Abstract
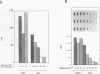
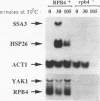
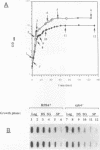
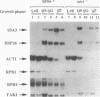
Cells respond to stress by altering gene expression, and these adjustments facilitate stress tolerance. Although transcriptional changes are integral to most stress responses, little is known about the mechanisms that permit the transcription apparatus itself to tolerate stress. Here we report that a major role of the RNA polymerase II subunit RPB4 is to permit appropriate transcriptional responses during stress. Yeast cells lacking RPB4 have essentially wild-type growth rates at moderate temperatures (18 to 22 degrees C), but their growth rates are substantially reduced at temperatures outside this range. When subjected to a heat shock, cells lacking RPB4 rapidly lose the ability to transcribe genes and experience a dramatic loss in viability. When cells lacking RPB4 are subjected to the nutrient stress that accompanies entry into stationary phase, they also exhibit a substantial decline in mRNA synthesis and in viability relative to wild-type cells. Interestingly, the portion of RNA polymerase II molecules that contain RPB4 is small in log phase but increases substantially as cells enter stationary phase. We propose that the association of RPB4 with the other RNA polymerase II subunits increases the tolerance of the enzyme to stress.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bataillé N., Régnacq M., Boucherie H. Induction of a heat-shock-type response in Saccharomyces cerevisiae following glucose limitation. Yeast. 1991 May-Jun;7(4):367–378. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boorstein W. R., Craig E. A. Regulation of a yeast HSP70 gene by a cAMP responsive transcriptional control element. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2543–2553. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07435.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucherie H. Protein synthesis during transition and stationary phases under glucose limitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):385–392. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.385-392.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choder M. A general topoisomerase I-dependent transcriptional repression in the stationary phase in yeast. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2315–2326. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choder M. A growth rate-limiting process in the last growth phase of the yeast life cycle involves RPB4, a subunit of RNA polymerase II. J Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;175(19):6358–6363. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.19.6358-6363.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. M., Kane C. M., Young R. A., Kornberg R. D. Two dissociable subunits of yeast RNA polymerase II stimulate the initiation of transcription at a promoter in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):71–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J., van der Vies S. M. Molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:321–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Ozkaynak E., Varshavsky A. The yeast polyubiquitin gene is essential for resistance to high temperatures, starvation, and other stresses. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90711-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet J., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Spot-immunodetection of conserved determinants in eukaryotic RNA polymerases. Study with antibodies to yeast RNA polymerases subunits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2613–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziej P. A., Woychik N., Liao S. M., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II subunit composition, stoichiometry, and phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1915–1920. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziej P. A., Young R. A. Epitope tagging and protein surveillance. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:508–519. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94038-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodziej P. A., Young R. A. Mutations in the three largest subunits of yeast RNA polymerase II that affect enzyme assembly. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4669–4678. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käppeli O. Regulation of carbon metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and related yeasts. Adv Microb Physiol. 1986;28:181–209. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60239-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M., Scafe C., Sexton J., Young R. Eucaryotic RNA polymerase conditional mutant that rapidly ceases mRNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1602–1611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petko L., Lindquist S. Hsp26 is not required for growth at high temperatures, nor for thermotolerance, spore development, or germination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90563-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Praekelt U. M., Meacock P. A. HSP12, a new small heat shock gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: analysis of structure, regulation and function. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):97–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00315801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K. Heat shock factor and the heat shock response. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):363–366. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90452-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Steinberg T. H., Aronson D. B., Burgess R. R. Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro transcription by monoclonal antibodies prepared against wheat germ RNA polymerase II that react with the heptapeptide repeat of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11511–11520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Gorenstein C. The synthesis of eucaryotic ribosomal proteins in vitro. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. J. The role of heat-shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;3(6):1033–1038. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90125-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Washburne M., Becker J., Kosic-Smithers J., Craig E. A. Yeast Hsp70 RNA levels vary in response to the physiological status of the cell. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2680–2688. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2680-2688.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woychik N. A., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II subunit RPB4 is essential for high- and low-temperature yeast cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2854–2859. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A. RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:689–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]