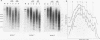Abstract
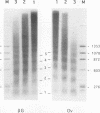
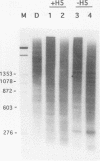
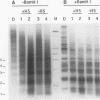
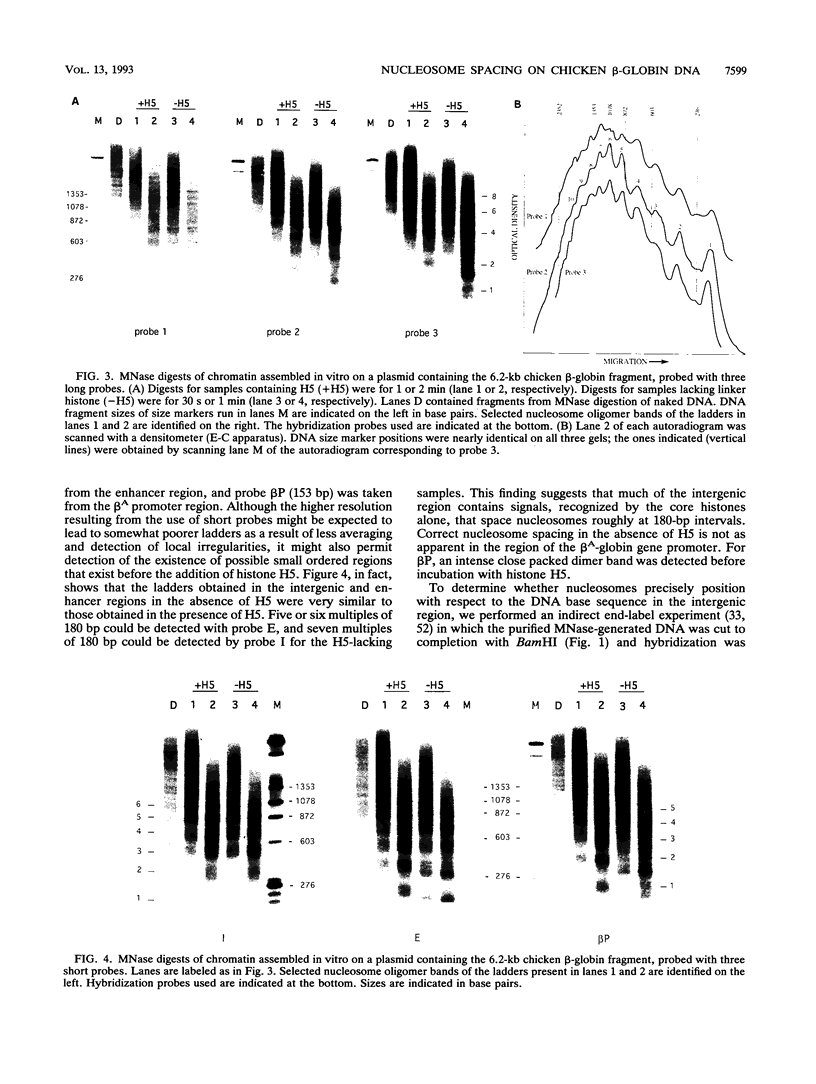
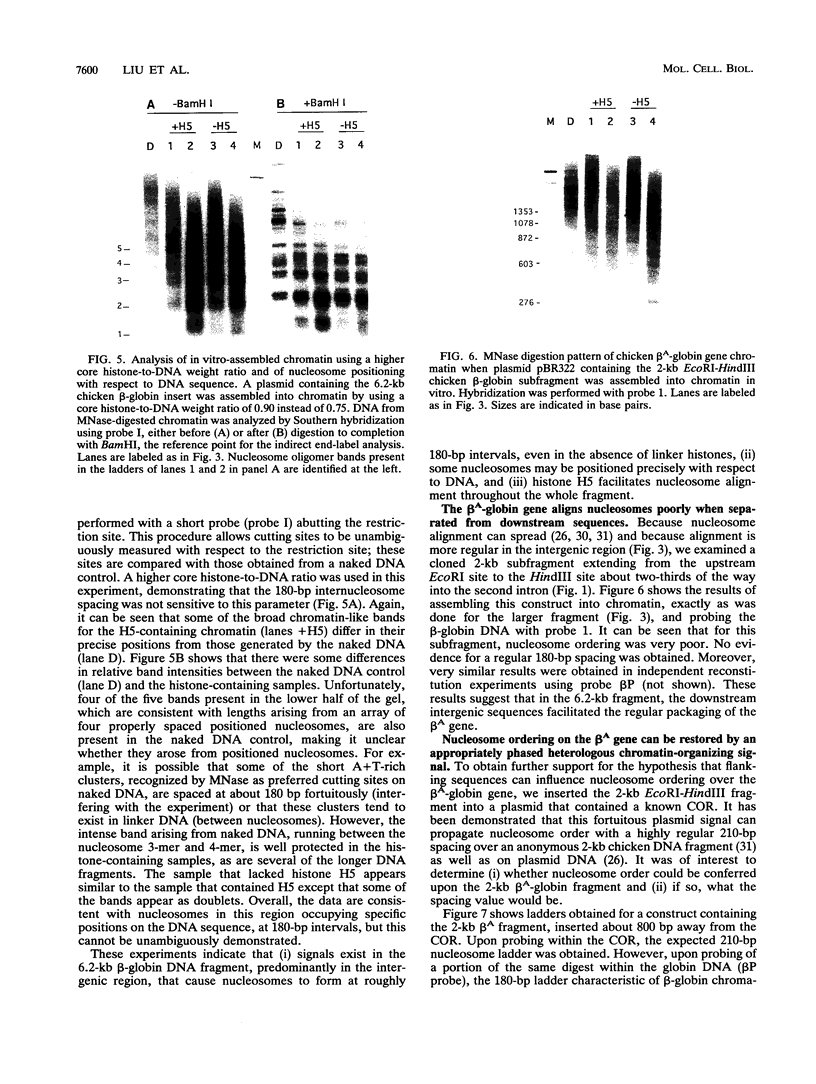
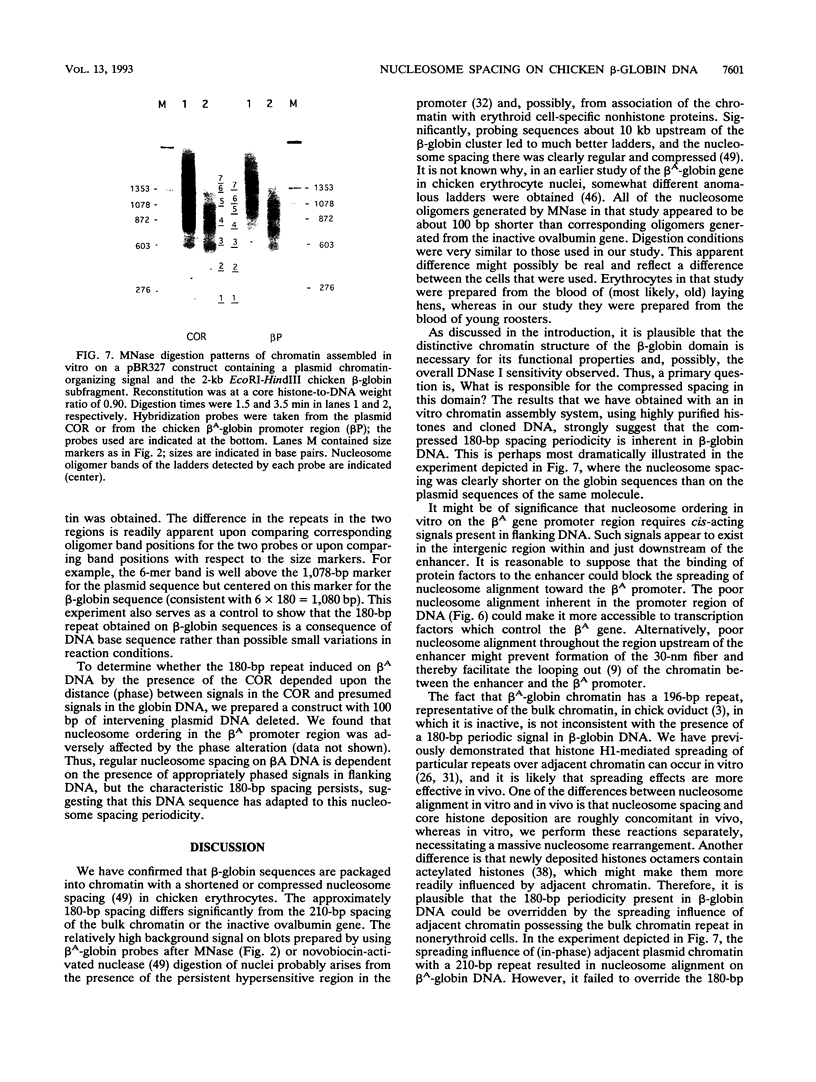
We have confirmed the result that chicken beta-globin gene chromatin, which possesses the characteristics of active chromatin in erythroid cells, has shortened internucleosome spacings compared with bulk chromatin or that of the ovalbumin gene, which is inactive. To understand how the short (approximately 180-bp) nucleosome repeat arises specifically on beta-globin DNA, we have studied chromatin assembly of cloned chicken beta-globin DNA in a defined in vitro system. With chicken erythrocyte core histones and linker histone H5 as the only cellular components, a cloned 6.2-kb chicken beta-globin DNA fragment assembled into chromatin possessing a regular 180 +/- 5-bp repeat, very similar to what is observed in erythroid cells. A 2-kb DNA subfragment containing the beta A gene and promoter region, but lacking the downstream intergenic region between the beta A and epsilon genes, failed to generate a regular nucleosome array in vitro, suggesting that the intergenic region facilitates linker histone-induced nucleosome alignment. When the beta A gene was placed on a plasmid that contained a known chromatin-organizing signal, nucleosome alignment with a 180-bp periodicity was restored, whereas nucleosomes on flanking plasmid sequences possessed a 210-bp spacing periodicity. Our results suggest that the shortened 180-bp nucleosome spacing periodicity observed in erythroid cells is encoded in the beta-globin DNA sequence and that nucleosome alignment by linker histones is facilitated by sequences in the beta A-epsilon intergenic region.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J., Staynov D. Z., Gould H. Reversible dissociation of linker histone from chromatin with preservation of internucleosomal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):885–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J. Structure and dynamics of transcriptionally active chromatin. J Cell Sci. 1992 May;102(Pt 1):1–5. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Dretzen G., Bellard F., Oudet P., Chambon P. Disruption of the typical chromatin structure in a 2500 base-pair region at the 5' end of the actively transcribed ovalbumin gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):223–230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnerot C., Grimber G., Briand P., Nicolas J. F. Patterns of expression of position-dependent integrated transgenes in mouse embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6331–6335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A., Kimura T., Gould H., Allan J. Perturbation of chromatin structure in the region of the adult beta-globin gene in chicken erythrocyte chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):57–70. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90626-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipev C. C., Wolffe A. P. Chromosomal organization of Xenopus laevis oocyte and somatic 5S rRNA genes in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):45–55. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. A 3' enhancer is required for temporal and tissue-specific transcriptional activation of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):731–734. doi: 10.1038/323731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi O. R., Engel J. D. Developmental regulation of beta-globin gene switching. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90005-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J. H., Whiteley M., Felsenfeld G. A 5' element of the chicken beta-globin domain serves as an insulator in human erythroid cells and protects against position effect in Drosophila. Cell. 1993 Aug 13;74(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80052-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. J., Thomas J. O. Salt-dependent co-operative interaction of histone H1 with linear DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 20;187(4):569–580. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. H., Reudelhuber T. L., Garrard W. T. Varigated chromatin structures of mouse ribosomal RNA genes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):133–155. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Lomonossoff G. P., Laskey R. A. High sequence specificity of micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2659–2673. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson J. B., Strommer J., Engel J. D. Isolation of the chicken beta-globin gene and a linked embryonic beta-like globin gene from a chicken DNA recombinant library. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90328-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg J. C., Elgin S. C. Boundary functions in the control of gene expression. Trends Genet. 1991 Oct;7(10):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90424-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. The formation and function of DNase I hypersensitive sites in the process of gene activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19259–19262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G., Reitman M. Control of globin gene transcription. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:95–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher E. A., Felsenfeld G. Comparison of the folding of beta-globin and ovalbumin gene containing chromatin isolated from chicken oviduct and erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):8010–8016. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Epner E., Driscoll M. C., Enver T., Brice M., Papayannopoulou T., Groudine M. A deletion of the human beta-globin locus activation region causes a major alteration in chromatin structure and replication across the entire beta-globin locus. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1637–1649. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman L. A., Garrard W. T. DNA supercoiling in chromatin structure and gene expression. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1992;2(2):165–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginder G. D., Wood W. I., Felsenfeld G. Isolation and characterization of recombinant clones containing the chicken adult beta-globin gene. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8099–8102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse J. E., Nickol J. M., Lieber M. R., Felsenfeld G. Regulated gene expression in transfected primary chicken erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4312–4316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Altenburger W. Sequence specific cleavage of DNA by micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2643–2658. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Käs E., Laemmli U. K. Highly preferential nucleation of histone H1 assembly on scaffold-associated regions. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 5;210(3):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong S. W., Lauderdale J. D., Stein A. Chromatin assembly on plasmid DNA in vitro. Apparent spreading of nucleosome alignment from one region of pBR327 by histone H5. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 20;222(4):1131–1147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90597-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucherlapati R., Skoultchi A. I. Introduction of purified genes into mammalian cells. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;16(4):349–379. doi: 10.3109/10409238409108719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Leffak M. Assembly of active chromatin. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2055–2060. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Käs E., Poljak L., Adachi Y. Scaffold-associated regions: cis-acting determinants of chromatin structural loops and functional domains. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Apr;2(2):275–285. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauderdale J. D., Stein A. Effects of plasmid length and positioned nucleosomes on chromatin assembly in vitro. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):489–499. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauderdale J. D., Stein A. Introns of the chicken ovalbumin gene promote nucleosome alignment in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6589–6596. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedospasov S. A., Georgiev G. P. Non-random cleavage of SV40 DNA in the compact minichromosome and free in solution by micrococcal nuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Lee E., Westphal H., Felsenfeld G. Site-independent expression of the chicken beta A-globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):749–752. doi: 10.1038/348749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M. Preferential and cooperative binding of histone I to chromosomal mammalian DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):733–736. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter G., Spierer P. Position effect variegation and chromatin proteins. Bioessays. 1992 Sep;14(9):605–612. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose S. M., Garrard W. T. Differentiation-dependent chromatin alterations precede and accompany transcription of immunoglobulin light chain genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8534–8544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Wangh L. J., Allfrey V. G. Processing of newly synthesized histone molecules. Science. 1975 Oct 10;190(4210):117–128. doi: 10.1126/science.1166303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A., Bina M. A model chromatin assembly system. Factors affecting nucleosome spacing. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):341–363. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A., Mitchell M. Generation of different nucleosome spacing periodicities in vitro. Possible origin of cell type specificity. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):1029–1043. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90127-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A. Reconstitution of chromatin from purified components. Methods Enzymol. 1989;170:585–603. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)70066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stief A., Winter D. M., Strätling W. H., Sippel A. E. A nuclear DNA attachment element mediates elevated and position-independent gene activity. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):343–345. doi: 10.1038/341343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strätling W. H., Dölle A., Sippel A. E. Chromatin structure of the chicken lysozyme gene domain as determined by chromatin fractionation and micrococcal nuclease digestion. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):495–502. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y. L., Xu Y. Z., Bellard M., Chambon P. Digestion of the chicken beta-globin gene chromatin with micrococcal nuclease reveals the presence of an altered nucleosomal array characterized by an atypical ladder of DNA fragments. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):293–300. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes T. M., Behringer R. R. Human globin locus activation region (LAR): role in temporal control. Trends Genet. 1990 Jul;6(7):219–223. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Brawley J., Martinson H. G. Nucleosome spacing is compressed in active chromatin domains of chick erythroid cells. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 11;31(5):1554–1563. doi: 10.1021/bi00120a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Assembly and propagation of repressed and depressed chromosomal states. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S. Active chromatin. Nature. 1982 May 27;297(5864):289–295. doi: 10.1038/297289a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]