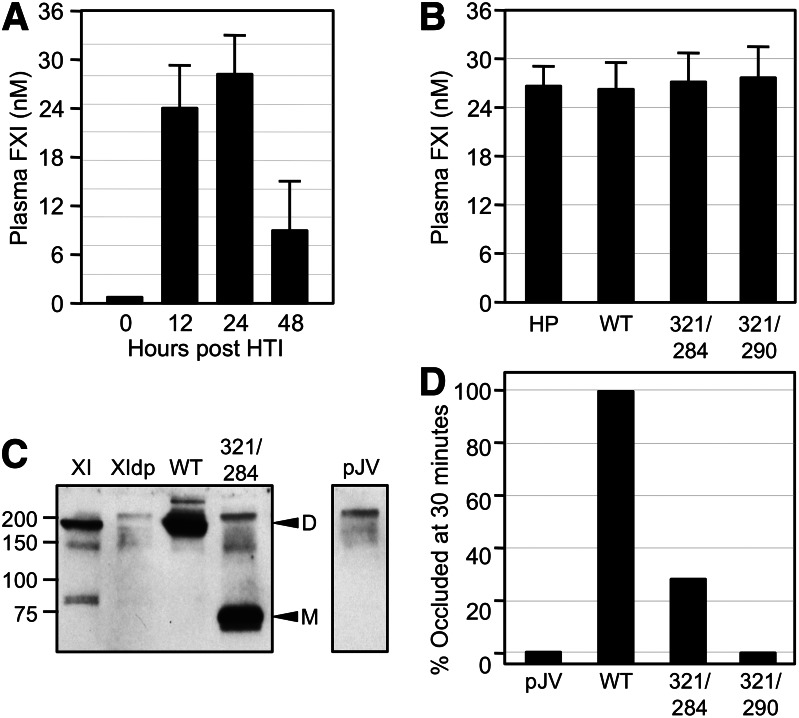
Figure 3.
FeCl3-induced carotid artery occlusion in fXI-deficient mice expressing human fXI. (A) FXI−/− mice underwent HTI with human fXIWT cDNA in expression vector pJVCMV. Shown are concentrations of human fXI in mouse plasma at various times post-HTI. (B) Concentrations of fXI levels in plasma from fXI−/− mice 24 hours post-HTI with constructs for human fXIWT (WT), fXIC321S,L284A (321/284), or fXIC321S,I290A (321/290). Normal human plasma is shown for comparison. For panels A and B, error bars represent 1 standard deviation. (C) Western blot of mouse plasmas 24 hours post-HTI with constructs for human fXIWT, fXIC321S,L284A, or empty vector control (pJV). A sample of pure human fXI (XI) and a sample of fXI-deficient mouse plasma (XIdp) are shown for comparison. Positions of molecular mass standard (kDa) are shown at the left of the blot. Positions for fXI dimer (D) and monomer (M) are indicated on the right. (D) Groups of 10 fXI−/− mice underwent HTI with constructs for fXIWT, fXIC321S,L284A, fXIC321S,I290A, or empty vector control (pJV). Twenty-four hours later, the animals were tested in a carotid artery thrombosis model in which thrombus formation is induced by exposing the vessel to 3.5% FeCl3. Each bar indicates the percent of mice in each group with occluded arteries 30 minutes after applying FeCl3. Plasma fXI levels of the mice in this study are shown in panel B.