Abstract
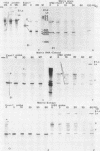
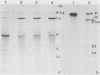
We examined the relationship between pre-mRNA splicing and the nuclear matrix by using an in vivo system that we have developed. Plasmids containing the inducible herpesvirus tk gene promoter linked to an intron-containing segment of the rabbit beta-globin gene were transfected into HeLa cells, and then the promoter was transactivated by infection with a TK- virus. Northern analysis revealed that the globin pre-mRNA and all its splicing intermediates and products are associated with the nuclear matrix prepared from such transfected cells. When the nuclear matrix was incubated with a HeLa cell in vitro splicing extract in the presence of ATP, the amount of matrix-associated precursor progressively decreased without a temporal lag in the reaction, with a corresponding increase in free intron lariat. Thus, most of the events of the splicing process (endonucleolytic cuts and branching) occur in this in vitro complementation reaction. However, ligation of exons cannot be monitored in this system because of the abundance of preexisting mature mRNA. Since the matrix is not a self-splicing entity, whereas the in vitro splicing system cannot process efficiently deproteinized matrix RNA, we conclude from our in vitro complementation results (which can be reproduced by using micrococcal nuclease-treated splicing extract) that the nuclear matrix preparation retains parts of preassembled ribonucleoprotein complexes that have the potential to function when supplemented with soluble factors (presumably other than most of the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins known to participate in splicing) present in the HeLa cell extract.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouteille M., Bouvier D., Seve A. P. Heterogeneity and territorial organization of the nuclear matrix and related structures. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;83:135–182. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61687-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody E., Abelson J. The "spliceosome": yeast pre-messenger RNA associates with a 40S complex in a splicing-dependent reaction. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3890181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Black D. L., LeMaster D. M., Steitz J. A. The 3' splice site of pre-messenger RNA is recognized by a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1344–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.2933810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciejek E. M., Nordstrom J. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Ribonucleic acid precursors are associated with the chick oviduct nuclear matrix. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):4945–4953. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ElKareh A., Murphy A. J., Fichter T., Efstratiadis A., Silverstein S. "Transactivation" control signals in the promoter of the herpesvirus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1002–1006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontichiaro K. L., Beck T. W., Millette R. L. In vitro transcription of herpes simplex virus genes: identification of a new initiation site and second intervening sequence in the immediate-early RNA-5 gene. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):235–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.235-242.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frendewey D., Keller W. Stepwise assembly of a pre-mRNA splicing complex requires U-snRNPs and specific intron sequences. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):355–367. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80131-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furneaux H. M., Perkins K. K., Freyer G. A., Arenas J., Hurwitz J. Isolation and characterization of two fractions from HeLa cells required for mRNA splicing in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4351–4355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallinaro H., Puvion E., Kister L., Jacob M. Nuclear matrix and hnRNP share a common structural constituent associated with premessenger RNA. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):953–960. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkle B., McAuslan B. R. Regulation of herpes simplex virus-induced thymidine kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 4;58(3):822–829. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80491-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Seiler S. R., Sharp P. A. A multicomponent complex is involved in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R., Boulikas T. Functional organization in the nucleus. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;79:165–214. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61674-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowler J. T. An assessment of the evidence for the role of ribonucleoprotein particles in the maturation of eukaryote mRNA. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;84:103–153. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W. Purification of a protein required for the splicing of pre-mRNA and its separation from the lariat debranching enzyme. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3571–3581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04119.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Hardison R. C., Quon D., Maniatis T. The linkage arrangement of four rabbit beta-like globin genes. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1273–1283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90238-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Buttyan R., Spear P. G. Herpes simplex virus gene expression in transformed cells. I. Regulation of the viral thymidine kinase gene in transformed L cells by products of superinfecting virus. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):413–424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.413-424.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariman E. C., van Eekelen C. A., Reinders R. J., Berns A. J., van Venrooij W. J. Adenoviral heterogeneous nuclear RNA is associated with the host nuclear matrix during splicing. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 5;154(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90420-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maundrell K., Maxwell E. S., Puvion E., Scherrer K. The nuclear matrix of duck erythroblasts is associated with globin mRNA coding sequences but not with the major proteins of 40S nuclear RNP. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Dec;136(2):435–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Silverstein S. Degradation of cellular mRNA during infection by herpes simplex virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2370–2374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross D. A., Yen R. W., Chae C. B. Association of globin ribonucleic acid and its precursors with the chicken erythroblast nuclear matrix. Biochemistry. 1982 Feb 16;21(4):764–771. doi: 10.1021/bi00533a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Green M. R. An RNA processing activity that debranches RNA lariats. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):135–140. doi: 10.1126/science.2990042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittler A., Gallinaro H., Jacob M. In vivo splicing of the premRNAs from early region 3 of adenovirus-2: the products of cleavage at the 5' splice site of the common intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 11;14(3):1187–1207. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.3.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley J. R. Construction in vitro and rescue of a thymidine kinase-deficient deletion mutation of herpes simplex virus. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):333–335. doi: 10.1038/285333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Vande Woude G. F. DNA sequence of an immediate-early gene (IEmRNA-5) of herpes simplex virus type I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):979–991. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. In vivo splicing products of the rabbit beta-globin pre-mRNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):589–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Eekelen C. A., van Venrooij W. J. hnRNA and its attachment to a nuclear protein matrix. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):554–563. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]