in mouse 3T3 cells by serum growth factors encodes a protein with "zinc finger" sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7857–7861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy B., Nathans D. DNA binding site of the growth factor-inducible protein Zif268. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8737–8741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J. Critical structural elements of the VP16 transcriptional activation domain. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1846049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosby S. D., Puetz J. J., Simburger K. S., Fahrner T. J., Milbrandt J. The early response gene NGFI-C encodes a zinc finger transcriptional activator and is a member of the GCGGGGGCG (GSG) element-binding protein family. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):3835–3841. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.3835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosby S. D., Veile R. A., Donis-Keller H., Baraban J. M., Bhat R. V., Simburger K. S., Milbrandt J. Neural-specific expression, genomic structure, and chromosomal localization of the gene encoding the zinc-finger transcription factor NGFI-C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4739–4743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosby S. D., Veile R. A., Donis-Keller H., Baraban J. M., Bhat R. V., Simburger K. S., Milbrandt J. Neural-specific expression, genomic structure, and chromosomal localization of the gene encoding the zinc-finger transcription factor NGFI-C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6663–6663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day M. L., Fahrner T. J., Aykent S., Milbrandt J. The zinc finger protein NGFI-A exists in both nuclear and cytoplasmic forms in nerve growth factor-stimulated PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15253–15260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond I. A., Madden S. L., Rohwer-Nutter P., Bell G. I., Sukhatme V. P., Rauscher F. J., 3rd Repression of the insulin-like growth factor II gene by the Wilms tumor suppressor WT1. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):674–678. doi: 10.1126/science.1323141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta M. P., Gupta M., Zak R., Sukhatme V. P. Egr-1, a serum-inducible zinc finger protein, regulates transcription of the rat cardiac alpha-myosin heavy chain gene. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12813–12816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel P. A., Gill R. M., Phillips R. A., Gallie B. L. Transcriptional repression of the E2-containing promoters EIIaE, c-myc, and RB1 by the product of the RB1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3431–3438. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Karin M. The regulation of transcription by phosphorylation. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire P., Revelant O., Bravo R., Charnay P. Two mouse genes encoding potential transcription factors with identical DNA-binding domains are activated by growth factors in cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4691–4695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire P., Vesque C., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H., Frank R., Charnay P. The serum-inducible mouse gene Krox-24 encodes a sequence-specific transcriptional activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3456–3467. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. The carboxy-terminal 30 amino acids of GAL4 are recognized by GAL80. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90670-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden S. L., Cook D. M., Morris J. F., Gashler A., Sukhatme V. P., Rauscher F. J., 3rd Transcriptional repression mediated by the WT1 Wilms tumor gene product. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1550–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.1654597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milbrandt J. A nerve growth factor-induced gene encodes a possible transcriptional regulatory factor. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):797–799. doi: 10.1126/science.3672127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patwardhan S., Gashler A., Siegel M. G., Chang L. C., Joseph L. J., Shows T. B., Le Beau M. M., Sukhatme V. P. EGR3, a novel member of the Egr family of genes encoding immediate-early transcription factors. Oncogene. 1991 Jun;6(6):917–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen R. E., Weaver C. A., Fahrner T. J., Milbrandt J. Domains regulating transcriptional activity of the inducible orphan receptor NGFI-B. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16491–16496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Morris J. F., Tournay O. E., Cook D. M., Curran T. Binding of the Wilms' tumor locus zinc finger protein to the EGR-1 consensus sequence. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1259–1262. doi: 10.1126/science.2244209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Sutherland G. R. Dynamic mutations: a new class of mutations causing human disease. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):709–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90302-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ptashne M. A vector for expressing GAL4(1-147) fusions in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7539–7539. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scafe C., Chao D., Lopes J., Hirsch J. P., Henry S., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II C-terminal repeat influences response to transcriptional enhancer signals. Nature. 1990 Oct 4;347(6292):491–494. doi: 10.1038/347491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukhatme V. P., Cao X. M., Chang L. C., Tsai-Morris C. H., Stamenkovich D., Ferreira P. C., Cohen D. R., Edwards S. A., Shows T. B., Curran T. A zinc finger-encoding gene coregulated with c-fos during growth and differentiation, and after cellular depolarization. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90485-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto Y., Wang Z. Y., Kobler K., Deuel T. F. Promoter region of the human platelet-derived growth factor A-chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1686–1690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesque C., Charnay P. Mapping functional regions of the segment-specific transcription factor Krox-20. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 25;20(10):2485–2492. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.10.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Y., Madden S. L., Deuel T. F., Rauscher F. J., 3rd The Wilms' tumor gene product, WT1, represses transcription of the platelet-derived growth factor A-chain gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):21999–22002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Prater C. A., Dean D. C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):259–261. doi: 10.1038/358259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Tjian R. Analysis of the DNA-binding and activation properties of the human transcription factor AP-2. Genes Dev. 1991 Apr;5(4):670–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.4.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T. E., Day M. L., Pexton T., Padgett K. A., Johnston M., Milbrandt J. In vivo mutational analysis of the NGFI-A zinc fingers. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 25;267(6):3718–3724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]