Abstract
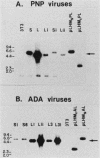
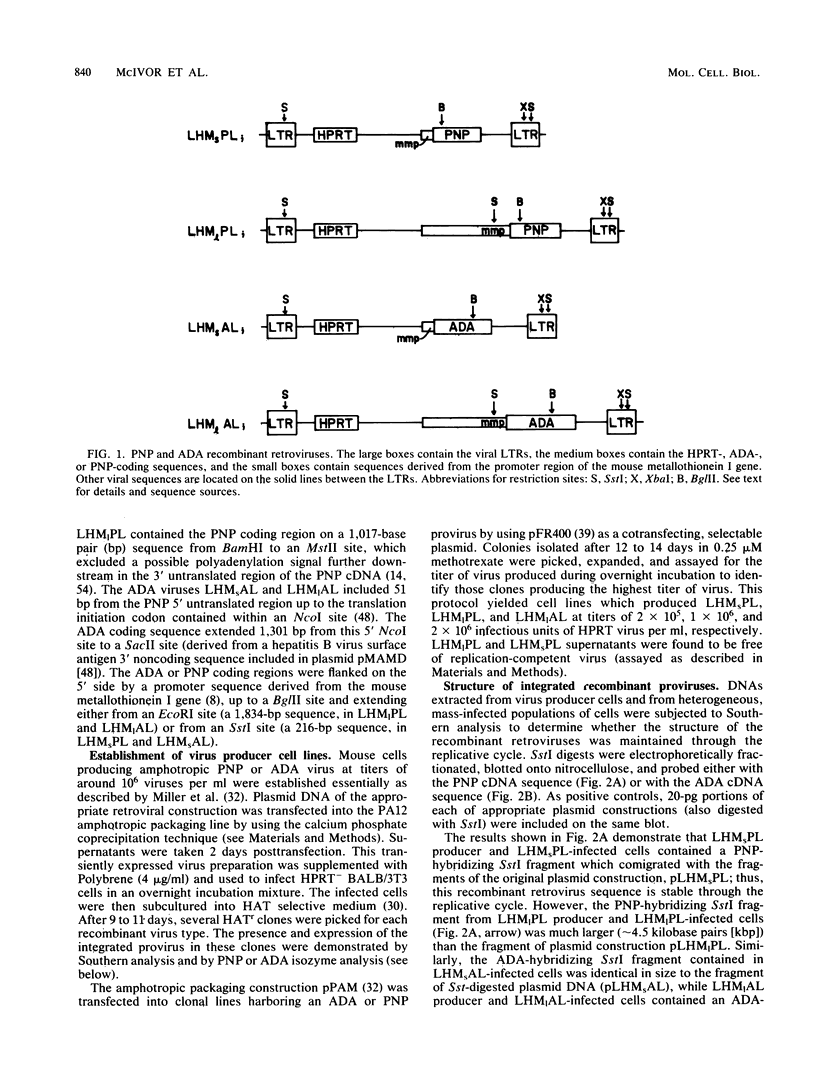
Cell lines were established which produced high titers (approximately 10(6) infectious units per ml) of amphotropic, replication-defective recombinant retroviruses which transduced sequences encoding either human purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) or adenosine deaminase (ADA). These viruses also contained a human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene as a selectable marker and a mouse metallothionein promoter (MMP) sequence just upstream from the PNP or ADA genes. Virus structure was maintained through the replication cycle if a short (216-base pair) MMP sequence was used. However, the use of a longer (1,834-base pair) MMP sequence resulted in the deletion of a significant portion of the recombinant virus genome, including the transcriptional regulatory elements of the MMP sequence. Northern analysis indicated a predominance of genome length transcripts in cells infected with deleted virus. The demonstration of substantial human PNP or ADA activity in virus-infected mouse fibroblasts by isozyme analysis suggested that active gene product was translated from either spliced or bicistronic message. The deleted ADA and PNP viruses were introduced into mouse hematopoietic stem cells by cocultivating freshly explanted bone marrow with virus producer cells. The infected marrow cells were injected into irradiated, syngeneic recipient mice, and the presence of integrated ADA or PNP proviral sequences was demonstrated in the DNA of spleen colonies by Southern analysis. Failure of these integrated proviral sequences to express active, human isozyme in spleen colony tissue indicated the existence of some regulatory constraint not active in cultured mouse cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson W. F. Prospects for human gene therapy. Science. 1984 Oct 26;226(4673):401–409. doi: 10.1126/science.6093246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belmont J. W., Henkel-Tigges J., Chang S. M., Wager-Smith K., Kellems R. E., Dick J. E., Magli M. C., Phillips R. A., Bernstein A., Caskey C. T. Expression of human adenosine deaminase in murine haematopoietic progenitor cells following retroviral transfer. Nature. 1986 Jul 24;322(6077):385–387. doi: 10.1038/322385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn M. J., Patt H. M. Increased survival of haemopoietic pluripotent stem cells in vitro induced by a marrow fibroblast factor. Br J Haematol. 1977 Nov;37(3):337–344. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1977.tb01004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. D., Mulligan R. C. High-efficiency gene transfer into mammalian cells: generation of helper-free recombinant retrovirus with broad mammalian host range. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick J. E., Magli M. C., Huszar D., Phillips R. A., Bernstein A. Introduction of a selectable gene into primitive stem cells capable of long-term reconstitution of the hemopoietic system of W/Wv mice. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Perrin F., Gannon F., Palmiter R. D. Isolation and characterization of the mouse metallothionein-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6511–6515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckner R. J., Hettrick K. L. Defective Friend spleen focus-forming virus: interfering properties and isolation free from standard leukemia-inducing helper virus. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):383–396. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.383-396.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglitis M. A., Kantoff P., Gilboa E., Anderson W. F. Gene expression in mice after high efficiency retroviral-mediated gene transfer. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1395–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.2999985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L. Expression of human adenosine deaminase using a transmissable murine retrovirus vector system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):703–707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Ammann A. J., Wara D. W., Sandman R., Diamond L. K. Nucleoside-phosphorylase deficiency in a child with severely defective T-cell immunity and normal B-cell immunity. Lancet. 1975 May 3;1(7914):1010–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91950-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giblett E. R., Anderson J. E., Cohen F., Pollara B., Meuwissen H. J. Adenosine-deaminase deficiency in two patients with severely impaired cellular immunity. Lancet. 1972 Nov 18;2(7786):1067–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard J. M., Caput D., Williams S. R., Martin D. W., Jr Cloning of human purine-nucleoside phosphorylase cDNA sequences by complementation in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4281–4285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Rigby P. W., Lane D. P. Negative regulation of viral enhancers in undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90109-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson G. S., Bradley T. R. Properties of haematopoietic stem cells surviving 5-fluorouracil treatment: evidence for a pre-CFU-S cell? Nature. 1979 Oct 4;281(5730):381–382. doi: 10.1038/281381a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Jähner D., Nobis P., Simon I., Löhler J., Harbers K., Grotkopp D. Chromosomal position and activation of retroviral genomes inserted into the germ line of mice. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G., Paige C., Gilboa E., Wagner E. F. Expression of a foreign gene in myeloid and lymphoid cells derived from multipotent haematopoietic precursors. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):149–154. doi: 10.1038/318149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Hapel A. J., Ihle J. N. Constitutive production of a unique lymphokine (IL 3) by the WEHI-3 cell line. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2393–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemischka I. R., Raulet D. H., Mulligan R. C. Developmental potential and dynamic behavior of hematopoietic stem cells. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):917–927. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90566-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linney E., Davis B., Overhauser J., Chao E., Fan H. Non-function of a Moloney murine leukaemia virus regulatory sequence in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):470–472. doi: 10.1038/308470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. W., Jr, Gelfand E. W. Biochemistry of diseases of immunodevelopment. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:845–877. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.004213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIvor R. S., Goddard J. M., Simonsen C. C., Martin D. W., Jr Expression of a cDNA sequence encoding human purine nucleoside phosphorylase in rodent and human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1349–1357. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIvor R. S., Valerio D., Williams S. R., Goddard J. M., Simonsen C. C., Duyvesteyn M. G., Van Ormondt H., van der Eb A. J., Martin D. W., Jr Mammalian expression of cloned cDNA sequences encoding human purine nucleoside phosphorylase and adenosine deaminase. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;451:245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb27115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Eckner R. J., Jolly D. J., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. Expression of a retrovirus encoding human HPRT in mice. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):630–632. doi: 10.1126/science.6377498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Jolly D. J., Friedmann T., Verma I. M. A transmissible retrovirus expressing human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT): gene transfer into cells obtained from humans deficient in HPRT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4709–4713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Law M. F., Verma I. M. Generation of helper-free amphotropic retroviruses that transduce a dominant-acting, methotrexate-resistant dihydrofolate reductase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):431–437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON C. C., SCHILDKRAUT C. L., APOSHIAN H. V., KORNBERG A. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. XIV. FURTHER PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:222–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Temin H. M. Formation of infectious progeny virus after insertion of herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene into DNA of an avian retrovirus. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90034-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Isolation and expression of an altered mouse dihydrofolate reductase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. W., Wilson S. M., Fred S. S. Kinetics of stem cell depletion and proliferation: effects of vinblastine and vincristine in normal and irradiated mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Apr;40(4):847–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., Wright D., Erdman V. D., Cutting A. E. Amphotropic retrovirus vector system for human cell gene transfer. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1730–1737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart T. A., Pattengale P. K., Leder P. Spontaneous mammary adenocarcinomas in transgenic mice that carry and express MTV/myc fusion genes. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90257-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TILL J. E., McCULLOCH E. A. A direct measurement of the radiation sensitivity of normal mouse bone marrow cells. Radiat Res. 1961 Feb;14:213–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Till J. E., McCulloch E. A. Hemopoietic stem cell differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 26;605(4):431–459. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullman B., Gudas L. J., Clift S. M., Martin D. W., Jr Isolation and characterization of purine-nucleoside phosphorylase-deficient T-lymphoma cells and secondary mutants with altered ribonucleotide reductase: genetic model for immunodeficiency disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valerio D., Duyvesteyn M. G., van der Eb A. J. Introduction of sequences encoding functional human adenosine deaminase into mouse cells using a retroviral shuttle system. Gene. 1985;34(2-3):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. E. Form and function of retroviral proviruses. Science. 1982 May 21;216(4548):812–820. doi: 10.1126/science.6177038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner E. F., Vanek M., Vennström B. Transfer of genes into embryonal carcinoma cells by retrovirus infection: efficient expression from an internal promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):663–666. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03680.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Lemischka I. R., Nathan D. G., Mulligan R. C. Introduction of new genetic material into pluripotent haematopoietic stem cells of the mouse. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):476–480. doi: 10.1038/310476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Orkin S. H., Mulligan R. C. Retrovirus-mediated transfer of human adenosine deaminase gene sequences into cells in culture and into murine hematopoietic cells in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2566–2570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. R., Goddard J. M., Martin D. W., Jr Human purine nucleoside phosphorylase cDNA sequence and genomic clone characterization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5779–5787. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]