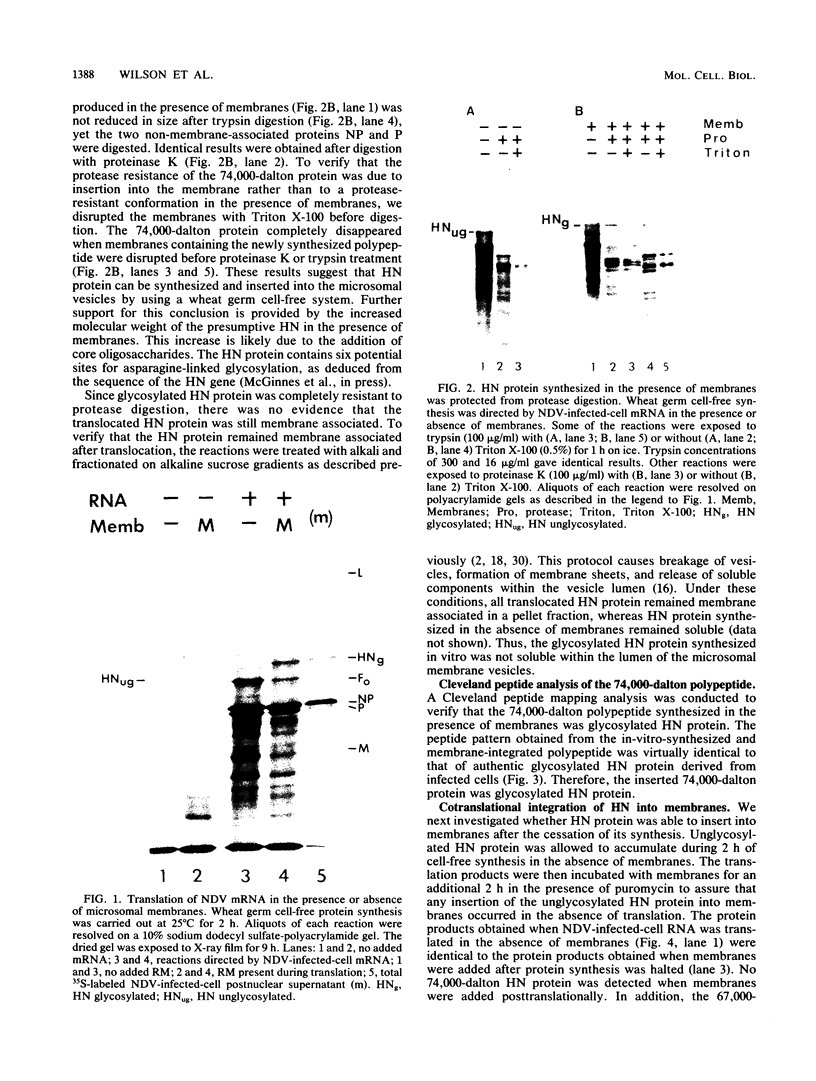
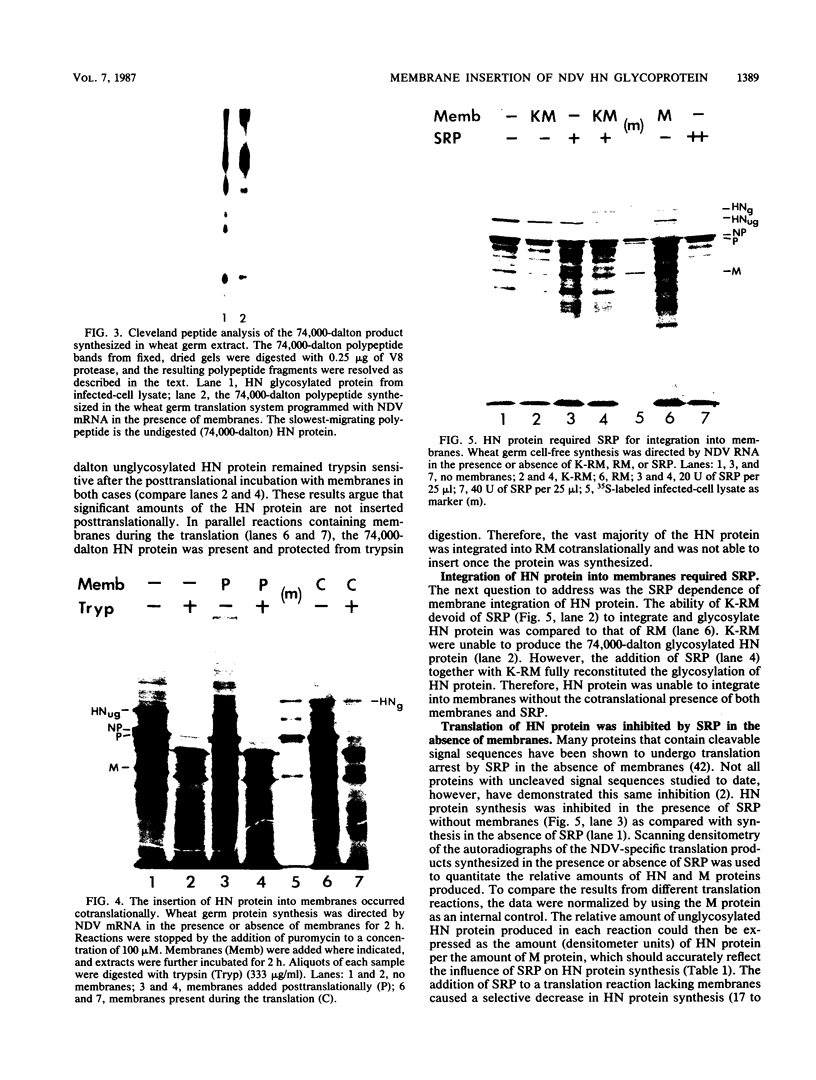
Abstract
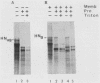
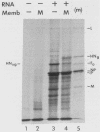
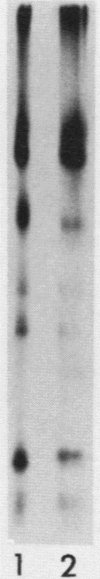
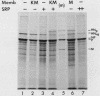
The hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) protein of paramyxoviruses is likely in the unusual class of glycoproteins with the amino terminus cytoplasmic and the carboxy terminus lumenal or external to the cell. The properties of the membrane insertion of the HN protein of Newcastle disease virus, a prototype paramyxovirus, were explored in wheat germ extracts containing microsomal membranes. HN protein was inserted into membranes cotranslationally, resulting in a glycosylated protein completely resistant to trypsin and proteinase K digestion. No detectable posttranslation insertion occurred. Insertion required signal recognition particle. Signal recognition particle in the absence of membranes inhibited HN protein synthesis. Comparisons of the trypsin digestion products of the HN protein made in the cell-free system with newly synthesized HN protein from infected cells showed that the cell-free product was in a conformation different from that of the pulse-labeled protein in infected cells. First, trypsin digestion of intact membranes from infected cells reduced the size of the 74,000-dalton HN protein by approximately 1,000 daltons, whereas trypsin digestion of HN protein made in the cell-free system had no effect on the size of the protein. Second, trypsin digestion of Triton X-100-permeabilized membranes isolated from infected cells resulted in a 67,000-dalton trypsin resistant HN protein fragment. A trypsin-resistant core of comparable size was not present in the digestion products of in-vitro-synthesized HN protein. Evidence is presented that the newly synthesized HN protein in infected cels contain intramolecular disulfide bonds not present in the cell-free product.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkhatib G., Briedis D. J. The predicted primary structure of the measles virus hemagglutinin. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):479–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Mostov K. E., Blobel G. Mechanisms of integration of de novo-synthesized polypeptides into membranes: signal-recognition particle is required for integration into microsomal membranes of calcium ATPase and of lens MP26 but not of cytochrome b5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7249–7253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Birkenmeier C. S. Inhibition of intractable nucleases with ribonucleoside--vanadyl complexes: isolation of messenger ribonucleic acid from resting lymphocytes. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 13;18(23):5143–5149. doi: 10.1021/bi00590a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman L. W., Kuehl W. M. Formation of an intrachain disulfide bond on nascent immunoglobulin light chains. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8869–8876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B., Giorgi C., Roux L., Raju R., Dowling P., Chollet A., Kolakofsky D. Sequence determination of the Sendai virus HN gene and its comparison to the influenza virus glycoproteins. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Davis A. R., Nayak D. P. NH2-terminal hydrophobic region of influenza virus neuraminidase provides the signal function in translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2327–2331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinkscales C. W., Bratt M. A., Morrison T. G. Synthesis of Newcastle disease virus polypeptides in a wheat germ cell-free system. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.97-101.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Hightower L. E., Ball L. A. Transcription and translation of Newcastle disease virus mRNA's in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):324–336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.324-336.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins P. L., Wertz G. W., Ball L. A., Hightower L. E. Coding assignments of the five smaller mRNAs of Newcastle disease virus. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1024–1031. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1024-1031.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elango N., Coligan J. E., Jambou R. C., Venkatesan S. Human parainfluenza type 3 virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein: nucleotide sequence of mRNA and limited amino acid sequence of the purified protein. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):481–489. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.481-489.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Blobel G. Cell-free translation of messenger RNA in a wheat germ system. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:38–50. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Hubbard A. L., Fowler S., Lazarow P. B. Isolation of intracellular membranes by means of sodium carbonate treatment: application to endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):97–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G. Transient involvement of signal recognition particle and its receptor in the microsomal membrane prior to protein translocation. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):677–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G. Translocation of secretory proteins across the microsomal membrane occurs through an environment accessible to aqueous perturbants. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Walter P., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. II. Isolation and characterization of the signal recognition particle receptor. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):470–477. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Paterson R. G., Lamb R. A. Hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein of the paramyxovirus simian virus 5: nucleotide sequence of the mRNA predicts an N-terminal membrane anchor. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.1-6.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hightower L. E., Bratt M. A. Protein metabolism during the steady state of Newcastle disease virus infection. I. Kinetics of amino acid and protein accumulation. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):696–706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.696-706.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland E. C., Drickamer K. Signal recognition particle mediates the insertion of a transmembrane protein which has a cytoplasmic NH2 terminus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1286–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Rittenhouse L., Perrault J., Summers D. F., Kolakofsky D. Plus and minus strand leader RNAs in negative strand virus-infected cells. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):735–747. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGinnes L. W., Semerjian A., Morrison T. Conformational changes in Newcastle disease virus fusion glycoprotein during intracellular transport. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):341–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.341-348.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G., Ward L. J. Intracellular processing of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein and the Newcastle disease virus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase glycoprotein. Virus Res. 1984;1(3):225–239. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T., Ward L. J., Semerjian A. Intracellular processing of the Newcastle disease virus fusion glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.851-857.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perara E., Lingappa V. R. A former amino terminal signal sequence engineered to an internal location directs translocation of both flanking protein domains. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2292–2301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele G., Jacoby R. Conformational changes associated with proteolytic processing of presecretory proteins allow glutathione-catalyzed formation of native disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12277–12282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Owen M. J., Banville D., Williams J. G. Primary structure of human transferrin receptor deduced from the mRNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):675–678. doi: 10.1038/311675b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuy W., Garten W., Linder D., Klenk H. D. The carboxyterminus of the hemagglutinin-neuraminidase of Newcastle disease virus is exposed at the surface of the viral envelope. Virus Res. 1984;1(5):415–426. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe J. C., Hightower L. E. Maturation of the envelope glycoproteins of Newcastle disease virus on cellular membranes. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):947–957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.947-957.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess M., Lodish H. F. An internal signal sequence: the asialoglycoprotein receptor membrane anchor. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):177–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stampfer M., Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Ribonucleic acid synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Species of ribonucleic acid found in Chinese hamster ovary cells infected with plaque-forming and defective particles. J Virol. 1969 Aug;4(2):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.2.154-161.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubin M., Mach B., Long E. O. The complete sequence of the mRNA for the HLA-DR-associated invariant chain reveals a polypeptide with an unusual transmembrane polarity. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):869–872. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01898.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. II. Signal recognition protein (SRP) mediates the selective binding to microsomal membranes of in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):551–556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Ibrahimi I., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Signal recognition protein (SRP) binds to in-vitro-assembled polysomes synthesizing secretory protein. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):545–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz G. W., Collins P. L., Huang Y., Gruber C., Levine S., Ball L. A. Nucleotide sequence of the G protein gene of human respiratory syncytial virus reveals an unusual type of viral membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4075–4079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. T., Lodish H. F. Multiple mechanisms of protein insertion into and across membranes. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):400–407. doi: 10.1126/science.4048938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost C. S., Hedgpeth J., Lingappa V. R. A stop transfer sequence confers predictable transmembrane orientation to a previously secreted protein in cell-free systems. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):759–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90532-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]