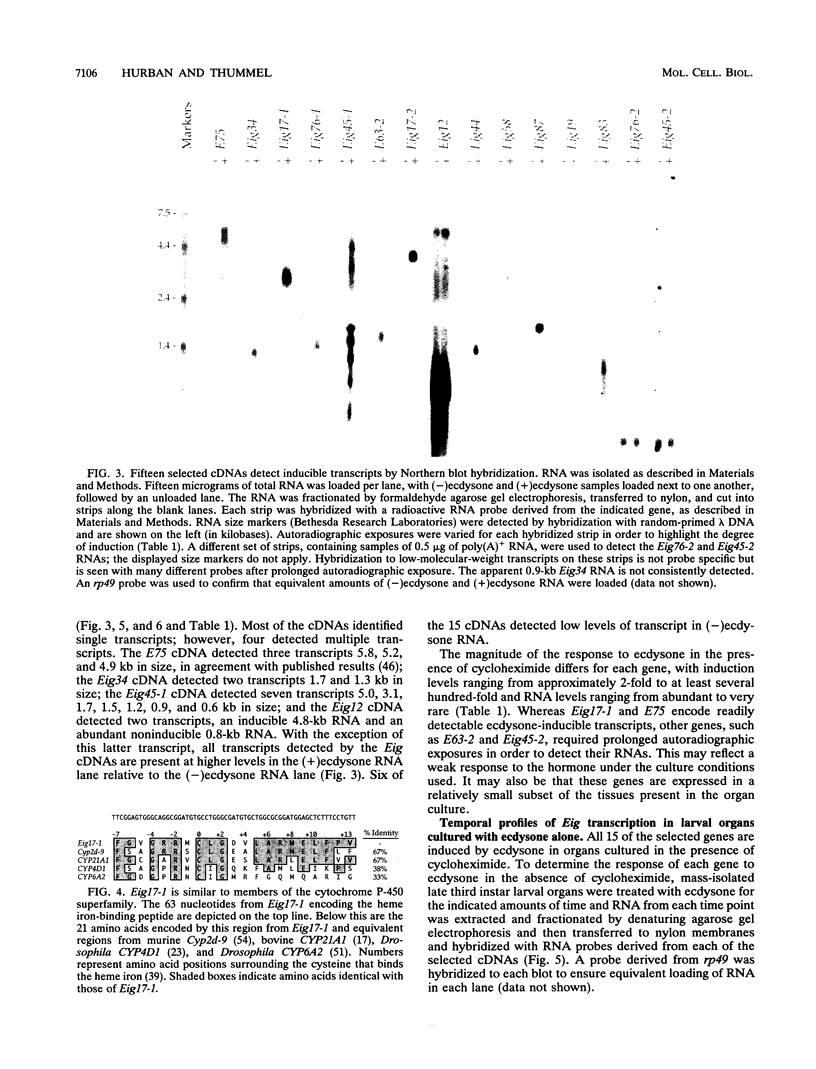
Abstract
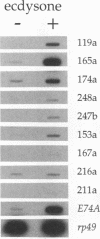
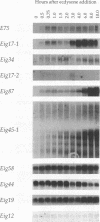
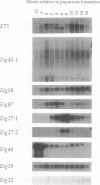
Our insights into the regulatory mechanisms by which the steroid hormone ecdysone triggers Drosophila melanogaster metamorphosis have largely depended on puffs in the larval salivary gland polytene chromosomes as a means of identifying genes of interest. Here, we describe an approach that provides access to ecdysone-inducible genes that are expressed in most larval and imaginal tissues, regardless of their ability to form puffs in the polytene chromosomes. Several hundred cDNAs were picked at random from subtracted cDNA libraries and subjected to a rapid and sensitive screen for their ability to detect mRNAs induced by ecdysone in the presence of cycloheximide. Of the 15 genes identified in this manner, 2 correspond to early puffs in the salivary gland polytene chromosomes, at 63F and 75B, confirming that this screen functions at the desired level of sensitivity and is capable of identifying novel primary-response genes. Three of the genes, Eig45-1, Eig58, and Eig87, are expressed coordinately with the salivary gland early genes; one of them, Eig58, maps to the 58BC puff that is active when the 74EF and 75B early puffs are at their maximal size. Another gene identified in this screen, Eig17-1, encodes a novel cytochrome P-450. On the basis of its sequence identity and temporal profile of expression, this gene may play a role in steroid hormone metabolism and thus could provide a mechanism for feedback regulation of ecdysone production. Although all 15 genes have patterns of transcription that are consistent with ecdysone regulation in vivo, 5 genes do not appear to be induced by the late larval ecdysone pulse. This indicates that ecdysone induction in larval organs cultured with cycloheximide is not always indicative of a primary response to the hormone.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andres A. J., Cherbas P. Tissue-specific ecdysone responses: regulation of the Drosophila genes Eip28/29 and Eip40 during larval development. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):865–876. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Patterns of puffing activity in the salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila. VI. Induction by ecdysone in salivary glands of D. melanogaster cultured in vitro. Chromosoma. 1972;38(3):255–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00290925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Puffing patterns in Drosophila melanogaster and related species. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1972;4:101–151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-37164-9_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Puffs, genes, and hormones revisited. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90205-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M. Sequential gene activation by ecdysone in polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. II. The effects of inhibitors of protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1974 Jul;39(1):141–157. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(74)80016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER H. J. [The puffs of salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophilia melanogaster. Part 1. Observations on the behavior of a typical puff in the normal strain and in two mutants, giant and lethal giant larvae]. Chromosoma. 1959;10:654–678. doi: 10.1007/BF00396591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd L., O'Toole E., Thummel C. S. Patterns of E74A RNA and protein expression at the onset of metamorphosis in Drosophila. Development. 1991 Aug;112(4):981–995. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.4.981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEVER U., KARLSON P. [Induction of puff changes in the salivary gland chromosomes of Chironomus tentans by ecdysone]. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Sep;20:623–626. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90141-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao A. T., Guild G. M. Molecular analysis of the ecdysterone-inducible 2B5 "early' puff in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):143–150. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04188.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T., Bunting M., Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Isolation and characterization of five Drosophila genes that encode an ets-related DNA binding domain. Dev Biol. 1992 May;151(1):176–191. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90225-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Miller W. L. Structure of a bovine gene for P-450c21 (steroid 21-hydroxylase) defines a novel cytochrome P-450 gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley T. E., Meyerowitz E. M. Steroid regulation of RNAs transcribed from the Drosophila 68c polytene chromosome puff. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):110–121. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90179-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBello P. R., Withers D. A., Bayer C. A., Fristrom J. W., Guild G. M. The Drosophila Broad-Complex encodes a family of related proteins containing zinc fingers. Genetics. 1991 Oct;129(2):385–397. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigl G., Gram M., Pongs O. A member of the steroid hormone receptor gene family is expressed in the 20-OH-ecdysone inducible puff 75B in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7167–7178. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi R., Varak E., Goldberg M. L. Molecular analysis of a cytochrome P450 gene of family 4 on the Drosophila X chromosome. DNA Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;11(5):397–404. doi: 10.1089/dna.1992.11.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgel P., Ramain P., Giangrande A., Dretzen G., Richards G., Bellard M. Sgs-3 chromatin structure and trans-activators: developmental and ecdysone induction of a glue enhancer-binding factor, GEBF-I, in Drosophila larvae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):523–532. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handler A. M. Ecdysteroid titers during pupal and adult development in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1982 Sep;93(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson L., Lambertsson A. Steroid regulation of glue protein genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Hereditas. 1989;110(1):61–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1989.tb00418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda S., Morohashi K., Nomura M., Takeya H., Kitajima M., Omura T. Ad4BP regulating steroidogenic P-450 gene is a member of steroid hormone receptor superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7494–7502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huet F., Ruiz C., Richards G. Puffs and PCR: the in vivo dynamics of early gene expression during ecdysone responses in Drosophila. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):613–627. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht R., Taube W., Lüdecke H. J., Pongs O. Characterization of a putative transcription factor gene expressed in the 20-OH-ecdysone inducible puff 74EF in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4455–4464. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Loper J. C. Proteins from eight eukaryotic cytochrome P-450 families share a segmented region of sequence similarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7221–7225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Ecdysone coordinates the timing and amounts of E74A and E74B transcription in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1067–1079. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Thummel C. S. Temporal coordination of regulatory gene expression by the steroid hormone ecdysone. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4083–4093. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05501.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lala D. S., Rice D. A., Parker K. L. Steroidogenic factor I, a key regulator of steroidogenic enzyme expression, is the mouse homolog of fushi tarazu-factor I. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Aug;6(8):1249–1258. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.8.1406703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavorgna G., Karim F. D., Thummel C. S., Wu C. Potential role for a FTZ-F1 steroid receptor superfamily member in the control of Drosophila metamorphosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):3004–3008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.3004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepesant J. A., Levine M., Garen A., Lepesant-Kejzlarvoa J., Rat L., Somme-Martin G. Developmentally regulated gene expression in Drosophila larval fat bodies. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):371–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miklos G. L., Cotsell J. N. Chromosome structure at interfaces between major chromatin types: alpha- and beta-heterochromatin. Bioessays. 1990 Jan;12(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morohashi K., Honda S., Inomata Y., Handa H., Omura T. A common trans-acting factor, Ad4-binding protein, to the promoters of steroidogenic P-450s. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17913–17919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natzle J. E., Hammonds A. S., Fristrom J. W. Isolation of genes active during hormone-induced morphogenesis in Drosophila imaginal discs. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5575–5583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Gonzalez F. J. P450 genes: structure, evolution, and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:945–993. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palazzolo M. J., Hyde D. R., VijayRaghavan K., Mecklenburg K., Benzer S., Meyerowitz E. Use of a new strategy to isolate and characterize 436 Drosophila cDNA clones corresponding to RNAs detected in adult heads but not in early embryos. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):527–539. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90211-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice D. A., Mouw A. R., Bogerd A. M., Parker K. L. A shared promoter element regulates the expression of three steroidogenic enzymes. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;5(10):1552–1561. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segraves W. A., Hogness D. S. The E75 ecdysone-inducible gene responsible for the 75B early puff in Drosophila encodes two new members of the steroid receptor superfamily. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):204–219. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sliter T. J., Gilbert L. I. Developmental arrest and ecdysteroid deficiency resulting from mutations at the dre4 locus of Drosophila. Genetics. 1992 Mar;130(3):555–568. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. S., Weis J. H. Development of a sensitive reverse transcriptase PCR assay, RT-RPCR, utilizing rapid cycle times. PCR Methods Appl. 1992 Nov;2(2):137–143. doi: 10.1101/gr.2.2.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Burtis K. C., Hogness D. S. Spatial and temporal patterns of E74 transcription during Drosophila development. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Zelhof A. C., Shaw B. J., Ch'ang L. Y. Possible involvement of the long terminal repeat of transposable element 17.6 in regulating expression of an insecticide resistance-associated P450 gene in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4855–4859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G., Kawajiri K., Negishi M. Gene family of male-specific testosterone 16 alpha-hydroxylase (C-P-450(16) alpha) in mouse liver: cDNA sequences, neonatal imprinting, and reversible regulation by androgen. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 29;26(26):8683–8690. doi: 10.1021/bi00400a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]