Abstract
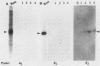
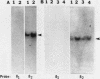
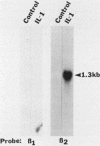
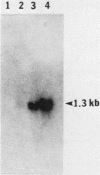
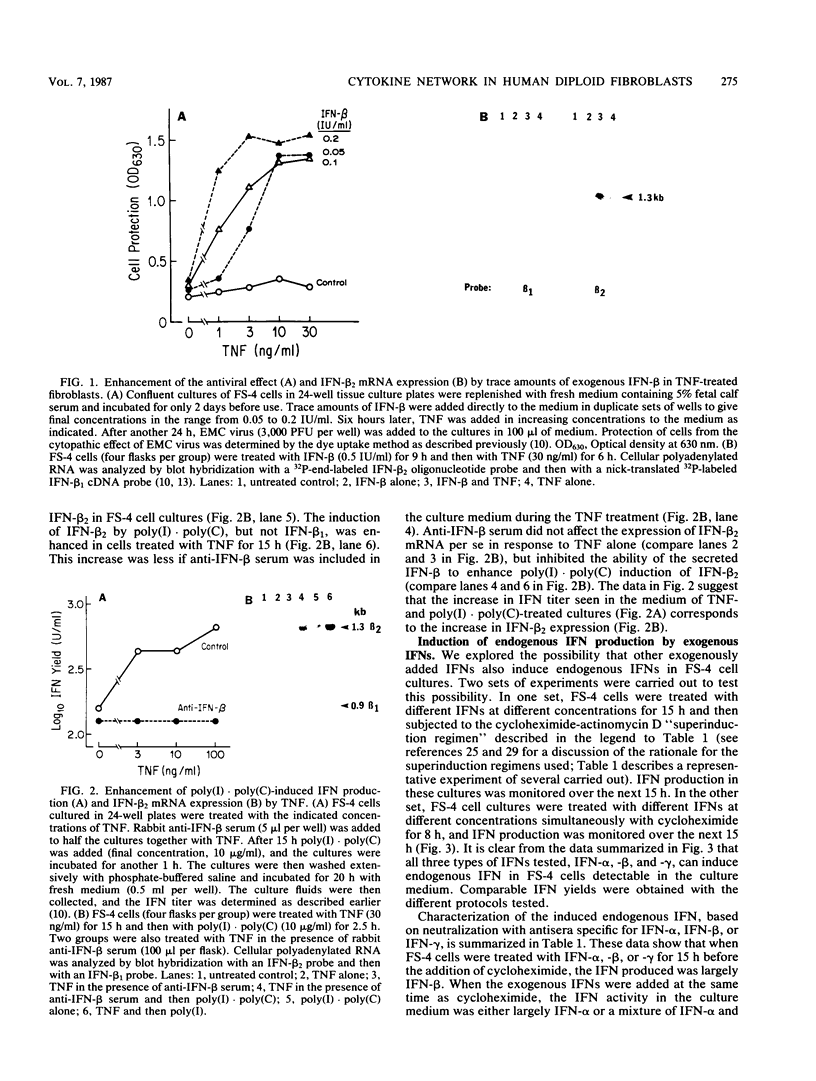
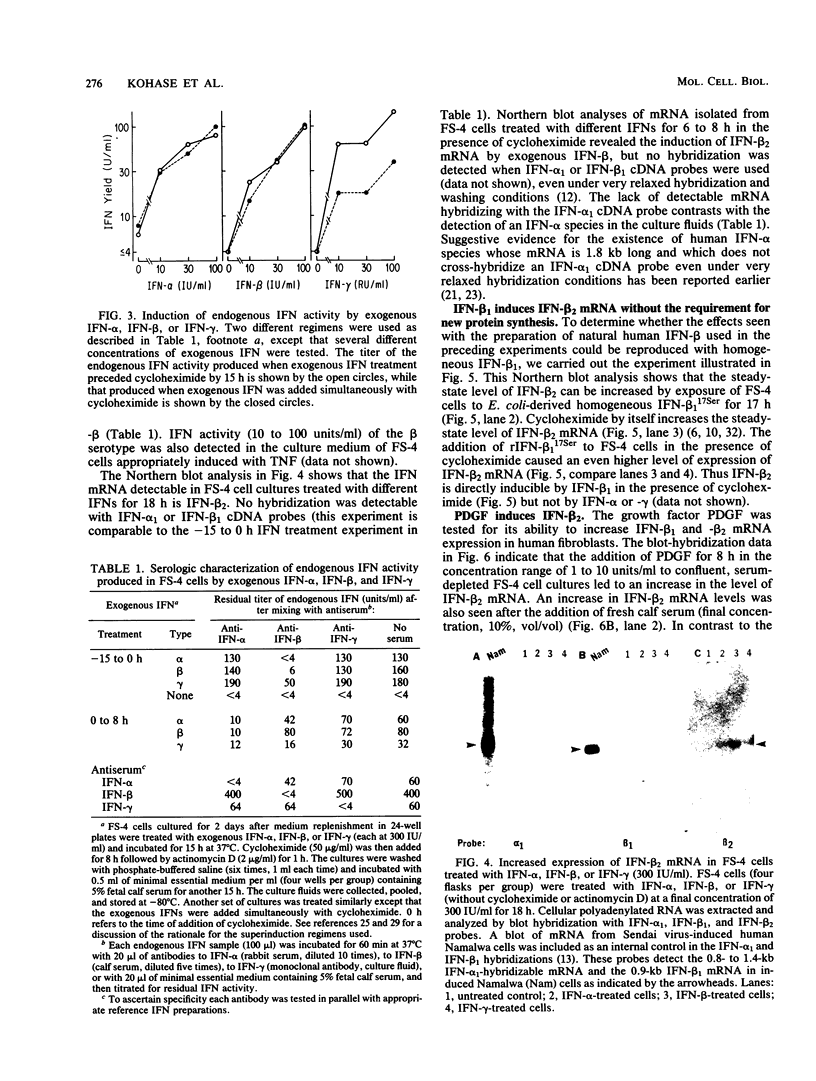
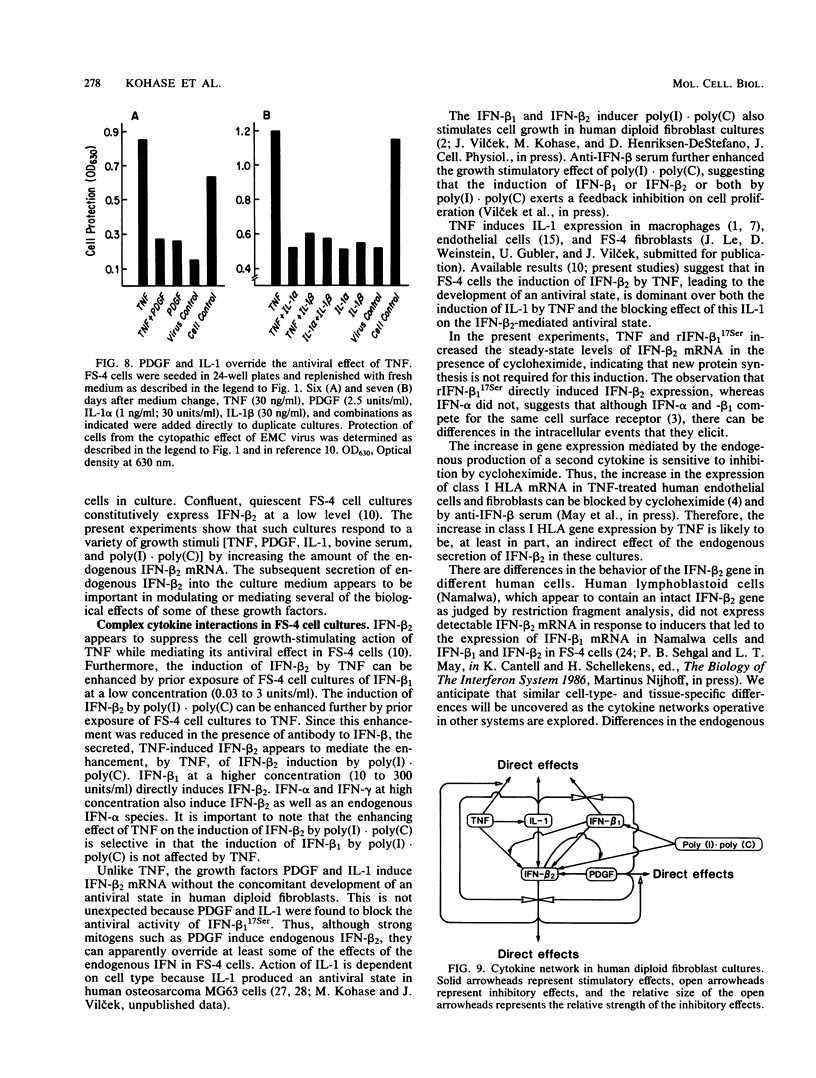
Earlier studies demonstrated the induction of beta 2-interferon (IFN-beta 2) in human diploid fibroblasts (FS-4 strain) exposed to tumor necrosis factor (TNF). These studies suggested that IFN-beta 2 mediates an antiviral effect in TNF-treated cells and exerts a feedback inhibition of the mitogenic effect of TNF. Here we demonstrate that the expression of the antiviral action of TNF can be enhanced by prior exposure of FS-4 cells to trace amounts of IFN-beta 1. IFN-beta 1, at a higher concentration, can directly increase the expression of IFN-beta 2. Exposure of cells to TNF enhanced IFN-beta 2 (but not IFN-beta 1) mRNA expression in response to poly(I).poly(C), an IFN inducer which is also known to stimulate FS-4 cell growth. Platelet-derived growth factor and interleukin-1 also led to the increased expression of IFN-beta 2. However, platelet-derived growth factor and interleukin-1 could override the antiviral effect of TNF and also that of exogenously added IFN-beta 1. Our data suggest that a complex network of interactions that involves the endogenous production of IFN-beta 2 is triggered by several growth-modulatory cytokines. Cellular homeostasis is likely to represent a balance between the induction of IFN-beta 2 by these cytokines and their ability to override the inhibitory actions of IFN-beta 2.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachwich P. R., Chensue S. W., Larrick J. W., Kunkel S. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates interleukin-1 and prostaglandin E2 production in resting macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):94–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90881-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrack E. R., Hollenberg M. D. Mitogenesis in normal human fibroblasts by polyinosinic . polycytidylic acid and other synthetic acidic polymers: enhancement of action by glucocorticoids. J Cell Physiol. 1981 Sep;108(3):445–454. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041080319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branca A. A., Baglioni C. Evidence that types I and II interferons have different receptors. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):768–770. doi: 10.1038/294768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Lapierre L. A., Fiers W., Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor increases mRNA levels and surface expression of HLA-A,B antigens in vascular endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):446–450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., De Wit L., Poupart P., Opdenakker G., Van Damme J., Billiau A. Induction of a 26-kDa-protein mRNA in human cells treated with an interleukin-1-related, leukocyte-derived factor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):253–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser I. On the varied biologic effects of interferon. Cell Immunol. 1977 Dec;34(2):406–415. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Berman B., Ogburn C. A., Berg K., Paucker K., Vilcek J. Two antigenically distinct species of human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2185–2187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohase M., Henriksen-DeStefano D., May L. T., Vilcek J., Sehgal P. B. Induction of beta 2-interferon by tumor necrosis factor: a homeostatic mechanism in the control of cell proliferation. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90780-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. L., Kikuchi T., Pledger W. J., Tamm I. Interferon inhibits the establishment of competence in Go/S-phase transition. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):356–359. doi: 10.1126/science.3726533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May L. T., Sehgal P. B., LaForge K. S., Inouye M. Expression of the native alpha and beta interferon genes in human cells. Virology. 1983 Aug;129(1):116–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90400-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. N., Larsen H. S., Horohov D. W., Rouse B. T. Endogenous regulation of macrophage proliferative expansion by colony-stimulating factor-induced interferon. Science. 1984 Jan 13;223(4632):178–181. doi: 10.1126/science.6606850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Bank I., Handley D., Cassimeris J., Chess L., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin interacts with endothelial cell receptors to induce release of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1363–1375. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleszak E., Inglot A. D. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) inhibits antiviral and anticellular actin of interferon in synchronized mouse or human cells. J Interferon Res. 1980 Fall;1(1):37–48. doi: 10.1089/jir.1980.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Yarden A., Zipori D., Kimchi A. Autocrine beta-related interferon controls c-myc suppression and growth arrest during hematopoietic cell differentiation. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90857-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar A. D., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Increased nuclease sensitivity of the human interferon-alpha 1-related genes and the interferon-beta 1 gene during induction by virus. J Interferon Res. 1985 Fall;5(4):597–604. doi: 10.1089/jir.1985.5.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar A. D., Sehgal P. B., Slate D. L., Ruddle F. H. Multiple human beta interferon genes. J Exp Med. 1982 Sep 1;156(3):744–755. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Inoue M., Tan Y. H. Detection of human beta-2 interferon using a radioimmunoassay. J Interferon Res. 1984;4(1):63–66. doi: 10.1089/jir.1984.4.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., May L. T., LaForge K. S., Inouye M. Unusually long mRNA species coding for human alpha and beta interferons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6932–6936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Sagar A. D., Braude I. A. Further heterogeneity of human alpha interferon mRNA species. Science. 1981 Nov 13;214(4522):803–805. doi: 10.1126/science.6170112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Sagar A. D. Heterogeneity of poly(I) x poly(C)-induced human fibroblast interferon mRNA species. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):95–97. doi: 10.1038/288095a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Zilberstein A., Ruggieri R. M., May L. T., Ferguson-Smith A., Slate D. L., Revel M., Ruddle F. H. Human chromosome 7 carries the beta 2 interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5219–5222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Shearer M., Rozengurt E. Inhibitory effect of interferon on cellular DNA synthesis: modulation by pure mitogenic factors. J Interferon Res. 1981;1(3):401–409. doi: 10.1089/jir.1981.1.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., De Ley M., Opdenakker G., Billiau A., De Somer P., Van Beeumen J. Homogeneous interferon-inducing 22K factor is related to endogenous pyrogen and interleukin-1. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):266–268. doi: 10.1038/314266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Opdenakker G., Billiau A., De Somer P., De Wit L., Poupart P., Content J. Stimulation of fibroblast interferon production by a 22K protein from human leukocytes. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):693–700. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Havell E. A. Stabilization of interferon messenger RNA activity by treatment of cells with metabolic inhibitors and lowering of the incubation temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3909–3913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilcek J., Palombella V. J., Henriksen-DeStefano D., Swenson C., Feinman R., Hirai M., Tsujimoto M. Fibroblast growth enhancing activity of tumor necrosis factor and its relationship to other polypeptide growth factors. J Exp Med. 1986 Mar 1;163(3):632–643. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.3.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Chernajovsky Y., Zeevi M., Shulman L., Soreq H., Nir U., Wallach D., Perricaudet M., Tiollais P., Revel M. Two interferon mRNAs in human fibroblasts: in vitro translation and Escherichia coli cloning studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7152–7156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zullo J. N., Cochran B. H., Huang A. S., Stiles C. D. Platelet-derived growth factor and double-stranded ribonucleic acids stimulate expression of the same genes in 3T3 cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90252-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]