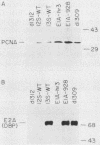
Abstract
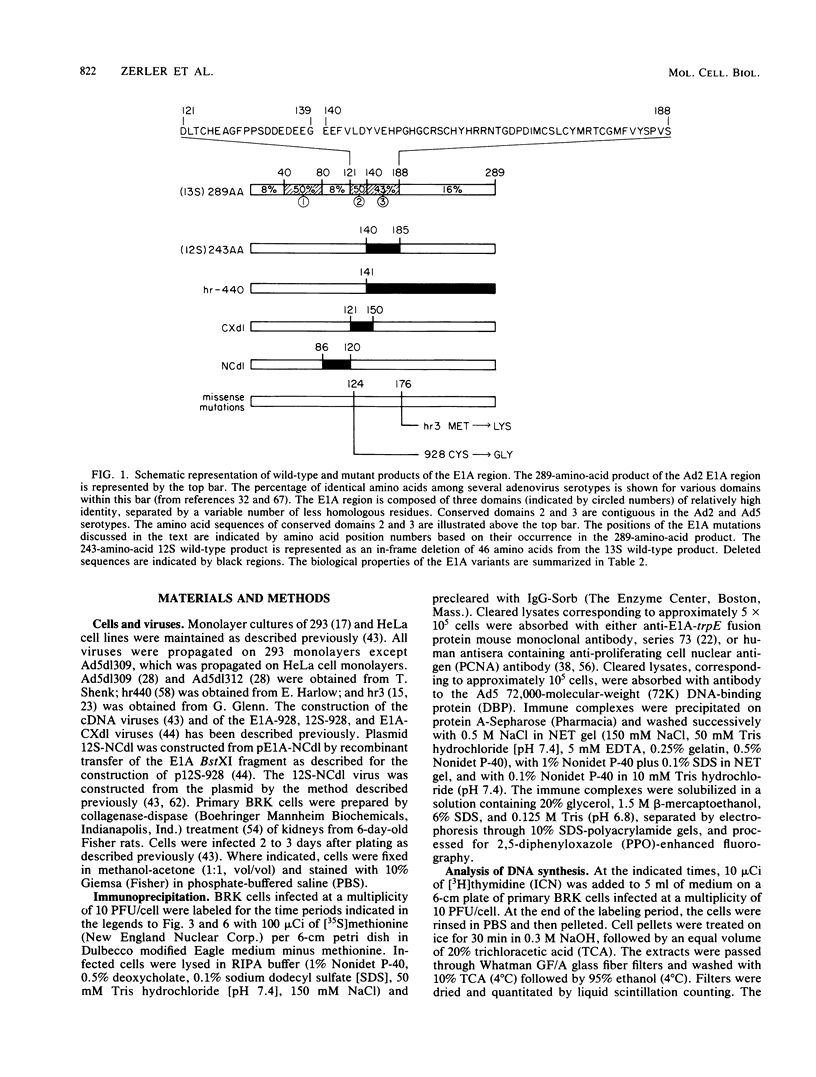
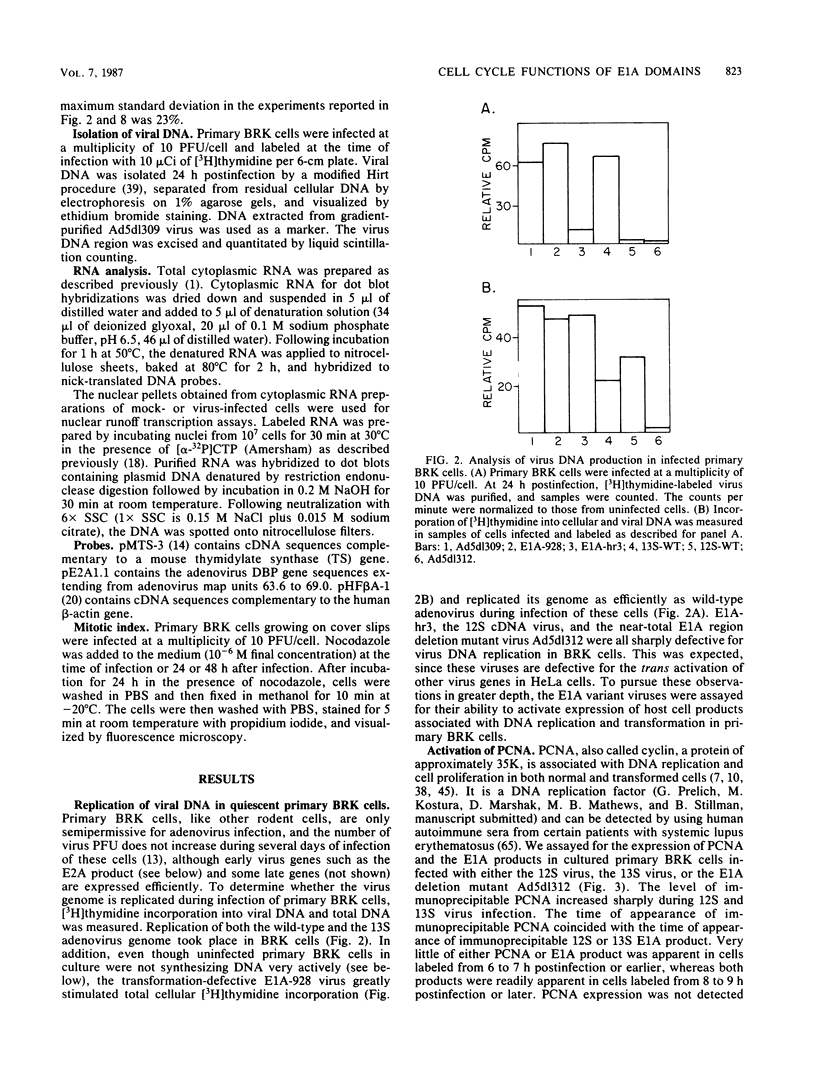
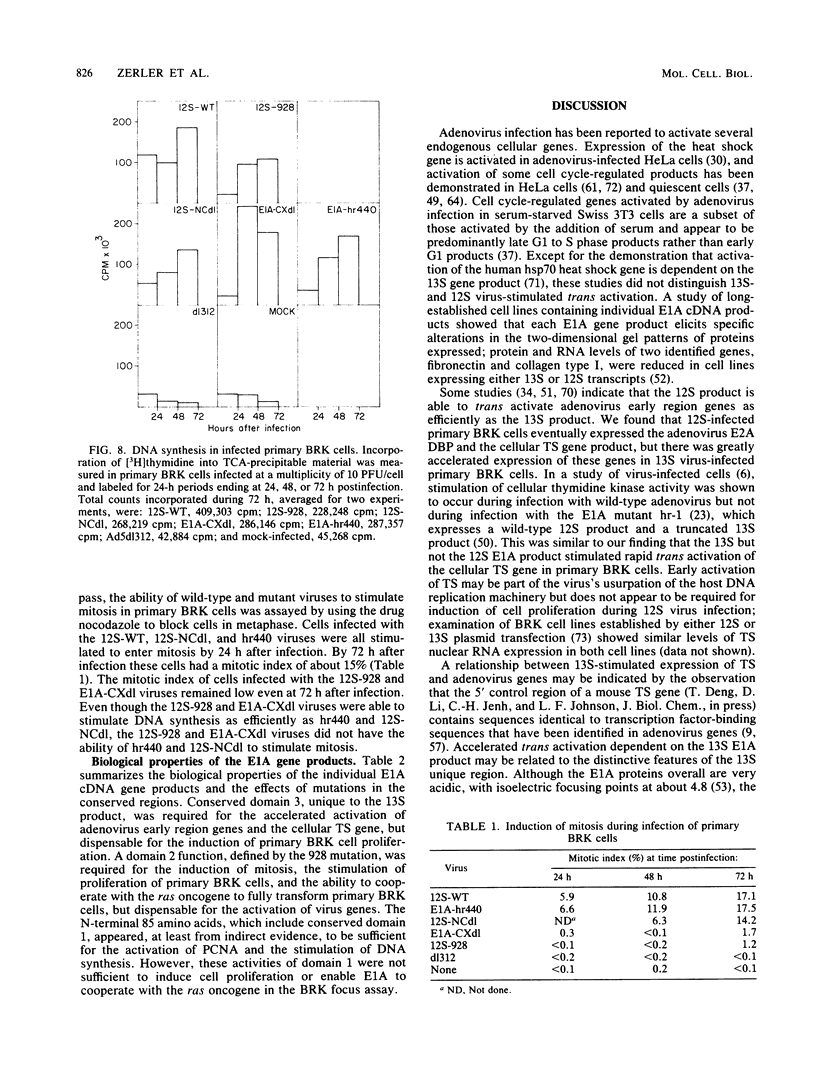
We have analyzed the cell cycle effects that different domains of the adenovirus E1A proteins have on quiescent primary BRK cells. Studies with deletion mutants that in combination removed all but the N-terminal 85 amino acids common to both the 12S and 13S proteins suggest that this region may be sufficient for the induction of synthesis of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and the stimulation of DNA synthesis. A second domain also common to the N-terminal exon of the 12S and 13S proteins was required for the induction of mitosis and stimulation of proliferation of primary BRK cells. A virus containing a mutation in this region was still able to stimulate DNA synthesis efficiently. A third domain, unique to the 13S protein, was required for the accelerated activation of the cellular thymidylate synthase gene in a manner similar to the 13S-dependent stimulation of adenovirus early region genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. Cell-free synthesis of adenovirus 2 proteins programmed by fractionated messenger RNA: a comparison of polypeptide products and messenger RNA lengths. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2756–2760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Cheetham B. F., Li P., Parish C. R., Waldron-Stevens L. K., Bellett A. J. Adenovirus-induced alterations of the cell growth cycle: a requirement for expression of E1A but not of E1B. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):192–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.192-199.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R. Synthesis of the nuclear protein cyclin (PCNA) and its relationship with DNA replication. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Apr;163(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Jones N. C. Transformation-defective mutant of adenovirus type 5 containing a single altered E1a mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.657-664.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Bravo R., Larsen P. M., Fey S. J. Cyclin: a nuclear protein whose level correlates directly with the proliferative state of normal as well as transformed cells. Leuk Res. 1984;8(2):143–157. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(84)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinnadurai G. Adenovirus 2 Ip+ locus codes for a 19 kd tumor antigen that plays an essential role in cell transformation. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):759–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggerding F. A., Pierce W. C. Molecular biology of adenovirus type 2 semipermissive infections. I. Viral growth and expression of viral replicative functions during restricted adenovirus infection. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):97–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90406-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Johnson L. F. Molecular cloning of DNA sequences complementary to mouse thymidylate synthase messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7206–7211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn G. M., Ricciardi R. P. Adenovirus 5 early region 1A host range mutants hr3, hr4, and hr5 contain point mutations which generate single amino acid substitutions. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):66–74. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.66-74.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Harrison T., Williams J. Defective transforming capacity of adenovirus type 5 host-range mutants. Virology. 1978 May 1;86(1):10–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoyle R. A., Osheroff W. P., Rossini M. Two functions encoded by adenovirus early region 1A are responsible for the activation and repression of the DNA-binding protein gene. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):707–713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03687.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley K. P., Overhauser J., Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S., Jones N. C. Transformation properties of type 5 adenovirus mutants that differentially express the E1A gene products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5734–5738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Schley C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for adenovirus early region 1A proteins: extensive heterogeneity in early region 1A products. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):533–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.533-546.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison T., Graham F., Williams J. Host-range mutants of adenovirus type 5 defective for growth in HeLa cells. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90428-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Chambon P. Repression of the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer by the adenovirus-2 E1A products. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1391–1394. doi: 10.1126/science.2999984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houweling A., van den Elsen P. J., van der Eb A. J. Partial transformation of primary rat cells by the leftmost 4.5% fragment of adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz D. R., Chinnadurai G. Evidence that a second tumor antigen coded by adenovirus early gene region E1a is required for efficient cell transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):163–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Ferguson B., Rosenberg M., Baserga R. Induction of cellular DNA synthesis by purified adenovirus E1A proteins. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao H. T., Nevins J. R. Transcriptional activation and subsequent control of the human heat shock gene during adenovirus infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2058–2065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D. A novel general approach to eucaryotic mutagenesis functionally identifies conserved regions within the adenovirus 13S E1A polypeptide. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1487–1496. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelman D., Miller J. S., Porter D., Roberts B. E. E1a regions of the human adenoviruses and of the highly oncogenic simian adenovirus 7 are closely related. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):399–409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.399-409.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Westphal H. The structure of adenovirus 2 early nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 15;137(1):23–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Elkaim R., Goding C. R., Jalinot P., Sassone-Corsi P., Perricaudet M., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Individual products of the adenovirus 12S and 13S EIa mRNAs stimulate viral EIIa and EIII expression at the transcriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Mathews M. B. Control of adenovirus early gene expression: a class of immediate early products. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M., Green M. R. An adenovirus E1a protein region required for transformation and transcriptional repression. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1043–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90704-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H. T., Baserga R., Mercer W. E. Adenovirus type 2 activates cell cycle-dependent genes that are a subset of those activated by serum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2936–2942. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Bernstein R. M., Franza B. R., Jr, Garrels J. I. Identity of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cyclin. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):374–376. doi: 10.1038/309374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Grodzicker T. Virus-associated RNAs of naturally occurring strains and variants of group C adenoviruses. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):849–862. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.849-862.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinnon R. D., Bacchetti S., Graham F. L. Tn5 mutagenesis of the transforming genes of human adenovirus type 5. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi K., Fritzler M. J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to a nuclear antigen in proliferating cells. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2228–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Courtois G., Eng C., Berk A. Complete transformation by adenovirus 2 requires both E1A proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Grodzicker T., Roberts R. J., Mathews M. B., Zerler B. Lytic and transforming functions of individual products of the adenovirus E1A gene. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):765–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.765-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Zerler B., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. Identification of separate domains in the adenovirus E1A gene for immortalization activity and the activation of virus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3470–3480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navalgund L. G., Rossana C., Muench A. J., Johnson L. F. Cell cycle regulation of thymidylate synthetase gene expression in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7386–7390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postel E. H., Levine A. J. Studies on the regulation of deoxypyrimidine kinases in normal, SV40-transformed and SV40- and adenovirus-infected mouse cells in culture. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):404–420. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Young P., Jones N. C., Krippl B., Rosenberg M., Ferguson B. A first exon-encoded domain of E1A sufficient for posttranslational modification, nuclear-localization, and induction of adenovirus E3 promoter expression in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8434–8438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Miller J. S., Kimelman D., Cepko C. L., Lemischka I. R., Mulligan R. C. Individual adenovirus type 5 early region 1A gene products elicit distinct alterations of cellular morphology and gene expression. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):404–413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.404-413.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Yee S. P., Otis J., Graham F. L., Branton P. E. Characterization of human adenovirus type 5 early region 1A polypeptides using antitumor sera and an antiserum specific for the carboxy terminus. Virology. 1983 Jun;127(2):253–271. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a look at yeasts divided. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):781–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90550-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadaie M. R., Mathews M. B. Immunochemical and biochemical analysis of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Apr;163(2):423–433. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D., Anderson M. A. Transformation-deficient adenovirus mutant defective in expression of region 1A but not region 1B. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. R., Eng C. Y., Berk A. J. An adenovirus early region 1A protein is required for maximal viral DNA replication in growth-arrested human cells. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):742–750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.742-750.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel S., Argos P., Philipson L. The release of growth arrest by microinjection of adenovirus E1A DNA. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2329–2336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R., Ziff E. B. HeLa cell beta-tubulin gene transcription is stimulated by adenovirus 5 in parallel with viral early genes by an E1a-dependent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2792–2801. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D. Cloning of a DNA fragment from the left-hand terminus of the adenovirus type 2 genome and its use in site-directed mutagenesis. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):171–180. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.171-180.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Adenovirus 2 early region 1A stimulates expression of both viral and cellular genes. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):789–794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Ueda S., Ogino T. Enhancement of the thymidine kinase activity of human embryonic kidney cells and newborn hamster kidney cells by infection with human adenovirus types 5 and 12. Virology. 1966 Dec;30(4):742–743. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Autoantibodies to nuclear antigens (ANA): their immunobiology and medicine. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:167–240. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60836-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Eb A. J., Mulder C., Graham F. L., Houweling A. Transformation with specific fragments of adenovirus DNAs. I. Isolation of specific fragments with transforming activity of adenovirus 2 and 5 DNA. Gene. 1977;2(3-4):115–132. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(77)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velcich A., Ziff E. Adenovirus E1a proteins repress transcription from the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks D. L., Jones N. C. E1A control of gene expression is mediated by sequences 5' to the transcriptional starts of the early viral genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1222–1234. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winberg G., Shenk T. Dissection of overlapping functions within the adenovirus type 5 E1A gene. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1907–1912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoder S. S., Robberson B. L., Leys E. J., Hook A. G., Al-Ubaidi M., Yeung C. Y., Kellems R. E., Berget S. M. Control of cellular gene expression during adenovirus infection: induction and shut-off of dihydrofolate reductase gene expression by adenovirus type 2. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):819–828. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerler B., Moran B., Maruyama K., Moomaw J., Grodzicker T., Ruley H. E. Adenovirus E1A coding sequences that enable ras and pmt oncogenes to transform cultured primary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):887–899. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ormondt H., Maat J., Dijkema R. Comparison of nucleotide sequences of the early E1a regions for subgroups A, B and C of human adenoviruses. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(1-2):63–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]