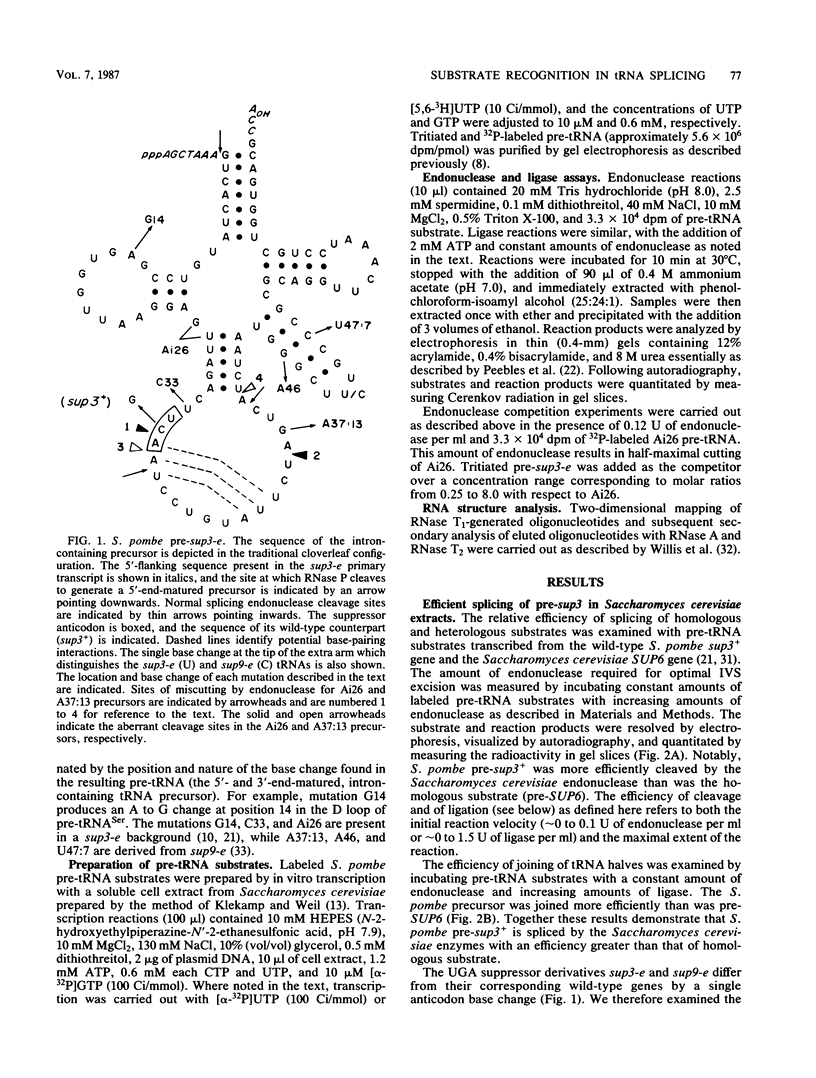
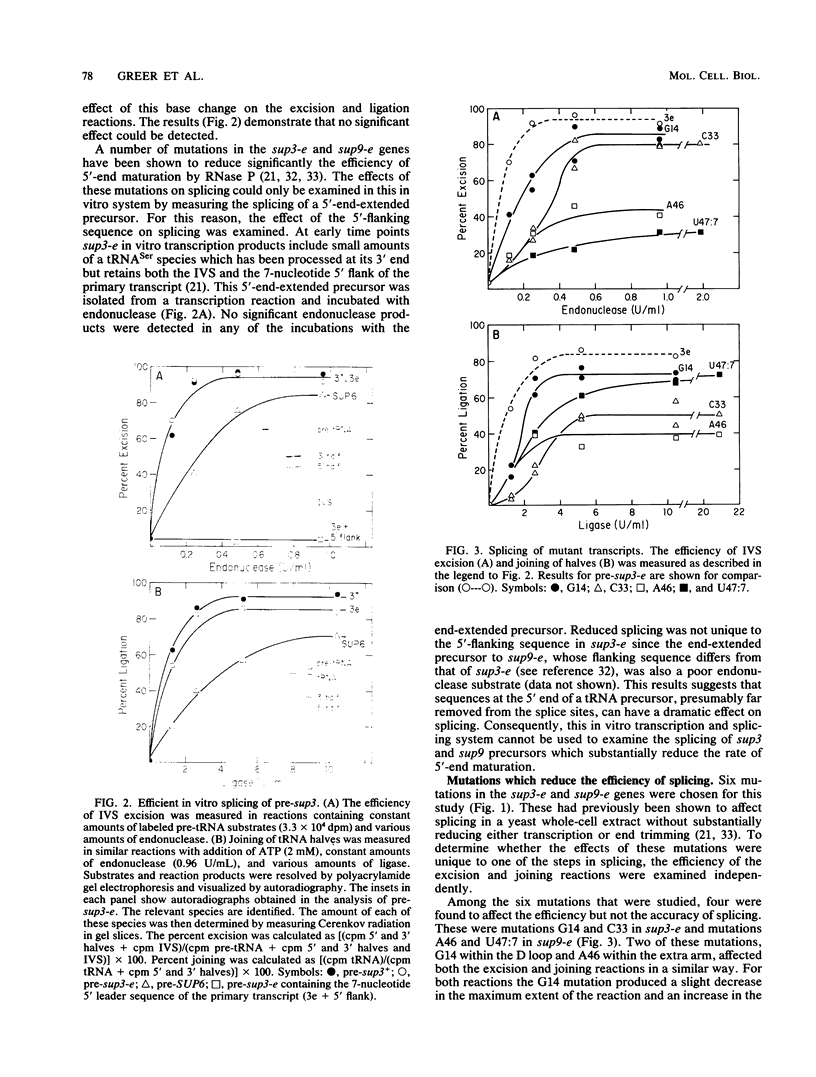
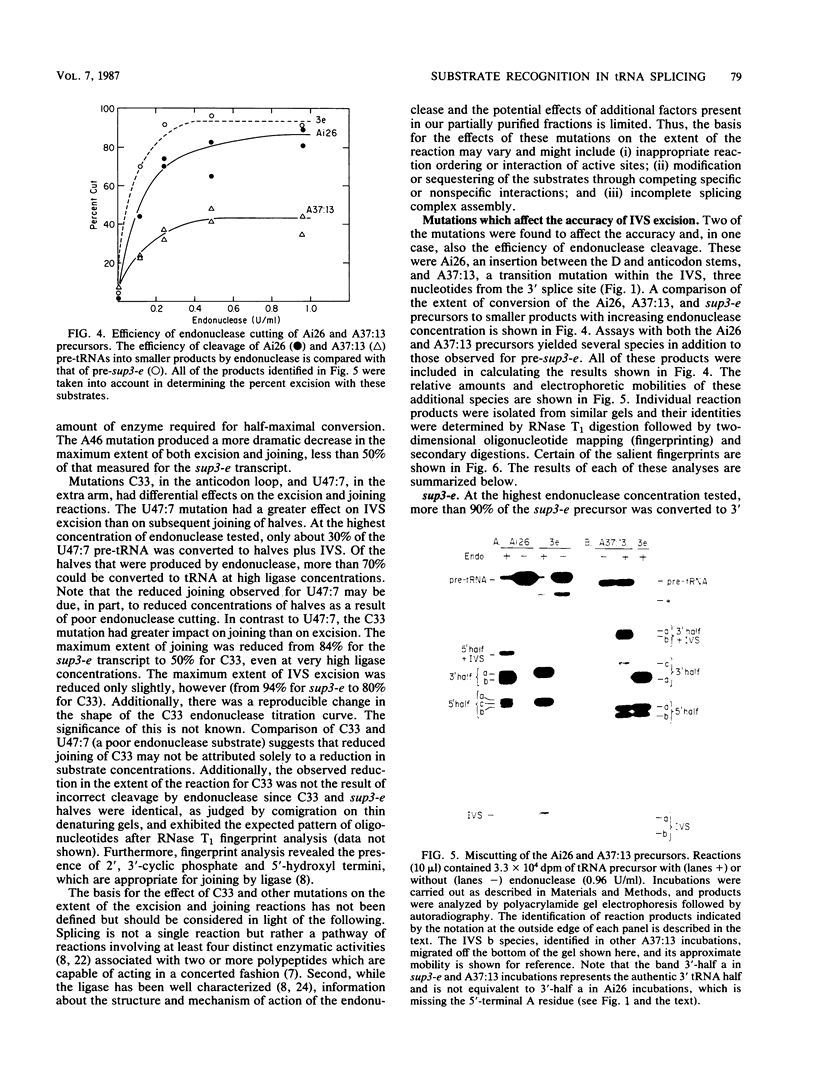
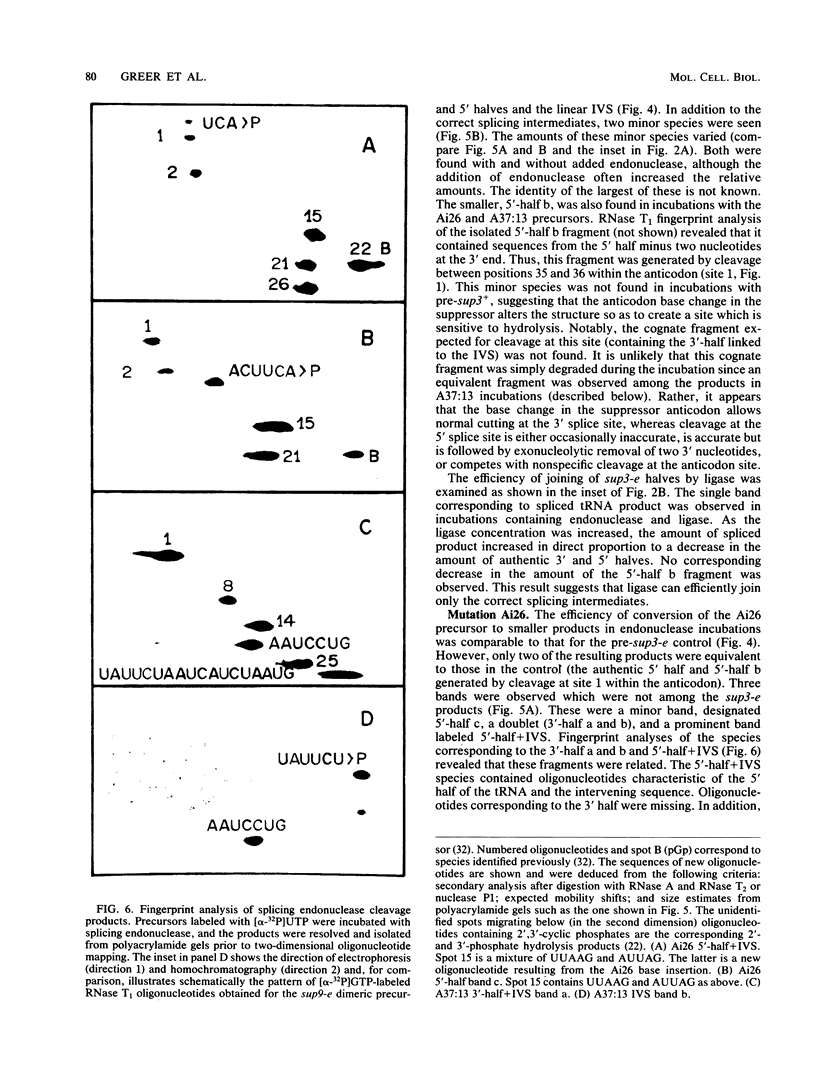
Abstract
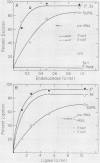
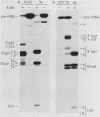
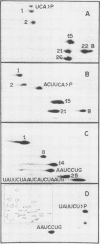
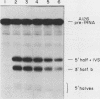
We have examined the substrate requirements for efficient and accurate splicing of tRNA precursors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The effects of Schizosaccharomyces pombe tRNASer gene mutations on the two steps in splicing, intron excision and joining of tRNA halves, were determined independently by using partially purified splicing endonuclease and tRNA ligase from S. cerevisiae. Two mutations (G14 and A46) reduced the efficiency of excision and joining in parallel, whereas two others (U47:7 and C33) produced differential effects on these two steps; U47:7 affected primarily the excision reaction, and C33 had a greater impact on ligation. These data indicate that endonuclease and ligase recognize both common and unique features of their substrates. Another two mutations (Ai26 and A37:13) induced miscutting, although with converse effects on the two splice sites. Thus, the two cutting events appear to be independent. Finally, we suggest that splice sites may be determined largely through their position relative to sites within the tRNA-like domain of the precursors. Several of these important sites were identified, and others are proposed based on the data described here.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attardi D. G., Margarit I., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Structural alterations in mutant precursors of the yeast tRNALeu3 gene which behave as defective substrates for a highly purified splicing endoribonuclease. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3289–3297. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan T., Sundaralingam M. Structlre of transfer RNA molecules containing the long variable loop. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Nov;3(11):3235–3250. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.11.3235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedergren R. J., Sankoff D., LaRue B., Grosjean H. The evolving tRNA molecule. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;11(1):35–104. doi: 10.3109/10409238109108699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby D., Leboy P. S., Guthrie C. Yeast tRNA precursor mutated at a splice junction is correctly processed in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):415–419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P. Processing of tRNA in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1984;17(1):45–71. doi: 10.3109/10409238409110269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Gegenheimer P., Abelson J. Nucleolytic processing of a tRNAArg-tRNAAsp dimeric precursor by a homologous component from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1271–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer C. L. Assembly of a tRNA splicing complex: evidence for concerted excision and joining steps in splicing in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):635–644. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer W. D., Munz P., Amstutz H., Aebi R., Gysler C., Schuchert P., Szankasi P., Leupold U., Kohli J., Gamulin V. Inactivation of nonsense suppressor transfer RNA genes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Intergenic conversion and hot spots of mutation. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 5;188(3):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hottinger H., Pearson D., Yamao F., Gamulin V., Cooley L., Cooper T., Söll D. Nonsense suppression in Schizosaccharomyces pombe: the S. pombe Sup3-e tRNASerUGA gene is active in S. cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):219–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00332678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klekamp M. S., Weil P. A. Specific transcription of homologous class III genes in yeast-soluble cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8432–8441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp G., Ogden R. C., Peebles C. L., Abelson J. Splicing of yeast tRNA precursors: structure of the reaction intermediates. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90351-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Hall B. D., Gillam S., Smith M. Mutations at the yeast SUP4 tRNATyr locus: DNA sequence changes in mutants lacking suppressor activity. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):701–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90316-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. C., Knapp G. Transfer RNA splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Secondary and tertiary structures of the substrates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3108–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninio J. Prediction of pairing schemes in RNA molecules-loop contributions and energy of wobble and non-wobble pairs. Biochimie. 1979;61(10):1133–1150. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(80)80227-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Kurjan J., Hall B. D., De Robertis E. M. Genetic analysis of the processing of a spliced tRNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):263–268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden R. C., Beckman J. S., Abelson J., Kang H. S., Söll D., Schmidt O. In vitro transcription and processing of a yeast tRNA gene containing an intervening sequence. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90166-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden R. C., Lee M. C., Knapp G. Transfer RNA splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: defining the substrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9367–9382. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson D., Willis I., Hottinger H., Bell J., Kumar A., Leupold U., Söll D. Mutations preventing expression of sup3 tRNASer nonsense suppressors of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):808–815. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Gegenheimer P., Abelson J. Precise excision of intervening sequences from precursor tRNAs by a membrane-associated yeast endonuclease. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90472-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Ogden R. C., Knapp G., Abelson J. Splicing of yeast tRNA precursors: a two-stage reaction. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phizicky E. M., Schwartz R. C., Abelson J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae tRNA ligase. Purification of the protein and isolation of the structural gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2978–2986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond G. J., Johnson J. D. The role of non-coding DNA sequences in transcription and processing of a yeast tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5969–5988. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., RajBhandary U. L. Transfer RNA: molecular structure, sequence, and properties. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:805–860. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Moll J., Meissner F., Hartmann T. Compilation of tRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13 (Suppl):r1–49. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.suppl.r1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Vorderwülbecke T., Hartmann T. Compilation of sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985;13 (Suppl):r51–104. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.suppl.r51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Venegas A., Rutter W. J. Yeast tRNA3Leu gene transcribed and spliced in a HeLa cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):5963–5967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.5963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow H., Guthrie C. Structure of intron-containing tRNA precursors. Analysis of solution conformation using chemical and enzymatic probes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5197–5207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Johnson P. F., Tanaka S., Schöld M., Itakura K., Abelson J. Directed deletion of a yeast transfer RNA intervening sequence. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1396–1400. doi: 10.1126/science.6997991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis I., Frendewey D., Nichols M., Hottinger-Werlen A., Schaack J., Söll D. A single base change in the intron of a serine tRNA affects the rate of RNase P cleavage in vitro and suppressor activity in vivo in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5878–5885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis I., Hottinger H., Pearson D., Chisholm V., Leupold U., Söll D. Mutations affecting excision of the intron from a eukaryotic dimeric tRNA precursor. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1573–1580. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]