Abstract
In the title compound, C10H9ClN2O4, the oxazolidinone ring adopts a near-planar conformation, with mean and maximum deviations of 0.0204 (8) and 0.0328 (8) Å, respectively. The nitro group is twisted slightly from the plane of the benzene ring, making a dihedral angle of 6.79 (3)°. The dihedral angle between the mean oxazolidinone plane and the benzene ring is 56.21 (3)°. In the crystal, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and N—O⋯π interactions [O⋯centroid distances = 3.478 (1) and 3.238 (1) Å] dominate the packing, forming infinite zigzag chains along the b-axis direction. Neighbouring chains are linked together through C—H⋯O and C—H⋯Cl interactions. The absolute configuration of the two stereogenic centres was determined using the anomalous dispersion of the Cl atom.
Related literature
For the biological activity of oxazolidinone derivatives, see: Michalska et al. (2012 ▶); Mathur et al. (2013 ▶); Jindal et al. (2013 ▶). For related structures, see: Bach et al. (2001 ▶); Tsui et al. (2013 ▶). For detailed of the synthesis, see: Madesclaire et al. (2013 ▶).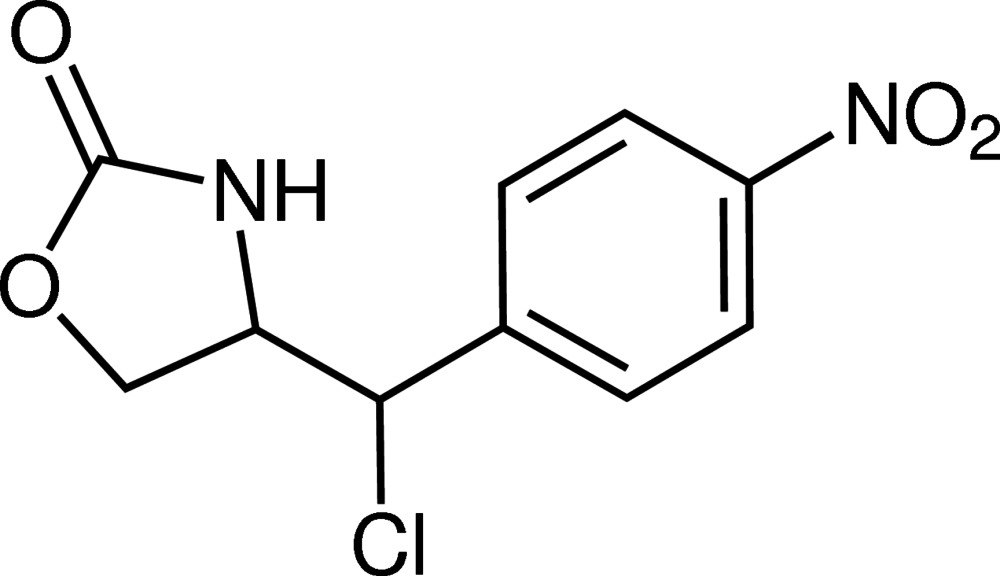
Experimental
Crystal data
C10H9ClN2O4
M r = 256.64
Monoclinic,

a = 7.2372 (1) Å
b = 6.6726 (1) Å
c = 11.7126 (2) Å
β = 106.715 (1)°
V = 541.71 (1) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.36 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.52 × 0.49 × 0.34 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012 ▶) T min = 0.915, T max = 1.000
12895 measured reflections
6114 independent reflections
5384 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.014
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.098
S = 1.06
6114 reflections
158 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.44 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 2348 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: −0.03 (3)
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2012 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2012 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813010398/kp2451sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813010398/kp2451Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813010398/kp2451Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3⋯O15i | 0.77 (2) | 2.32 (2) | 3.095 (1) | 179 (2) |
| C6—H6⋯O16ii | 0.98 | 2.46 | 3.309 (2) | 145 |
| C11—H11⋯Cl17iii | 0.93 | 2.83 | 3.582 (1) | 139 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Oxazolidinones are a new class of synthetic antimicrobial agents. Linezolid is the first oxazolidinone approved for human use in the treatment of multidrug-resistant gram-positive bacterial infections (Michalska et al., 2012; Mathur et al., 2013). Linezolid may also offer novel disease modifying and symptomatic therapeutic potential for the treatment of anxiety disorders (Jindal et al., 2013).
The molecular structure of the title compound (Fig. 1) reveals a planar oxazolidinone ring with a mean deviation of 0.0204 (8) Å, maximum deviation from planarity being 0.0328 (8) Å for atom C5. The dihedral angle between the mean oxazolidinone plane and the phenyl ring is 56.21 (3)°. The p-NO2 group form a interplanar angle of 6.79° with the benzene ring. In the crystal, molecules are linked through N3—H3···O15 hydrogen bonds into infinite zigzag chains extending along the b axis (Table 1, Fig. 2). In chains, molecules are regularly arranged in head-to-tail sequence allowing N—O···π stacking interactions which reinforce the chain cohesion (Fig. 2 and 3). These stacking forces are characterized by two N13—O15···Cgi, iv [symmetry code: i: -x + 1, y + 1/2, -z + 1; iv: -x + 1, y - 1/2, -z + 1] interactions with distances of 3.478 (1) Å and 3.238 (1) Å between the O15 atom and centroid, Cg, of the (C7—C12) aromatic rings. Adjacent chains build the three dimensional network via C6—H6···O16 and C11—H11···Cl17 interactions (Table 1).
The title coumpound exhibits structural similarities with related structures (Bach et al., 2001; Tsui et al., 2013).
Experimental
The title compound was obtained as a by-product from the reaction of 4-[hydroxy(4-nitrophenyl)methyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one and benzenesulfonyl chloride with pyridine in chloroform. The synthesis process is described by Madesclaire et al. (2013). After isolation and purification by column chromatography, crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation from a mixture of ethyl acetate-cyclohexane (1:1 vol.) solution.
Refinement
H atoms were all found in a difference map, but those bonded to C were refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C) and C—H = 0.93–0.98 Å. The H atom bonded to N was freely refined. The highest peak and the deepest hole in the difference Fourier map are located 0.70 and 1.02 Å, respectively from C11 and C8 atoms. The absolute structure was determined on the basis of 2348 Friedel pairs.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure showing the atom labelling scheme and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms.
Fig. 2.
Projection along a axis, showing zigzag chain of C10H9ClN2O4 molecules connected by N—H···O hydrogen bonds and N—O···π interactions (dashed lines). H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity.
Fig. 3.
Projection along b axis, showing shift between adjacent chains. N—H···O hydrogen bonds and N—O···π interactions are represented as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C10H9ClN2O4 | F(000) = 264 |
| Mr = 256.64 | Dx = 1.573 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Melting point: 414 K |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.2372 (1) Å | Cell parameters from 6817 reflections |
| b = 6.6726 (1) Å | θ = 4.0–39.2° |
| c = 11.7126 (2) Å | µ = 0.36 mm−1 |
| β = 106.715 (1)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 541.71 (1) Å3 | Block prism, colourless |
| Z = 2 | 0.52 × 0.49 × 0.34 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 6114 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 5384 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.014 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 41.1°, θmin = 4.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2012) | h = −11→13 |
| Tmin = 0.915, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −12→10 |
| 12895 measured reflections | l = −21→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.098 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0548P)2 + 0.0254P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 6114 reflections | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 158 parameters | Δρmin = −0.44 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 2348 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: −0.03 (3) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | −0.27342 (14) | 1.09892 (14) | 0.00860 (7) | 0.04046 (18) | |
| C2 | −0.09939 (17) | 1.16003 (16) | 0.07729 (9) | 0.03409 (18) | |
| N3 | −0.04803 (15) | 1.04959 (14) | 0.17795 (9) | 0.0379 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.035 (3) | 1.073 (4) | 0.234 (2) | 0.064 (7)* | |
| C4 | −0.18727 (13) | 0.89934 (14) | 0.18369 (8) | 0.02872 (15) | |
| H4 | −0.2438 | 0.9293 | 0.2484 | 0.034* | |
| C5 | −0.33823 (17) | 0.9297 (2) | 0.06159 (11) | 0.0423 (2) | |
| H5A | −0.3460 | 0.8116 | 0.0121 | 0.051* | |
| H5B | −0.4646 | 0.9553 | 0.0716 | 0.051* | |
| C6 | −0.09944 (12) | 0.68917 (13) | 0.19899 (7) | 0.02377 (12) | |
| H6 | −0.0574 | 0.6564 | 0.1288 | 0.029* | |
| C7 | 0.07040 (11) | 0.67131 (13) | 0.30890 (7) | 0.02336 (12) | |
| C8 | 0.04894 (13) | 0.68896 (17) | 0.42314 (7) | 0.02948 (16) | |
| H8 | −0.0736 | 0.7054 | 0.4323 | 0.035* | |
| C9 | 0.20770 (14) | 0.68227 (17) | 0.52297 (7) | 0.03020 (16) | |
| H9 | 0.1936 | 0.6931 | 0.5992 | 0.036* | |
| C10 | 0.38832 (12) | 0.65896 (14) | 0.50598 (7) | 0.02706 (14) | |
| C11 | 0.41443 (13) | 0.64207 (18) | 0.39412 (9) | 0.03193 (17) | |
| H11 | 0.5374 | 0.6270 | 0.3855 | 0.038* | |
| C12 | 0.25405 (13) | 0.64796 (18) | 0.29494 (8) | 0.02991 (16) | |
| H12 | 0.2691 | 0.6363 | 0.2190 | 0.036* | |
| N13 | 0.55799 (13) | 0.64956 (14) | 0.61094 (8) | 0.03406 (16) | |
| O14 | 0.53442 (16) | 0.6452 (3) | 0.70939 (8) | 0.0556 (3) | |
| O15 | 0.71821 (13) | 0.6472 (2) | 0.59423 (9) | 0.0488 (2) | |
| O16 | −0.0129 (2) | 1.29556 (17) | 0.04888 (10) | 0.0528 (3) | |
| Cl17 | −0.28820 (3) | 0.51760 (4) | 0.20713 (2) | 0.03492 (6) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0460 (4) | 0.0391 (4) | 0.0291 (3) | 0.0070 (3) | −0.0005 (3) | 0.0078 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0433 (5) | 0.0272 (4) | 0.0324 (4) | 0.0033 (4) | 0.0119 (4) | 0.0008 (3) |
| N3 | 0.0380 (4) | 0.0299 (4) | 0.0352 (4) | −0.0064 (3) | −0.0062 (3) | 0.0051 (3) |
| C4 | 0.0271 (4) | 0.0286 (3) | 0.0258 (3) | 0.0025 (3) | 0.0002 (3) | 0.0024 (3) |
| C5 | 0.0337 (5) | 0.0426 (5) | 0.0383 (5) | −0.0012 (4) | −0.0092 (4) | 0.0089 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0232 (3) | 0.0272 (3) | 0.0201 (3) | 0.0001 (2) | 0.0049 (2) | 0.0002 (2) |
| C7 | 0.0223 (3) | 0.0262 (3) | 0.0209 (3) | 0.0023 (2) | 0.0051 (2) | 0.0020 (2) |
| C8 | 0.0229 (3) | 0.0433 (5) | 0.0221 (3) | 0.0036 (3) | 0.0063 (2) | 0.0017 (3) |
| C9 | 0.0285 (4) | 0.0399 (4) | 0.0210 (3) | 0.0030 (3) | 0.0052 (3) | 0.0024 (3) |
| C10 | 0.0248 (3) | 0.0277 (3) | 0.0250 (3) | 0.0037 (3) | 0.0013 (2) | 0.0025 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0225 (3) | 0.0415 (5) | 0.0311 (4) | 0.0062 (3) | 0.0067 (3) | 0.0010 (3) |
| C12 | 0.0256 (3) | 0.0409 (4) | 0.0239 (3) | 0.0057 (3) | 0.0083 (2) | 0.0008 (3) |
| N13 | 0.0301 (3) | 0.0315 (3) | 0.0330 (4) | 0.0043 (3) | −0.0029 (3) | 0.0024 (3) |
| O14 | 0.0484 (5) | 0.0801 (8) | 0.0293 (4) | 0.0045 (5) | −0.0032 (3) | 0.0063 (5) |
| O15 | 0.0270 (3) | 0.0631 (6) | 0.0483 (5) | 0.0074 (4) | −0.0018 (3) | 0.0020 (5) |
| O16 | 0.0723 (7) | 0.0370 (4) | 0.0576 (6) | −0.0051 (4) | 0.0321 (5) | 0.0057 (4) |
| Cl17 | 0.03212 (10) | 0.03645 (11) | 0.03473 (10) | −0.00833 (9) | 0.00727 (7) | −0.00087 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C2 | 1.3480 (15) | C7—C12 | 1.3938 (12) |
| O1—C5 | 1.4310 (16) | C7—C8 | 1.3956 (11) |
| C2—O16 | 1.2004 (15) | C8—C9 | 1.3844 (13) |
| C2—N3 | 1.3487 (14) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C4 | 1.4367 (14) | C9—C10 | 1.3863 (13) |
| N3—H3 | 0.77 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C6 | 1.5288 (12) | C10—C11 | 1.3811 (13) |
| C4—C5 | 1.5431 (13) | C10—N13 | 1.4679 (11) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9800 | C11—C12 | 1.3866 (13) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9700 | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5B | 0.9700 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.5073 (11) | N13—O14 | 1.2136 (14) |
| C6—Cl17 | 1.8058 (9) | N13—O15 | 1.2303 (13) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9800 | ||
| C2—O1—C5 | 110.26 (8) | C4—C6—H6 | 109.0 |
| O16—C2—O1 | 122.33 (11) | Cl17—C6—H6 | 109.0 |
| O16—C2—N3 | 128.27 (12) | C12—C7—C8 | 119.65 (7) |
| O1—C2—N3 | 109.38 (9) | C12—C7—C6 | 118.66 (7) |
| C2—N3—C4 | 113.67 (9) | C8—C7—C6 | 121.59 (7) |
| C2—N3—H3 | 126.1 (18) | C9—C8—C7 | 120.85 (8) |
| C4—N3—H3 | 119.1 (18) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.6 |
| N3—C4—C6 | 111.84 (8) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.6 |
| N3—C4—C5 | 100.62 (8) | C8—C9—C10 | 118.05 (8) |
| C6—C4—C5 | 112.87 (8) | C8—C9—H9 | 121.0 |
| N3—C4—H4 | 110.4 | C10—C9—H9 | 121.0 |
| C6—C4—H4 | 110.4 | C11—C10—C9 | 122.49 (8) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 110.4 | C11—C10—N13 | 118.76 (8) |
| O1—C5—C4 | 105.81 (9) | C9—C10—N13 | 118.74 (8) |
| O1—C5—H5A | 110.6 | C10—C11—C12 | 118.85 (8) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 110.6 | C10—C11—H11 | 120.6 |
| O1—C5—H5B | 110.6 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.6 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 110.6 | C11—C12—C7 | 120.10 (8) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 108.7 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C7—C6—C4 | 112.46 (7) | C7—C12—H12 | 119.9 |
| C7—C6—Cl17 | 110.38 (6) | O14—N13—O15 | 123.18 (10) |
| C4—C6—Cl17 | 107.00 (6) | O14—N13—C10 | 118.97 (9) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 109.0 | O15—N13—C10 | 117.84 (9) |
| C5—O1—C2—O16 | 177.34 (12) | Cl17—C6—C7—C8 | −53.58 (10) |
| C5—O1—C2—N3 | −3.94 (14) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −0.42 (15) |
| O16—C2—N3—C4 | 179.45 (12) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −176.72 (9) |
| O1—C2—N3—C4 | 0.83 (14) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.44 (15) |
| C2—N3—C4—C6 | 122.37 (10) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.12 (16) |
| C2—N3—C4—C5 | 2.29 (13) | C8—C9—C10—N13 | −179.40 (9) |
| C2—O1—C5—C4 | 5.25 (13) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.22 (17) |
| N3—C4—C5—O1 | −4.35 (12) | N13—C10—C11—C12 | 179.06 (10) |
| C6—C4—C5—O1 | −123.69 (10) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | 0.23 (17) |
| N3—C4—C6—C7 | 57.76 (10) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 0.08 (16) |
| C5—C4—C6—C7 | 170.37 (8) | C6—C7—C12—C11 | 176.48 (10) |
| N3—C4—C6—Cl17 | 179.12 (6) | C11—C10—N13—O14 | −173.10 (13) |
| C5—C4—C6—Cl17 | −68.26 (9) | C9—C10—N13—O14 | 6.21 (16) |
| C4—C6—C7—C12 | −110.50 (10) | C11—C10—N13—O15 | 7.17 (15) |
| Cl17—C6—C7—C12 | 130.09 (8) | C9—C10—N13—O15 | −173.52 (11) |
| C4—C6—C7—C8 | 65.84 (11) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3···O15i | 0.77 (2) | 2.32 (2) | 3.095 (1) | 179 (2) |
| C6—H6···O16ii | 0.98 | 2.46 | 3.309 (2) | 145 |
| C11—H11···Cl17iii | 0.93 | 2.83 | 3.582 (1) | 139 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1; (ii) −x, y−1/2, −z; (iii) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: KP2451).
References
- Bach, T., Schlummer, B. & Harms, K. (2001). Chem. Eur. J. 7, 2581–2594. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2012). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Jindal, A., Mahesh, R. & Kumar, B. (2013). Prog. NeuroPsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry, 40, 47–53. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Madesclaire, M., Coudert, P., Leal, F., Tarrit, S., Zaitseva, J. V. & Zaitsev, V. P. (2013). Chem. Heterocycl. Compd In preparation.
- Mathur, T., Kalia, V., Barman, T. K., Singhal, S., Khan, S., Upadhyay, D. J., Rattan, A. & Raj, V. S. (2013). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents, 41, 36–40. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Michalska, K., Karpiuk, I., Król, M. & Tyski, S. (2012). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 21, 577–591. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tsui, G. C., Ninnemann, N. M., Hosotani, A. & Lautens, M. (2013). Org. Lett. 15, 1064–1067. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813010398/kp2451sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813010398/kp2451Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813010398/kp2451Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





