Abstract
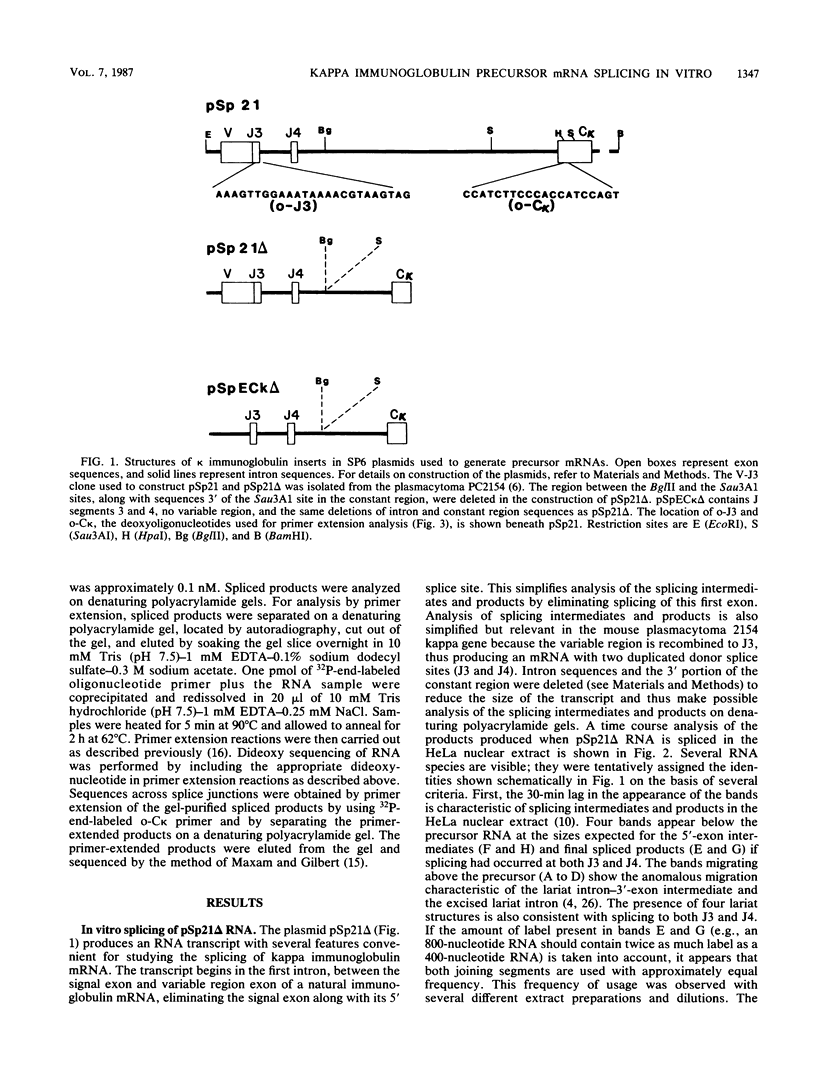
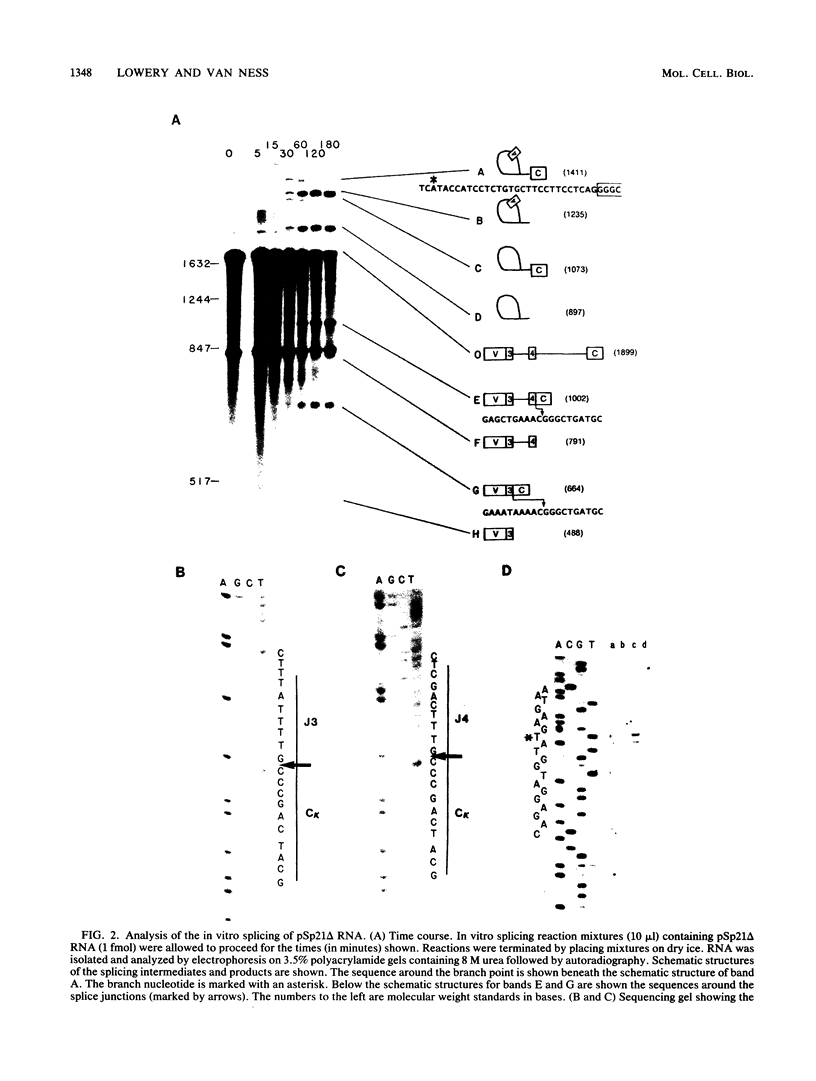
The in vitro splicing of kappa immunoglobulin precursor mRNA was studied as an example of a naturally occurring mRNA possessing multiple 5' splice sites. Several kappa mRNAs were generated in vitro by using an SP6 transcription system and were spliced in nuclear extracts derived from HeLa cells. Products and intermediates resulting from in vitro splicing were identified and characterized. In contrast to the in vivo situation, in which apparently only the 5'-most splice donor site is used, all of the 5' splice sites were used in vitro with equal frequency. Neither the presence or absence of variable region coding sequences nor the deletion of intron sequences had an effect on in vitro splice site selection.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Padgett R. A., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Sequence requirements for splicing of higher eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Messenger RNA splicing in vitro: an excised intervening sequence and a potential intermediate. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):415–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90372-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Keller W. Splicing of in vitro synthesized messenger RNA precursors in HeLa cell extracts. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Wiedemann L. M., Pittet A. C., Strauss S., Nelson K. J., Davis J., Van Ness B., Perry R. P. Nonproductive kappa immunoglobulin genes: recombinational abnormalities and other lesions affecting transcription, RNA processing, turnover, and translation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1660–1675. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohavong P., Gattoni R., Schmitt P., Stévenin J. The different intron 2 species excised in vivo from the E2A premRNA of adenovirus-2: an approach to analyse alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5207–5227. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole R., Weissman S. M. Accurate in vitro splicing of human beta-globin RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 25;10(18):5429–5445. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.18.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühne T., Wieringa B., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Evidence against a scanning model of RNA splicing. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):727–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang K. M., Spritz R. A. RNA splice site selection: evidence for a 5' leads to 3' scanning model. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.6304877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Alternatives for splicing: recognizing the ends of introns. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):324–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The nucleotide sequence of a 5.5-kilobase DNA segment containing the mouse kappa immunoglobulin J and C region genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5116–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Lin R. J., Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Molecular consequences of specific intron mutations on yeast mRNA splicing in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):335–344. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Splicing of adenovirus RNA in a cell-free transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5230–5234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., Kelley D. E., Coleclough C., Seidman J. G., Leder P., Tonegawa S., Matthyssens G., Weigert M. Transcription of mouse kappa chain genes: implications for allelic exclusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1937–1941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotch S. J., Krug R. M. In vitro splicing of influenza viral NS1 mRNA and NS1-beta-globin chimeras: possible mechanisms for the control of viral mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5444–5448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rautmann G., Matthes H. W., Gait M. J., Breathnach R. Synthetic donor and acceptor splice sites function in an RNA polymerase B (II) transcription unit. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2021–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02085.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. Intron sequences involved in lariat formation during pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Alternative splicing caused by RNA secondary structure. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90239-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonegawa S. Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):575–581. doi: 10.1038/302575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Hofer E., Weissmann C. A minimal intron length but no specific internal sequence is required for splicing the large rabbit beta-globin intron. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90426-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]