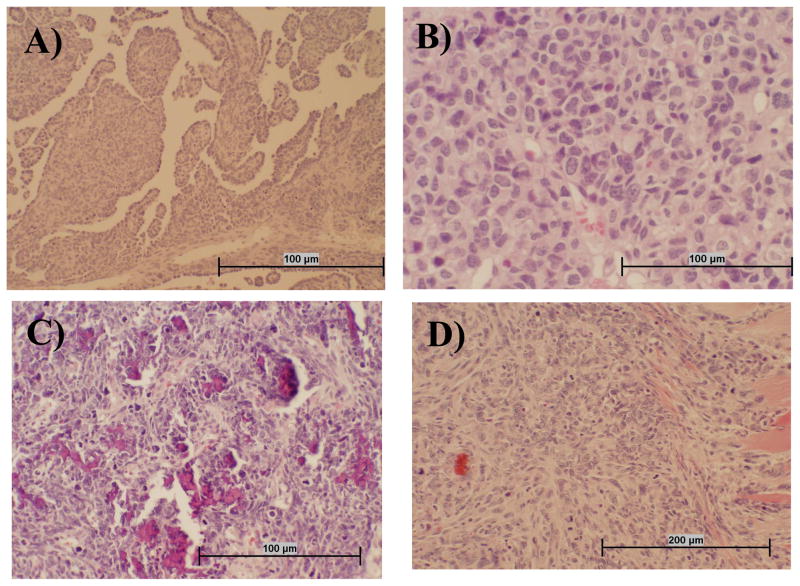
Fig. 1.
Representative tumor types that developed following i.v. inoculation of SV40. Sections of hamster tissue were collected at necropsy, formalin fixed, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Panel A: Mesothelioma tissue is characterized by infiltrative mass of atypical round to spindle cells often having papillary structures that are lined in one layer of round to cuboidal medium-sized cells with prominent nuclei. Panel B: Lymphoma tissue appears as highly cellular tumor tissue composed of homogeneous round cells that often have an indented nucleus and multiple nucleoli. Panel C: Osteosarcoma tissue is composed of atypical pleomorphic cells that are stellate, pyriform, and polyhedral, with tumor cells often oriented around small spicules of pale osteoid. There are also numerous fragments of bone in this section that are not decalcified. Panel D: The spindle cell carcinoma shown has an infiltrative mass into muscle composed of atypical enlongate to spindle cells with prominent nuclei and multiple nucleoli.