Abstract
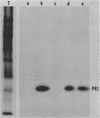
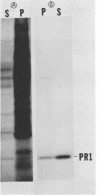
The PR1 family of pathogenesis-related proteins from tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) leaves is induced by a variety of pathogenic and chemical agents and is associated with resistance to tobacco mosaic virus. The majority of the PR1 proteins did not copurify with mesophyll protoplasts (the major cell type of the leaf) isolated from tobacco mosaic virus-infected N. tabacum cv. Xanthi-nc leaves. However, these isolated protoplasts were capable of synthesizing and selectively secreting the PR1 proteins. Using monoclonal antibodies for immunofluorescence microscopy, we localized these proteins to the extracellular spaces predominantly in regions adjacent to viral lesions as well as in xylem elements of infected leaves.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry J. O., Nikolau B. J., Carr J. P., Klessig D. F. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene expression in light- and dark-grown amaranth cotyledons. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2238–2246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr J. P., Dixon D. C., Klessig D. F. Synthesis of pathogenesis-related proteins in tobacco is regulated at the level of mRNA accumulation and occurs on membrane-bound polysomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7999–8003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelissen B. J., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. A., Van Loon L. C., Bol J. F. Molecular characterization of messenger RNAs for 'pathogenesis related' proteins la, lb and lc, induced by TMV infection of tobacco. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):37–40. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04174.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R. A., Cornelissen B. J., van Loon L. C., van Boom J. H., Tromp M., Bol J. F. Virus-induced synthesis of messenger RNAs for precursors of pathogenesis-related proteins in tobacco. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2167–2171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03911.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G. Derivation and diversification of monoclonal antibodies. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1359–1365. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03787.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS A. F. Localized acquired resistance to plant virus infection in hypersensitive hosts. Virology. 1961 Jul;14:329–339. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSS A. F. Systemic acquired resistance induced by localized virus infections in plants. Virology. 1961 Jul;14:340–358. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90319-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]