Abstract
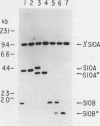
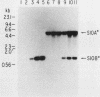
The phosphorylation of mammalian ribosomal protein S6 is affected by a variety of agents, including growth factors and tumor promoters, as well as by expressed oncogenes. Its potential role in the regulation of protein synthesis has been the object of much study. We have developed strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in which the phosphorylatable serines of the equivalent ribosomal protein (S10) were converted to alanines by site-directed mutagenesis. The S10 of such cells is not phosphorylated. Comparison of these cells with the parental cells, whose genomes differ by only six nucleotides, revealed no differences in the lag phase or logarithmic phase of a growth cycle, in growth on different carbon sources, in sporulation, or in sensitivity to heat shock. We conclude that in S. cerevisiae the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S10 may play no role in regulating the synthesis of proteins. This conclusion leads one to ask whether certain protein phosphorylations are simply the adventitious, if easily observable, result of the imperfect specificity of one or another protein kinase.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abovich N., Rosbash M. Two genes for ribosomal protein 51 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae complement and contribute to the ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1871–1879. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballinger D. G., Hunt T. Fertilization of sea urchin eggs is accompanied by 40 S ribosomal subunit phosphorylation. Dev Biol. 1981 Oct 30;87(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Regulation of a ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, serum, or phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7621–7625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J., Erikson R. L. Stimulation of ribosomal protein S6 kinase activity by pp60v-src or by serum: dissociation from phorbol ester-stimulated activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1733–1737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhard S. J., Traugh J. A. Changes in ribosome function by cAMP-dependent and cAMP-independent phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14003–14008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in avian sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4112–4115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., McConkey E. H. Preferential utilization of phosphorylated 40-S ribosomal subunits during initiation complex formation. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):535–538. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06564.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion E. A., Warner J. R. An RNA polymerase I enhancer in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2089–2097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. A protein kinase from Xenopus eggs specific for ribosomal protein S6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):742–746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry M. J., Gebhardt A., Parker P. J., Foulkes J. G. Phosphatidylinositol turnover and transformation of cells by Abelson murine leukaemia virus. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3173–3178. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabrielli B., Wettenhall R. E., Kemp B. E., Quinn M., Bizonova L. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and a peptide analogue of S6 by a protease-activated kinase isolated from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 1;175(2):219–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80740-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover C. V. Heat shock induces rapid dephosphorylation of a ribosomal protein in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1781–1785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Nielsen P. J., Manchester K. L., Towbin H., Jimenez de Asua L., Thomas G. Criteria for establishment of the biological significance of ribosomal protein phosphorylation. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1982;21:89–99. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152821-8.50008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowicz T. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation changes in yeast ribosomal proteins S2 and S6 during growth under normal and hyperthermal conditions. Acta Biochim Pol. 1985;32(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristiansen K., Krüger A. Ribosomal proteins in growing and starved Tetrahymena pyriformis. Starvation-induced phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 21;521(2):435–451. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90285-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse C., Johnson S. P., Warner J. R. Phosphorylation of the yeast equivalent of ribosomal protein S6 is not essential for growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7515–7519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Thomas A., Voorma H. O. The protein synthetic activity in vitro of ribosomes differing in the extent of phosphorylation of their ribosomal proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 27;656(1):69–75. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Molenaar C. M., Cohen L. H., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. The structure of the gene coding for the phosphorylated ribosomal protein S10 in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5869–5878. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Molenaar C. M., Witsenboer H. M., Mager W. H., Planta R. J. Yeast contains two functional genes coding for ribosomal protein S10. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jul 25;13(14):5027–5039. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.14.5027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Thomas G. EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin induce the phosphorylation of identical S6 peptides in swiss mouse 3T3 cells: effect of cAMP on early sites of phosphorylation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90222-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastropaolo W., Henshaw E. C. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in the Ehrlich ascites tumor cell. Lack of effect of phosphorylation upon ribosomal function in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec 28;656(2):246–255. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Thomas G., Maller J. L. Increased phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 during meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2937–2941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. Epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of an S6 kinase in Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10314–10319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka E., Kumazaki T., Matsumoto K. In vivo phosphorylation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribosomal protein S10 by cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):713–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.713-715.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Katan M., Waterfield M. D., Leader D. P. The phosphorylation of eukaryotic ribosomal protein S6 by protein kinase C. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):579–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson N. J., Fried H. M., Warner J. R. Yeast use translational control to compensate for extra copies of a ribosomal protein gene. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perisic O., Traugh J. A. Protease-activated kinase II mediates multiple phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13998–14002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. The nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae 5.8 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3860–3875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf K. D., Nover L. Heat-shock-induced alterations of ribosomal protein phosphorylation in plant cell cultures. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):427–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Wejksnora P. J., Warner J. R., Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Insulin-stimulated protein phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2725–2729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szyszka R., Gasior E. Phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins during differentiation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Acta Biochim Pol. 1984;31(4):375–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabarini D., Heinrich J., Rosen O. M. Activation of S6 kinase activity in 3T3-L1 cells by insulin and phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4369–4373. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terao K., Ogata K. Proteins of small subunits of rat liver ribosomes that interact with poly(U). II. Cross-links between poly(U) and ribosomal proteins in 40 S subunits induced by UV irradiation. J Biochem. 1979 Sep;86(3):605–617. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G., Martin-Pérez J., Siegmann M., Otto A. M. The effect of serum, EGF, PGF2 alpha and insulin on S6 phosphorylation and the initiation of protein and DNA synthesis. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto A. S., Ponticelli A., Berk A. J., Gaynor R. B. Genetic mapping of a major site of phosphorylation in adenovirus type 2 E1A proteins. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):14–22. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.14-22.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Gorenstein C. The ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;20:45–60. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)62008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Cohen P., Caudwell B., Holland R. Differential phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in isolated rat hepatocytes after incubation with insulin and glucagon. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 8;148(2):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80809-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wettenhall R. E., Morgan F. J. Phosphorylation of hepatic ribosomal protein S6 on 80 and 40 S ribosomes. Primary structure of S6 in the region of the major phosphorylation sites for cAMP-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2084–2091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder N. D., Boeke J. D. The filamentous phage (Ff) as vectors for recombinant DNA--a review. Gene. 1982 Jul-Aug;19(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]