Abstract
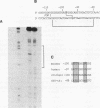
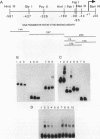
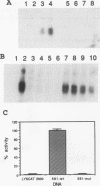
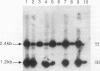
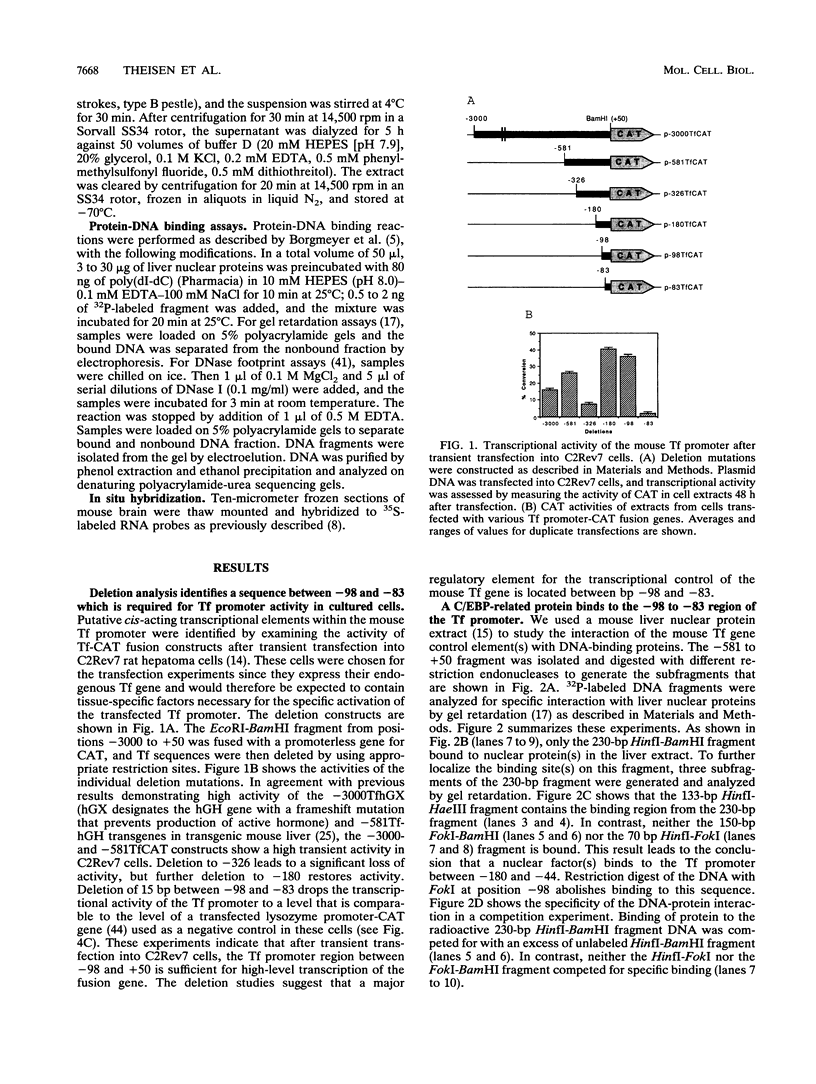
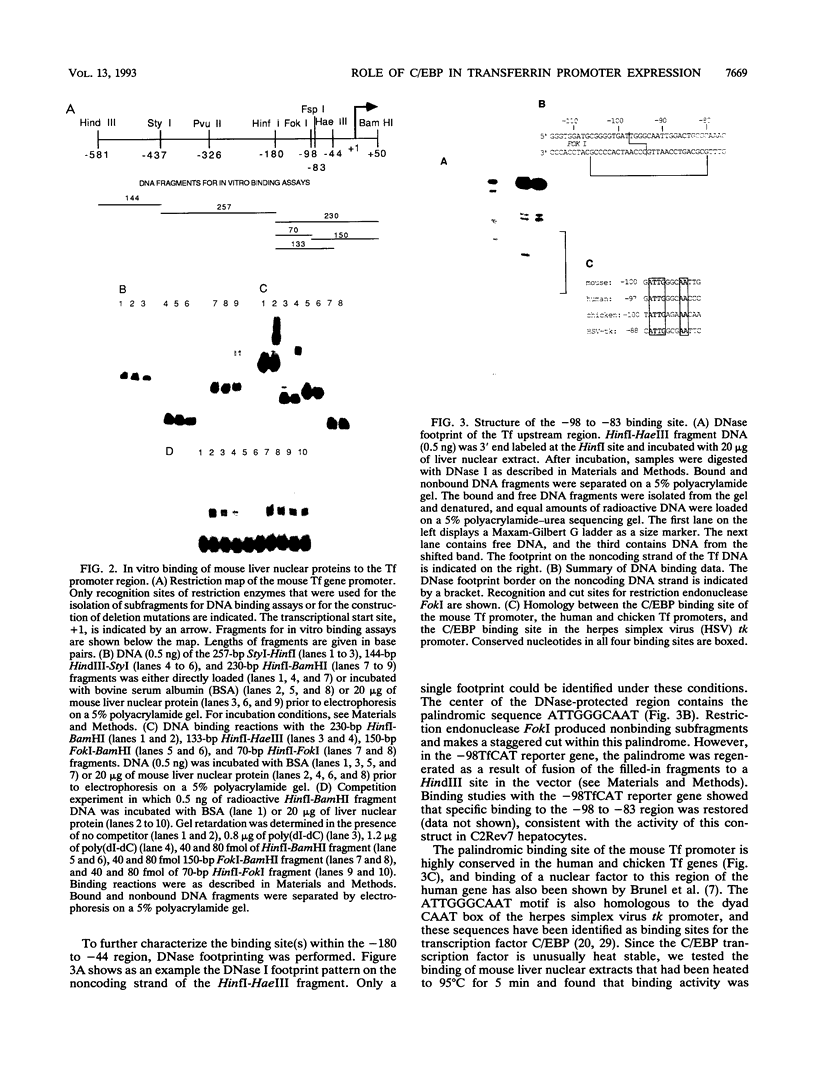
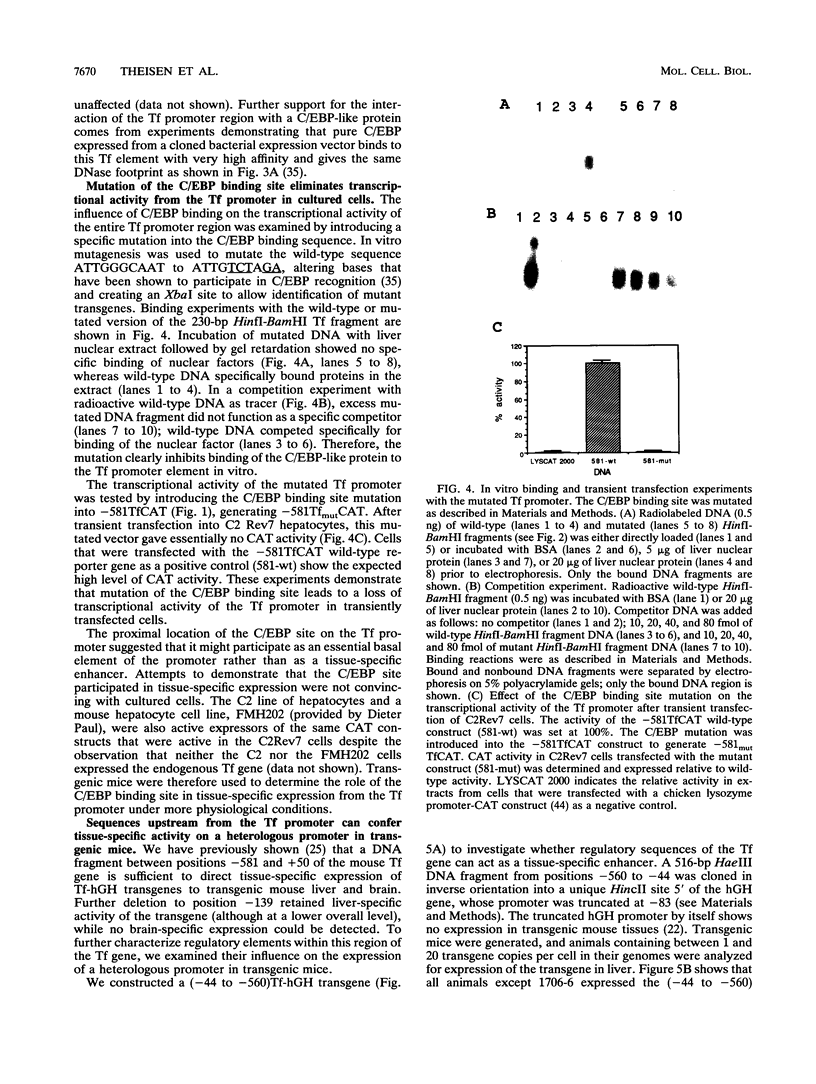
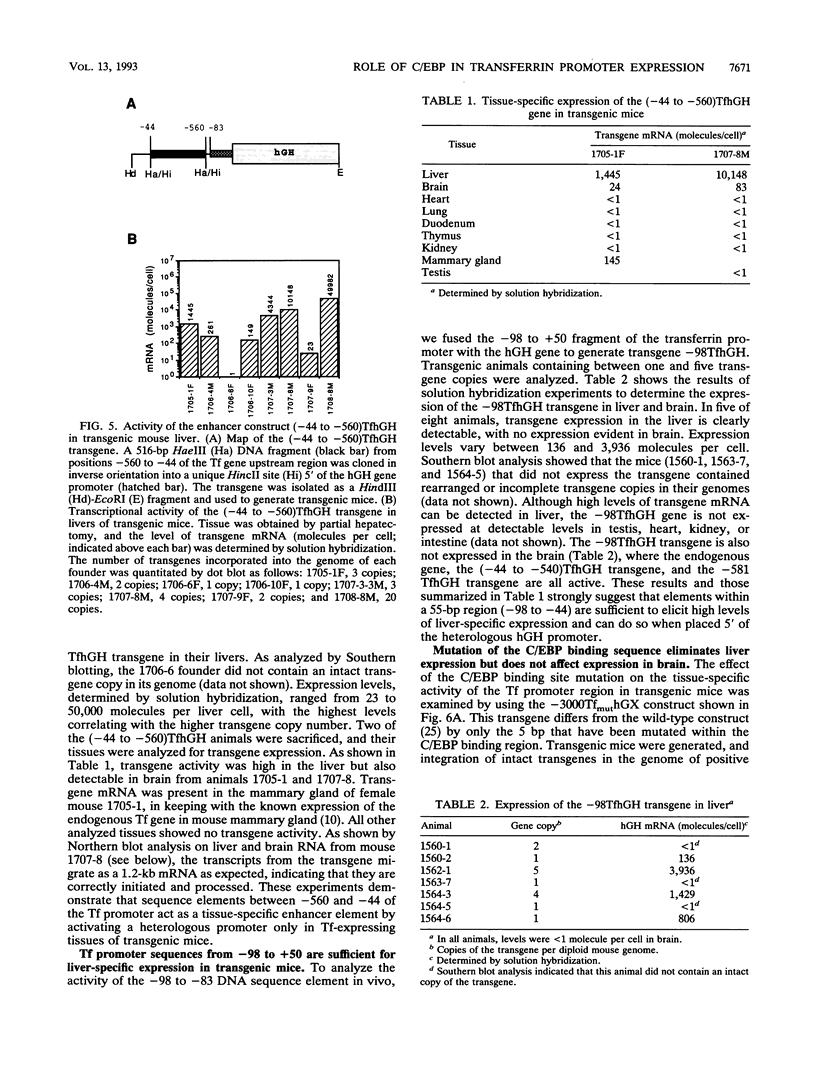
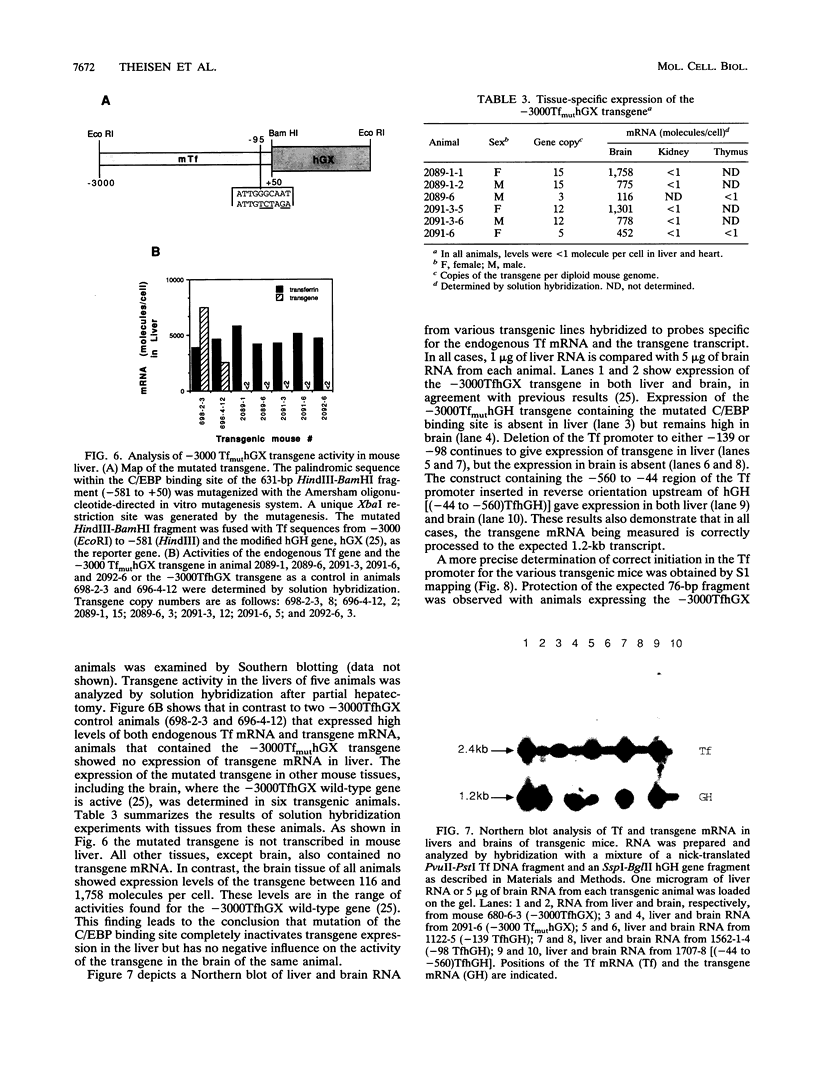
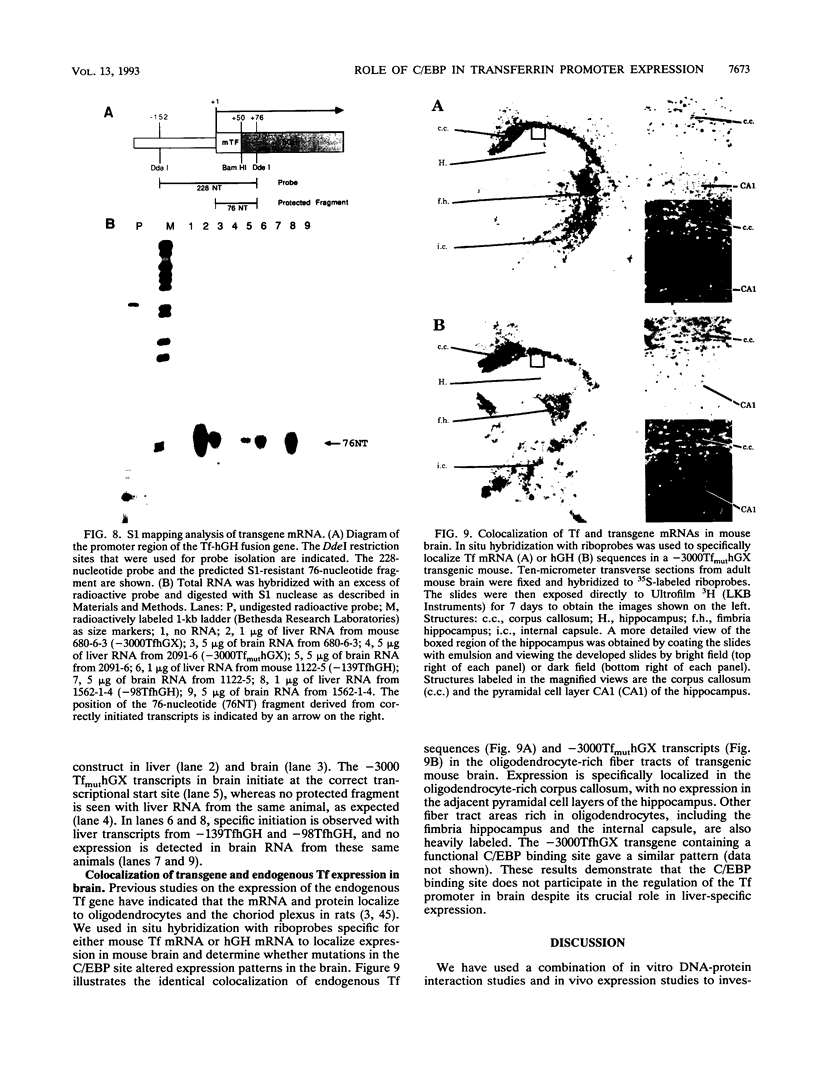
The gene for the iron-binding protein transferrin is transcribed at a high level in liver hepatocytes but is also active in several other cell types, including oligodendrocytes in the brain. Enhancer elements between bp -560 and -44 of the transferrin gene promoter specifically activated transcription from a heterologous promoter in transgenic mouse liver and brain. Within this region, a potent cis-acting element between bp -98 and -83 was found to be essential for gene activity in both cultured hepatocytes and transgenic mouse liver. The -98 to -83 element contains a CCAAT sequence and is specifically bound by a nuclear factor from mouse liver that is homologous to rat liver C/EBP (CAAT enhancer-binding protein). Point mutations within this binding site inhibit factor binding and abolish transcription in transfected hepatoma cells. When placed in the context of the 3,000-bp transferrin promoter, the C/EBP binding site mutation causes a complete loss of transcription in transgenic mouse liver; however, transgene expression in the brain of the same animals was unaffected. These results suggest a modular structure for the transferrin promoter and demonstrate that deletions or specific point mutations can be used to generate transgene promoters with an activity more restricted than that of their endogenous counterparts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian G. S., Bowman B. H., Herbert D. C., Weaker F. J., Adrian E. K., Robinson L. K., Walter C. A., Eddy C. A., Riehl R., Pauerstein C. J. Human transferrin. Expression and iron modulation of chimeric genes in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13344–13350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloch B., Popovici T., Levin M. J., Tuil D., Kahn A. Transferrin gene expression visualized in oligodendrocytes of the rat brain by using in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6706–6710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissier F., Augé-Gouillou C., Schaeffer E., Zakin M. M. The enhancer of the human transferrin gene is organized in two structural and functional domains. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9822–9828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borgmeyer U., Nowock J., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA-binding protein: a eukaryotic nuclear protein recognizing a symmetrical sequence on double-stranded linear DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4295–4311. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M., Senear A. W., Warren R., Palmiter R. D. Somatic expression of herpes thymidine kinase in mice following injection of a fusion gene into eggs. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90376-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunel F., Ochoa A., Schaeffer E., Boissier F., Guillou Y., Cereghini S., Cohen G. N., Zakin M. M. Interactions of DNA-binding proteins with the 5' region of the human transferrin gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10180–10185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadd G., McKnight G. S. Distinct patterns of cAMP-dependent protein kinase gene expression in mouse brain. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. H., Bissell M. J. Transferrin mRNA level in the mouse mammary gland is regulated by pregnancy and extracellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17247–17250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Yang V. W., Ntambi J. M., Geiman D. E., Landschulz W. H., Friedman A. D., Nakabeppu Y., Kelly T. J., Lane M. D. Differentiation-induced gene expression in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes: CCAAT/enhancer binding protein interacts with and activates the promoters of two adipocyte-specific genes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1323–1335. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet M., Gannon F., Hen R., Maroteaux L., Perrin F., Chambon P. Organization and sequence studies of the 17-piece chicken conalbumin gene. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):567–574. doi: 10.1038/282567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley M., Brownlee G. G. Disruption of a C/EBP binding site in the factor IX promoter is associated with haemophilia B. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):444–446. doi: 10.1038/345444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschatrette J., Moore E. E., Dubois M., Cassio D., Weiss M. C. Dedifferentiated variants of a rat hepatoma: analysis by cell hybridization. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Nov;5(6):697–718. doi: 10.1007/BF01542636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freytag S. O., Geddes T. J. Reciprocal regulation of adipogenesis by Myc and C/EBP alpha. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):379–382. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M. G., Crothers D. M. Equilibrium studies of the cyclic AMP receptor protein-DNA interaction. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jan 25;172(3):241–262. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., McKnight S. L. Identification of two polypeptide segments of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein required for transcriptional activation of the serum albumin gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1416–1426. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillou F., Zakin M. M., Part D., Boissier F., Schaeffer E. Sertoli cell-specific expression of the human transferrin gene. Comparison with the liver-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9876–9884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. E., Swift G. H., Ornitz D. M., Quaife C. J., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., MacDonald R. J. The rat elastase I regulatory element is an enhancer that directs correct cell specificity and developmental onset of expression in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2956–2967. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman L. M., Fritsch M. K., Gorski J. Probable nuclear precursors of preprolactin mRNA in rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2597–2600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huggenvik J. I., Idzerda R. L., Haywood L., Lee D. C., McKnight G. S., Griswold M. D. Transferrin messenger ribonucleic acid: molecular cloning and hormonal regulation in rat Sertoli cells. Endocrinology. 1987 Jan;120(1):332–340. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-1-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idzerda R. L., Behringer R. R., Theisen M., Huggenvik J. I., McKnight G. S., Brinster R. L. Expression from the transferrin gene promoter in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5154–5162. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idzerda R. L., Huebers H., Finch C. A., McKnight G. S. Rat transferrin gene expression: tissue-specific regulation by iron deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3723–3727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. A., McCormick C. A., Bray S. J., Hirsh J. A neuron-specific enhancer of the Drosophila dopa decarboxylase gene. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):676–686. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucero M. A., Schaeffer E., Cohen G. N., Zakin M. M. The 5' region of the human transferrin gene: structure and potential regulatory sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8692–8692. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The role of cis-acting promoter elements in tissue-specific albumin gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2711183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger S., Leff T., Breslow J. L. Nuclear factors AF-1 and C/EBP bind to the human ApoB gene promoter and modulate its transcriptional activity in hepatic cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9978–9983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miksicek R., Heber A., Schmid W., Danesch U., Posseckert G., Beato M., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid responsiveness of the transcriptional enhancer of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):283–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90745-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Graves B. J. Alkylation interference identifies essential DNA contacts for sequence-specific binding of the eukaryotic transcription factor C/EBP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3992–3996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L. Differential regulation of metallothionein-thymidine kinase fusion genes in transgenic mice and their offspring. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):701–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos I., Augé-Gouillou C., Zakin M. M. Characterization of the active part of the human transferrin gene enhancer and purification of two liver nuclear factors interacting with the TGTTTGC motif present in this region. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24220–24225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Platero J. S., Shuman J., Calame K. Ig/EBP-1: a ubiquitously expressed immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein that is similar to C/EBP and heterodimerizes with C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1404–1415. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Habener J. F. CHOP, a novel developmentally regulated nuclear protein that dimerizes with transcription factors C/EBP and LAP and functions as a dominant-negative inhibitor of gene transcription. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):439–453. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer E., Boissier F., Py M. C., Cohen G. N., Zakin M. M. Cell type-specific expression of the human transferrin gene. Role of promoter, negative, and enhancer elements. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7153–7160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A., Galas D. J. The interaction of RNA polymerase and lac repressor with the lac control region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jan;6(1):111–137. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Kruse F., MacDonald R. J., Hammer R. E. Differential requirements for cell-specific elastase I enhancer domains in transfected cells and transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):687–696. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. A novel myoblast enhancer element mediates MyoD transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4994–5003. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theisen M., Stief A., Sippel A. E. The lysozyme enhancer: cell-specific activation of the chicken lysozyme gene by a far-upstream DNA element. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):719–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsumi M., Skinner M. K., Sanders-Bush E. Transferrin gene expression and synthesis by cultured choroid plexus epithelial cells. Regulation by serotonin and cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9626–9631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umek R. M., Friedman A. D., McKnight S. L. CCAAT-enhancer binding protein: a component of a differentiation switch. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):288–292. doi: 10.1126/science.1987644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Cantwell C. A., Johnson P. F. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1553–1567. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xanthopoulos K. G., Prezioso V. R., Chen W. S., Sladek F. M., Cortese R., Darnell J. E., Jr The different tissue transcription patterns of genes for HNF-1, C/EBP, HNF-3, and HNF-4, protein factors that govern liver-specific transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3807–3811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakin M. M. Regulation of transferrin gene expression. FASEB J. 1992 Nov;6(14):3253–3258. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.14.1426763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D. E., Rabek J. P., Hsieh C. C., Torres-Ramos C., Papaconstantinou J. Functional analysis of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein enhancers and their subfragments in primary mouse hepatocyte cultures. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10676–10682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]