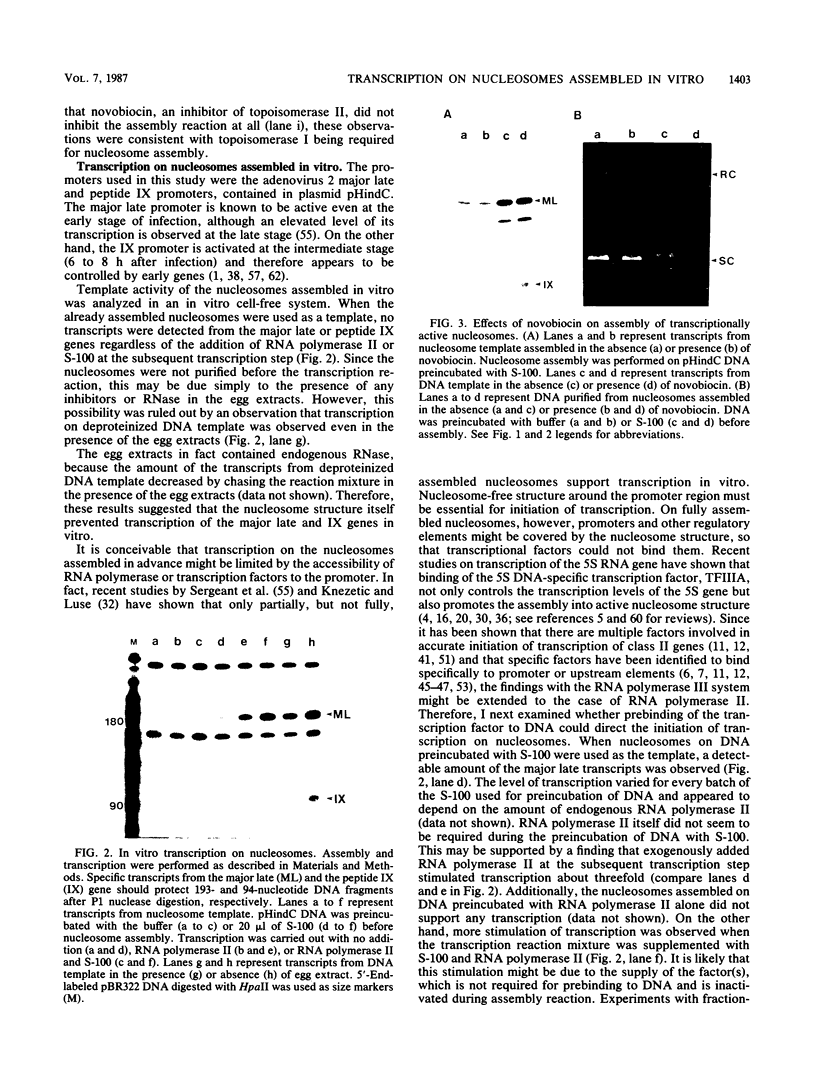
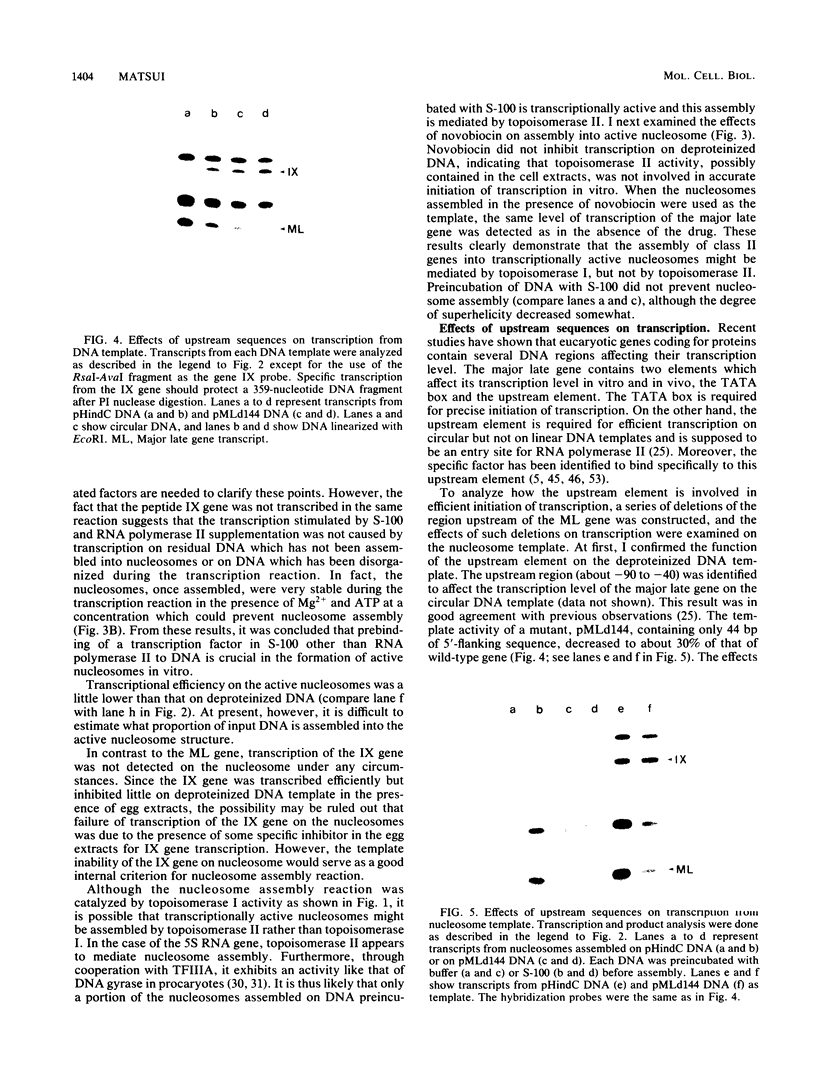
Abstract
Plasmid DNA containing adenovirus 2 major late and peptide IX genes was assembled into nucleosomes in vitro, and the assembled nucleosomes were used as a template to study the regulatory mechanism of transcription initiation under these conditions. Neither the major late nor peptide IX genes was transcribed on the already-assembled nucleosomes. However, the major late gene, but not the peptide IX gene, was transcribed efficiently when the DNA was incubated with HeLa cell extracts prior to assembly into nucleosomes. These results indicate that prebinding of some component in the cell extracts to DNA is essential to activate transcription of the major late gene on nucleosomes assembled under the conditions used here. Since gene IX on the nucleosomes was not transcriptionally active regardless of preincubation of DNA with the extracts, some other component or another, different template structure which is not able to be identified in an in vitro system with deproteinized DNA template might be required for activation of peptide IX gene transcription. To know the function of the upstream sequences of the major late gene, effects of the deletion on transcription of nucleosomes were compared with that of deproteinized DNA. The result showed that depression of transcription by deleting the upstream sequences had more effect on nucleosomes than on deproteinized DNA.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Ziff E. B. Promoters and heterogeneous 5' termini of the messenger RNAs of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):189–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D. The role of stable complexes that repress and activate eucaryotic genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Mantei N., Weissmann C. DNA sequences preceding the rabbit beta-globin gene are required for formation in mouse L cells of beta-globin RNA with the correct 5' terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Baty D., Chambon P. The repeated GC-rich motifs upstream from the TATA box are important elements of the SV40 early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2447–2464. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garel A., Axel R. Selective digestion of transcriptionally active ovalbumin genes from oviduct nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3966–3970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargiulo G., Razvi F., Worcel A. Assembly of transcriptionally active chromatin in Xenopus oocytes requires specific DNA binding factors. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):511–521. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90506-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Lebowitz P., Frisque R. J., Gluzman Y. Identification of a promoter component involved in positioning the 5' termini of simian virus 40 early mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):100–104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Ruberti I., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vitro studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J., Bloomer L. S. Assembly of transcriptionally active 5S RNA gene chromatin in vitro. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):781–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G. C., de Boer E., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. DNA sequences necessary for transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in vivo. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):120–126. doi: 10.1038/295120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss P., Dhar R., Khoury G. Simian virus 40 tandem repeated sequences as an element of the early promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):943–947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Borrelli E., Sassone-Corsi P., Chambon P. An enhancer element is located 340 base pairs upstream from the adenovirus-2 E1A capsite. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Dec 20;11(24):8747–8760. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.24.8747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. A nucleosome-free region in SV40 minichromosomes. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):263–265. doi: 10.1038/285263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongstra J., Reudelhuber T. L., Oudet P., Benoist C., Chae C. B., Jeltsch J. M., Mathis D. J., Chambon P. Induction of altered chromatin structures by simian virus 40 enhancer and promoter elements. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):708–714. doi: 10.1038/307708a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Manley J. L. In vitro transcription from the adenovirus 2 major late promoter utilizing templates truncated at promoter-proximal sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8513–8521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Characterization of purified DNA-relaxing enzyme from human tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2550–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Ryoji M., Worcel A. Gyration is required for 5S RNA transcription from a chromatin template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1305–1309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Worcel A. The positive transcription factor of the 5S RNA gene induces a 5S DNA-specific gyration in Xenopus oocyte extracts. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):945–953. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knezetic J. A., Luse D. S. The presence of nucleosomes on a DNA template prevents initiation by RNA polymerase II in vitro. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90541-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Koller T. Structure of the active nucleolar chromatin of Xenopus laevis Oocytes. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):279–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90346-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen A., Weintraub H. An altered DNA conformation detected by S1 nuclease occurs at specific regions in active chick globin chromatin. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D., Morris N. R. Assembly of SV40 chromatin in a cell-free system from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Hamer D. H., Roeder R. G. Stable transcription complex on a class III gene in a minichromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):40–45. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A., Noll M. Chromatin fine structure of active and repressed genes. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):198–203. doi: 10.1038/289198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Esche H., Smart J. E., Stillman B. W., Harter M. L., Mathews M. B. Organization and expression of the left third of the genome of adenovirus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):493–508. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Berg L., Weiher H., Botchan M. Bovine papilloma virus contains an activator of gene expression at the distal end of the early transcription unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1108–1122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T. In vitro accurate initiation of transcription on the adenovirus type 2 IVa2 gene which does not contain a TATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7089–7101. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Murayama M., Mita T. Adenovirus 2 peptide IX gene is expressed only on replicated DNA molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4149–4154. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Specific interaction between a transcription factor and the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3563–3570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04118.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Wintzerith M., Hen R., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription by the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter involves a specific factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8779–8799. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific enhancer in the mouse immunoglobulin kappa gene. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):80–82. doi: 10.1038/307080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D., Robbins A., Myers R., Tjian R. Regulation of simian virus 40 early transcription in vitro by a purified tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5706–5710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Moyne G., Yaniv M. Absence of nucleosomes in a fraction of SV40 chromatin between the origin of replication and the region coding for the late leader RNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheer U. Changes of nucleosome frequency in nucleolar and non-nucleolar chromatin as a function of transcription: an electron microscopic study. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sergeant A., Bohmann D., Zentgraf H., Weiher H., Keller W. A transcription enhancer acts in vitro over distances of hundreds of base-pairs on both circular and linear templates but not on chromatin-reconstituted DNA. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):577–600. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar V. E., Roeder R. G. Purification and subunit structure of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase III from the mouse plasmacytoma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1976 Feb 25;251(4):1064–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J., McGrogan M., Raskas H. J. Regulation of the appearance of cytoplasmic RNAs from region 1 of the adenovirus 2 genome. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):395–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. P., Mathews M. B. DNA replication and the early to late transition in adenovirus infection. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Augereau P., Chambon P. The SV40 72 bp repeat preferentially potentiates transcription starting from proximal natural or substitute promoter elements. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90470-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Assembly and propagation of repressed and depressed chromosomal states. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Groudine M. Chromosomal subunits in active genes have an altered conformation. Science. 1976 Sep 3;193(4256):848–856. doi: 10.1126/science.948749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Control of messenger RNA concentration by differential cytoplasmic half-life. Adenovirus messenger RNAs from transcription units 1A and 1B. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):231–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wong Y. C., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: II. Disruption of chromatin structure during gene activity. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Olson L., Tyndall C., Schaffner W. Transcriptional 'enhancers' from SV40 and polyoma virus show a cell type preference. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):7965–7976. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.7965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W. A small segment of polyoma virus DNA enhances the expression of a cloned beta-globin gene over a distance of 1400 base pairs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6251–6264. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]