Abstract
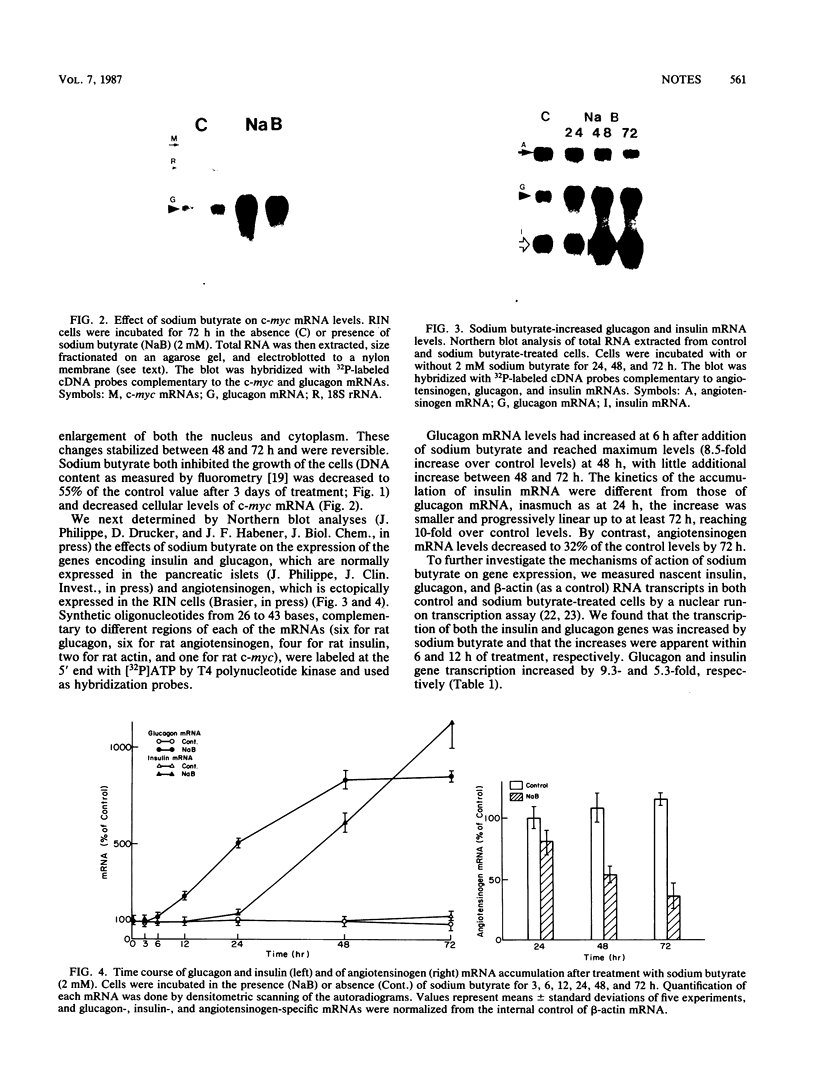
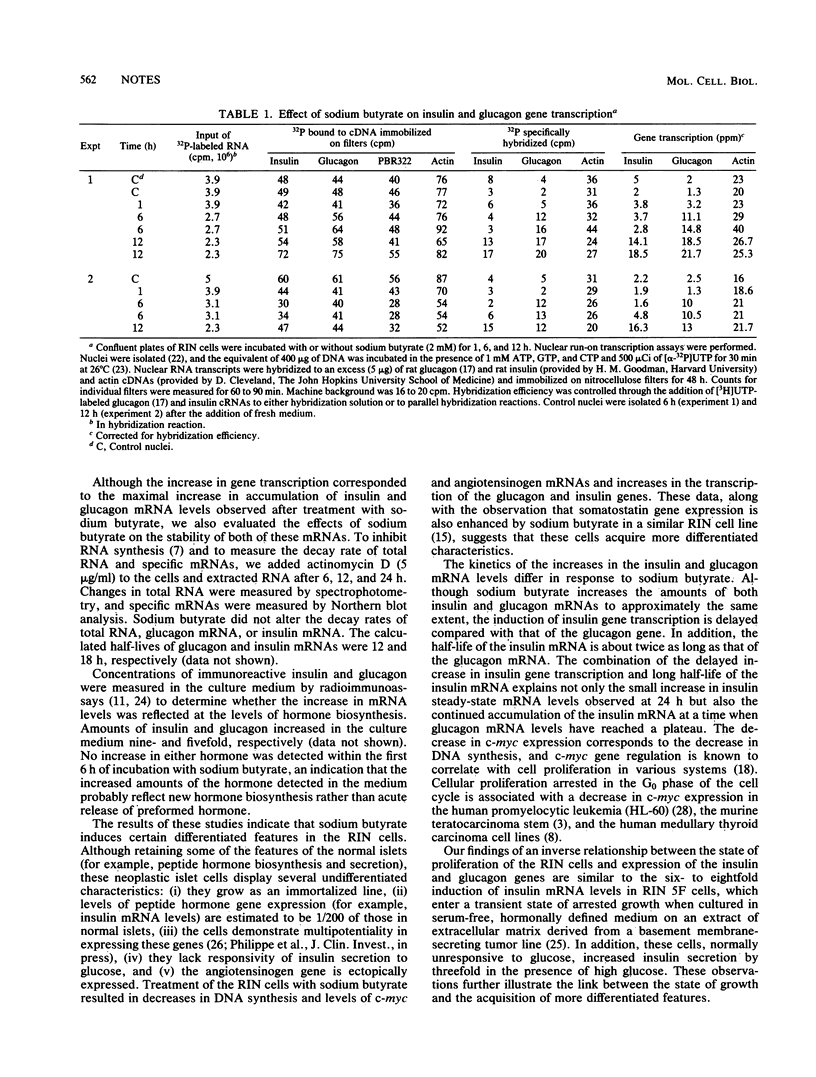
The state of differentiation of various neoplastic cell lines is inversely correlated with the rate of cellular growth. To delineate the changes in hormone gene expression associated with an induced decrease in the growth rate of rat insulinoma cells, we studied the effects of sodium butyrate on the expression of the genes encoding insulin, glucagon, and angiotensinogen. Sodium butyrate inhibited cellular proliferation and decreased levels of c-myc mRNA. Concomitantly, steady-state levels of mRNAs encoding insulin and glucagon increased by 10- and 8.5-fold, respectively, as a result of a specific increase in the transcription of both genes. Sodium butyrate also inhibited angiotensinogen gene expression, which was ectopic in the insulinoma cells. These observations suggest that sodium butyrate induces a pattern of events leading to the differentiation of the rat insulinoma cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birren B. W., Herschman H. R. Regulation of the rat metallothionein-I gene by sodium butyrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):853–867. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boffa L. C., Gruss R. J., Allfrey V. G. Manifold effects of sodium butyrate on nuclear function. Selective and reversible inhibition of phosphorylation of histones H1 and H2A and impaired methylation of lysine and arginine residues in nuclear protein fractions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9612–9621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chick W. L., Warren S., Chute R. N., Like A. A., Lauris V., Kitchen K. C. A transplantable insulinoma in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):628–632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman J. K., Weich N., Schoenbrun B., Schneiderman N., Acs G. Hypomethylation of DNA during differentiation of Friend erythroleukemia cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):366–370. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and other polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2458–2462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., El Sabouty S., Marty L., Jeanteur P. Extreme instability of myc mRNA in normal and transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G., McGhee J. Methylation and gene control. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):602–603. doi: 10.1038/296602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenz C. R., Nelson D. A. N-Butyrate incubation of immature chicken erythrocytes preferentially enhances the solubility of beta A chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1977–1995. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Chick W. L., Oie H. K., Sims H. L., King D. L., Weir G. C., Lauris V. Continuous, clonal, insulin- and somatostatin-secreting cell lines established from a transplantable rat islet cell tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3519–3523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller R., Levenson R., Housman D. Significance of the cell cycle in commitment of murine erythroleukemia cells to erythroid differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 1978 May;95(2):213–222. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040950211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh M. K., Cox R. P. Production of human chorionic gonadotropin in HeLa cell cultures. Nature. 1976 Feb 5;259(5542):416–417. doi: 10.1038/259416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg E., Salomon D., Sreevalsan T., Freese E. Growth inhibition and morphological changes caused by lipophilic acids in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2457–2461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Shields D. Sodium butyrate stimulates somatostatin production by cultured cells. Endocrinology. 1984 Jun;114(6):1990–1994. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-6-1990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagopian H. K., Riggs M. G., Swartz L. A., Ingram V. M. Effect of n-butyrate on DNA synthesis in chick fibroblasts and HeLa cells. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):855–860. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90284-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich G., Gros P., Lund P. K., Bentley R. C., Habener J. F. Pre-proglucagon messenger ribonucleic acid: nucleotide and encoded amino acid sequences of the rat pancreatic complementary deoxyribonucleic acid. Endocrinology. 1984 Dec;115(6):2176–2181. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-6-2176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Leder P. Butyric acid, a potent inducer of erythroid differentiation in cultured erythroleukemic cells. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):319–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90107-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Orkin S., Leder P. Differentiation of erythroleukemic cells in the presence of inhibitors of DNA synthesis. Science. 1975 Nov 28;190(4217):893–894. doi: 10.1126/science.1059262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A. Transcriptional regulation of the prolactin gene by ergocryptine and cyclic AMP. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):94–97. doi: 10.1038/294094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mojsov S., Heinrich G., Wilson I. B., Ravazzola M., Orci L., Habener J. F. Preproglucagon gene expression in pancreas and intestine diversifies at the level of post-translational processing. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11880–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel R., Khoury G., Reid L. M. Regulation of insulin mRNA abundance and adenylation: dependence on hormones and matrix substrata. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):337–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oie H. K., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D., Weir G. C., Baylin S. B. Clonal analysis of insulin and somatostatin secretion and L-dopa decarboxylase expression by a rat islet cell tumor. Endocrinology. 1983 Mar;112(3):1070–1075. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-3-1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad K. N., Sinha P. K. Effect of sodium butyrate on mammalian cells in culture: a review. In Vitro. 1976 Feb;12(2):125–132. doi: 10.1007/BF02796360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitsma P. H., Rothberg P. G., Astrin S. M., Trial J., Bar-Shavit Z., Hall A., Teitelbaum S. L., Kahn A. J. Regulation of myc gene expression in HL-60 leukaemia cells by a vitamin D metabolite. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):492–494. doi: 10.1038/306492a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs M. G., Whittaker R. G., Neumann J. R., Ingram V. M. n-Butyrate causes histone modification in HeLa and Friend erythroleukaemia cells. Nature. 1977 Aug 4;268(5619):462–464. doi: 10.1038/268462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein P., Sealy L., Marshall S., Chalkley R. Cellular protein synthesis and inhibition of cell division are independent of butyrate-induced histone hyperacetylation. Nature. 1979 Aug 23;280(5724):692–693. doi: 10.1038/280692a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterner R., Vidali G., Allfrey V. G. Studies of acetylation and deacetylation in high mobility group proteins. Identification of the sites of acetylation in high mobility group proteins 14 and 17. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8892–8895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidali G., Boffa L. C., Bradbury E. M., Allfrey V. G. Butyrate suppression of histone deacetylation leads to accumulation of multiacetylated forms of histones H3 and H4 and increased DNase I sensitivity of the associated DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2239–2243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bustros A., Baylin S. B., Berger C. L., Roos B. A., Leong S. S., Nelkin B. D. Phorbol esters increase calcitonin gene transcription and decrease c-myc mRNA levels in cultured human medullary thyroid carcinoma. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):98–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]