Abstract
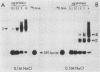
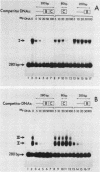
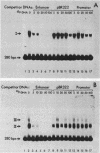
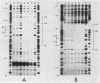
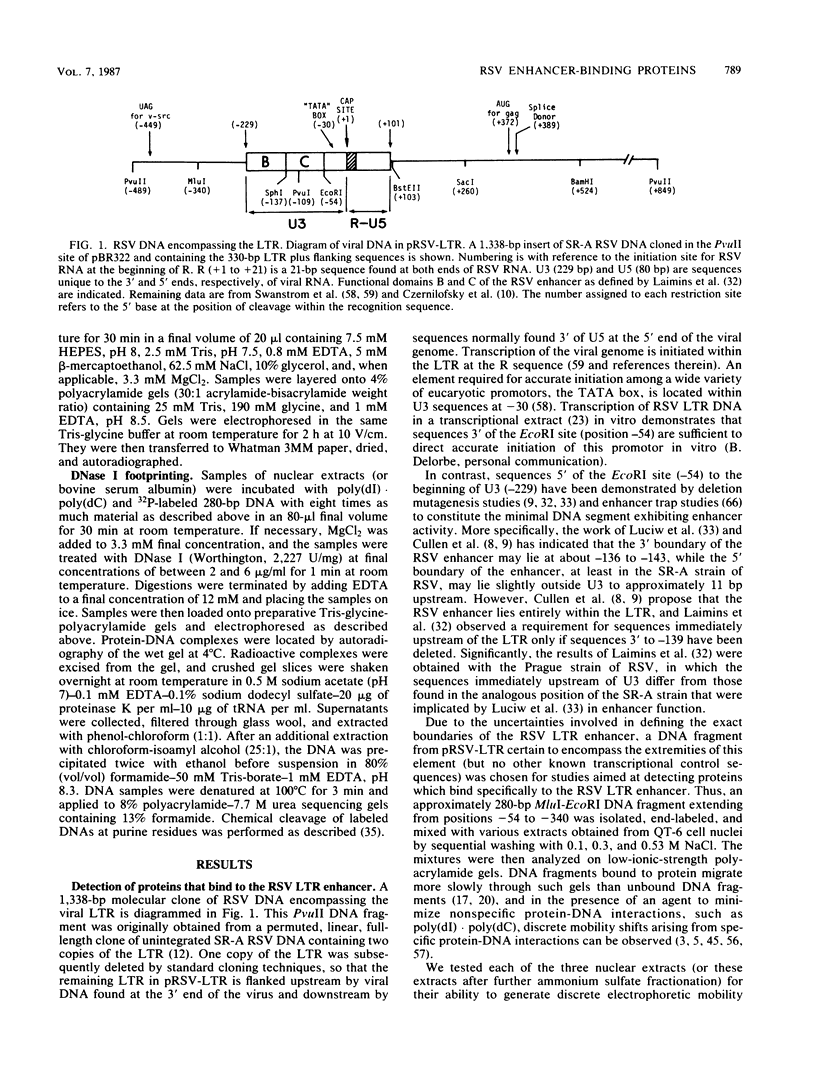
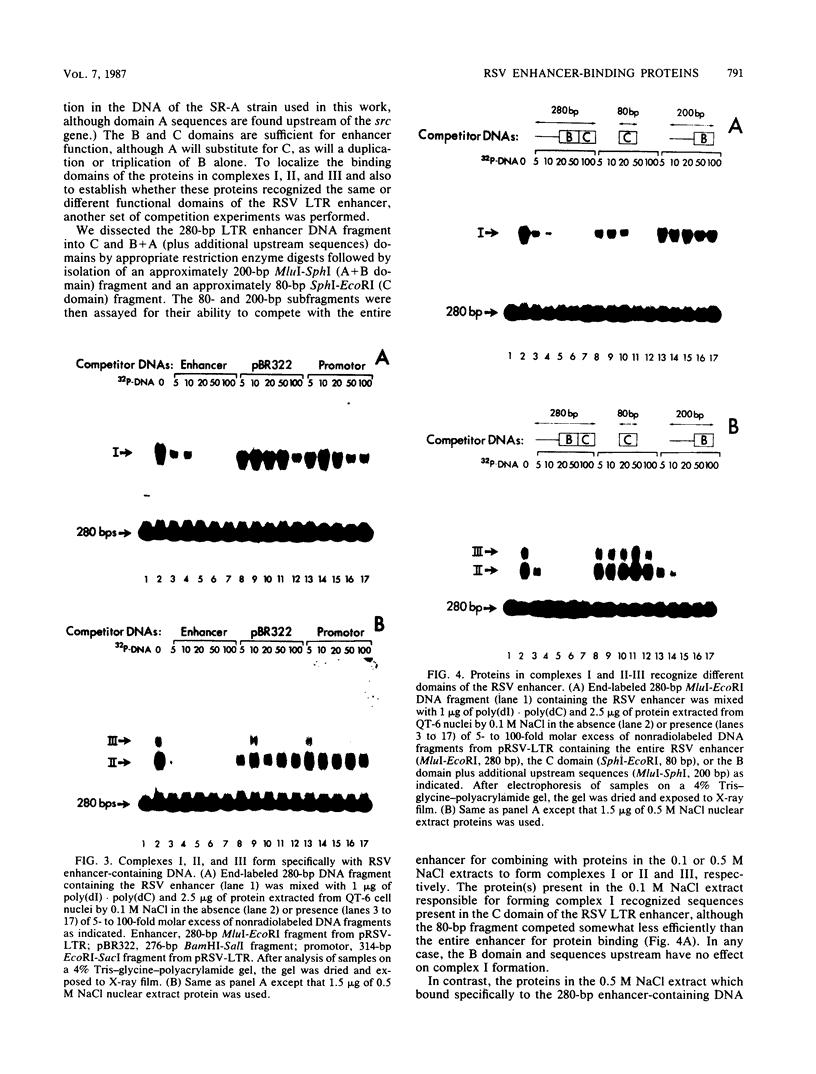
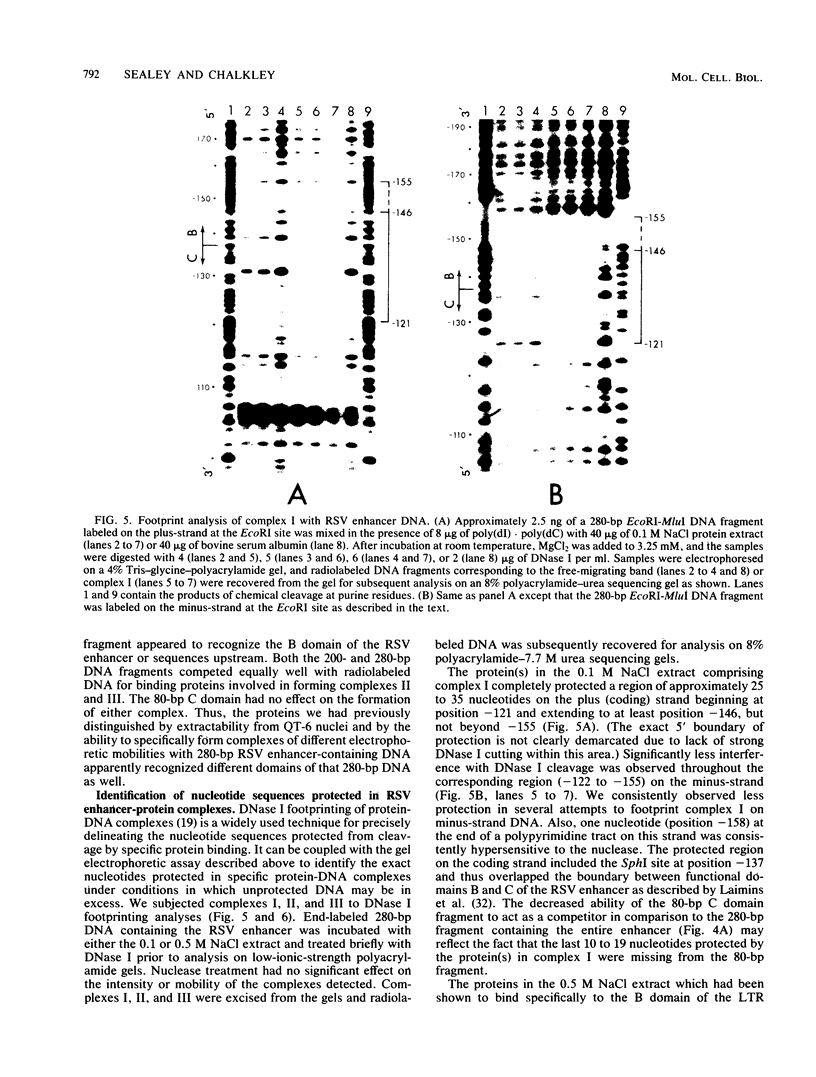
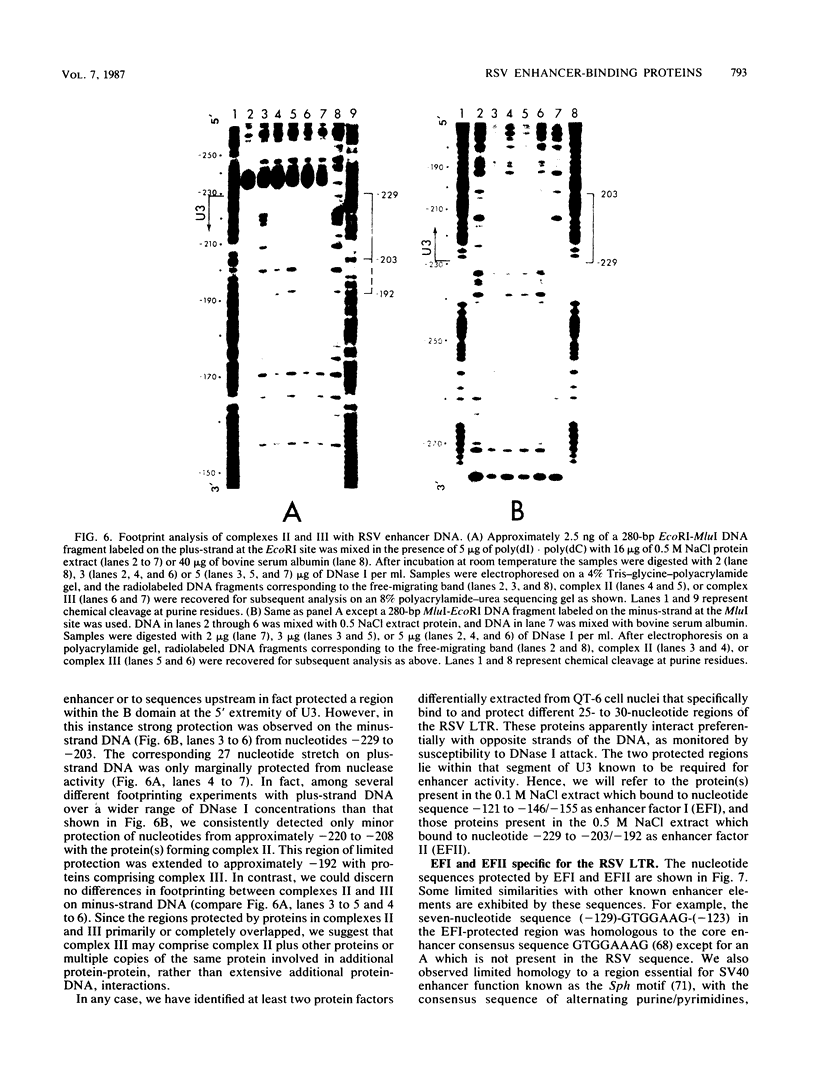
We used the sensitive gel electrophoresis DNA-binding assay and DNase I footprinting to detect at least two protein factors (EFI and EFII) that bound specifically to the Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) enhancer in vitro. These factors were differentially extracted from quail cell nuclei, recognized different nucleotide sequences in the U3 region of the RSV long terminal repeat, and appeared to bind preferentially to opposite DNA strands as monitored by the DNase I protection assay. The EFI- and EFII-protected regions within U3 corresponded closely to sequences previously demonstrated by deletion mutagenesis to be required for enhancer activity, strongly suggesting a functional significance for these proteins. Only weak homologies between other enhancer consensus sequence motifs and the EFI and EFII recognition sites were observed, and other viral enhancers from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus did not compete effectively with the RSV enhancer for binding either factor.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartley J. A., Chalkley R. The binding of deoxyribonucleic acid and histone in native nucleohistone. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 10;247(11):3647–3655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Häsler K., Fleckenstein B., Schaffner W. A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):521–530. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Gruss P. Interaction of distinct nuclear proteins with sequences controlling the expression of polyomavirus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1401–1411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Ephrussi A., Gilbert W., Tonegawa S. Cell-type-specific contacts to immunoglobulin enhancers in nuclei. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):798–801. doi: 10.1038/313798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Adams J. M., Dunn A. R., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas in which the cellular myc oncogene has been activated by retroviral insertion. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Functional analysis of the transcription control region located within the avian retroviral long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):438–447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Transcriptional activity of avian retroviral long terminal repeats directly correlates with enhancer activity. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):515–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.515-521.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., DeLorbe W., Swanstrom R., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Tischer E., Goodman H. M. The nucleotide sequence of an untranslated but conserved domain at the 3' end of the avian sarcoma virus genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2967–2984. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorbe W. J., Luciw P. A., Goodman H. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus circular DNA molecules. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.50-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschamps J., Meijlink F., Verma I. M. Identification of a transcriptional enhancer element upstream from the proto-oncogene fos. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1174–1177. doi: 10.1126/science.3865371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch-Häsler K., Keil G. M., Weber F., Jasin M., Schaffner W., Koszinowski U. H. A long and complex enhancer activates transcription of the gene coding for the highly abundant immediate early mRNA in murine cytomegalovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8325–8329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., DeFeo D., Maryak J. M., Young H. A., Shih T. Y., Chang E. H., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. Dual evolutionary origin for the rat genetic sequences of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):408–420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.408-420.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimura F. K. Nuclear activity from F9 embryonal carcinoma cells binding specifically to the enhancers of wild-type polyoma virus and PyEC mutant DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):2845–2861. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.2845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Folsom V., Tonegawa S. Cell type-specific enhancer element associated with a mouse MHC gene, E beta. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):594–597. doi: 10.1038/310594a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodbourn S., Zinn K., Maniatis T. Human beta-interferon gene expression is regulated by an inducible enhancer element. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):509–520. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslinger A., Karin M. Upstream promoter element of the human metallothionein-IIA gene can act like an enhancer element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8572–8576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Clarke J. The SV40 enhancer is composed of multiple functional elements that can compensate for one another. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):461–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gluzman Y. Duplications of a mutated simian virus 40 enhancer restore its activity. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):711–714. doi: 10.1038/313711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Tsichlis P., Khoury G. Multiple enhancer domains in the 3' terminus of the Prague strain of Rous sarcoma virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6427–6442. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciw P. A., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E., Capecchi M. R. Location and function of retroviral and SV40 sequences that enhance biochemical transformation after microinjection of DNA. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Goverman J., Mirell C., Calame K. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer requires one or more tissue-specific factors. Science. 1985 Jan 18;227(4684):266–270. doi: 10.1126/science.3917575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Jimenez H., Lai M. M., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Continuous tissue culture cell lines derived from chemically induced tumors of Japanese quail. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled simian virus 40 DNA contains Z-DNA segments within transcriptional enhancer sequences. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):674–679. doi: 10.1038/303674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusse R., Varmus H. E. Many tumors induced by the mouse mammary tumor virus contain a provirus integrated in the same region of the host genome. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Sperling L., Herbomel P., Yaniv M., Weiss M. C. Tissue-specific expression is conferred by a sequence from the 5' end of the rat albumin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2505–2510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. S., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Multiple arrangements of viral DNA and an activated host oncogene in bursal lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):209–214. doi: 10.1038/295209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D. Viral and cellular transcription enhancers. Oxf Surv Eukaryot Genes. 1985;2:24–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Kryszke M. H., Yaniv M. Specific interaction of cellular factors with the B enhancer of polyoma virus. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2675–2685. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Stafford J. Fine mapping of an immunoglobulin gene activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1042–1049. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. L., Blais B. M., Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. At least two regions of the viral genome determine the oncogenic potential of avian leukosis viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1225–1229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Dougherty J. P., Wasylyk B., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from heterologous promoters by the simian virus 40 enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):308–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Wildeman A., Chambon P. A trans-acting factor is responsible for the simian virus 40 enhancer activity in vitro. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):458–463. doi: 10.1038/313458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Weissmann C. A rapid, sensitive, and specific method for the determination of protein in dilute solution. Anal Biochem. 1973 Dec;56(2):502–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90217-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholer H., Haslinger A., Heguy A., Holtgreve H., Karin M. In vivo competition between a metallothionein regulatory element and the SV40 enhancer. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):76–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3006253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Cell type-specific transcriptional enhancement in vitro requires the presence of trans-acting factors. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):3005–3013. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., DeLorbe W. J., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence of cloned unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: viral DNA contains direct and inverted repeats similar to those in transposable elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):124–128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the 5' noncoding region and part of the gag gene of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):535–541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.535-541.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theisen M., Stief A., Sippel A. E. The lysozyme enhancer: cell-specific activation of the chicken lysozyme gene by a far-upstream DNA element. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):719–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Donehower L., Hager G., Zeller N., Malavarca R., Astrin S., Skalka A. M. Sequence comparison in the crossover region of an oncogenic avian retrovirus recombinant and its nononcogenic parent: genetic regions that control growth rate and oncogenic potential. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1331–1338. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldman G. M., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyomavirus enhancer contains multiple redundant sequence elements that activate both DNA replication and gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;5(4):649–658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.4.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., Schaffner W. Enhancer activity correlates with the oncogenic potential of avian retroviruses. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):949–956. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03723.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber F., de Villiers J., Schaffner W. An SV40 "enhancer trap" incorporates exogenous enhancers or generates enhancers from its own sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., Botchan M. R. An enhancer sequence from bovine papilloma virus DNA consists of two essential regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2901–2916. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Sassone-Corsi P., Grundström T., Zenke M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription from the SV40 early promoter by the enhancer involves a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3129–3133. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Zenke M., Schatz C., Wintzerith M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Takahashi K., Chambon P. Specific protein binding to the simian virus 40 enhancer in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2098–2105. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenke M., Grundström T., Matthes H., Wintzerith M., Schatz C., Wildeman A., Chambon P. Multiple sequence motifs are involved in SV40 enhancer function. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):387–397. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]