Abstract
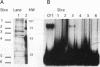
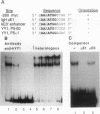
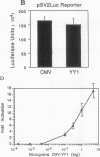
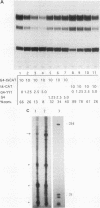
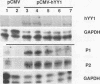
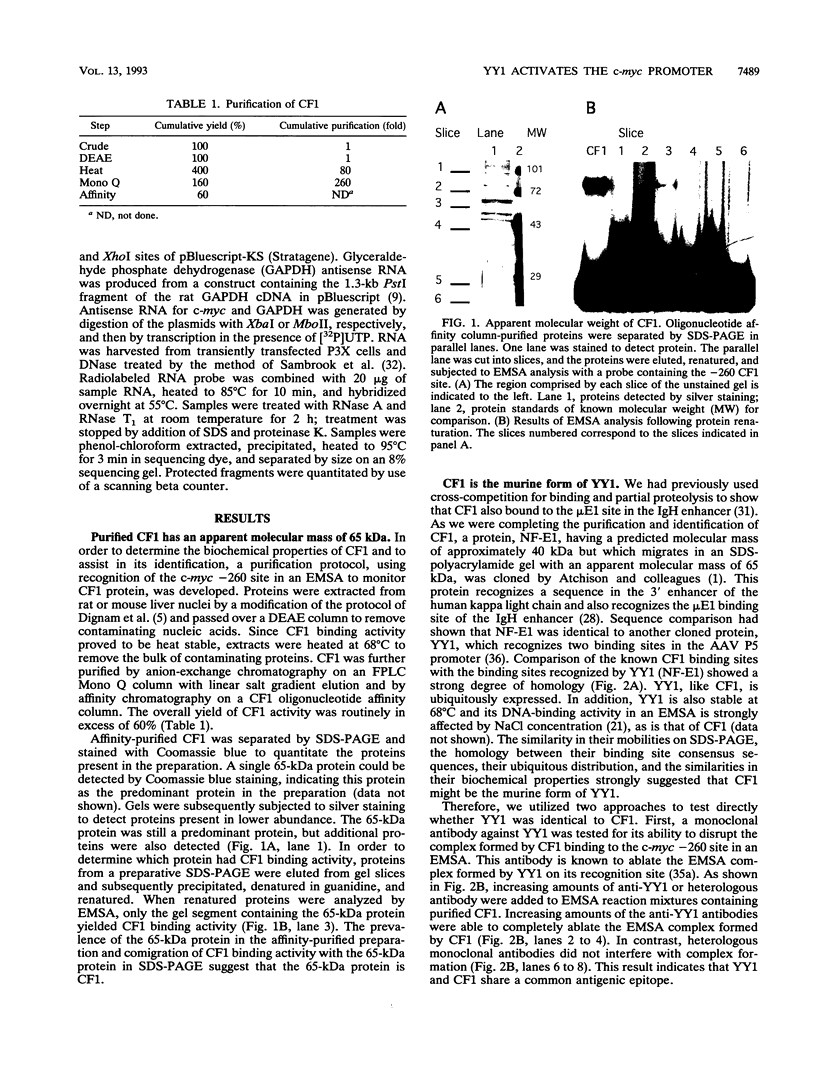
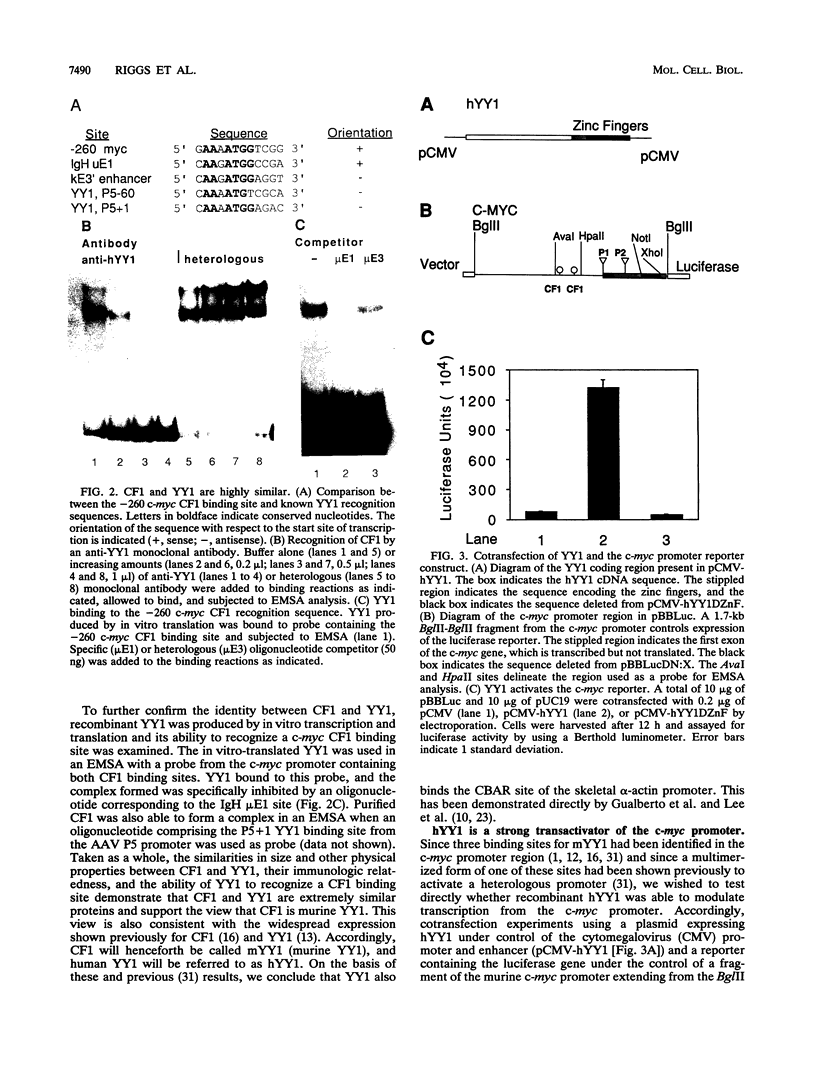
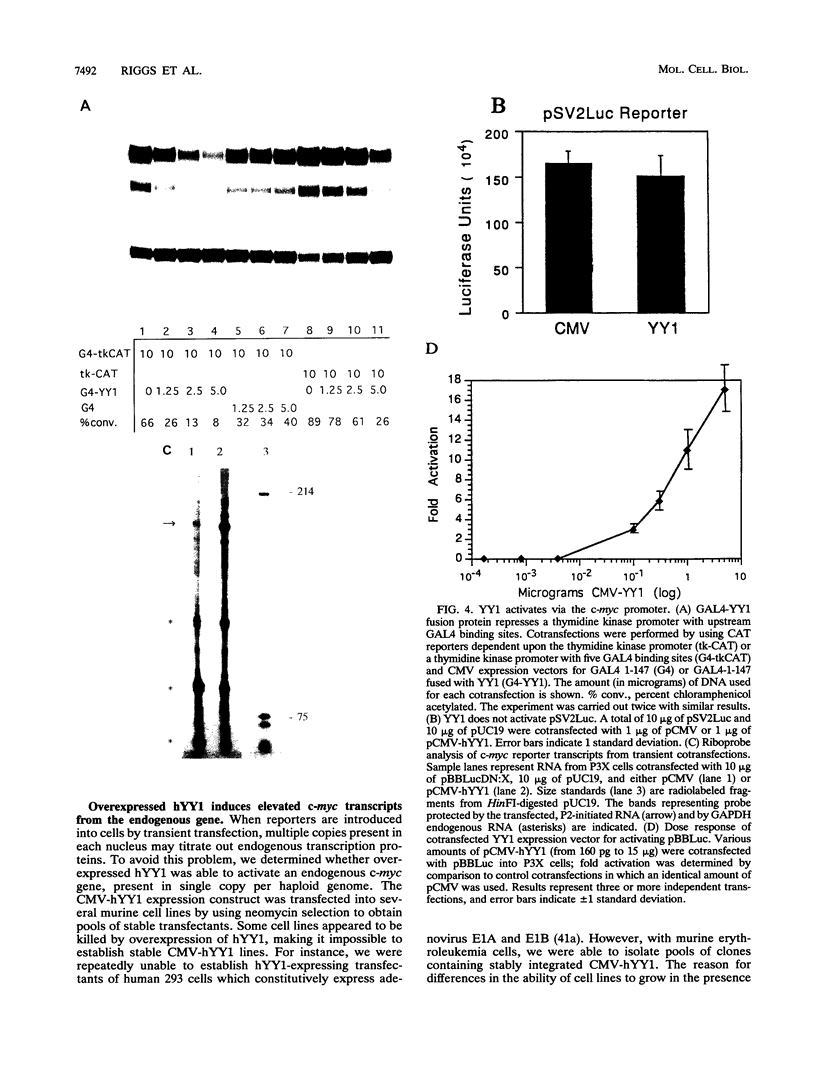
Previous studies on the murine c-myc promoter demonstrated that a ubiquitously present protein, common factor 1 (CF1), bound at two sites located -260 and -390 bp from the P1 transcription start site. CF1 has been purified to near homogeneity and shown to be identical to the zinc finger protein Yin-yang 1 (YY1) as judged by similarity of molecular weight and other biochemical properties, immunological cross-reactivity, and the ability of recombinant YY1 to bind to CF1 sites. In cotransfection experiments, YY1 is a strong activator of transcription from c-myc promoter-based reporters. Furthermore, in murine erythroleukemia cells, overexpressed YY1 causes increased levels of c-myc mRNA initiated from both major transcription initiation sites of the endogenous c-myc gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atchison M. L., Meyuhas O., Perry R. P. Localization of transcriptional regulatory elements and nuclear factor binding sites in mouse ribosomal protein gene rpL32. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):2067–2074. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.2067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Cress W. D., Cress A., Triezenberg S. J., Guarente L. Selective inhibition of activated but not basal transcription by the acidic activation domain of VP16: evidence for transcriptional adaptors. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1199–1208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90684-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis N., Blanc S., Leibovitch M. P., Nicolaiew N., Dautry F., Raymondjean M., Kruh J., Kitzis A. c-myc oncogene expression inhibits the initiation of myogenic differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Sep;172(1):212–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90107-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Hoey T., Tjian R. Isolation of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falcone G., Tatò F., Alemà S. Distinctive effects of the viral oncogenes myc, erb, fps, and src on the differentiation program of quail myogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):426–430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J. R., Becker K. G., Ennist D. L., Gleason S. L., Driggers P. H., Levi B. Z., Appella E., Ozato K. Cloning of a negative transcription factor that binds to the upstream conserved region of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):38–44. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualberto A., LePage D., Pons G., Mader S. L., Park K., Atchison M. L., Walsh K. Functional antagonism between YY1 and the serum response factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4209–4214. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Delta, a transcription factor that binds to downstream elements in several polymerase II promoters, is a functionally versatile zinc finger protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9799–9803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Equipotent mouse ribosomal protein promoters have a similar architecture that includes internal sequence elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1789–1800. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Lipp M., Nevins J. R. E1A-dependent trans-activation of the human MYC promoter is mediated by the E2F factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson T., Allard M. F., Sreenan C. M., Doss L. K., Bishop S. P., Swain J. L. The c-myc proto-oncogene regulates cardiac development in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3709–3716. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakkis E., Calame K. A plasmacytoma-specific factor binds the c-myc promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7031–7035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakkis E., Riggs K. J., Gillespie W., Calame K. A transcriptional repressor of c-myc. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):718–721. doi: 10.1038/339718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Tohyama N., Tada T. Autocrine growth and tumorigenicity of interleukin 2-dependent helper T cells transfected with IL-2 gene. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):13–25. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Flanagan P. M., Kornberg R. D. A novel mediator between activator proteins and the RNA polymerase II transcription apparatus. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1209–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90685-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Chow K. L., Fang P., Schwartz R. J. Activation of skeletal alpha-actin gene transcription: the cooperative formation of serum response factor-binding complexes over positive cis-acting promoter serum response elements displaces a negative-acting nuclear factor enriched in replicating myoblasts and nonmyogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5090–5100. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. C., Shi Y., Schwartz R. J. Displacement of BrdUrd-induced YY1 by serum response factor activates skeletal alpha-actin transcription in embryonic myoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9814–9818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M., Pierce J. W., Baltimore D. Protein-binding sites in Ig gene enhancers determine transcriptional activity and inducibility. Science. 1987 Jun 19;236(4808):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3109035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp M., Schilling R., Bernhardt G. Trans-activation of human MYC: the second promoter is target for the stimulation by adenovirus E1a proteins. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):535–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Bossone S. A., Patel A. J. myc function and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:809–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.004113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. J. c-myc inhibition of MyoD and myogenin-initiated myogenic differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2842–2851. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A., Metcalf D. Subunit promiscuity among hemopoietic growth factor receptors. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90564-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K., Atchison M. L. Isolation of a candidate repressor/activator, NF-E1 (YY-1, delta), that binds to the immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain mu E1 site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9804–9808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Mutul J., Macchi M., Wasylyk B. Mutational analysis of the contribution of sequence motifs within the IgH enhancer to tissue specific transcriptional activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6085–6096. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. L., Herskowitz I. Characterization of the yeast SWI1, SWI2, and SWI3 genes, which encode a global activator of transcription. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90192-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs K. J., Merrell K. T., Wilson G., Calame K. Common factor 1 is a transcriptional activator which binds in the c-myc promoter, the skeletal alpha-actin promoter, and the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1765–1769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F., Jäckle H. Concentration-dependent transcriptional activation or repression by Krüppel from a single binding site. Nature. 1991 Oct 10;353(6344):563–566. doi: 10.1038/353563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Shi Y., Shenk T. YY1 is an initiator sequence-binding protein that directs and activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):241–245. doi: 10.1038/354241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T., Flint J. Transcriptional and transforming activities of the adenovirus E1A proteins. Adv Cancer Res. 1991;57:47–85. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60995-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Seto E., Chang L. S., Shenk T. Transcriptional repression by YY1, a human GLI-Krüppel-related protein, and relief of repression by adenovirus E1A protein. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Coactivators for a proline-rich activator purified from the multisubunit human TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12A):2212–2224. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12a.2212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalmeier K., Synovzik H., Mertz R., Winnacker E. L., Lipp M. Nuclear factor E2F mediates basic transcription and trans-activation by E1a of the human MYC promoter. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):527–536. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao B. P., Wang X. F., Peterson C. L., Calame K. In vivo functional analysis of in vitro protein binding sites in the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3239–3253. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R., Sabbatini P., Denton A. Adenovirus E1B 19-kilodalton protein overcomes the cytotoxicity of E1A proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2968–2978. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2968-2978.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. Q., Bauer S. R., Mushinski J. F., Marcu K. B. Chromosome translocations clustered 5' of the murine c-myc gene qualitatively affect promoter usage: implications for the site of normal c-myc regulation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1441–1447. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03800.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zonneveld A. J., Curriden S. A., Loskutoff D. J. Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene: functional analysis and glucocorticoid regulation of its promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5525–5529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]