Abstract
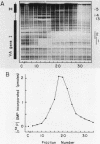
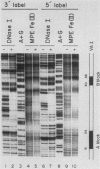
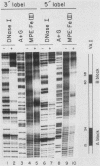
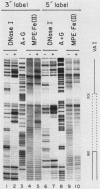
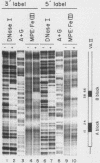
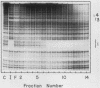
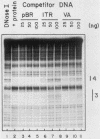
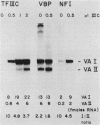
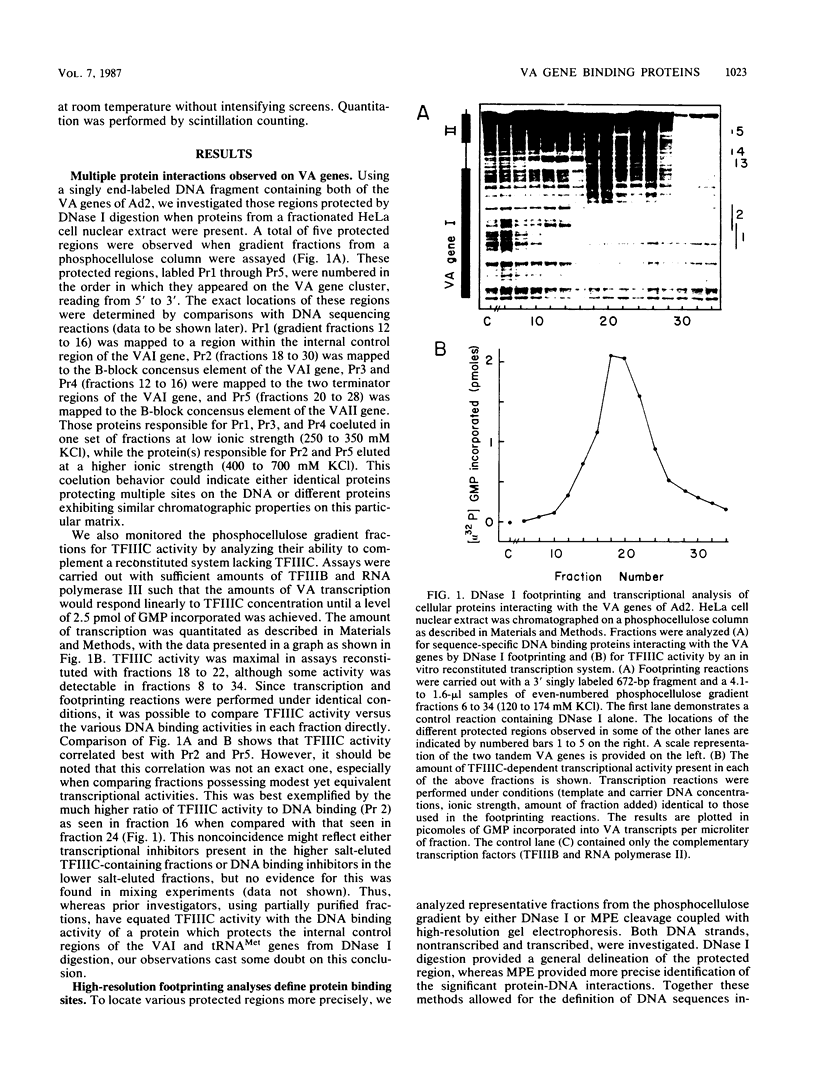
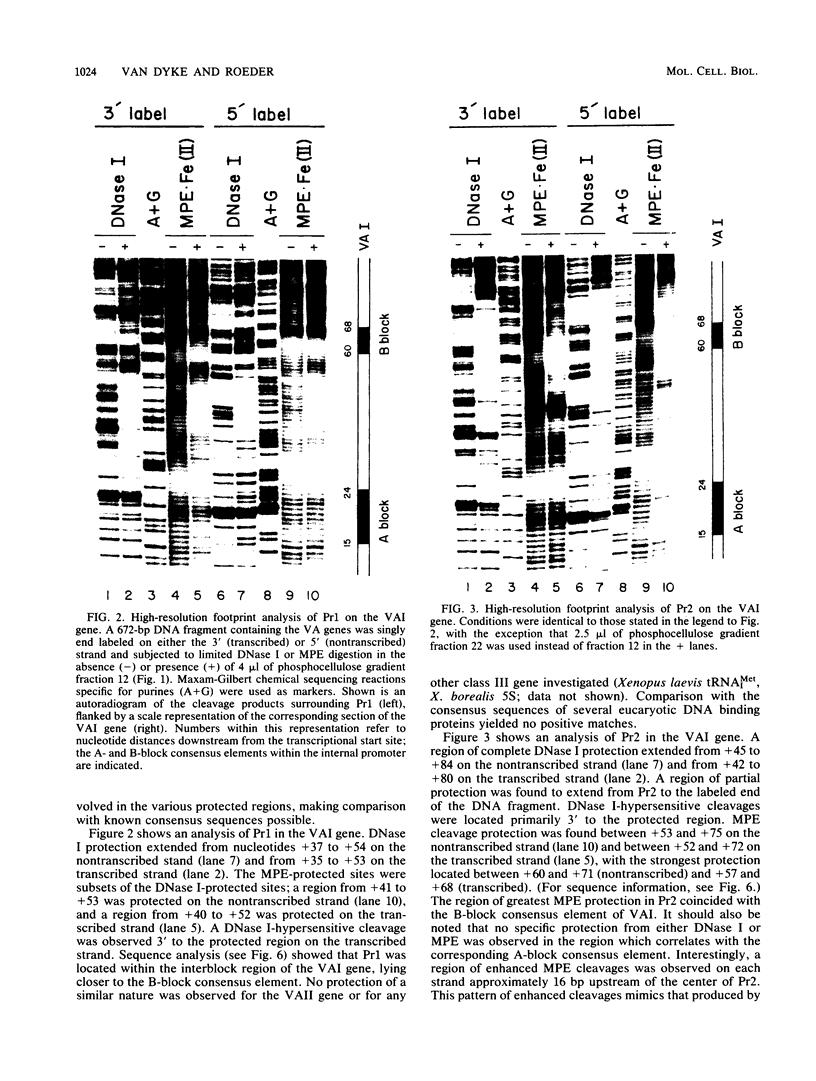
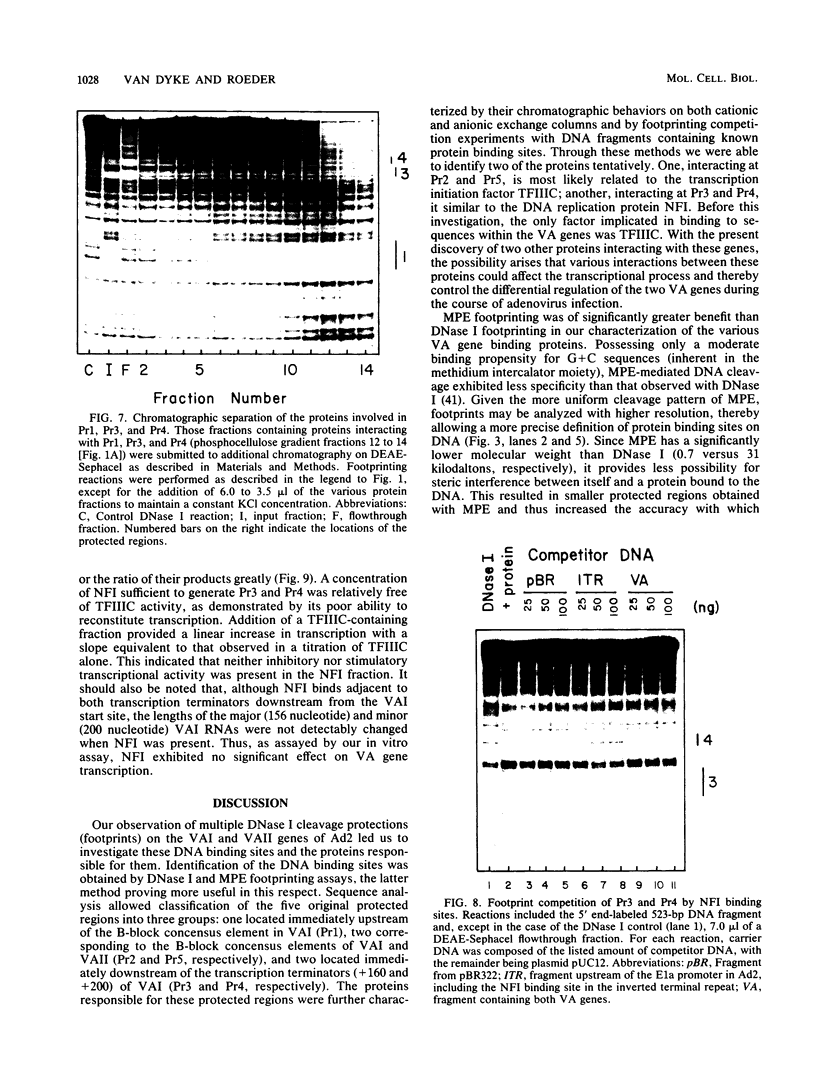
Using fractionated HeLa cell nuclear extracts and both nuclease (DNase I) cleavage and chemical cleavage (methidiumpropyl-EDTA X Fe(II) protection methodologies, we demonstrated the presence of three proteins which interacted specifically, yet differentially, with the two VA genes of adenovirus type 2. One, previously identified as transcription initiation factor TFIIIC, bound to a site centered on the transcriptionally essential B-block concensus element of the VAI gene and, with a lower affinity, to the analogous site in the VAII gene. Another, identified as the cellular protein involved in adenovirus replication, nuclear factor I, bound to sites immediately downstream from the two VAI terminators (at approximately +160 and +200). The third, a previously unrecognized VA gene binding protein termed VBP, bound immediately upstream of the B-block element in the VAI gene but showed no binding to VAII. Possible roles for these proteins in VA gene transcription were investigated in in vitro assay systems reconstituted with partially purified transcription factors (RNA polymerase III, TFIIIB, and TFIIIC). Although TFIIIC activity was present predominantly in fractions containing B-block binding activity, there was not complete correspondence between functional and DNA binding activities. The nuclear factor I-like protein had no effect when added to a complete transcription reaction. The presence of VBP appeared to depress the intrinsic ratio of VAI-VAII synthesis, thereby simulating the relative transcription levels observed early in adenovirus infection of HeLa cells. These observations suggest a model, involving both intragenic binding factors (VBP and TFIIIC) and variable template concentrations, for the differential regulation of VA transcription during the course of adenovirus infection.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akusjärvi G., Mathews M. B., Andersson P., Vennström B., Pettersson U. Structure of genes for virus-associated RNAI and RNAII of adenovirus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R. A., Domer P. H., Thimmappaya B. Structural requirements of adenovirus VAI RNA for its translation enhancement function. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):187–196. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R. A., Metz B., Thimmappaya B. Organization of the noncontiguous promoter components of adenovirus VAI RNA gene is strikingly similar to that of eucaryotic tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):1996–2005. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R. A., Thimmappaya B. Adenovirus mutants with DNA sequence perturbations in the intragenic promoter of VAI RNA gene allow the enhanced transcription of VAII RNA gene in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7377–7388. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90522-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon R. E., Wu G. J., Railey J. F. Functions of and interactions between the A and B blocks in adenovirus type 2-specific VARNA1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1285–1289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M. F., Gerrard S. P., Cozzarelli N. R. Analysis of RNA polymerase III transcription complexes by gel filtration. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4309–4317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celma M. L., Pan J., Weissman S. M. Studies of low molecular weight RNA from cells infected with adenovirus 2. I. The sequences at the 3' end of VA-RNA I. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):9032–9042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R., Gerrard S. P., Schlissel M., Brown D. D., Bogenhagen D. F. Purified RNA polymerase III accurately and efficiently terminates transcription of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):829–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90540-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R. Structural specificities of five commonly used DNA nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):535–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions of the adenovirus VAI RNA gene. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francoeur A. M., Mathews M. B. Interaction between VA RNA and the lupus antigen La: formation of a ribonucleoprotein particle in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6772–6776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Engelke D. R., Geiduschek E. P. HeLa cell RNA polymerase III transcription factors. Functional characterization of a fraction identified by its activity in a second template rescue assay. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1934–1943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B. Cleavage of DNA with methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II): reaction conditions and product analyses. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3934–3945. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaehning J. A., Stewart C. C., Roeder R. G. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase levels during the response of human peripheral lymphocytes to phytohemagglutinin. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasher M. S., Pintel D., Ward D. C. Rapid enrichment of HeLa transcription factors IIIB and IIIC by using affinity chromatography based on avidin-biotin interactions. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3117–3127. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kean J. M., White S. A., Draper D. E. Detection of high-affinity intercalator sites in a ribosomal RNA fragment by the affinity cleavage intercalator methidiumpropyl-EDTA-iron(II). Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 10;24(19):5062–5070. doi: 10.1021/bi00340a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leegwater P. A., van der Vliet P. C., Rupp R. A., Nowock J., Sippel A. E. Functional homology between the sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins nuclear factor I from HeLa cells and the TGGCA protein from chicken liver. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):381–386. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04223.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Hardin J. A., Steitz J. A. Two novel classes of small ribonucleoproteins detected by antibodies associated with lupus erythematosus. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):400–402. doi: 10.1126/science.6164096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monstein H. J., Philipson L. The conformation of adenovirus VAI-RNA in solution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4239–4250. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Enomoto T., Lichy J. H., Hurwitz J. Adenovirus DNA replication in vitro: identification of a host factor that stimulates synthesis of the preterminal protein-dCMP complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6438–6442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Guggenheimer R. A., Hurwitz J. Specific binding of a cellular DNA replication protein to the origin of replication of adenovirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6177–6181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowock J., Borgmeyer U., Püschel A. W., Rupp R. A., Sippel A. E. The TGGCA protein binds to the MMTV-LTR, the adenovirus origin of replication, and the BK virus enhancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2045–2061. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Mariano T. M., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. A mechanism for the control of protein synthesis by adenovirus VA RNAI. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson U., Philipson L. Location of sequences on the adenovirus genome coding for the 5.5S RNA. Cell. 1975 Sep;6(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price R., Penman S. A distinct RNA polymerase activity, synthesizing 5-5 s, 5 s and 4 s RNA in nuclei from adenovirus 2-infected HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Oct 14;70(3):435–450. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90551-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich P. R., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. RNA of low molecular weight in KB cells infected with adenovirus type 2. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;17(2):428–439. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz P. G., Dervan P. B. Sequence-specific double-strand cleavage of DNA by penta-N-methylpyrrolecarboxamide-EDTA X Fe(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6834–6837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderlund H., Pettersson U., Vennström B., Philipson L., Mathews M. B. A new species of virus-coded low molecular weight RNA from cells infected with adenovirus type 2. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Jones N., Shenk T. A mutation which alters initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase III on the Ad5 chromosome. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):947–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thimmappaya B., Weinberger C., Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA is required for efficient translation of viral mRNAs at late times after infection. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Dervan P. B. Methidiumpropyl-EDTA.Fe(II) and DNase I footprinting report different small molecule binding site sizes on DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5555–5567. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann R., Raskas H. J., Roeder R. G. Role of DNA-dependent RNA polymerases II and III in transcription of the adenovirus genome late in productive infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3426–3439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]