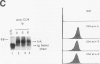
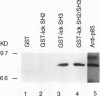
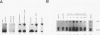Abstract
CD4 serves as a receptor for major histocompatibility complex class II antigens and as a receptor for the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) viral coat protein gp120. It is coupled to the protein-tyrosine kinase p56lck, an interaction necessary for an optimal response of certain T cells to antigen. In addition to the protein-tyrosine kinase domain, p56lck possesses Src homology 2 and 3 (SH2 and SH3) domains as well as a unique N-terminal region. The mechanism by which p56lck generates intracellular signals is unclear, although it has the potential to interact with various downstream molecules. One such downstream target is the lipid kinase phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase), which has been found to bind to activated pp60src and receptor-tyrosine kinases. In this study, we verified that PI 3-kinase associates with the CD4:p56lck complex as judged by the presence of PI 3-phosphate generated from anti-CD4 immunoprecipitates and detected by high-pressure liquid chromatographic analysis. However, surprisingly, CD4-p56lck was also found to associate with another lipid kinase, phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase (PI 4-kinase). The level of associated PI 4-kinase was generally higher than PI 3-kinase activity. HIV-1 gp120 and antibody-mediated cross-linking induced a 5- to 10-fold increase in the level of CD4-associated PI 4- and PI 3-kinases. The use of glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins carrying Lck-SH2, Lck-SH3, and Lck-SH2/SH3 domains showed PI 3-kinase binding to the SH3 domain of p56lck, an interaction facilitated by the presence of an adjacent SH2 domain. PI 4-kinase bound to neither the SH2 nor the SH3 domain of p56lck. CD4-p56lck contributes PI 3- and PI 4-kinase to the activation process of T cells and may play a role in HIV-1-induced immune defects.
Full text
PDF


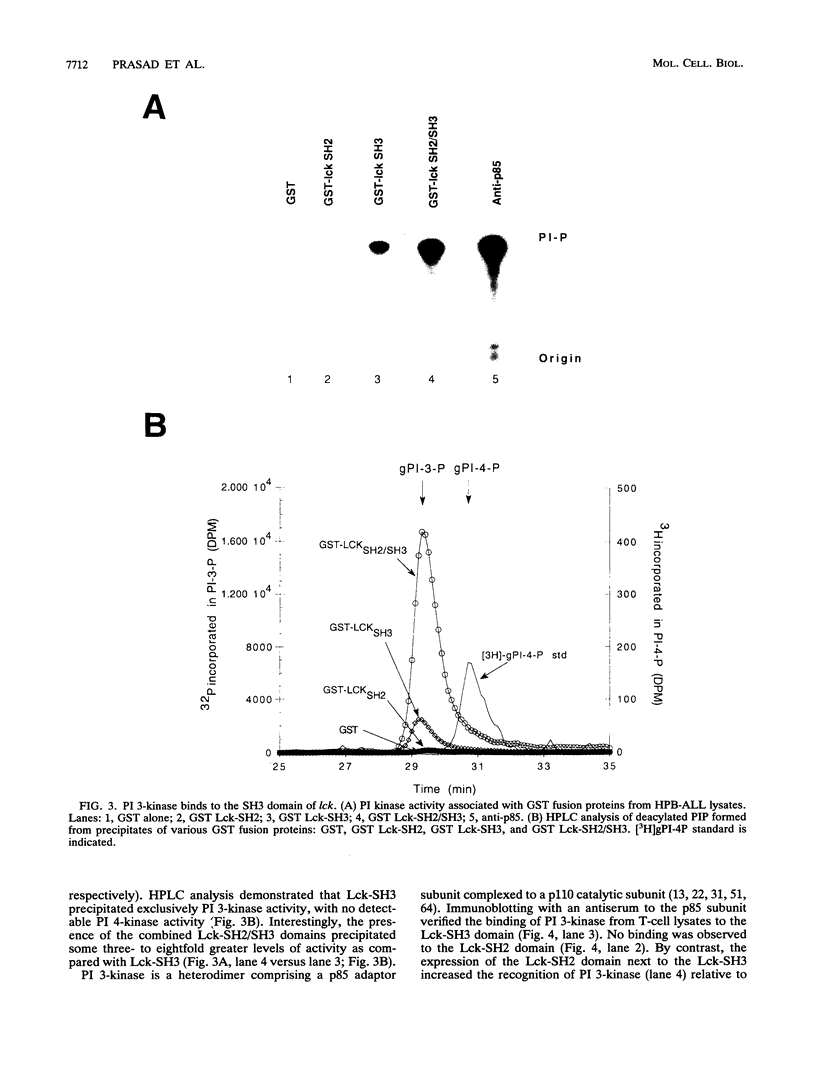

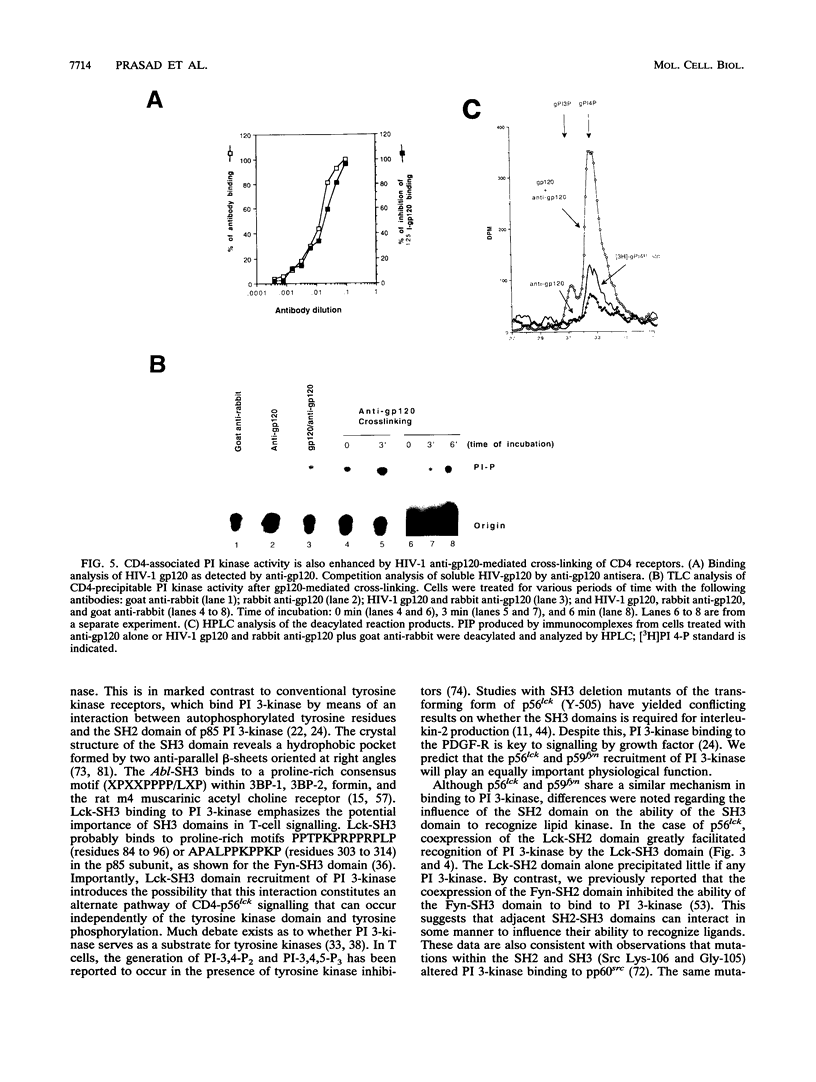



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham N., Miceli M. C., Parnes J. R., Veillette A. Enhancement of T-cell responsiveness by the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1991 Mar 7;350(6313):62–66. doi: 10.1038/350062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Blue M. L., Morimoto C., Schlossman S. F. Cross-linking of T3 (CD3) with T4 (CD4) enhances the proliferation of resting T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):678–682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auger K. R., Serunian L. A., Soltoff S. P., Libby P., Cantley L. C. PDGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates production of novel polyphosphoinositides in intact cells. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustine J. A., Sutor S. L., Abraham R. T. Interleukin 2- and polyomavirus middle T antigen-induced modification of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in activated T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4431–4440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber E. K., Dasgupta J. D., Schlossman S. F., Trevillyan J. M., Rudd C. E. The CD4 and CD8 antigens are coupled to a protein-tyrosine kinase (p56lck) that phosphorylates the CD3 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3277–3281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedinger P., Moriarty A., von Borstel R. C., 2nd, Donovan N. J., Steimer K. S., Littman D. R. Internalization of the human immunodeficiency virus does not require the cytoplasmic domain of CD4. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):162–165. doi: 10.1038/334162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyers A. D., Spruyt L. L., Williams A. F. Molecular associations between the T-lymphocyte antigen receptor complex and the surface antigens CD2, CD4, or CD8 and CD5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2945–2949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess K. E., Odysseos A. D., Zalvan C., Druker B. J., Anderson P., Schlossman S. F., Rudd C. E. Biochemical identification of a direct physical interaction between the CD4:p56lck and Ti(TcR)/CD3 complexes. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jul;21(7):1663–1668. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess K. E., Yamamoto M., Prasad K. V., Rudd C. E. CD5 acts as a tyrosine kinase substrate within a receptor complex comprising T-cell receptor zeta chain/CD3 and protein-tyrosine kinases p56lck and p59fyn. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9311–9315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron L., Abraham N., Pawson T., Veillette A. Structural requirements for enhancement of T-cell responsiveness by the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase p56lck. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2720–2729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Cantley L. C. Phosphoinositide kinases. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 25;29(51):11147–11156. doi: 10.1021/bi00503a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Duckworth B. C., Auger K. R., Cohen B., Schaffhausen B. S., Cantley L. C. Purification and characterization of phosphoinositide 3-kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19704–19711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan A. C., Irving B. A., Fraser J. D., Weiss A. The zeta chain is associated with a tyrosine kinase and upon T-cell antigen receptor stimulation associates with ZAP-70, a 70-kDa tyrosine phosphoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9166–9170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicchetti P., Mayer B. J., Thiel G., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein that binds to the SH3 region of Abl and is similar to Bcr and GAP-rho. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):803–806. doi: 10.1126/science.1379745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Filhol O., Payrastre B., Hunter T., Gill G. N. Interaction between the epidermal growth factor receptor and phosphoinositide kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):637–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Role of phosphatidylinositol kinase in PDGF receptor signal transduction. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1191–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.2466336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans J. P., Kanner S. B., Torres R. M., Ledbetter J. A. Interaction of CD4:lck with the T cell receptor/CD3 complex induces early signaling events in the absence of CD45 tyrosine phosphatase. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Mar;22(3):661–668. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichmann K., Jönsson J. I., Falk I., Emmrich F. Effective activation of resting mouse T lymphocytes by cross-linking submitogenic concentrations of the T cell antigen receptor with either Lyt-2 or L3T4. Eur J Immunol. 1987 May;17(5):643–650. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmrich F., Strittmatter U., Eichmann K. Synergism in the activation of human CD8 T cells by cross-linking the T-cell receptor complex with the CD8 differentiation antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8298–8302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo J. A., Navankasattusas S., Kavanaugh W. M., Milfay D., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. cDNA cloning of a novel 85 kd protein that has SH2 domains and regulates binding of PI3-kinase to the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90409-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Martin G. A., Turck C. W., del Rosario M., McCormick F., Williams L. T. Distinct phosphotyrosines on a growth factor receptor bind to specific molecules that mediate different signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90444-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. The human immunodeficiency virus: infectivity and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):617–622. doi: 10.1126/science.3277274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase activity associates with viral p60src protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1651–1658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaichenhaus N., Shastri N., Littman D. R., Turner J. M. Requirement for association of p56lck with CD4 in antigen-specific signal transduction in T cells. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):511–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90235-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haughn L., Gratton S., Caron L., Sékaly R. P., Veillette A., Julius M. Association of tyrosine kinase p56lck with CD4 inhibits the induction of growth through the alpha beta T-cell receptor. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):328–331. doi: 10.1038/358328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman P. K., Emr S. D. Characterization of VPS34, a gene required for vacuolar protein sorting and vacuole segregation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6742–6754. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiles I. D., Otsu M., Volinia S., Fry M. J., Gout I., Dhand R., Panayotou G., Ruiz-Larrea F., Thompson A., Totty N. F. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: structure and expression of the 110 kd catalytic subunit. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90166-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I. D., Popovic M., Horak E. M., Lucas P. J., Gress R. E., June C. H., Bolen J. B. No T-cell tyrosine protein kinase signalling or calcium mobilization after CD4 association with HIV-1 or HIV-1 gp120. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):557–560. doi: 10.1038/348557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Lammers R., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Interaction of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-associated p85 with epidermal growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):981–990. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- June C. H., Fletcher M. C., Ledbetter J. A., Samelson L. E. Increases in tyrosine phosphorylation are detectable before phospholipase C activation after T cell receptor stimulation. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1591–1599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juszczak R. J., Turchin H., Truneh A., Culp J., Kassis S. Effect of human immunodeficiency virus gp120 glycoprotein on the association of the protein tyrosine kinase p56lck with CD4 in human T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11176–11183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann R., Laroche D., Buchner K., Hucho F., Rudd C., Lindschau C., Ludwig P., Höer A., Oberdisse E., Kopp J. The HIV-1 surface protein gp120 has no effect on transmembrane signal transduction in T cells. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(8):760–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavanaugh W. M., Klippel A., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Modification of the 85-kilodalton subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3415–3424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Kashishian A., Cooper J. A., Valius M. GTPase-activating protein and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase bind to distinct regions of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta subunit. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2534–2544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K. L., Ruderman N. B., Chen K. S. Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase in isolated rat adipocytes. Activation by insulin and subcellular distribution. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3423–3428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman D. R. The structure of the CD4 and CD8 genes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:561–584. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.05.040187.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X., Marengere L. E., Koch C. A., Pawson T. The v-Src SH3 domain binds phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5225–5232. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K. X., Sefton B. M. Cross-linking of T-cell surface molecules CD4 and CD8 stimulates phosphorylation of the lck tyrosine protein kinase at the autophosphorylation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5305–5313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K., Sefton B. M. Activated lck tyrosine protein kinase stimulates antigen-independent interleukin-2 production in T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4724–4732. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohagheghpour N., Chakrabarti R., Stein B. S., Gowda S. D., Engleman E. G. Early activation events render T cells susceptible to HIV-1-induced syncytia formation. Role of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7233–7238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina T. J., Kishihara K., Siderovski D. P., van Ewijk W., Narendran A., Timms E., Wakeham A., Paige C. J., Hartmann K. U., Veillette A. Profound block in thymocyte development in mice lacking p56lck. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):161–164. doi: 10.1038/357161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Boyd A. W., Hagan M., Brown H. M., Kornacki M. M., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human helper inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3762–3769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Torimoto Y., Levinson G., Rudd C. E., Schrieber M., Dang N. H., Letvin N. L., Schlossman S. F. 1F7, a novel cell surface molecule, involved in helper function of CD4 cells. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3430–3439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Noble M., Pauptit R., Wierenga R., Saraste M. Crystal structure of a Src-homology 3 (SH3) domain. Nature. 1992 Oct 29;359(6398):851–855. doi: 10.1038/359851a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier J. P., Raabe T., Henkemeyer M., Dickson B., Mbamalu G., Margolis B., Schlessinger J., Hafen E., Pawson T. A Drosophila SH2-SH3 adaptor protein implicated in coupling the sevenless tyrosine kinase to an activator of Ras guanine nucleotide exchange, Sos. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90170-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Hiles I., Gout I., Fry M. J., Ruiz-Larrea F., Panayotou G., Thompson A., Dhand R., Hsuan J., Totty N. Characterization of two 85 kd proteins that associate with receptor tyrosine kinases, middle-T/pp60c-src complexes, and PI3-kinase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90411-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Gish G. D. SH2 and SH3 domains: from structure to function. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):359–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleiman C. M., Clark M. R., Gauen L. K., Winitz S., Coggeshall K. M., Johnson G. L., Shaw A. S., Cambier J. C. Mapping of sites on the Src family protein tyrosine kinases p55blk, p59fyn, and p56lyn which interact with the effector molecules phospholipase C-gamma 2, microtubule-associated protein kinase, GTPase-activating protein, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5877–5887. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad K. V., Janssen O., Kapeller R., Raab M., Cantley L. C., Rudd C. E. Src-homology 3 domain of protein kinase p59fyn mediates binding to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7366–7370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad K. V., Rudd C. E. A Raf-1-related p110 polypeptide associates with the CD4-p56lck complex in T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5260–5267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Meuer S. C., Schlossman S. F. The human T cell receptor: analysis with cytotoxic T cell clones. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:83–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Mayer B. J., Cicchetti P., Baltimore D. Identification of a ten-amino acid proline-rich SH3 binding site. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.8438166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. S., Klionsky D. J., Banta L. M., Emr S. D. Protein sorting in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation of mutants defective in the delivery and processing of multiple vacuolar hydrolases. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4936–4948. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein D. M., da Silva A., Sugita K., Yamamoto M., Prasad K. V., Morimoto C., Schlossman S. F., Rudd C. E. Human CD4/CD45RA+ and CD4/CD45RA- T cell subsets express CD4-p56lck complexes, CD4-associated lipid kinases, TCR/CD3-p59fyn complexes, and share similar tyrosine kinase substrates. Int Immunol. 1993 Apr;5(4):409–418. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.4.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Anderson P., Morimoto C., Streuli M., Schlossman S. F. Molecular interactions, T-cell subsets and a role of the CD4/CD8:p56lck complex in human T-cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1989 Oct;111:225–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Janssen O., Prasad K. V., Raab M., da Silva A., Telfer J. C., Yamamoto M. src-related protein tyrosine kinases and their surface receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Aug 23;1155(2):239–266. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(93)90007-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Morimoto C., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The subdivision of the T4 (CD4) subset on the basis of the differential expression of L-C/T200 antigens. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1758–1773. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Dodson G. S., Rubin G. M. An SH3-SH2-SH3 protein is required for p21Ras1 activation and binds to sevenless and Sos proteins in vitro. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90169-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleckman B. P., Peterson A., Foran J. A., Gorga J. C., Kara C. J., Strominger J. L., Burakoff S. J., Greenstein J. L. Functional analysis of a cytoplasmic domain-deleted mutant of the CD4 molecule. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Whitman M., Cantley L. C., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmage D. A., Freund R., Young A. T., Dahl J., Dawe C. J., Benjamin T. L. Phosphorylation of middle T by pp60c-src: a switch for binding of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and optimal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90869-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson P. A., Gutkind J. S., Robbins K. C., Ledbetter J. A., Bolen J. B. Identification of distinct populations of PI-3 kinase activity following T-cell activation. Oncogene. 1992 Apr;7(4):719–725. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Samelson L. E., Bolen J. B. Signal transduction through the CD4 receptor involves the activation of the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):257–259. doi: 10.1038/338257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wages D. S., Keefer J., Rall T. B., Weber M. J. Mutations in the SH3 domain of the src oncogene which decrease association of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase activity with pp60v-src and alter cellular morphology. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1866–1874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1866-1874.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Kominos D., Robertson S. C., Pant N., Baltimore D., Birge R. B., Cowburn D., Hanafusa H., Mayer B. J., Overduin M. Crystal structure of the phosphotyrosine recognition domain SH2 of v-src complexed with tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):646–653. doi: 10.1038/358646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. G., Ley S. C., MacPhee C., Cantrell D. A. Regulation of D-3 phosphoinositides during T cell activation via the T cell antigen receptor/CD3 complex and CD2 antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jan;22(1):45–49. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. R., Bell G. M., Han M. Y., Pawson T., Imboden J. B. Association of the tyrosine kinase LCK with phospholipase C-gamma 1 after stimulation of the T cell antigen receptor. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):373–379. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinhold K. J., Lyerly H. K., Stanley S. D., Austin A. A., Matthews T. J., Bolognesi D. P. HIV-1 GP120-mediated immune suppression and lymphocyte destruction in the absence of viral infection. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3091–3097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Downes C. P., Keeler M., Keller T., Cantley L. Type I phosphatidylinositol kinase makes a novel inositol phospholipid, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):644–646. doi: 10.1038/332644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D. R., Schaffhausen B., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):239–242. doi: 10.1038/315239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonezawa K., Ueda H., Hara K., Nishida K., Ando A., Chavanieu A., Matsuba H., Shii K., Yokono K., Fukui Y. Insulin-dependent formation of a complex containing an 85-kDa subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and tyrosine-phosphorylated insulin receptor substrate 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25958–25965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Koga Y., Moroi Y., Kimura G., Nomoto K. The effect of p56lck, a lymphocyte specific protein tyrosine kinase, on the syncytium formation induced by human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein. Int Immunol. 1992 Feb;4(2):233–242. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Rosen M. K., Shin T. B., Seidel-Dugan C., Brugge J. S., Schreiber S. L. Solution structure of the SH3 domain of Src and identification of its ligand-binding site. Science. 1992 Dec 4;258(5088):1665–1668. doi: 10.1126/science.1280858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]