Abstract
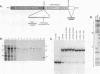
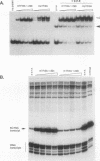
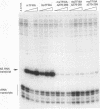
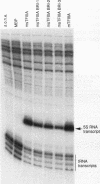
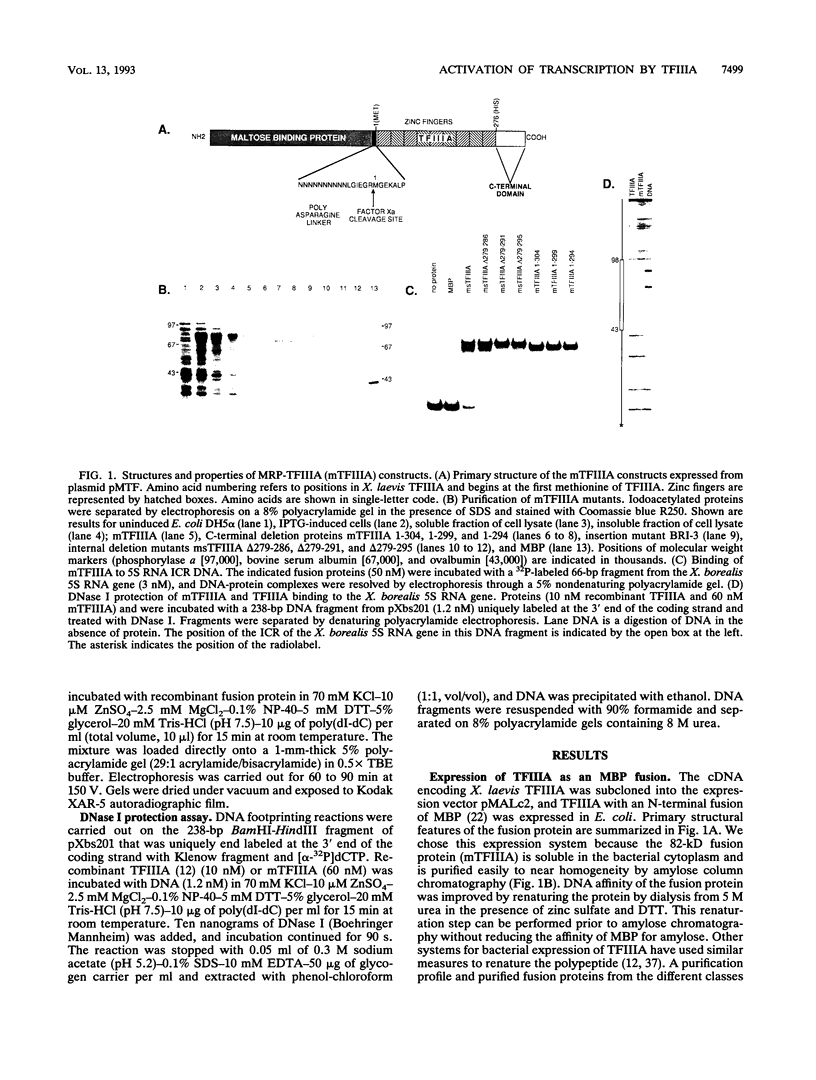
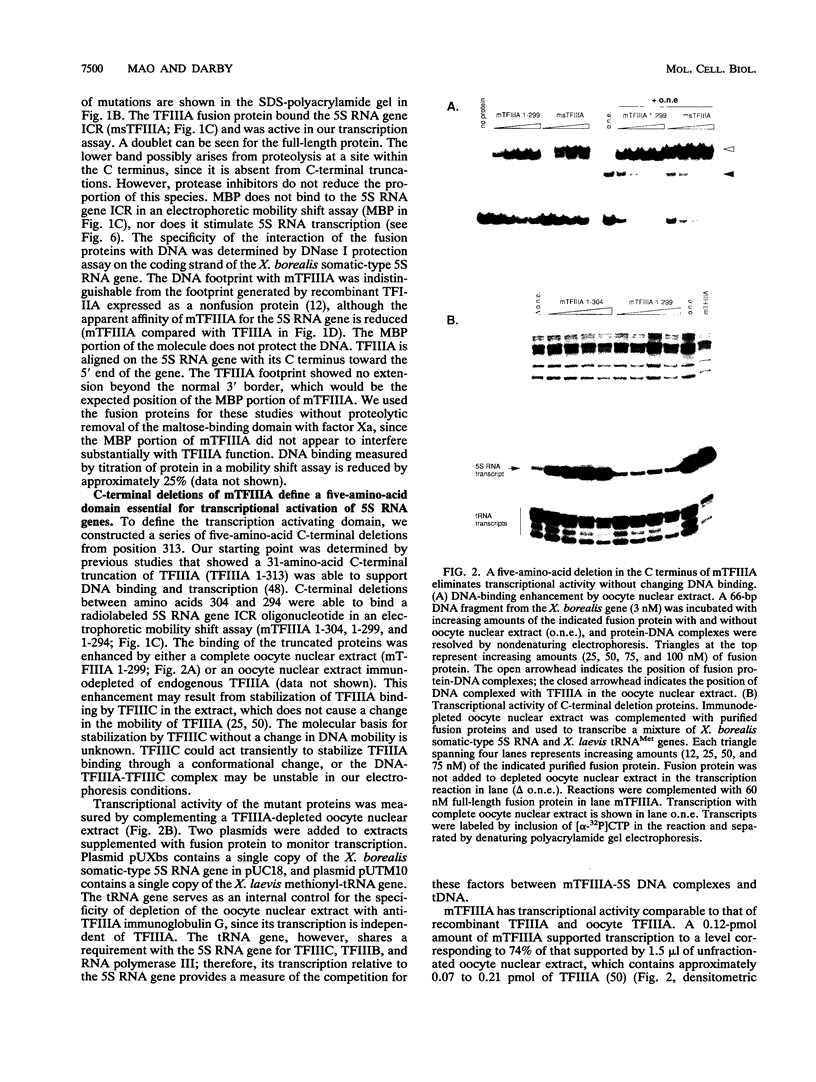
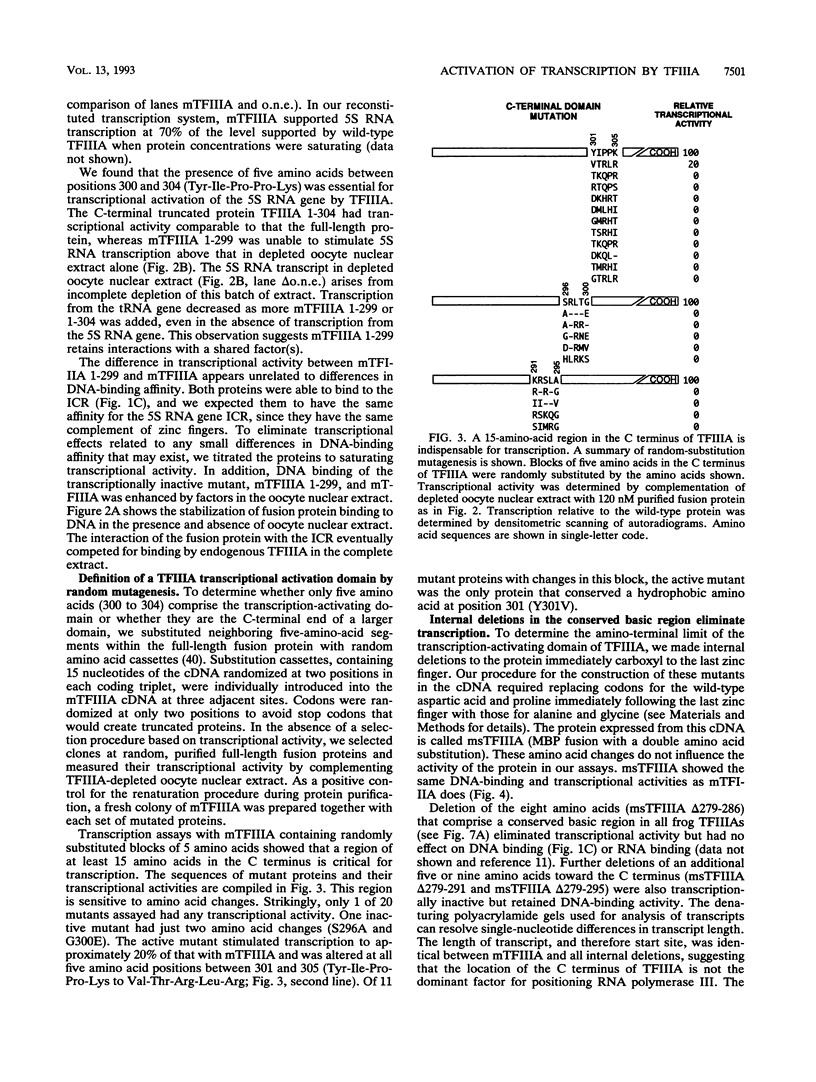
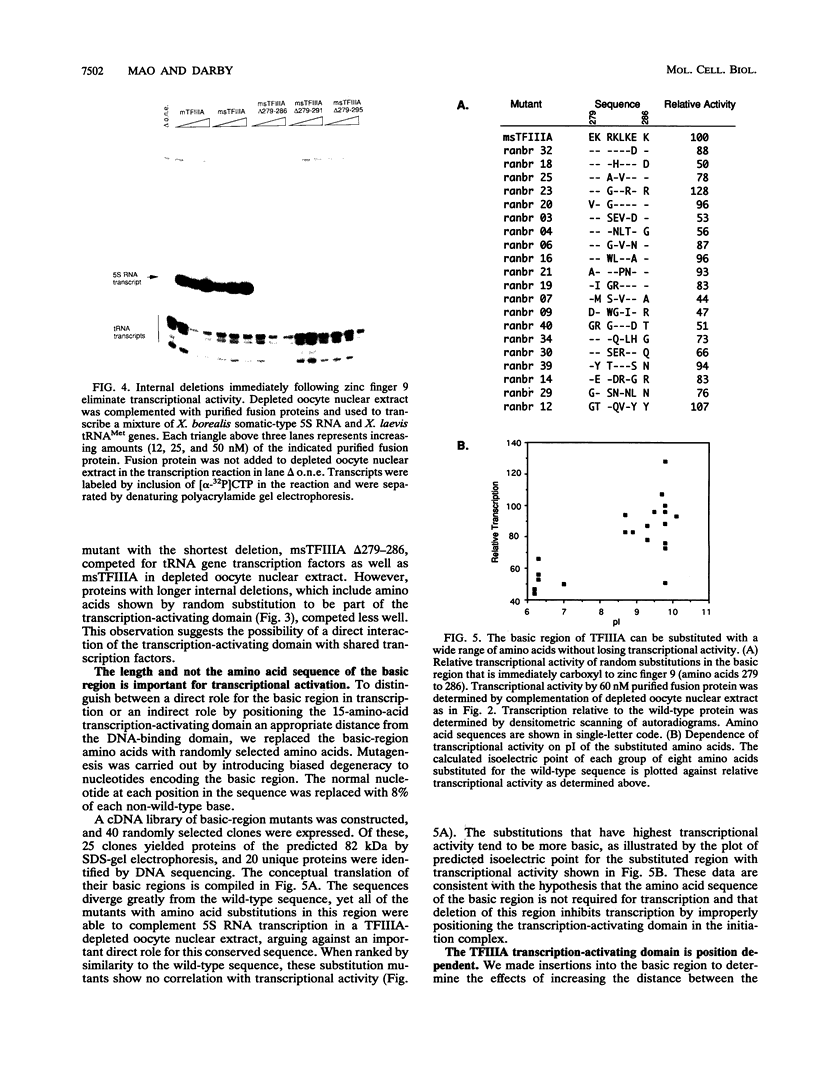
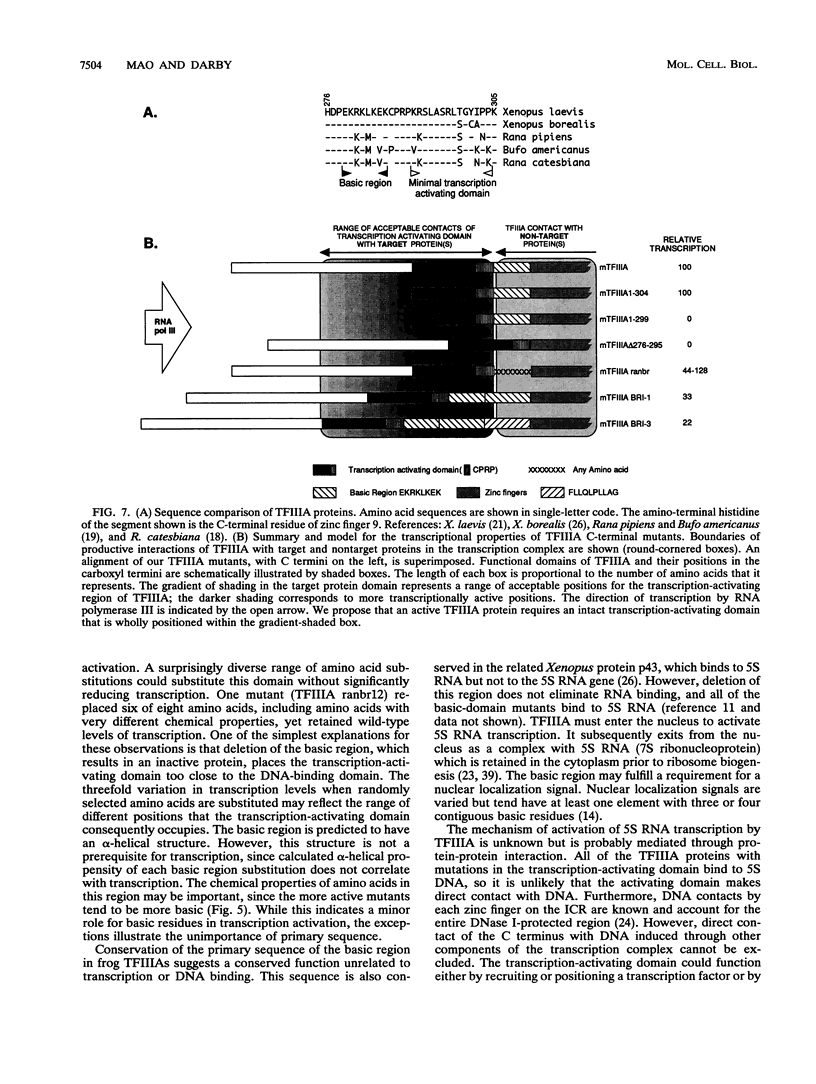
Transcription of the Xenopus 5S RNA gene by RNA polymerase III requires the gene-specific factor TFIIIA. To identify domains within TFIIIA that are essential for transcriptional activation, we have expressed C-terminal deletion, substitution, and insertion mutants of TFIIIA in bacteria as fusions with maltose-binding protein (MBP). The MBP-TFIIIA fusion protein specifically binds to the 5S RNA gene internal control region and complements transcription in a TFIIIA-depleted oocyte nuclear extract. Random, cassette-mediated mutagenesis of the carboxyl region of TFIIIA, which is not required for promoter binding, has defined a 14-amino-acid region that is critical for transcriptional activation. In contrast to activators of RNA polymerase II, the activity of the TFIIIA activation domain is strikingly sensitive to its position relative to the DNA-binding domain. When the eight amino acids that separate the transcription-activating domain from the last zinc finger are deleted, transcriptional activity is lost. Surprisingly, diverse amino acids can replace these eight amino acids with restoration of full transcriptional activity, suggesting that the length and not the sequence of this region is important. Insertion of amino acids between the zinc finger region and the transcription-activating domain causes a reduction in transcription proportional to the number of amino acids introduced. We propose that to function, the transcription-activating domain of TFIIIA must be correctly positioned at a minimum distance from the DNA-binding domain.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archambault J., Milne C. A., Schappert K. T., Baum B., Friesen J. D., Segall J. The deduced sequence of the transcription factor TFIIIA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals extensive divergence from Xenopus TFIIIA. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3282–3288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew B., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Two components of Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor IIIB (TFIIIB) are stereospecifically located upstream of a tRNA gene and interact with the second-largest subunit of TFIIIC. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5181–5189. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieker J. J., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Formation of a rate-limiting intermediate in 5S RNA gene transcription. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):119–127. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Brown D. D., Jordan E. A nuclear extract of Xenopus laevis oocytes that accurately transcribes 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1077–1086. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camier S., Gabrielsen O., Baker R., Sentenac A. A split binding site for transcription factor tau on the tRNA3Glu gene. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):491–500. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. F., Gerrard S. P., Cozzarelli N. R. Analysis of RNA polymerase III transcription complexes by gel filtration. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4309–4317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipev C. C., Wolffe A. P. Chromosomal organization of Xenopus laevis oocyte and somatic 5S rRNA genes in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):45–55. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormack B. P., Struhl K. The TATA-binding protein is required for transcription by all three nuclear RNA polymerases in yeast cells. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):685–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby M. K., Andrews M. T., Brown D. D. Transcription complexes that program Xenopus 5S RNA genes are stable in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5516–5520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darby M. K., Joho K. E. Differential binding of zinc fingers from Xenopus TFIIIA and p43 to 5S RNA and the 5S RNA gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3155–3164. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Rio S., Setzer D. R. The role of zinc fingers in transcriptional activation by transcription factor IIIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):168–172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Río S., Setzer D. R. High yield purification of active transcription factor IIIA expressed in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6197–6203. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Engelke D. R., Geiduschek E. P. HeLa cell RNA polymerase III transcription factors. Functional characterization of a fraction identified by its activity in a second template rescue assay. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1934–1943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskins C. J., Fiser-Littell R. M., Duke A. L., Hanas J. S. Species variation in transcription factor IIIA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):781–794. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskins C. J., Hanas J. S. Sequence variation in transcription factor IIIA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):2117–2123. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskins C. J., Smith J. F., Ogilvie M. K., Hanas J. S. Comparison of the sequence and structure of transcription factor IIIA from Bufo americanus and Rana pipiens. Gene. 1992 Oct 21;120(2):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg A. M., King B. O., Roeder R. G. Xenopus 5S gene transcription factor, TFIIIA: characterization of a cDNA clone and measurement of RNA levels throughout development. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guddat U., Bakken A. H., Pieler T. Protein-mediated nuclear export of RNA: 5S rRNA containing small RNPs in xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):619–628. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90665-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. J., Clemens K. R. Locations of contacts between individual zinc fingers of Xenopus laevis transcription factor IIIA and the internal control region of a 5S RNA gene. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 24;31(46):11600–11605. doi: 10.1021/bi00161a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J., Tullius T. D., Wolffe A. P. A protein-protein interaction is essential for stable complex formation on a 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6009–6012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho K. E., Darby M. K., Crawford E. T., Brown D. D. A finger protein structurally similar to TFIIIA that binds exclusively to 5S RNA in Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90809-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Bartholomew B., Blanco J. A., Johnson T. E., Geiduschek E. P. Two essential components of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor TFIIIB: transcription and DNA-binding properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7308–7312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Joazeiro C. A., Pisano M., Geiduschek E. P., Colbert T., Hahn S., Blanco J. A. The role of the TATA-binding protein in the assembly and function of the multisubunit yeast RNA polymerase III transcription factor, TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1055–1064. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90399-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Riggs D. L., Negri R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription factor IIIB generates extended DNA interactions in RNA polymerase III transcription complexes on tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2551–2566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Tanaka M., Sullivan M. L., Hernandez N. A TBP complex essential for transcription from TATA-less but not TATA-containing RNA polymerase III promoters is part of the TFIIIB fraction. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1029–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90397-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majowski K., Mentzel H., Pieler T. A split binding site for TFIIIC on the Xenopus 5S gene. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3057–3063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller F., Clarkson S. G., Galas D. J. Sequence of a 3.18 kb tandem repeat of Xenopus laevis DNA containing 8 tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7191–7191. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao C. I., Lee T. C., Liao Y. D., Wu C. W. An N-terminally fused Xenopus transcription factor IIIA synthesized in Escherichia coli is biologically active. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10295–10299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. C., Doering J. L., Brown D. D. Characterization of two xenopus somatic 5S DNAs and one minor oocyte-specific 5S DNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):131–141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Wegnez M. Isolation of a 7S particle from Xenopus laevis oocytes: a 5S RNA-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):241–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidhaar-Olson J. F., Bowie J. U., Breyer R. M., Hu J. C., Knight K. L., Lim W. A., Mossing M. C., Parsell D. A., Shoemaker K. R., Sauer R. T. Random mutagenesis of protein sequences using oligonucleotide cassettes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;208:564–586. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)08029-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. Assembly of a yeast 5 S RNA gene transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11578–11584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setzer D. R., Brown D. D. Formation and stability of the 5 S RNA transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2483–2492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Differential binding of a S. cerevisiae RNA polymerase III transcription factor to two promoter segments of a tRNA gene. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):847–853. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart A. K., Fisher T. S., Pugh B. F. The TATA-binding protein and associated factors are components of pol III transcription factor TFIIIB. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1015–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90396-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theunissen O., Rudt F., Guddat U., Mentzel H., Pieler T. RNA and DNA binding zinc fingers in Xenopus TFIIIA. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):679–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrana K. E., Churchill M. E., Tullius T. D., Brown D. D. Mapping functional regions of transcription factor TFIIIA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1684–1696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. J., Jackson S. P. Mechanism of TATA-binding protein recruitment to a TATA-less class III promoter. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1041–1053. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90398-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Developmental regulation of two 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1626–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Differential 5S RNA gene expression in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):733–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes through a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex without disrupting it. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Morse R. H. The transcription complex of the Xenopus somatic 5 S RNA gene. A functional analysis of protein-DNA interactions outside of the internal control region. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4592–4599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Transcription fraction TFIIIC can regulate differential Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription in vitro. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):1071–1079. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Guan C., Li P., Riggs P. D., Inouye H. Vectors that facilitate the expression and purification of foreign peptides in Escherichia coli by fusion to maltose-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]