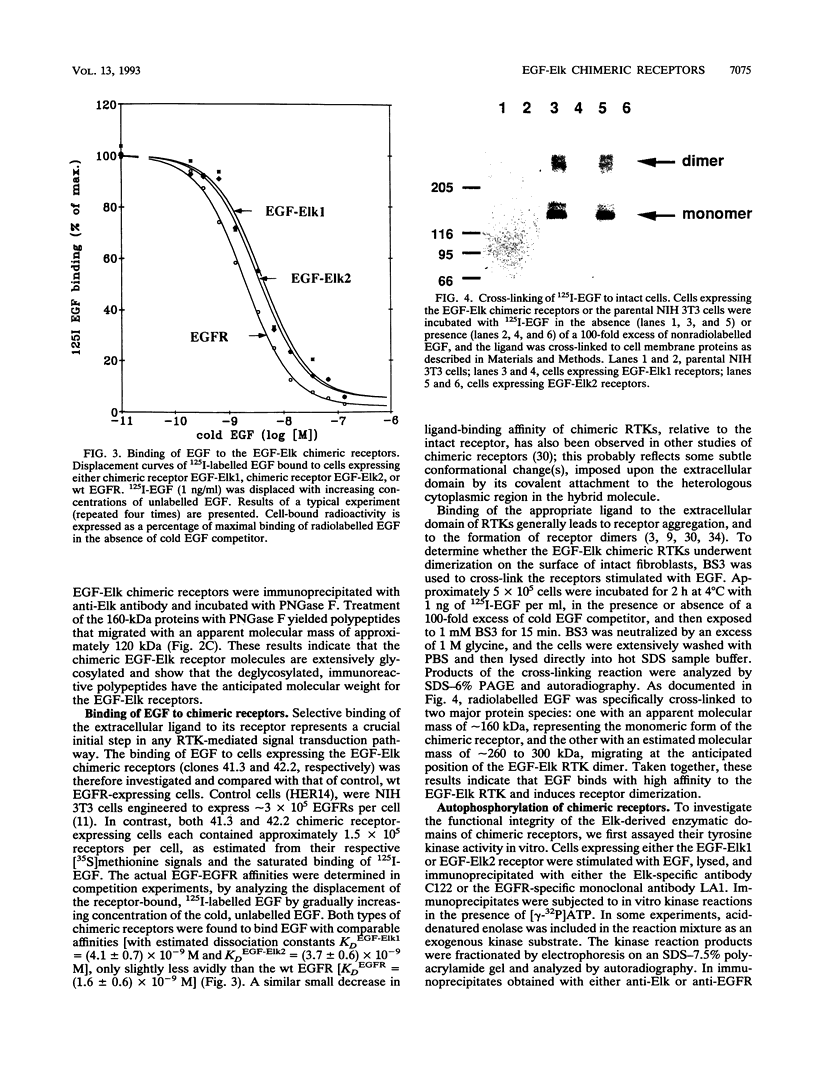
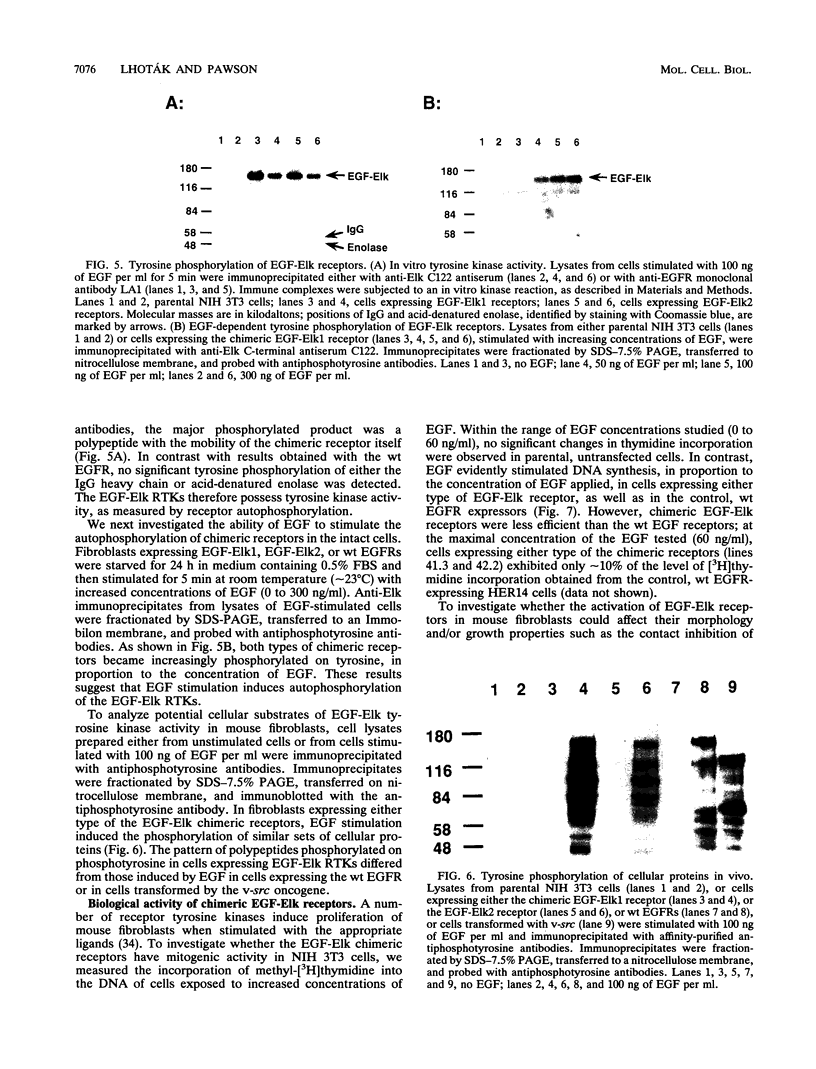
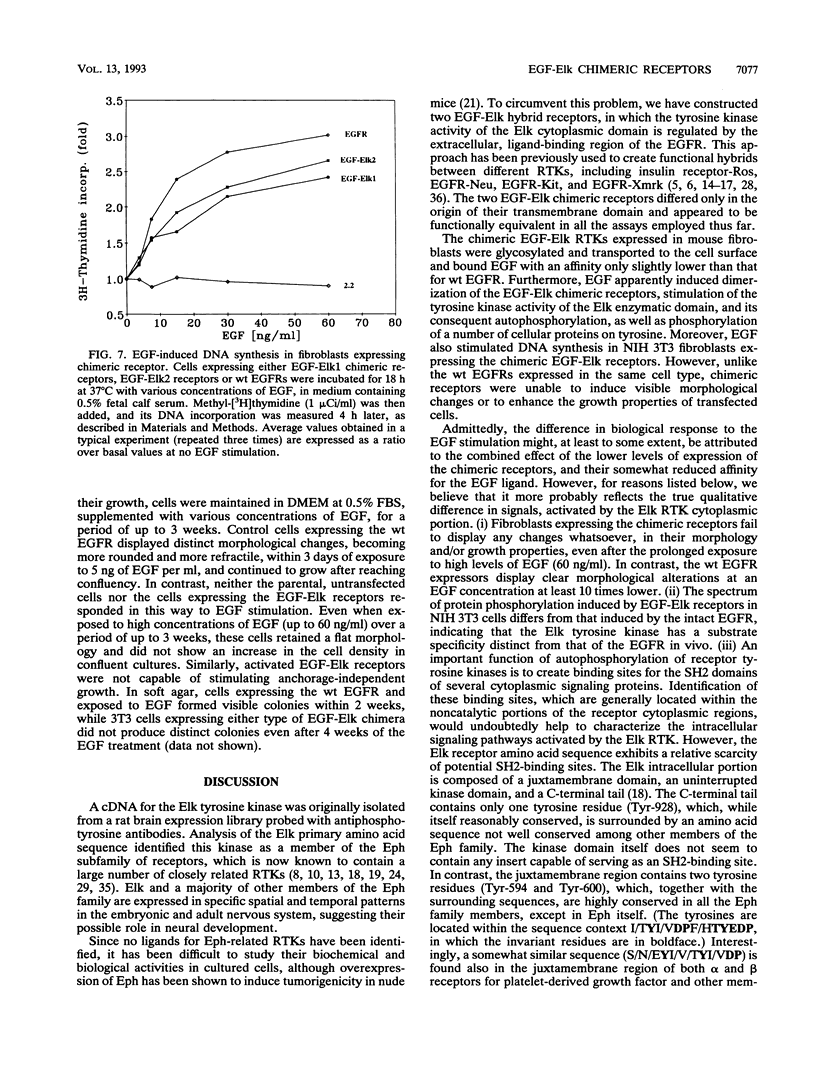
Abstract
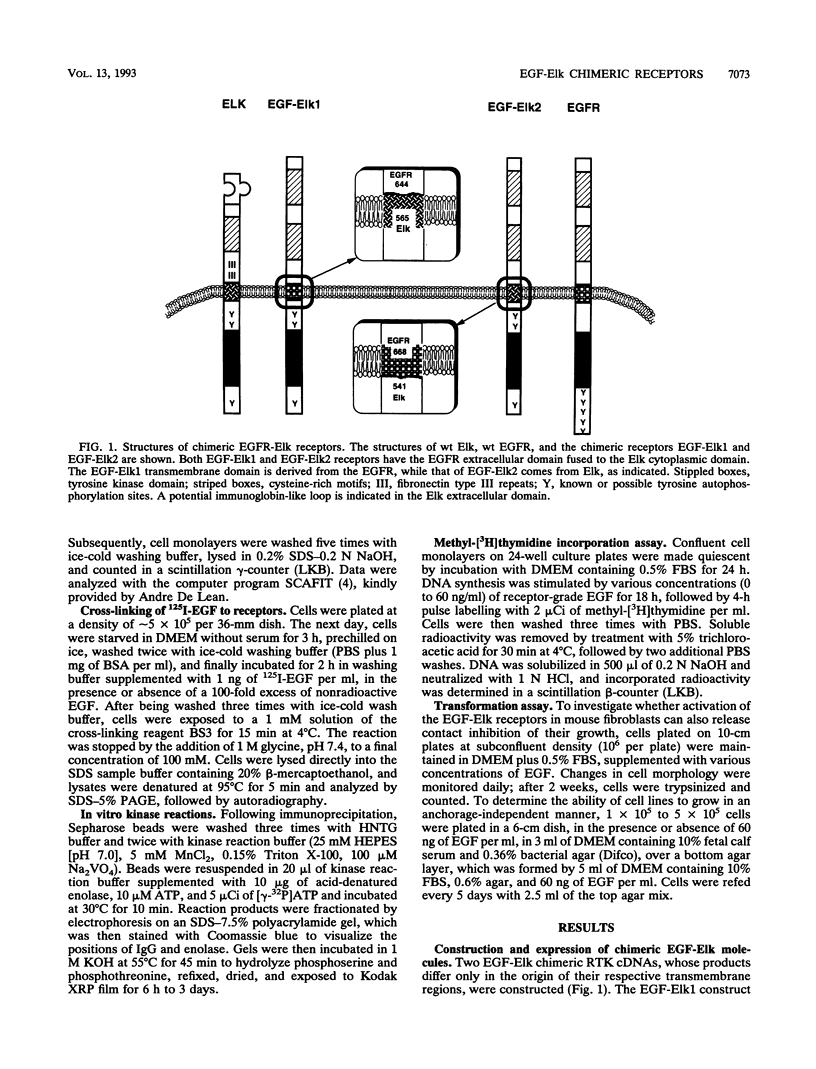
Eph, Elk, and Eck are prototypes of a large family of transmembrane protein-tyrosine kinases, which are characterized by a highly conserved cysteine-rich domain and two fibronectin type III repeats in their extracellular regions. Despite the extent of the Eph family, no extracellular ligands for any family member have been identified, and hence, little is known about the biological and biochemical properties of these receptor-like tyrosine kinases. In the absence of a physiological ligand for the Elk receptor, we constructed chimeric receptor molecules, in which the extracellular region of the Elk receptor is replaced by the extracellular, ligand-binding domain of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor. These chimeric receptors were expressed in NIH 3T3 cells that lack endogenous EGF receptors to analyze their signaling properties. The chimeric EGF-Elk receptors became glycosylated, were correctly localized to the plasma membrane, and bound EGF with high affinity. The chimeric receptors underwent autophosphorylation and induced the tyrosine phosphorylation of a specific set of cellular proteins in response to EGF. EGF stimulation also induced DNA synthesis in fibroblasts stably expressing the EGF-Elk receptors. In contrast, EGF stimulation of these cells did not lead to visible changes in cellular morphology, nor did it induce loss of contact inhibition in confluent monolayers or growth in semisolid media. The Elk cytoplasmic domain is therefore able to induce tyrosine phosphorylation and DNA synthesis in response to an extracellular ligand, suggesting that Elk and related polypeptides function as ligand-dependent receptor tyrosine kinases.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao H., Bangalore L., Bormann B. J., Stern D. F. A subdomain in the transmembrane domain is necessary for p185neu* activation. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):923–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
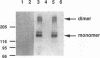
- Cochet C., Kashles O., Chambaz E. M., Borrello I., King C. R., Schlessinger J. Demonstration of epidermal growth factor-induced receptor dimerization in living cells using a chemical covalent cross-linking agent. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3290–3295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Hancock A. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Validation and statistical analysis of a computer modeling method for quantitative analysis of radioligand binding data for mixtures of pharmacological receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;21(1):5–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Segatto O., Taylor W. G., Aaronson S. A., Pierce J. H. EGF receptor and erbB-2 tyrosine kinase domains confer cell specificity for mitogenic signaling. Science. 1990 Apr 6;248(4951):79–83. doi: 10.1126/science.2181668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Morgan D. O., Jong S. M., Wang L. H., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Heterologous transmembrane signaling by a human insulin receptor-v-ros hybrid in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5101–5105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Barr P. J., Williams L. T. Role of tyrosine kinase and membrane-spanning domains in signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5126–5131. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi-Hebenstreit P., Nieto M. A., Frain M., Mattéi M. G., Chestier A., Wilkinson D. G., Charnay P. An Eph-related receptor protein tyrosine kinase gene segmentally expressed in the developing mouse hindbrain. Oncogene. 1992 Dec;7(12):2499–2506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Ernlund A., Rorsman C., Rönnstrand L. Dimerization of B-type platelet-derived growth factor receptors occurs after ligand binding and is closely associated with receptor kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8905–8912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai H., Maru Y., Hagiwara K., Nishida J., Takaku F. A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the eph gene. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1717–1720. doi: 10.1126/science.2825356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence for epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced intermolecular autophosphorylation of the EGF receptors in living cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4035–4044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
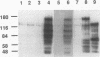
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C., Lemke G. An extended family of protein-tyrosine kinase genes differentially expressed in the vertebrate nervous system. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):691–704. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J., Dull T. J., Lax I., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. HER2 cytoplasmic domain generates normal mitogenic and transforming signals in a chimeric receptor. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):167–173. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03361.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehväslaiho H., Lehtola L., Sistonen L., Alitalo K. A chimeric EGF-R-neu proto-oncogene allows EGF to regulate neu tyrosine kinase and cell transformation. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):159–166. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev S., Givol D., Yarden Y. A specific combination of substrates is involved in signal transduction by the kit-encoded receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):647–654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07993.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev S., Yarden Y., Givol D. Receptor functions and ligand-dependent transforming potential of a chimeric kit proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):6064–6068. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.6064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lhoták V., Greer P., Letwin K., Pawson T. Characterization of elk, a brain-specific receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2496–2502. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. A., Hunter T. cDNA cloning and characterization of eck, an epithelial cell receptor protein-tyrosine kinase in the eph/elk family of protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6316–6324. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Bellot F., Honegger A. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Zilberstein A. Tyrosine kinase activity is essential for the association of phospholipase C-gamma with the epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):435–441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maru Y., Hirai H., Takaku F. Overexpression confers an oncogenic potential upon the eph gene. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):445–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Rönnstrand L., Yokote K., Engström A., Courtneidge S. A., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H. Identification of two juxtamembrane autophosphorylation sites in the PDGF beta-receptor; involvement in the interaction with Src family tyrosine kinases. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2257–2264. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto M. A., Gilardi-Hebenstreit P., Charnay P., Wilkinson D. G. A receptor protein tyrosine kinase implicated in the segmental patterning of the hindbrain and mesoderm. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):1137–1150. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquale E. B., Deerinck T. J., Singer S. J., Ellisman M. H. Cek5, a membrane receptor-type tyrosine kinase, is in neurons of the embryonic and postnatal avian brain. J Neurosci. 1992 Oct;12(10):3956–3967. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-10-03956.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquale E. B. Identification of chicken embryo kinase 5, a developmentally regulated receptor-type tyrosine kinase of the Eph family. Cell Regul. 1991 Jul;2(7):523–534. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.7.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Bernstein A. Receptor tyrosine kinases: genetic evidence for their role in Drosophila and mouse development. Trends Genet. 1990 Nov;6(11):350–356. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90276-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel H., Dull T. J., Honegger A. M., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Cytoplasmic domains determine signal specificity, cellular routing characteristics and influence ligand binding of epidermal growth factor and insulin receptors. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2943–2954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajjadi F. G., Pasquale E. B., Subramani S. Identification of a new eph-related receptor tyrosine kinase gene from mouse and chicken that is developmentally regulated and encodes at least two forms of the receptor. New Biol. 1991 Aug;3(8):769–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. The epidermal growth factor receptor as a multifunctional allosteric protein. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3119–3123. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Felder S., Millauer B., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Analysis of platelet-derived growth factor receptor domain function using a novel chimeric receptor approach. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12424–12431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicks I. P., Wilkinson D., Salvaris E., Boyd A. W. Molecular cloning of HEK, the gene encoding a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed by human lymphoid tumor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1611–1615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittbrodt J., Lammers R., Malitschek B., Ullrich A., Schartl M. The Xmrk receptor tyrosine kinase is activated in Xiphophorus malignant melanoma. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4239–4246. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]