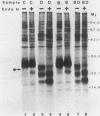
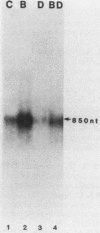
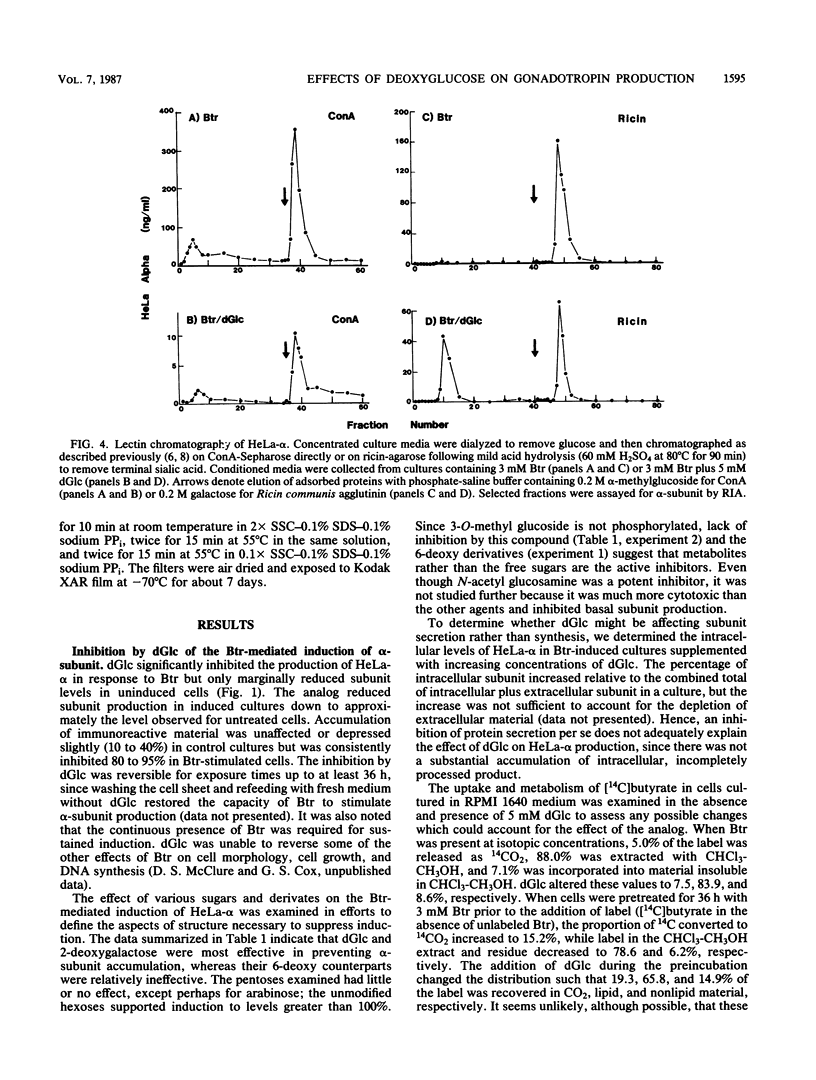
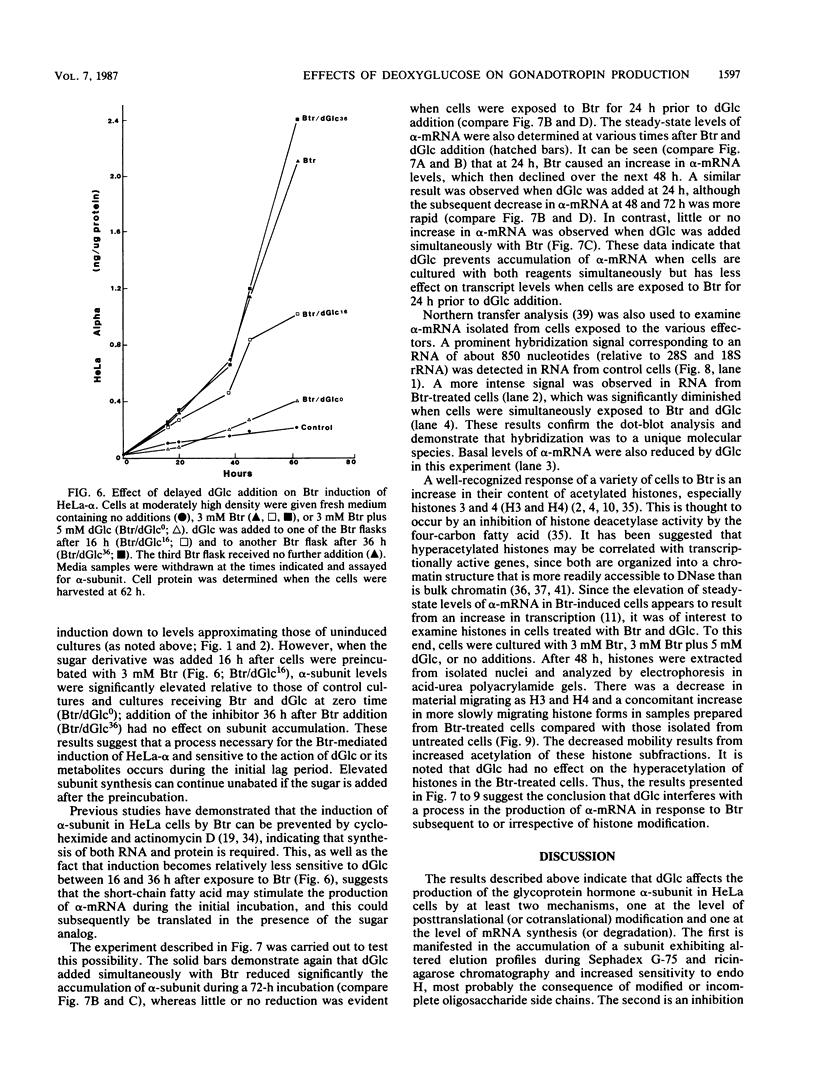
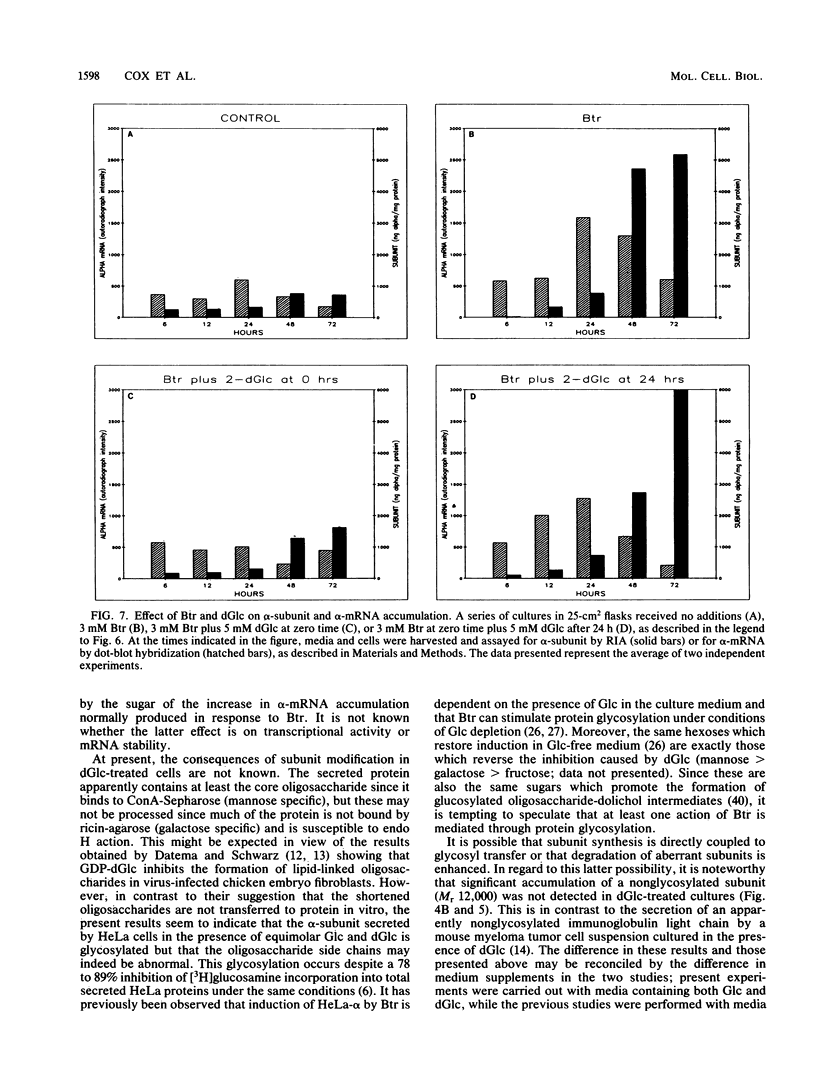
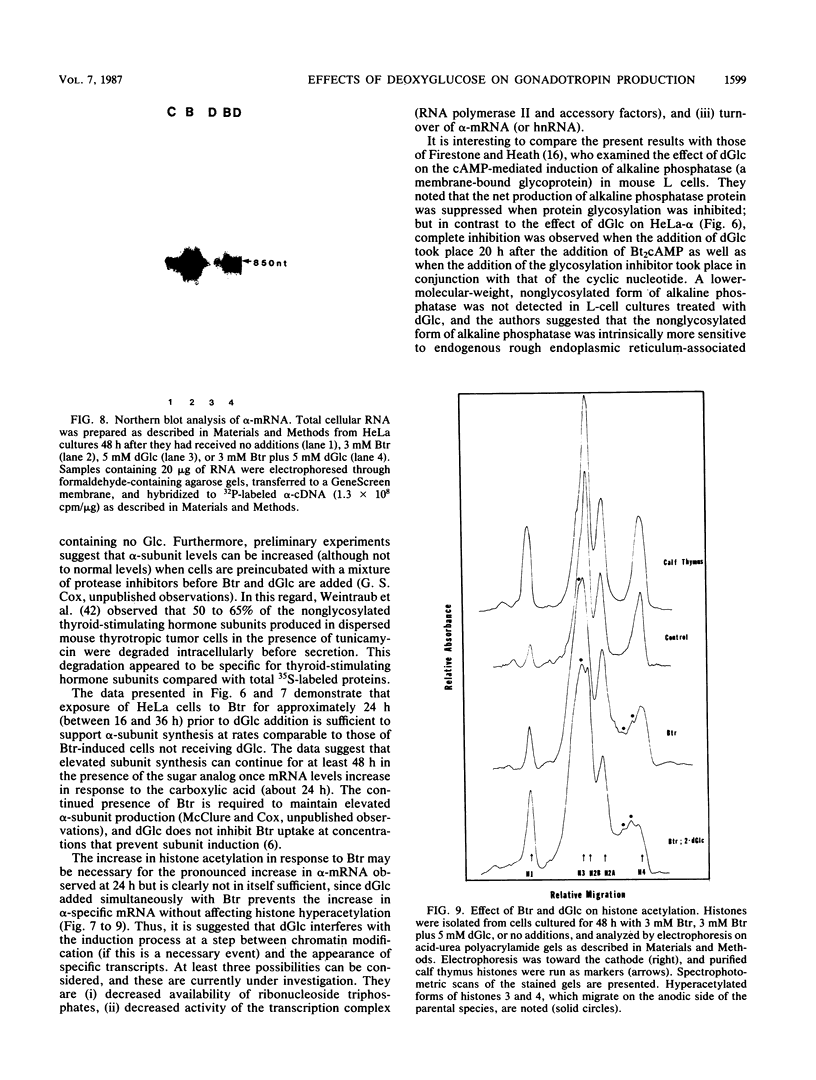
Abstract
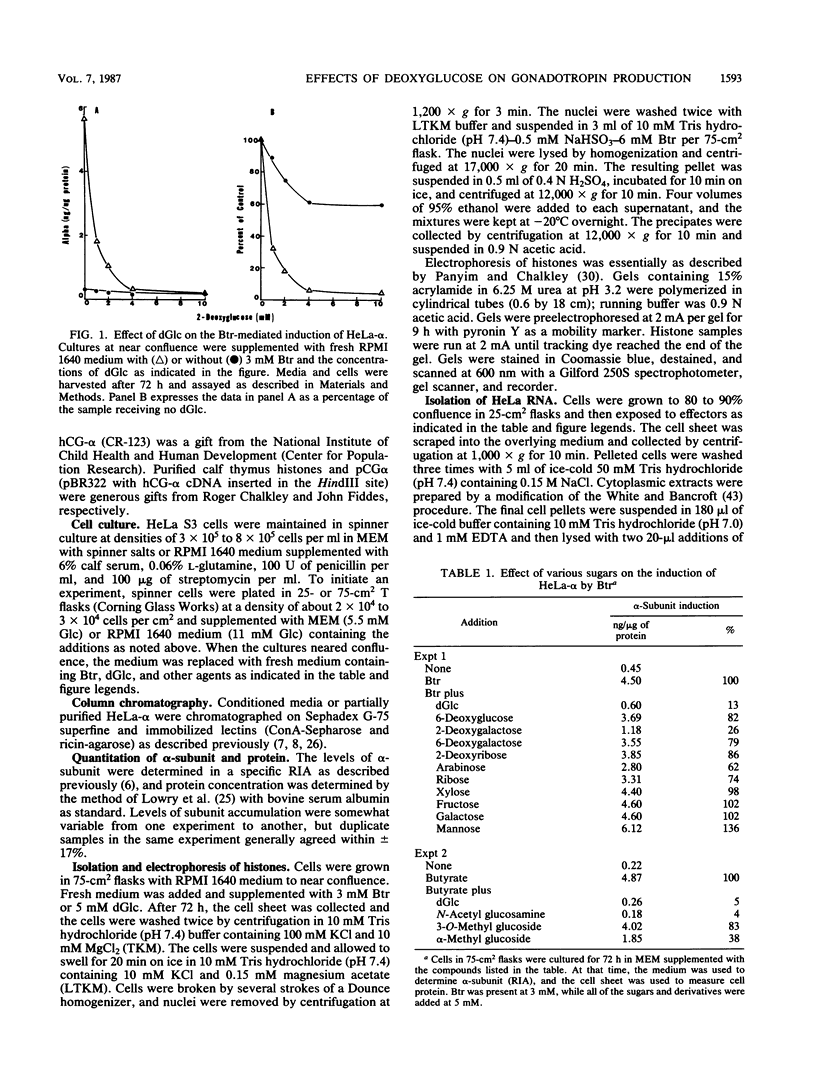
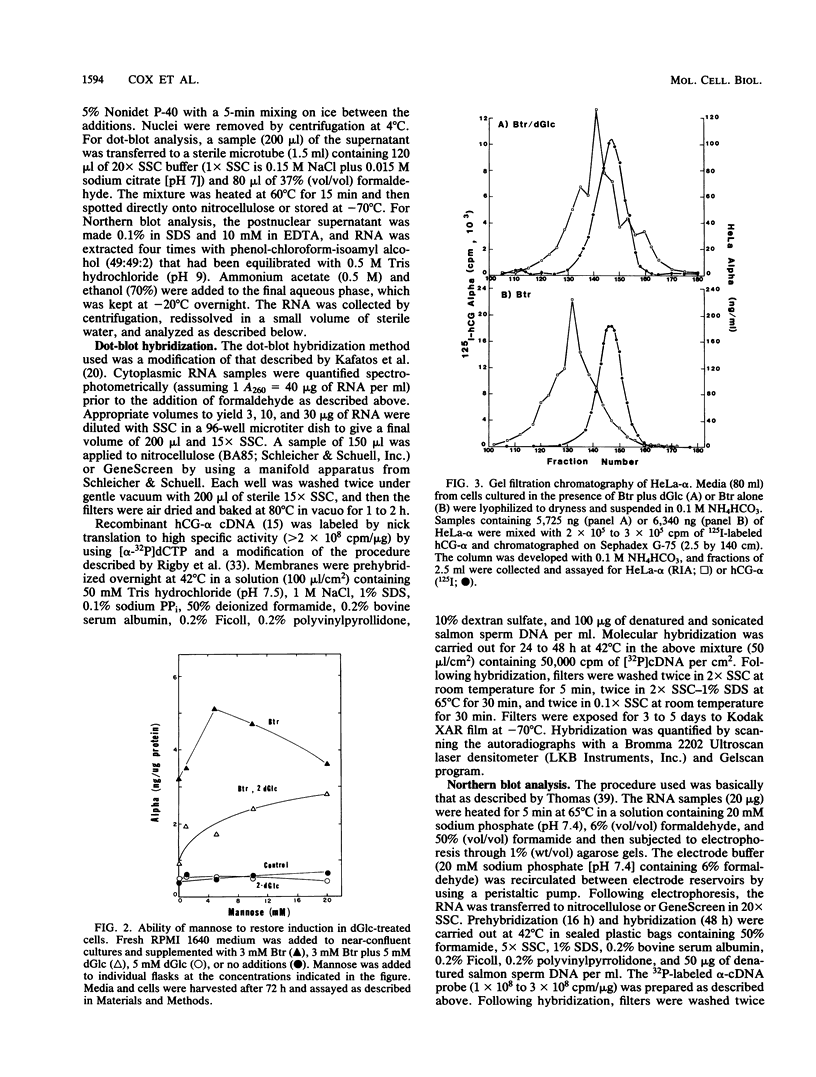
Sodium butyrate (Btr) (3 mM) causes a 10-fold increase in production of the glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit in HeLa cells. The following report demonstrates that this response could be inhibited about 95% by 5 mM 2-deoxy-D-glucose (dGlc), whereas alpha-subunit production in uninduced cells was affected little or not at all. Addition of D-mannose restored the Btr induction of Hela-alpha in cultures that had been treated with dGlc. When the alpha-subunits secreted by cells cultured in Btr plus dGlc or in Btr alone were compared by gel filtration (Sephadex G-75) and lectin affinity (concanavalin A and ricin) chromatography, differences were noted that probably reflect changes in their carbohydrate moieties. Immunoprecipitation of [35S]methionine-labeled HeLa-alpha and incubation with endoglycosidase H indicated that the subunit secreted from cells in the presence of dGlc contained oligosaccharide side chains that were not processed to the complex type. Cells that were simultaneously treated with Btr plus dGlc showed no increase in alpha-subunit production over cells receiving Btr only; in contrast, cells that were preincubated with Btr for either 16 or 36 h before dGlc was added exhibited high levels of subunit synthesis. Measurement of alpha-mRNA levels at various times after Btr and dGlc were added to cultures indicated that Btr brought about a dramatic increase in alpha-specific mRNA about 24 h after being added to cultures. This increase could be prevented by dGlc when added simultaneously with Btr but not when added after a 24-h preincubation. Although dGlc prevented the induction of alpha-subunit and alpha-mRNA in response to Btr, it had no effect on histone hyperacetylation, suggesting that if this chromatin modification is necessary for the induction process, it is not in itself sufficient. Together, the data demonstrate that dGlc inhibits the accumulation of alpha-subunit mRNA normally produced in response to Btr and that the subunit produced contains altered oligosaccharide constituents.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOWER B. F., GORDAN G. S. HORMONAL EFFECTS OF NONENDOCRINE TUMORS. Annu Rev Med. 1965;16:83–118. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.16.020165.000503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman M. R., Rosen S. W., Weintraub B. D. Ectopic hormones. Adv Intern Med. 1978;23:85–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boffa L. C., Gruss R. J., Allfrey V. G. Manifold effects of sodium butyrate on nuclear function. Selective and reversible inhibition of phosphorylation of histones H1 and H2A and impaired methylation of lysine and arginine residues in nuclear protein fractions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9612–9621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Candido E. P., Reeves R., Davie J. R. Sodium butyrate inhibits histone deacetylation in cultured cells. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90305-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y. Regulation of the synthesis of human chorionic gonadotropin by strains of HeLa cells in culture. In Vitro. 1978 Sep;14(9):775–778. doi: 10.1007/BF02617971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. S. Glycosylation of the chorionic gonadotropin alpha subunit synthesized by HeLa cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Aug;41(8):3087–3094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. S. Nature of the difference in apparent molecular weights between the alpha subunit of urinary human chorionic gonadotropin and the alpha protein secreted by HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Feb 27;98(4):942–951. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. S., Park K. H. Induction of alkaline phosphatase and the glycoprotein hormone alpha subunit in HeLa cells by inhibitors of DNA polymerase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jun;216(1):234–246. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. S. Synthesis of the glycoprotein hormone alpha subunit and placental alkaline phosphatase by HeLa cells: effect of tunicamycin, 2-deoxyglucose, and sodium butyrate. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4893–4900. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Anna J. A., Tobey R. A., Gurley L. R. Concentration-dependent effects of sodium butyrate in Chinese hamster cells: cell-cycle progression, inner-histone acetylation, histone H1 dephosphorylation, and induction of an H1-like protein. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2656–2671. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell R. B. Independent regulation by sodium butyrate of gonadotropin alpha gene expression and cell cycle progression in HeLa cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):829–839. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datema R., Schwarz R. T. Formation of 2-deoxyglucose-containing lipid-linked oligosaccharides. Interference with glycosylation of glycoproteins. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):505–516. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datema R., Schwarz R. T. Interference with glycosylation of glycoproteins. Inhibition of formation of lipid-linked oligosaccharides in vivo. Biochem J. 1979 Oct 15;184(1):113–123. doi: 10.1042/bj1840113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagon P. K., Heath E. C. Glycoprotein biosynthesis in myeloma cells. Characterization on nonglycosylated immunoglobulin light chain secreted in presence of 2-deoxy-D-glucose. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2372–2383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddes J. C., Goodman H. M. Isolation, cloning and sequence analysis of the cDNA for the alpha-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin. Nature. 1979 Oct 4;281(5730):351–356. doi: 10.1038/281351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestone G. L., Heath E. C. Role of protein glycosylation in the cAMP-mediated induction of alkaline phosphatase in mouse L-cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1404–1411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh M. K., Cox R. P. Production of human chorionic gonadotropin in HeLa cell cultures. Nature. 1976 Feb 5;259(5542):416–417. doi: 10.1038/259416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh N. K., Cox R. P. Induction of human follicle-stimulating hormone in HeLa cells by sodium butyrate. Nature. 1977 Jun 2;267(5610):435–437. doi: 10.1038/267435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh N. K., Rukenstein A., Cox R. P. Induction of human choriogonadotropin in heLa-cell cultures by aliphatic monocarboxylates and inhibitors of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 15;166(2):265–274. doi: 10.1042/bj1660265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddle G. W., Nicholson W. E., Island D. P., Orth D. N., Abe K., Lowder S. C. Clinical and laboratory studies of ectopic humoral syndromes. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1969;25:283–314. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571125-8.50009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieblich J. M., Weintraub B. D., Rosen S. W., Chou J. Y., Robinson J. C. HeLa cells secrete alpha subunit of glycoprotein tropic hormones. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):530–532. doi: 10.1038/260530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieblich J. M., Weintraub B. D., Rosen S. W., Ghosh N. K., Cox R. P. Secretion of hCG-alpha subunit and hCG by HeLa strains. Nature. 1977 Feb 24;265(5596):746–746. doi: 10.1038/265746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsett M. B. Humoral syndromes associated with cancer. Cancer Res. 1965 Aug;25(7):1068–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure D. S., Cox G. S. Glucose requirement for induction by sodium butyrate of the glycoprotein hormone alpha subunit in HeLa cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Aug 15;233(1):93–105. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90605-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. S., Weintraub B. D., Rosen S. W. Butyrate regulates glycosylation of the glycoprotein hormone alpha subunit secreted by "glucose-starved" human liver cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 15;112(1):115–125. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91805-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Diesterhaft M., Granner D. Evidence for a dual effect of dibutyryl cyclic AMP on the synthesis of tyrosine aminotransferase in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2386–2390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees L. H. The biosynthesis of hormones by non-endocrine tumours--a review. J Endocrinol. 1975 Oct;67(1):143–175. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0670143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. H., Means G. E. Radioactive labeling of proteins in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):831–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddon R. W., Anderson C., Meade K. S., Aldenderfer P. H., Neuwald P. D. Content of gonadotropins in cultured human malignant cells and effects of sodium butyrate treatment on gonadotropin secretion by HeLa cells. Cancer Res. 1979 Oct;39(10):3885–3892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Chalkley R. DNA associated with hyperacetylated histone is preferentially digested by DNase I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):1863–1876. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.1863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Chalkley R. The effect of sodium butyrate on histone modification. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Structure of chromatin containing extensively acetylated H3 and H4. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):691–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staneloni R. J., Ugalde R. A., Leloir L. F. Addition of glucose to dolichyl diphosphate oligosaccharide and transfer to protein. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Apr;105(2):275–278. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco S. J. Modification of oligosaccharide-lipid synthesis and protein glycosylation in glucose-deprived cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Dec;205(2):330–339. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidali G., Boffa L. C., Bradbury E. M., Allfrey V. G. Butyrate suppression of histone deacetylation leads to accumulation of multiacetylated forms of histones H3 and H4 and increased DNase I sensitivity of the associated DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2239–2243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub B. D., Stannard B. S., Meyers L. Glycosylation of thyroid-stimulating hormone in pituitary tumor cells: influence of high mannose oligosaccharide units on subunit aggregation, combination, and intracellular degradation. Endocrinology. 1983 Apr;112(4):1331–1345. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-4-1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]