Abstract
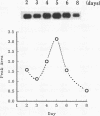
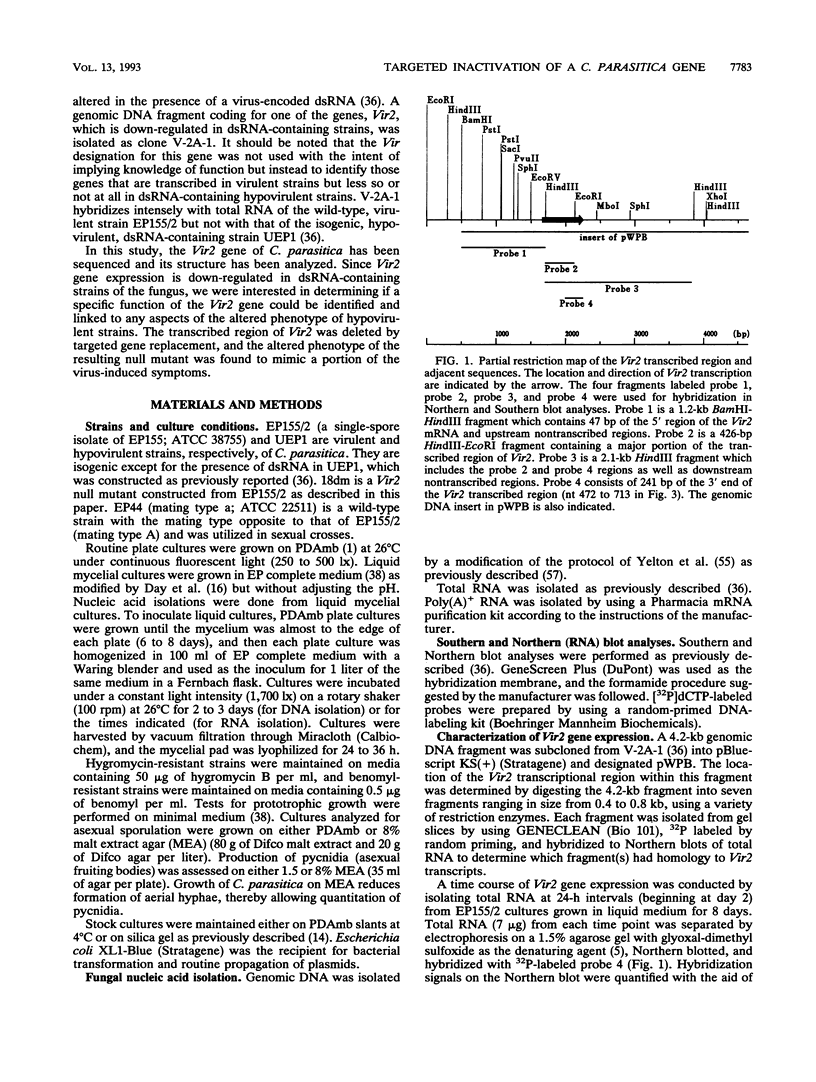
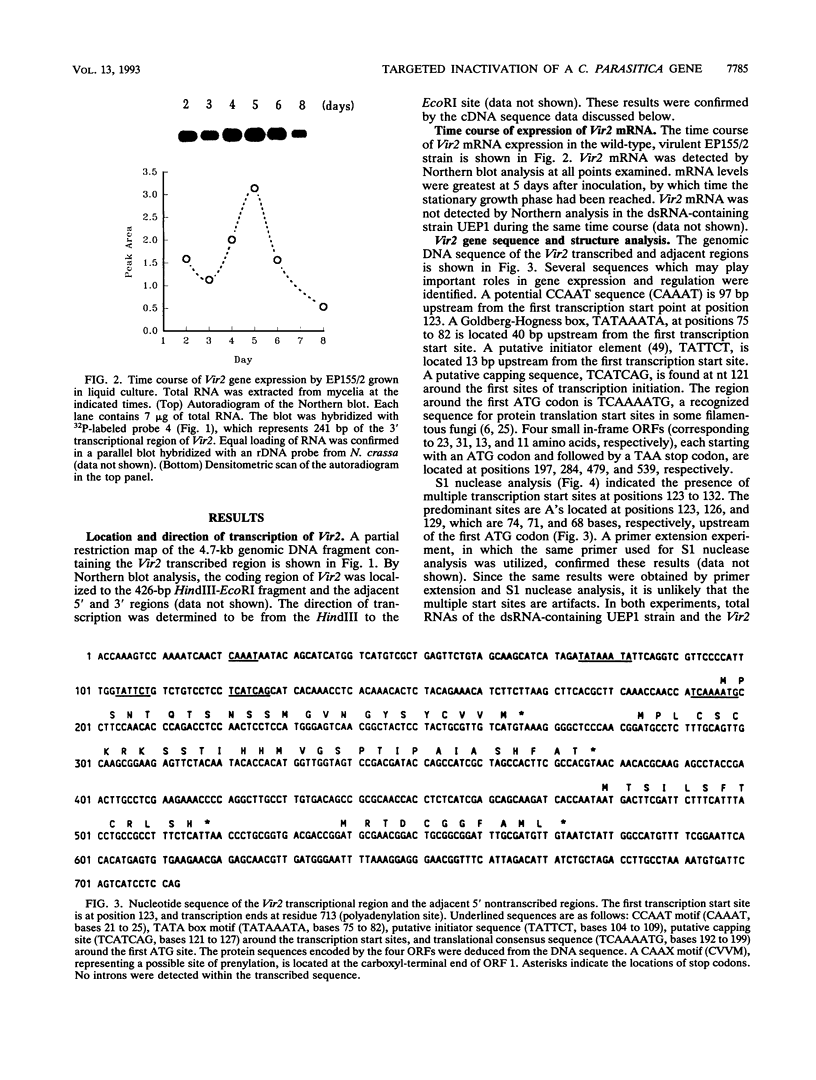
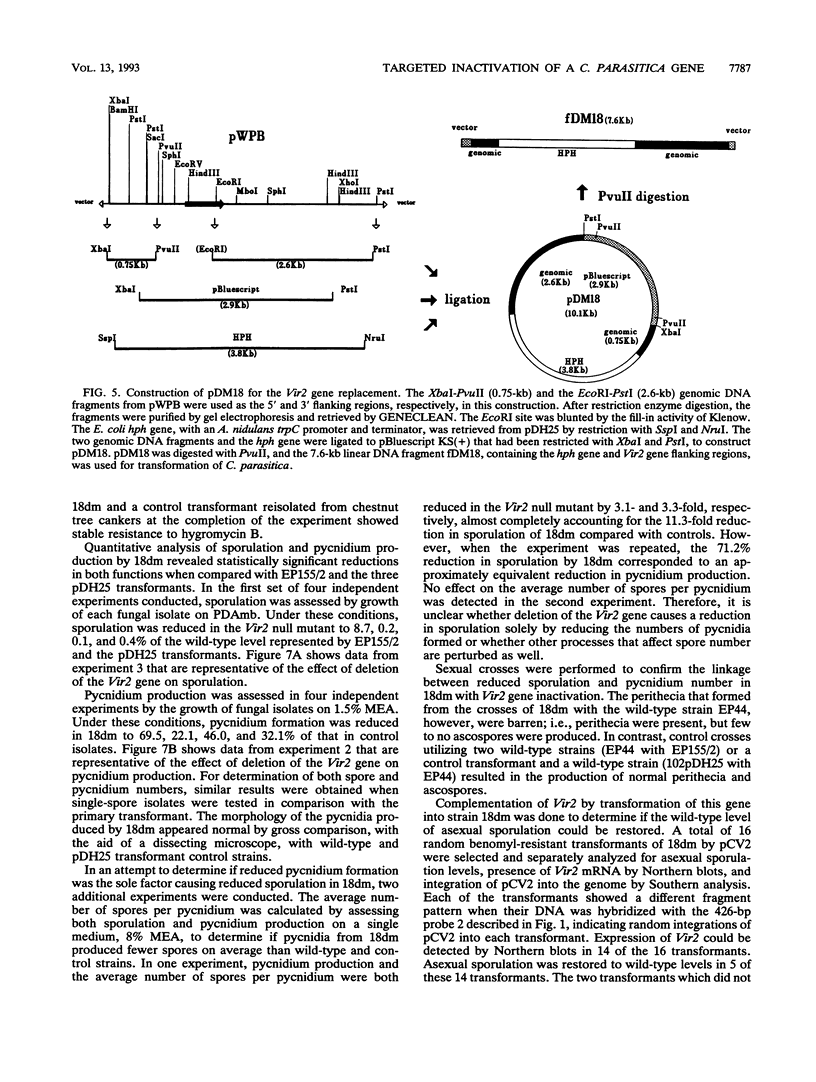
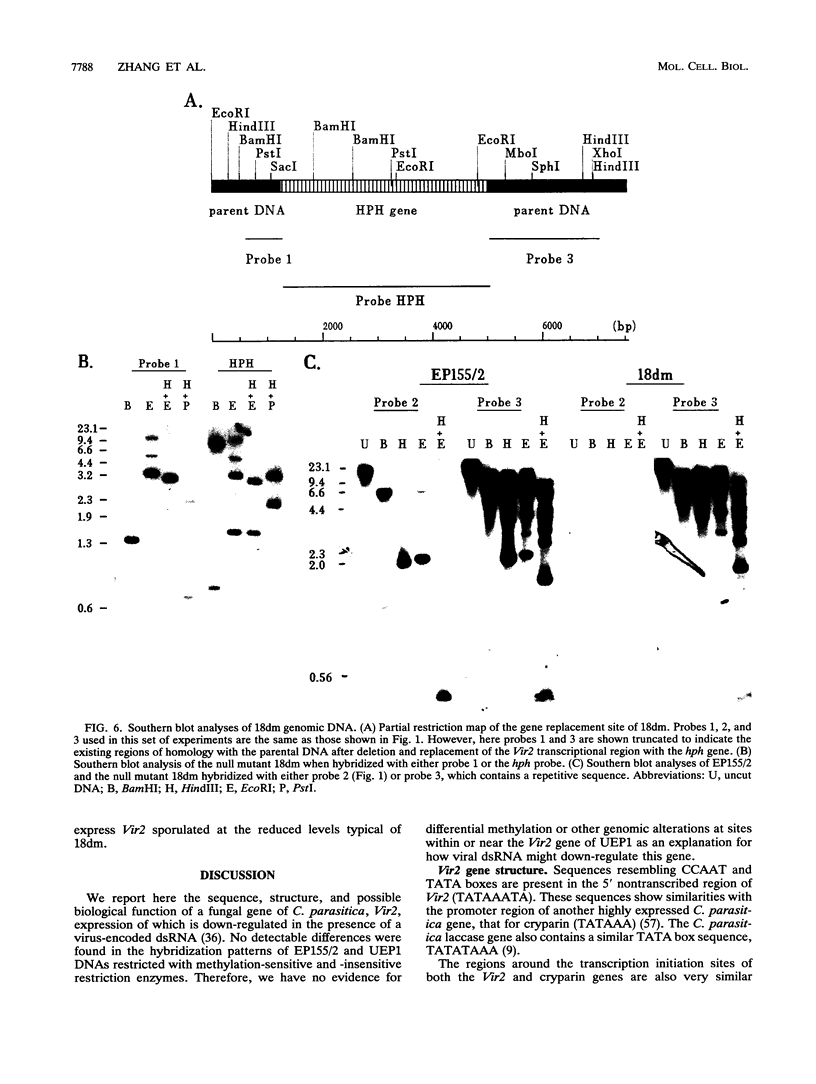
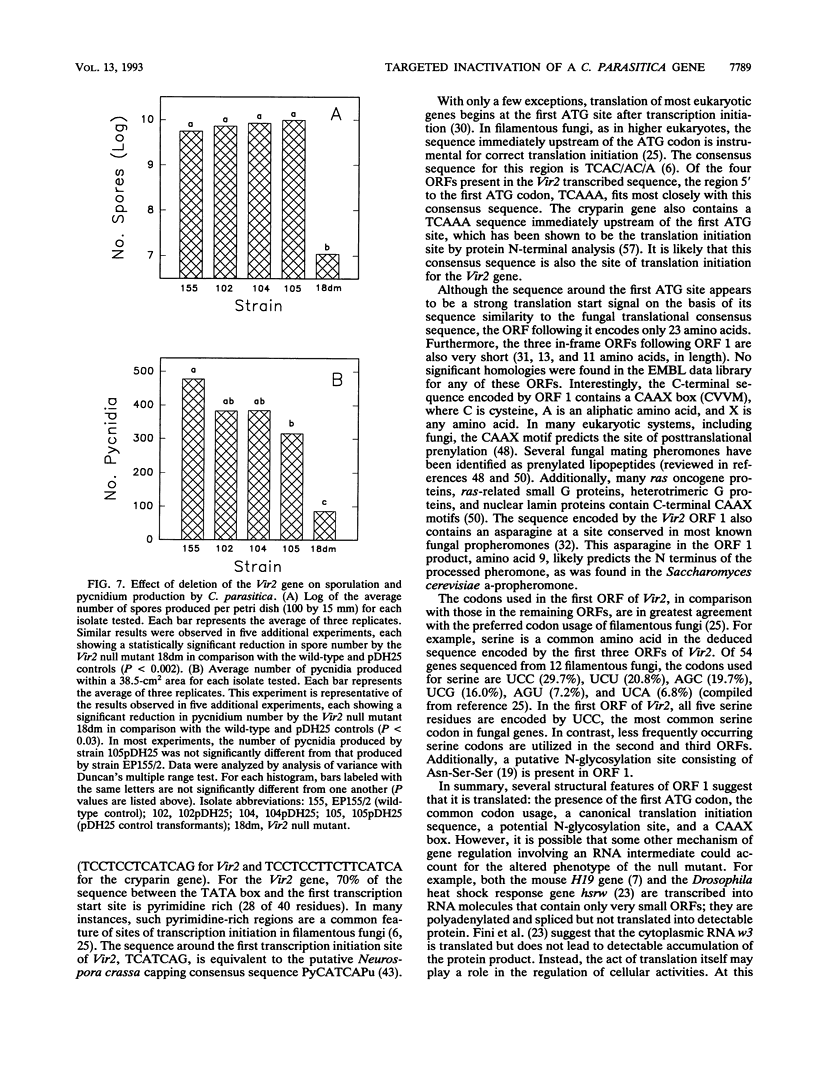
Expression of the Vir2 gene of Cryphonectria parasitica is down-regulated in strains of the fungus containing a double-stranded RNA genetic element that reduces fungal virulence (W. A. Powell and N. K. Van Alfen, Mol. Cell. Biol. 7:3688-3693, 1987). We have sequenced the Vir2 gene and characterized its structure; the mRNA contains a short open reading frame whose product has structural similarities to several fungal pheromones. A null mutant was constructed by homologous recombination to determine the function of the Vir2 gene and whether its disruption resulted in any of the altered phenotypes exhibited by many hypovirulent strains, such as reductions in virulence, pigmentation, and sporulation. The Vir2 null mutant (18dm) exhibited a wild-type phenotype with respect to gross colony morphology, growth rate, pigmentation, asexual spore viability, and virulence in apple fruit and chestnut trees. However, numbers of asexual fruiting bodies (pycnidia) and conidia were reduced significantly in comparison with the wild-type strain EP155/2. In sexual crosses of 18dm with a wild-type strain of the opposite mating type, perithecia (sexual fruiting bodies) developed but were barren. Deletion of the Vir2 gene results in a phenotype that mimics that of many double-stranded-RNA-containing hypovirulent strains; i.e., the null mutant exhibits significant reductions in asexual sporulation and pycinidum production as well as impaired sexual crossing ability. To our knowledge, this is the first report of the partial reproduction of a virus-induced phenotype by deletion of a virus-perturbed host gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostakis S. L. Biological control of chestnut blight. Science. 1982 Jan 29;215(4532):466–471. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4532.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannan C. I., Dees E. C., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):28–36. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. E., Mueller R. J., Kazmierczak P., Zhang L., Villalon D. K., Van Alfen N. K. Effect of a virus on accumulation of a tissue-specific cell-surface protein of the fungus Cryphonectria (Endothia) parasitica. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 Jan-Feb;5(1):55–61. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi G. H., Larson T. G., Nuss D. L. Molecular analysis of the laccase gene from the chestnut blight fungus and selective suppression of its expression in an isogenic hypovirulent strain. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 Mar-Apr;5(2):119–128. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi G. H., Nuss D. L. A viral gene confers hypovirulence-associated traits to the chestnut blight fungus. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):473–477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05077.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi G. H., Nuss D. L. Hypovirulence of chestnut blight fungus conferred by an infectious viral cDNA. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):800–803. doi: 10.1126/science.1496400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi G. H., Pawlyk D. M., Nuss D. L. The autocatalytic protease p29 encoded by a hypovirulence-associated virus of the chestnut blight fungus resembles the potyvirus-encoded protease HC-Pro. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):747–752. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91004-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi G. H., Shapira R., Nuss D. L. Cotranslational autoproteolysis involved in gene expression from a double-stranded RNA genetic element associated with hypovirulence of the chestnut blight fungus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1167–1171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen D., Leong S. A., Wilson L. J., Henner D. J. Transformation of Aspergillus nidulans with the hygromycin-resistance gene, hph. Gene. 1987;57(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Sal G., Manfioletti G., Schneider C. A one-tube plasmid DNA mini-preparation suitable for sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9878–9878. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahima T., Kazmierczak P., Hansen D. R., Pfeiffer P., Van Alfen N. K. Membrane-associated replication of an unencapsidated double-strand RNA of the fungus, Cryphonectria parasitica. Virology. 1993 Jul;195(1):81–89. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fini M. E., Bendena W. G., Pardue M. L. Unusual behavior of the cytoplasmic transcript of hsr omega: an abundant, stress-inducible RNA that is translated but yields no detectable protein product. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2045–2057. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gritz L., Davies J. Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonin E. V., Choi G. H., Nuss D. L., Shapira R., Carrington J. C. Evidence for common ancestry of a chestnut blight hypovirulence-associated double-stranded RNA and a group of positive-strand RNA plant viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10647–10651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore T. D., Edman J. C. The alpha-mating type locus of Cryptococcus neoformans contains a peptide pheromone gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1962–1970. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. A., Jr, Van Alfen N. K. Two nonhomologus viruses of Cryphonectria (Endothia) parasitica reduce accumulation of specific virulence-associated polypeptides. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5324–5326. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5324-5326.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell W. A., Van Alfen N. K. Differential accumulation of poly(A)+ RNA between virulent and double-stranded RNA-induced hypovirulent strains of Cryphonectria (Endothia) parasitica. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3688–3693. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigling D., Van Alfen N. K. Regulation of laccase biosynthesis in the plant-pathogenic fungus Cryphonectria parasitica by double-stranded RNA. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):8000–8003. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.8000-8003.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. N., Berlin V., Hager K. M., Yanofsky C. Molecular analysis of a Neurospora crassa gene expressed during conidiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2411–2418. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira R., Choi G. H., Hillman B. I., Nuss D. L. The contribution of defective RNAs to the complexity of viral-encoded double-stranded RNA populations present in hypovirulent strains of the chestnut blight fungus Cryphonectria parasitica. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):741–746. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08005.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira R., Choi G. H., Nuss D. L. Virus-like genetic organization and expression strategy for a double-stranded RNA genetic element associated with biological control of chestnut blight. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):731–739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira R., Nuss D. L. Gene expression by a hypovirulence-associated virus of the chestnut blight fungus involves two papain-like protease activities. Essential residues and cleavage site requirements for p48 autoproteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19419–19425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Lutz R. J. The prenylation of proteins. Bioessays. 1992 Jan;14(1):25–31. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimmel J. B., Deschenes R. J., Volker C., Stock J., Clarke S. Evidence for an S-farnesylcysteine methyl ester at the carboxyl terminus of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAS2 protein. Biochemistry. 1990 Oct 16;29(41):9651–9659. doi: 10.1021/bi00493a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley D. A., Podila G. K., Hiremath S. T. Cutinase in Cryphonectria parasitica, the chestnut blight fungus: suppression of cutinase gene expression in isogenic hypovirulent strains containing double-stranded RNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4539–4544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer S. J., Yanofsky C. Efficient cloning of genes of Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4869–4873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelton M. M., Hamer J. E., Timberlake W. E. Transformation of Aspergillus nidulans by using a trpC plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1470–1474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]