Abstract
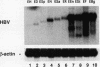
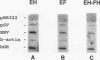
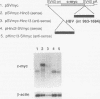
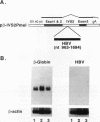
Many viruses possess complex mechanisms involving multiple gene products and cis-regulatory elements in order to achieve a fine control of their gene expression at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and retroviruses share many structural and functional similarities. In this study, by genetic and biochemical analyses, we have demonstrated the existence of a novel genetic element within the HBV genome which is essential for high-level expression of viral gene products. This element is located 3' to the envelope coding region. We have shown that this genetic element is cis acting at the posttranscriptional level and that its function is exerted at the level of RNA processing as part of transcribed sequences. This RNA element is also functional in the context of a heterologous gene. Similar to the function of Rev-Rev response element interaction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, this element appears to inhibit the splicing process and facilitate the transport and utilization of HBV transcripts.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso-Caplen F. V., Krug R. M. Regulation of the extent of splicing of influenza virus NS1 mRNA: role of the rates of splicing and of the nucleocytoplasmic transport of NS1 mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1092–1098. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonucci T. K., Rutter W. J. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) promoters are regulated by the HBV enhancer in a tissue-specific manner. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):579–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.579-583.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum H. E., Zhang Z. S., Galun E., von Weizsäcker F., Garner B., Liang T. J., Wands J. R. Hepatitis B virus X protein is not central to the viral life cycle in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1223–1227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1223-1227.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Berg P. Comparison of intron-dependent and intron-independent gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4395–4405. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Sharp P. A. Regulation by HIV Rev depends upon recognition of splice sites. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):789–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colgrove R., Simon G., Ganem D. Transcriptional activation of homologous and heterologous genes by the hepatitis B virus X gene product in cells permissive for viral replication. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4019–4026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4019-4026.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Regulatory pathways governing HIV-1 replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Human immunodeficiency virus as a prototypic complex retrovirus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1053–1056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1053-1056.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikstein R., Faktor O., Ben-Levy R., Shaul Y. Functional organization of the hepatitis B virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3683–3689. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R., Ellmeier W., Birnstiel M. L. Mature mRNA 3' end formation stimulates RNA export from the nucleus. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3513–3522. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faktor O., Budlovsky S., Ben-Levy R., Shaul Y. A single element within the hepatitis B virus enhancer binds multiple proteins and responds to multiple stimuli. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1861–1863. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1861-1863.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Cladaras C., Copeland T., Pavlakis G. N. rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects the stability and transport of the viral mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1495–1499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H., Leder P. Splicing and the formation of stable RNA. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1299–1302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu K. Q., Vierling J. M., Siddiqui A. Trans-activation of HLA-DR gene by hepatitis B virus X gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7140–7144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. T., Gorman C. M. The simian virus 40 small-t intron, present in many common expression vectors, leads to aberrant splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1805–1810. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Mattaj I. W. Transport of RNA between nucleus and cytoplasm. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;3(4):279–288. doi: 10.1016/1043-4682(92)90029-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Cole M. D. Rapid cytoplasmic turnover of c-myc mRNA: requirement of the 3' untranslated sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4513–4521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko S., Miller R. H. X-region-specific transcript in mammalian hepatitis B virus-infected liver. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3979–3984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3979-3984.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwee L., Lucito R., Aufiero B., Schneider R. J. Alternate translation initiation on hepatitis B virus X mRNA produces multiple polypeptides that differentially transactivate class II and III promoters. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4382–4389. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4382-4389.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Cabrera M., Letovsky J., Hu K. Q., Siddiqui A. Multiple liver-specific factors bind to the hepatitis B virus core/pregenomic promoter: trans-activation and repression by CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5069–5073. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire H. F., Hoeffler J. P., Siddiqui A. HBV X protein alters the DNA binding specificity of CREB and ATF-2 by protein-protein interactions. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):842–844. doi: 10.1126/science.1827531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Hauber J., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 rev trans-activator acts through a structured target sequence to activate nuclear export of unspliced viral mRNA. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):254–257. doi: 10.1038/338254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattox W., Ryner L., Baker B. S. Autoregulation and multifunctionality among trans-acting factors that regulate alternative pre-mRNA processing. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19023–19026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura I., Koike K. Identification of a binding protein to the X gene promoter region of hepatitis B virus. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):533–540. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90228-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel N. U., Jameel S., Isom H., Siddiqui A. Interactions between nuclear factors and the hepatitis B virus enhancer. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5293–5301. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5293-5301.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips T. R., Lamont C., Konings D. A., Shacklett B. L., Hamson C. A., Luciw P. A., Elder J. H. Identification of the Rev transactivation and Rev-responsive elements of feline immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5464–5471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5464-5471.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raney A. K., Milich D. R., McLachlan A. Complex regulation of transcription from the hepatitis B virus major surface antigen promoter in human hepatoma cell lines. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4805–4811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4805-4811.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Blau H. M. Genetic complementation reveals a novel regulatory role for 3' untranslated regions in growth and differentiation. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):903–917. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90579-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Miller R. H., Marion P. L. Hepadnaviruses and retroviruses share genome homology and features of replication. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1 Suppl):64S–73S. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Intragenic cis-acting art gene-responsive sequences of the human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2071–2075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Distinct RNA sequences in the gag region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 decrease RNA stability and inhibit expression in the absence of Rev protein. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):150–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.150-159.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden R. F., Howie K. B., Rowe M. E., Goodman H. M., Moore D. D. Human growth hormone as a reporter gene in regulation studies employing transient gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3173–3179. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Mitchell P. J., Yen T. S. Transactivation by the hepatitis B virus X protein depends on AP-2 and other transcription factors. Nature. 1990 Mar 1;344(6261):72–74. doi: 10.1038/344072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Yen T. S., Peterlin B. M., Ou J. H. Trans-activation of the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by the hepatitis B virus X protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8286–8290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Jameel S., Mapoles J. Expression of the hepatitis B virus X gene in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2513–2517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui A., Jameel S., Mapoles J. Transcriptional control elements of hepatitis B surface antigen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):566–570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:527–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. S., Lai C. J., Huang J. L., Lin L. H., Yauk Y. K., Chang C. M., Lo S. J., Han S. H. Hepatitis B virus transcript produced by RNA splicing. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4011–4018. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4011-4018.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannice J. L., Levinson A. D. Properties of the human hepatitis B virus enhancer: position effects and cell-type nonspecificity. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1305–1313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1305-1313.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Zindy F., Chenivesse X., Lamas E., Henglein B., Bréchot C. Modification of cyclin A expression by hepatitis B virus DNA integration in a hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1653–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. L., Chen P. J., Tu S. J., Lin M. H., Lai M. Y., Chen D. S. Characterization and genetic analysis of alternatively spliced transcripts of hepatitis B virus in infected human liver tissues and transfected HepG2 cells. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1680–1686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1680-1686.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]