Abstract
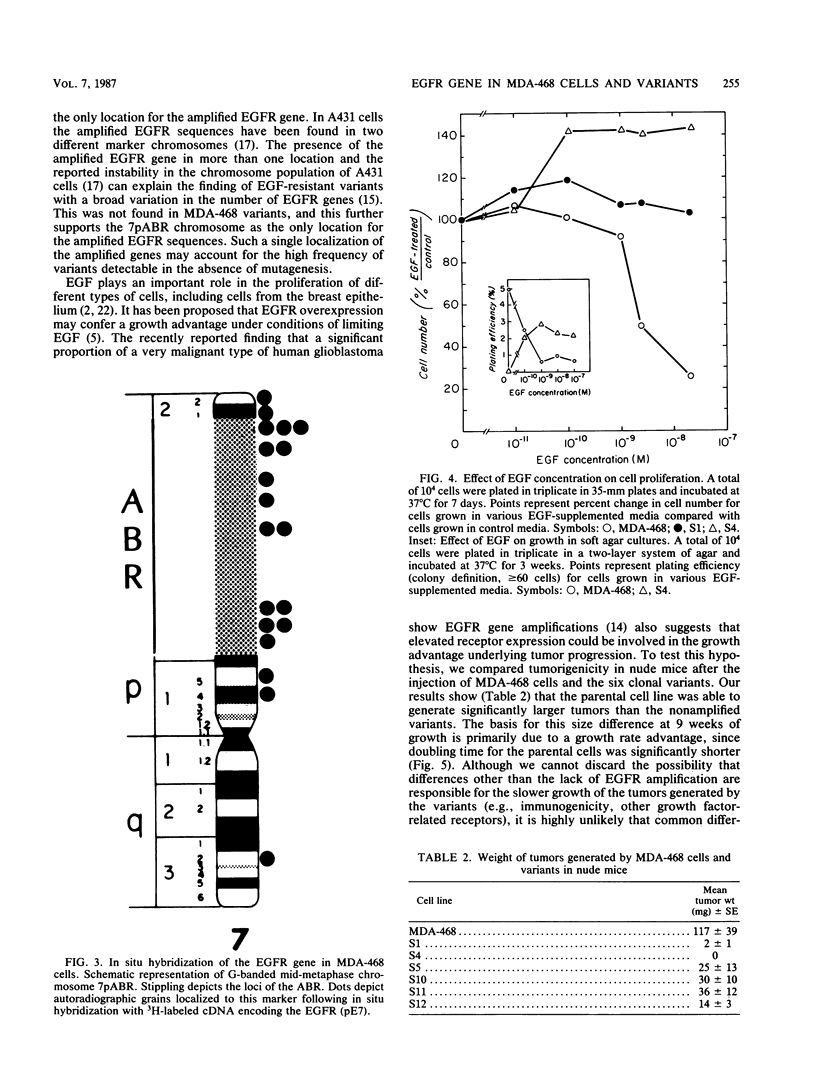
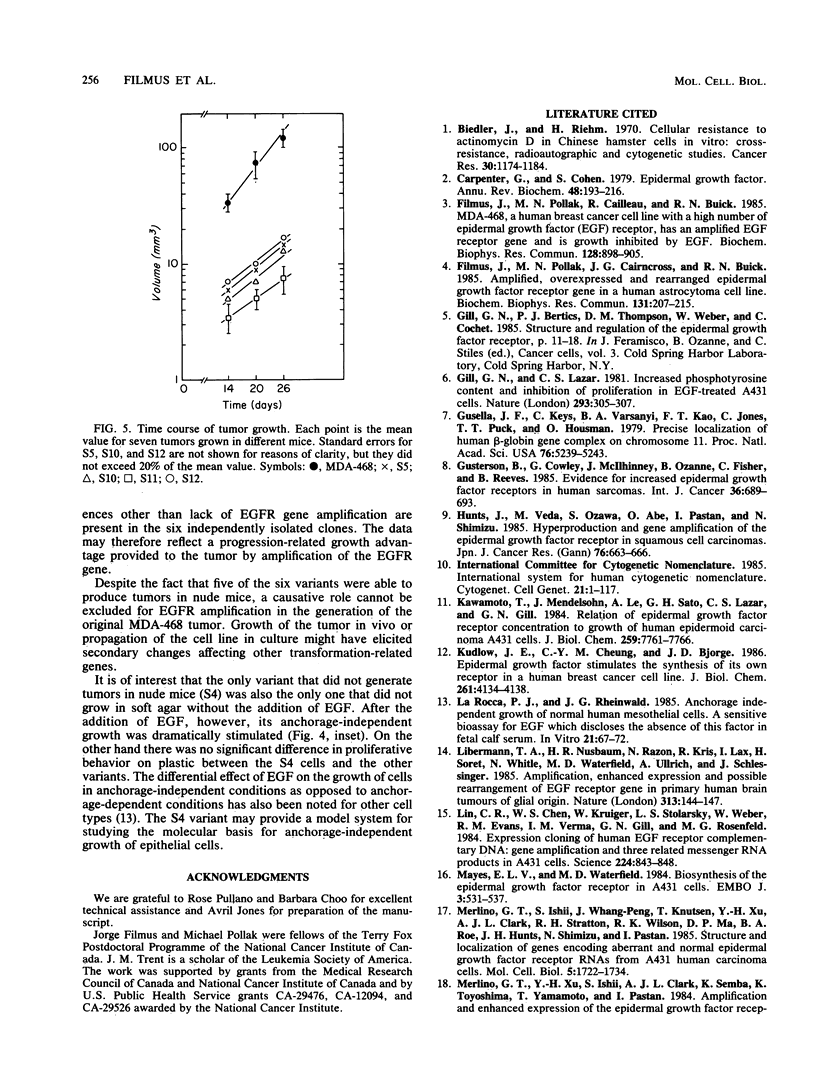
We have recently reported (J. Filmus, M. N. Pollak, R. Cailleau, and R. N. Buick, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 128:898-905, 1985) that MDA-468, a human breast cancer cell line with a high number of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors, has an amplified EGF receptor gene and is growth inhibited in vitro pharmacological doses of EGF. We have derived several MDA-468 clonal variants which are resistant to EGF-induced growth inhibition. These clones had a number of EGF receptors, similar to normal human fibroblasts, and had lost the EGF receptor gene amplification. Karyotype analysis showed that MDA-468 cells had an abnormally banded region (ABR) in chromosome 7p which was not present in the variants. It was shown by in situ hybridization that the amplified EGF receptor sequences were located in that chromosome, 7pABR. Five of the six variants studied were able to generate tumors in nude mice, but their growth rate was significantly lower than that of tumors derived from the parental cell line. The variant that was unable to produce tumors was found to be uniquely dependent on EGF for growth in soft agar.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biedler J. L., Riehm H. Cellular resistance to actinomycin D in Chinese hamster cells in vitro: cross-resistance, radioautographic, and cytogenetic studies. Cancer Res. 1970 Apr;30(4):1174–1184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filmus J., Pollak M. N., Cailleau R., Buick R. N. MDA-468, a human breast cancer cell line with a high number of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptors, has an amplified EGF receptor gene and is growth inhibited by EGF. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):898–905. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filmus J., Pollak M. N., Cairncross J. G., Buick R. N. Amplified, overexpressed and rearranged epidermal growth factor receptor gene in a human astrocytoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):207–215. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91790-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Lazar C. S. Increased phosphotyrosine content and inhibition of proliferation in EGF-treated A431 cells. Nature. 1981 Sep 24;293(5830):305–307. doi: 10.1038/293305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J., Varsanyi-Breiner A., Kao F. T., Jones C., Puck T. T., Keys C., Orkin S., Housman D. Precise localization of human beta-globin gene complex on chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5239–5242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusterson B., Cowley G., McIlhinney J., Ozanne B., Fisher C., Reeves B. Evidence for increased epidermal growth factor receptors in human sarcomas. Int J Cancer. 1985 Dec 15;36(6):689–693. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunts J., Ueda M., Ozawa S., Abe O., Pastan I., Shimizu N. Hyperproduction and gene amplification of the epidermal growth factor receptor in squamous cell carcinomas. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1985 Aug;76(8):663–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Mendelsohn J., Le A., Sato G. H., Lazar C. S., Gill G. N. Relation of epidermal growth factor receptor concentration to growth of human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7761–7766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudlow J. E., Cheung C. Y., Bjorge J. D. Epidermal growth factor stimulates the synthesis of its own receptor in a human breast cancer cell line. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4134–4138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Rocca P. J., Rheinwald J. G. Anchorage-independent growth of normal human mesothelial cells: a sensitive bioassay for EGF which discloses the absence of this factor in fetal calf serum. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1985 Jan;21(1):67–72. doi: 10.1007/BF02620917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Nusbaum H. R., Razon N., Kris R., Lax I., Soreq H., Whittle N., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Amplification, enhanced expression and possible rearrangement of EGF receptor gene in primary human brain tumours of glial origin. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):144–147. doi: 10.1038/313144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Chen W. S., Kruiger W., Stolarsky L. S., Weber W., Evans R. M., Verma I. M., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression cloning of human EGF receptor complementary DNA: gene amplification and three related messenger RNA products in A431 cells. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):843–848. doi: 10.1126/science.6326261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayes E. L., Waterfield M. D. Biosynthesis of the epidermal growth factor receptor in A431 cells. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):531–537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlino G. T., Ishii S., Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Xu Y. H., Clark A. J., Stratton R. H., Wilson R. K., Ma D. P., Roe B. A. Structure and localization of genes encoding aberrant and normal epidermal growth factor receptor RNAs from A431 human carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1722–1734. doi: 10.1128/MCB.5.7.1722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlino G. T., Xu Y. H., Ishii S., Clark A. J., Semba K., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T., Pastan I. Amplification and enhanced expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor gene in A431 human carcinoma cells. Science. 1984 Apr 27;224(4647):417–419. doi: 10.1126/science.6200934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak S., Siciliano M. J., Cailleau R., Wiseman C. L., Hsu T. C. A human breast adenocarcinoma with chromosome and isoenzyme markers similar to those of the HeLa line. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Feb;62(2):263–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taketani Y., Oka T. Biological action of epidermal growth factor and its functional receptors in normal mammary epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2647–2650. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Olson S., Lawn R. M. Chromosomal localization of human leukocyte, fibroblast, and immune interferon genes by means of in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M. Protocols of procedures and techniques in chromosome analysis of tumor stem cell cultures in soft agar. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1980;48:345–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y. H., Richert N., Ito S., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression in malignant and normal human cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7308–7312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]