Abstract
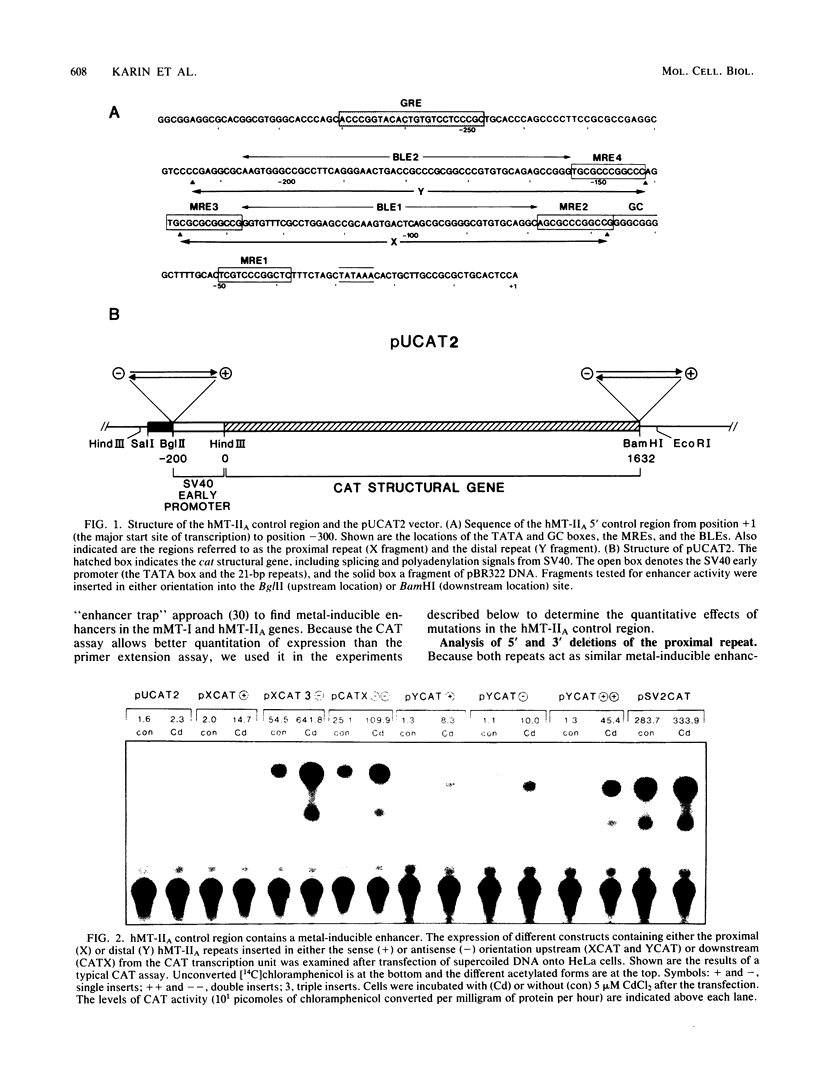
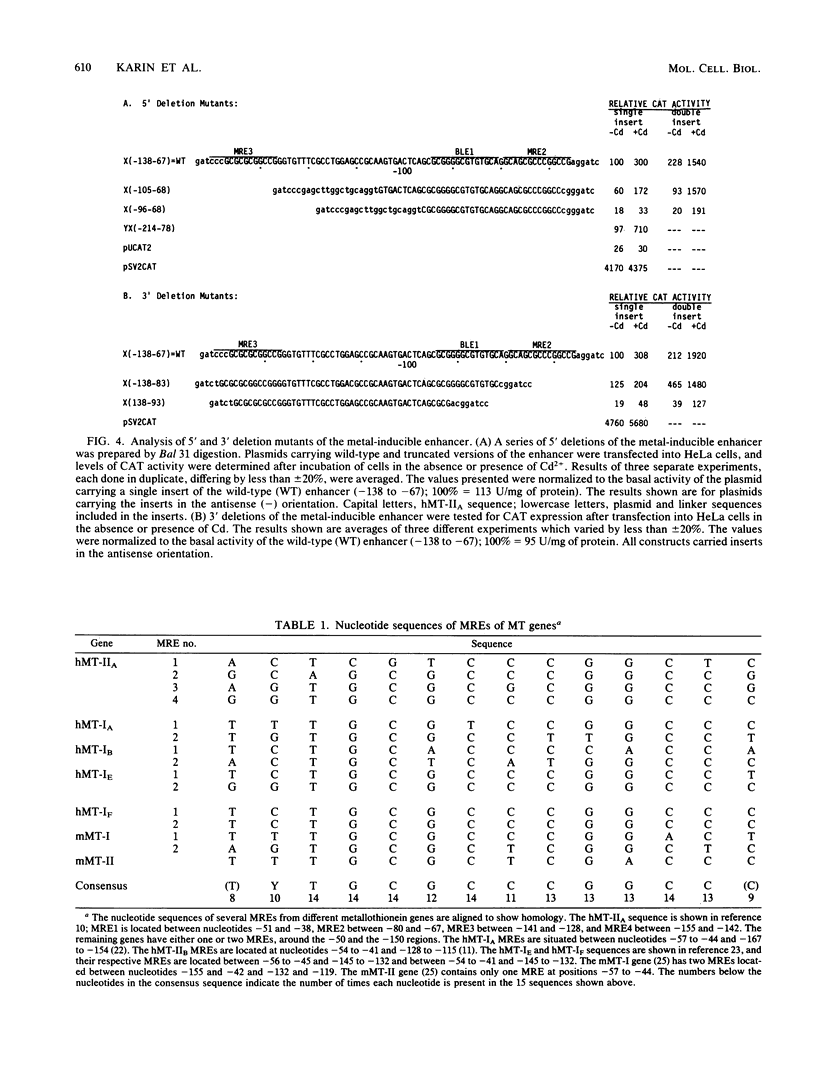
The human metallothionein IIA (hMT-IIA) gene contains two enhancer elements whose activity is induced by heavy-metal ions such as Cd2+. To determine the nature of the relationship between the metal-responsive elements and the element(s) responsible for the basal activity of the enhancers, the basal-level enhancer element(s), the hMT-IIA enhancers were subjected to mutational analysis. We show that deletion of the metal-responsive elements had no effect on the basal activity of the enhancer but prevented further induction by Cd2+. On the other hand, replacement of the basal-level enhancer element with linker DNA led to inactivation of the enhancer both before and after treatment with Cd2+. Therefore, the metal-responsive elements seems to act as a positive modulator of enhancer function in the presence of heavy-metal ions. In addition to the two enhancers, the hMT-IIA promoter contained one other element, the GC box, required for its basal expression. Unlike deletion of the basal-level enhancer element, replacement of the GC box with linker DNA had no effect on the ability of the promoter to be induced by Cd2+.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton N. K., Vapnek D. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the chloramphenicol resistance transposon Tn9. Nature. 1979 Dec 20;282(5741):864–869. doi: 10.1038/282864a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter A. D., Felber B. K., Walling M. J., Jubier M. F., Schmidt C. J., Hamer D. H. Duplicated heavy metal control sequences of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7392–7396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J., Wasylyk B., Buchwalder A., Sassone-Corsi P., Kedinger C., Chambon P. Promoter sequences of eukaryotic protein-coding genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1406–1414. doi: 10.1126/science.6251548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslinger A., Karin M. Upstream promoter element of the human metallothionein-IIA gene can act like an enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8572–8576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heguy A., West A., Richards R. I., Karin M. Structure and tissue-specific expression of the human metallothionein IB gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2149–2157. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A., Kimura A., Fournier A., Fellous M., Kourilsky P. Interferon response sequence potentiates activity of an enhancer in the promoter region of a mouse H-2 gene. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):743–746. doi: 10.1038/322743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Cathala G., Slater E., Baxter J. D. Activation of a heterologous promoter in response to dexamethasone and cadmium by metallothionein gene 5'-flanking DNA. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Holtgreve H. Nucleotide sequence requirements for transient expression of human metallothionein-IIA-thymidine kinase fusion genes. DNA. 1984 Aug;3(4):319–326. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M. Metallothioneins: proteins in search of function. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):9–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. The nucleotide sequence and transcript map of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponta H., Kennedy N., Skroch P., Hynes N. E., Groner B. Hormonal response region in the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat can be dissociated from the proviral promoter and has enhancer properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1020–1024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. I., Heguy A., Karin M. Structural and functional analysis of the human metallothionein-IA gene: differential induction by metal ions and glucocorticoids. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90322-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Jubier M. F., Hamer D. H. Structure and expression of two human metallothionein-I isoform genes and a related pseudogene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7731–7737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholer H., Haslinger A., Heguy A., Holtgreve H., Karin M. In vivo competition between a metallothionein regulatory element and the SV40 enhancer. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):76–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3006253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Davison B. L., Stuart G. W., Wilkie T. M., Norstedt G., Palmiter R. D. Regulation, linkage, and sequence of mouse metallothionein I and II genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1221–1230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searle P. F., Stuart G. W., Palmiter R. D. Building a metal-responsive promoter with synthetic regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1480–1489. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serfling E., Lübbe A., Dorsch-Häsler K., Schaffner W. Metal-dependent SV40 viruses containing inducible enhancers from the upstream region of metallothionein genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3851–3859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04157.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart G. W., Searle P. F., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. A 12-base-pair DNA motif that is repeated several times in metallothionein gene promoters confers metal regulation to a heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7318–7322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., de Villiers J., Schaffner W. An SV40 "enhancer trap" incorporates exogenous enhancers or generates enhancers from its own sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]